
Hypovitaminosis D
Encyclopedia
Hypovitaminosis D is a deficiency of Vitamin D
. It can result from: inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D coupled with inadequate sunlight exposure (in particular sunlight with adequate ultra violet B rays), disorders that limit vitamin D absorption, and conditions that impair the conversion of vitamin D into active metabolite
s including certain liver
, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency results in impaired bone mineralization and leads to bone softening diseases including rickets
in children and osteomalacia
and osteoporosis
in adults.
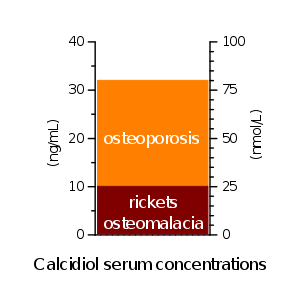 Hypovitaminosis D is typically diagnosed by measuring the concentration in blood of the compound 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcidiol
Hypovitaminosis D is typically diagnosed by measuring the concentration in blood of the compound 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcidiol
), which is a precursor to the active form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol
). One 2008 review has proposed the following four categories for hypovitaminosis D:
Note that 1.0 nmol/L = 0.4 ng/mL for this compound. Other authors have suggested that a 25-hydroxyvitamin D level of 75-80 nmol/L (30-32 ng/mL) may be sufficient although a majority of healthy young people with comparatively extreme sun exposure did not reach this level in a study done in Hawaii.
The putative benefits of higher levels were not borne out in a 2010 study which found that women with a seasonally adjusted 25(OH)D concentration under 50 nmol/L or 20 ng/ml, (a level considered deficient by most researchers) were not at an increased risk of adverse consequences for any musculoskeletal outcome, including fracture, falls, bone density, grip strength or any nonskeletal outcomes, including death, myocardial infarction, cancer, heart failure, diabetes, or adverse changes in blood pressure, weight, body composition, cholesterol, or glucose. There is also a growing body of research suggesting that serum levels above 125 nmol/L may have adverse health effects.
 Vitamin D deficiency is known to cause several bone diseases including:
Vitamin D deficiency is known to cause several bone diseases including:
The role of diet in the development of rickets
was determined by Edward Mellanby between 1918–1920. In 1921 Elmer McCollum
identified an anti-rachitic substance found in certain fats that could prevent rickets. Because the newly discovered substance was the fourth vitamin identified, it was called vitamin D. The 1928 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Adolf Windaus, who discovered the steroid 7-dehydrocholesterol, the precursor of vitamin D.
Prior to the fortification of milk products with vitamin D, rickets was a major public health problem. In the United States, milk has been fortified with 10 micrograms (400 IU
) of vitamin D per quart
since the 1930s, leading to a dramatic decline in the number of rickets cases.
is generally fortified with vitamin D.
rays are approximately 20% stronger than at sea level on the same latitude almost two thirds of 500 children had mild rickets in the late 1920s. An increase in the proportion of animal protein in the 20th century American diet coupled with increased consumption of milk fortified with relatively small quantities of vitamin D coincided with a dramatic decline in the number of rickets cases.
, but also to patients with primary hyperparathyroidism
) or with hypoparathyroidism
. Patients with chronic liver disease
or intestinal malabsorption disorders may also require larger doses of vitamin D (up to 40,000 IU or 1 mg (1000 micrograms) daily).
It has been argued that there is little evidence to support the use of high dose therapy to attain thresholds for vitamin D deficiency that greatly exceed widely used definitions of vitamin D deficiency (25OHD <10 ng/ml or 25 nmol/L), and for vitamin D insufficiency (25OHD < 20 ng/ml or 50 nmol/L). Studies are potentially subject to confounding by frailty as people with poorer health are likely to remain indoors, receive less sun exposure, and have low 25OHD levels compared to their healthy peers (rather than low vitamin D levels causing ill health). Those leading sedentary lives are at increased risk of obesity, and increased fat mass is inversely associated with 25OHD levels. This association may confound the reported relationships between low vitamin D status and conditions such as diabetes, ischaemic heart disease, hypertension, and cancer that occur more commonly in obesity. Confounding by health status can be powerful, as evidenced by the disparate results of randomised controlled trials and observational studies of postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy. (see Hormone replacement therapy (menopause)
. Obesity remains a likely confounding factor for the associations between low 25(OH)D levels and poor health. Some continue to argue the reverse — that obese and sedentary people are at high risk of many diseases specifically because they have low serum 25(OH)D levels
with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 8 can theoretically inhibit more than 95% of vitamin D production in the skin. In practice, however, sunscreen is applied so as to have a negligible effect on vitamin D status. The vitamin D status of those in Australia and New Zealand
is unlikely to have been affected by campaigns advocating sunscreen. Instead, wearing clothing is more effective at reducing the amount of skin exposed to UVB and reducing natural vitamin D synthesis.
Another risk factor arising from lack of sun exposure is clothing which covers a large prortion of the skin. This clothing when worn on a consistent and regular basis, such as the burqa
, is correlated with lower vitamin D levels and an increased prevalence of hypovitaminosis D.
acts like a sun-block, dark-skinned
individuals, in particular, may require extra vitamin D to avoid deficiency at higher latitudes. The natural selection hypothesis suggests that lighter skin color evolved to optimise vitamin D production in extreme northern and southern latitudes.
Rickets is sometimes due to genetic disorders such as autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets
or X-linked hypophosphatemia
and associated with consanguineous
marriage, and possibly founder effect
. In Kashmir, India patients with pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets had grossly raised 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. Skin colour has also been associated with low 25(OH)D, especially in Africans living in countries with a temperate climate. For example 25-OHD under 10 ng/mL (25 nmol/l) in 44% of asymptomatic East African children living in Melbourne However a study of healthy young Ethiopians living in Addis Ababa (10 degrees N) found average 25(OH)D levels of 23.5nmol/L. A review of Vitamin D in Africa gives the median levels for equatorial countries: Kenya 65.5 nmol/L and Congo-Kinshasa 65nmol/L, concluding that it remains to be established if associations between vitamin D status and health outcomes identified in Western countries can be replicated in African countries.
Vitamin D levels are approximately 30% higher in northern Europe than in central and southern Europe; higher vitamin D concentrations in northern countries may have a genetic basis. In a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies on serum 25(OH)D concentrations globally the levels averaged 54 nmol/l and were higher in women than men, and higher in Caucasians than in non-Caucasians. There was no trend in serum 25(OH)D level with latitude. African Americans often have a very low circulating 25(OH)D level. However, those of African descent have higher parathyroid hormone
and 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol associated with lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D than other ethnic groups; moreover, they have the greatest bone density
and lowest risk of fragility fractures compared to other populations. Deficiency results in impaired bone mineralization, and leads to bone softening diseases
One study found that vitamin D3 raised 25-hydroxy-vitamin D blood levels more than did vitamin D2, but this difference has been adequately disproved to allow reasonable assumption that D2 and D3 are equal for maintaining 25-hydroxy-vitamin D status.
There has been variability in results of laboratory analyses of the level of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D. Falsely low or high values have been obtained depending on the particular test or laboratory used. Beginning in July 2009 a standard reference material became available which should allow laboratories to standardise their procedures.
There is some disagreement concerning the exact levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D needed for good health. A level lower than 10 ng/mL (25 nmol/L) is associated with the most severe deficiency diseases: rickets in infants and children, and osteomalacia
in adults. A concentration above 15 ng/ml (37.5 nmol/L) is generally considered adequate for those in good health. Levels above 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/L) are proposed by some as desirable for achieving optimum health, but there is not yet enough evidence to support this.
Levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D that are consistently above 200 ng/mL (500 nmol/L) are thought to be potentially toxic, although data from humans are sparse. In animal studies levels up to 400 ng/mL (1,000 nmol/L) were not associated with toxicity. Vitamin D toxicity usually results from taking supplements in excess. Hypercalcemia is typically the cause of symptoms, and levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D above 150 ng/mL (375 nmol/L) are usually found, although in some cases 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels may appear to be normal. It is recommended to periodically measure serum calcium in individuals receiving large doses of vitamin D.
In overweight persons increased fat mass is inversely associated with 25(OH)D levels. This association may confound the reported relationships between low vitamin D status and conditions which occur more commonly in obesity as the circulating 25(OH)D underestimates their total body stores. However, as vitamin D is fat-soluble, excess amounts can be stored in fat tissue and used during winter months, when sun exposure is limited.
A study of highly sun exposed (tanned) healthy young skateboarders and surfers in Hawaii found levels below the proposed higher minimum of 30 ng/ml in 51% of the subjects. The highest 25(OH)D concentration was around 60 ng/ml (150nmol/L). A similarstudy in Hawaii found a range of (11–71 ng/mL) in a population with prolonged extensive skin exposure while as part of the same study Wisconsin breastfeeding mothers were given supplements. The range of circulating 25(OH)D levels in women in the supplementated group was from 12–77 ng/mL. It is noteworthy that the levels in the supplemented population in Wisconsin were higher than the sun exposed group in Hawaii (which again included surfers because it was the same data set).
Another study of African Americans found that blood levels of 25(OH)D decreased linearly with increasing African ancestry, the decrease being 2.5-2.75 nmol/L per 10% increase in African ancestry. Sunlight and diet were 46% less effective in raising these levels among subjects with high African ancestry than among those with low/medium African ancestry. It could be possible that vitamin-D metabolism differs by ethnicity.
study analyzed data from the third national Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to examine the relationship between levels of circulating vitamin D in the blood and cancer mortality in a group of 16,818 participants aged 17 and older. It found no support for an association between 25(OH)D and total cancer mortality. Unlike other studies, this one was carried out prospectively
meaning that participants were followed looking forward and the researchers used actual blood tests to measure the amount of vitamin D in blood, rather than trying to infer vitamin D levels from potentially inaccurate predictive models.
The molecular basis for thinking that vitamin D has the potential to prevent cancer
lies in its role as a nuclear transcription factor
that regulates cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis
and a wide range of cellular mechanisms central to the development of cancer. These effects may be mediated through vitamin D receptors expressed in cancer cells. Polymorphisms
of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene have been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, although a study of 78 Turkish breast cancer patients showed that the prevalence of the VDR Taq I and Bsm I alleles and the genotype frequencies in patients with breast cancer was similar to that in the normal population. Impairment of the VDR-mediated gene expression is thought to alter mammary gland
development or function and may predispose cells to malignant transformation
. Women with homozygous FOK1 mutations in the VDR gene had an increased risk of breast cancer compared with the women who did not. FOK1 mutation has also been associated with decreasing bone mineral density which in turn may be associated with an increase in the risk of breast cancer. Research is also being done on the use of calcitriol in the medical treatment of patients with advanced prostate cancer
.
Research has also suggested that cancer patients who have surgery or treatment in the summer — and therefore make more endogenous vitamin D — have a better chance of surviving their cancer than those who undergo treatment in the winter when they are exposed to less sunlight, (however, see flu season
for the factors apart from vitamin D that influence rates of infection during winter).
Correlation of the vitamin D levels of a population with the solar irradiance to which they are exposed can be confounded by other factors such as age, gender, skin pigmentation, latitude, sunscreen use, and clothing. Moreover, there are genetic factors involved with cancer incidence and mortality which are more common in northern latitudes.
A 2005 metastudy
found correlations between serum levels of vitamin D and cancer, drawing from a meta-analysis
of 63 observational studies of vitamin D status. The authors suggested that intake of an additional 1,000 international units (IU) (or 25 micrograms) of vitamin D daily reduced an individual's colon cancer risk by 50%, and breast
and ovarian cancer
risks by 30%. Low levels of vitamin D in serum have been correlated with breast cancer
disease progression and bone metastases.
Another 2006 study found that taking the U.S. RDA of vitamin D (400 IU per day) cut the risk of pancreatic cancer
by 43% in a sample of more than 120,000 people from two long-term health surveys. However, in male smokers, a 3-fold increased risk for pancreatic cancer in the highest compared to lowest quintile
of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration has been found.
A randomized intervention study involving 1,200 women, published in June 2007, reports that vitamin D supplementation (1,100 international units (IU)/day) resulted in a 60% reduction in cancer incidence, during a four-year clinical trial, rising to a 77% reduction for cancers diagnosed after the first year (and therefore excluding those cancers more likely to have originated prior to the vitamin D intervention). The study was criticized on several grounds including lack of data, use of statistical techniques and comparison with a self-selected (i.e. non-randomized) observational study that found long term convergence of breast cancer incidence The author's response provided the required data, explained their statistical usage and commented that even if the vitamin D merely delayed the appearance of cancer (which they did not believe, based on other studies), that that was still a considerable benefit.
A study by Cedric F. Garland and Frank C. Garland
of the University of California, San Diego
analyzed the blood from 25,000 volunteers from Washington County, Maryland
, finding that those with the highest levels of levels of Calcifediol had one-fifth the risk of colon cancer compared to typical rates.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
. It can result from: inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D coupled with inadequate sunlight exposure (in particular sunlight with adequate ultra violet B rays), disorders that limit vitamin D absorption, and conditions that impair the conversion of vitamin D into active metabolite
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
s including certain liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency results in impaired bone mineralization and leads to bone softening diseases including rickets
Rickets
Rickets is a softening of bones in children due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D, magnesium , phosphorus or calcium, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries...
in children and osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is the softening of the bones caused by defective bone mineralization secondary to inadequate amounts of available phosphorus and calcium, or because of overactive resorption of calcium from the bone as a result of hyperparathyroidism...
and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
in adults.
Classification

Calcidiol
Calcifediol , also known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D , is a prehormone that is produced in the liver by hydroxylation of vitamin D3 by the enzyme cholecalciferol 25-hydroxylase...
), which is a precursor to the active form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol
Calcitriol
Calcitriol , also called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is the hormonally active form of vitamin D with three hydroxyl groups...
). One 2008 review has proposed the following four categories for hypovitaminosis D:
- Insufficient 50-100 nmol/L (20-40 ng/mL)
- Mild 25-50 nmol/L (10-20 ng/mL)
- Moderate 12.5-25.0 nmol/L (5-10 ng/mL)
- Severe < 12.5 nmol/L (< 5 ng/mL)
Note that 1.0 nmol/L = 0.4 ng/mL for this compound. Other authors have suggested that a 25-hydroxyvitamin D level of 75-80 nmol/L (30-32 ng/mL) may be sufficient although a majority of healthy young people with comparatively extreme sun exposure did not reach this level in a study done in Hawaii.
Vitamin D status and supplementation
The increased risk of vascular events in healthy older women receiving calcium supplementation found in a controlled trial has led to some specialists questioning the use of vitamin D supplementation to attaining the relatively high serum concentrations of vitamin D now being promoted as sufficient. Most specialists, however, agree that vitamin D supplementation is an effective way of curing gout.The putative benefits of higher levels were not borne out in a 2010 study which found that women with a seasonally adjusted 25(OH)D concentration under 50 nmol/L or 20 ng/ml, (a level considered deficient by most researchers) were not at an increased risk of adverse consequences for any musculoskeletal outcome, including fracture, falls, bone density, grip strength or any nonskeletal outcomes, including death, myocardial infarction, cancer, heart failure, diabetes, or adverse changes in blood pressure, weight, body composition, cholesterol, or glucose. There is also a growing body of research suggesting that serum levels above 125 nmol/L may have adverse health effects.
Signs and symptoms

- RicketsRicketsRickets is a softening of bones in children due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D, magnesium , phosphorus or calcium, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries...
, a childhood disease characterized by impeded growth, and deformity, of the long bones. The earliest sign of subclinical vitamin D deficiency is CraniotabesCraniotabesCraniotabes is an abnormal softening or thinning of the skull, although normally present in newborns. Seen mostly in occipital bone and posterior part of parietal bone. Bone is soft and has a ping pong ball like feeling on pressing. The term is derived from the Latin words cranium for skull and...
, abnormal softening or thinning of the skull. - OsteomalaciaOsteomalaciaOsteomalacia is the softening of the bones caused by defective bone mineralization secondary to inadequate amounts of available phosphorus and calcium, or because of overactive resorption of calcium from the bone as a result of hyperparathyroidism...
, a bone-thinning disorder that occurs exclusively in adults and is characterized by proximal muscle weakness and bone fragility. - OsteoporosisOsteoporosisOsteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
, a condition characterized by reduced bone mineral density and increased bone fragility. - Muscle aches and weakness (in particular proximal limb girdle)
- Muscle twitching (Fasciculations)
The role of diet in the development of rickets
Rickets
Rickets is a softening of bones in children due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D, magnesium , phosphorus or calcium, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries...
was determined by Edward Mellanby between 1918–1920. In 1921 Elmer McCollum
Elmer McCollum
Elmer Verner McCollum was an American biochemist known for his work on the influence of diet on health.-Life and education:McCollum was born on a farm near Fort Scott, Kansas, where he spent his first seventeen years...
identified an anti-rachitic substance found in certain fats that could prevent rickets. Because the newly discovered substance was the fourth vitamin identified, it was called vitamin D. The 1928 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Adolf Windaus, who discovered the steroid 7-dehydrocholesterol, the precursor of vitamin D.
Prior to the fortification of milk products with vitamin D, rickets was a major public health problem. In the United States, milk has been fortified with 10 micrograms (400 IU
International unit
In pharmacology, the International Unit is a unit of measurement for the amount of a substance, based on biological activity or effect. It is abbreviated as IU, as UI , or as IE...
) of vitamin D per quart
Quart
The quart is a unit of volume equal to a quarter of a gallon, two pints, or four cups. Since gallons of various sizes have historically been in use, quarts of various sizes have also existed; see gallon for further discussion. Three of these kinds of quarts remain in current use, all approximately...
since the 1930s, leading to a dramatic decline in the number of rickets cases.
Age
The amount of vitamin D recommended for all infants, children, and adolescents has recently doubled—from 200 to 400 IU per day. As of October 2008, the American Pediatric Association advises vitamin D supplementation of 400 IU/day (10μg/d) from birth onwards. (1 IU Vitamin D is the biological equivalent of 0.025 μg cholecalciferol/ergocalciferol). The daily dose of 400 IU is required to prevent rickets and possibly also a wide range of chronic nonskeletal diseases. The Canadian Paediatric Society recommends that pregnant or breastfeeding women consider taking 2000 IU/day, that all babies who are exclusively breastfed receive a supplement of 400 IU/day, and that babies living above 55 degrees latitude get 800 IU/day from October to April. Health Canada recommends 400IU/day (10μg/d). Infant formulaInfant formula
Infant formula is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepared for bottle-feeding or cup-feeding from powder or liquid . The U.S...
is generally fortified with vitamin D.
Malnutrition
Although rickets and osteomalacia are now rare in Britain, there have been outbreaks in some immigrant communities in which osteomalacia sufferers included women with seemingly adequate daylight outdoor exposure wearing Western clothing. Having darker skin and reduced exposure to sunshine did not produce rickets unless the diet deviated from a Western omnivore pattern characterized by high intakes of meat, fish and eggs, and low intakes of high-extraction cereals. The dietary risk factors for rickets include abstaining from animal foods . Vitamin D deficiency remains the main cause of rickets among young infants in most countries, because breast milk is low in vitamin D and social customs and climatic conditions can prevent adequate UVB exposure. In sunny countries such as Nigeria, South Africa, and Bangladesh where the disease occurs among older toddlers and children it has been attributed to low dietary calcium intakes, which are characteristic of cereal-based diets with limited access to dairy products. Rickets was formerly a major public health problem among the US population; in Denver where ultravioletUltraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
rays are approximately 20% stronger than at sea level on the same latitude almost two thirds of 500 children had mild rickets in the late 1920s. An increase in the proportion of animal protein in the 20th century American diet coupled with increased consumption of milk fortified with relatively small quantities of vitamin D coincided with a dramatic decline in the number of rickets cases.
Obesity
Obese individuals have lower levels of the circulating form of vitamin D, probably because of reduced bioavailability, and are at higher risk of deficiency. To maintain blood levels of calcium, therapeutic vitamin D doses are sometimes administered (up to 100,000 IU or 2.5 mg daily) to patients who have had their parathyroid glands removed (most commonly renal dialysis patients who have had tertiary hyperparathyroidismTertiary hyperparathyroidism
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is a state of excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone after a long period of secondary hyperparathyroidism and resulting hypercalcemia...
, but also to patients with primary hyperparathyroidism
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Primary hyperparathyroidism causes hypercalcemia through the excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone , usually by an adenoma of the parathyroid glands.-Epidemiology:...
) or with hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with under production of parathyroid hormone. This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany , and several other symptoms...
. Patients with chronic liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
or intestinal malabsorption disorders may also require larger doses of vitamin D (up to 40,000 IU or 1 mg (1000 micrograms) daily).
It has been argued that there is little evidence to support the use of high dose therapy to attain thresholds for vitamin D deficiency that greatly exceed widely used definitions of vitamin D deficiency (25OHD <10 ng/ml or 25 nmol/L), and for vitamin D insufficiency (25OHD < 20 ng/ml or 50 nmol/L). Studies are potentially subject to confounding by frailty as people with poorer health are likely to remain indoors, receive less sun exposure, and have low 25OHD levels compared to their healthy peers (rather than low vitamin D levels causing ill health). Those leading sedentary lives are at increased risk of obesity, and increased fat mass is inversely associated with 25OHD levels. This association may confound the reported relationships between low vitamin D status and conditions such as diabetes, ischaemic heart disease, hypertension, and cancer that occur more commonly in obesity. Confounding by health status can be powerful, as evidenced by the disparate results of randomised controlled trials and observational studies of postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy. (see Hormone replacement therapy (menopause)
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause)
Hormone replacement therapy is a system of medical treatment for surgically menopausal, perimenopausal and to a lesser extent postmenopausal women...
. Obesity remains a likely confounding factor for the associations between low 25(OH)D levels and poor health. Some continue to argue the reverse — that obese and sedentary people are at high risk of many diseases specifically because they have low serum 25(OH)D levels
Sun exposure
The use of sunscreenSunscreen
Sunblock is a lotion, spray, gel or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet radiation on the skin exposed to sunlight and thus helps protect against sunburn...
with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 8 can theoretically inhibit more than 95% of vitamin D production in the skin. In practice, however, sunscreen is applied so as to have a negligible effect on vitamin D status. The vitamin D status of those in Australia and New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
is unlikely to have been affected by campaigns advocating sunscreen. Instead, wearing clothing is more effective at reducing the amount of skin exposed to UVB and reducing natural vitamin D synthesis.
Another risk factor arising from lack of sun exposure is clothing which covers a large prortion of the skin. This clothing when worn on a consistent and regular basis, such as the burqa
Burqa
A burqa is an enveloping outer garment worn by women in some Islamic religion to cover their bodies in public places. The burqa is usually understood to be the woman's loose body-covering , plus the head-covering , plus the face-veil .-Etymology:A speculative and unattested etymology...
, is correlated with lower vitamin D levels and an increased prevalence of hypovitaminosis D.
Darker skin color
It has been suggested the reduced pigmentation of light-skinned individuals results in higher vitamin D levels and that, because melaninMelanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
acts like a sun-block, dark-skinned
Human skin color
Human skin color is primarily due to the presence of melanin in the skin. Skin color ranges from almost black to white with a pinkish tinge due to blood vessels underneath. Variation in natural skin color is mainly due to genetics, although the evolutionary causes are not completely certain...
individuals, in particular, may require extra vitamin D to avoid deficiency at higher latitudes. The natural selection hypothesis suggests that lighter skin color evolved to optimise vitamin D production in extreme northern and southern latitudes.
Rickets is sometimes due to genetic disorders such as autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets
Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets
Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets is a rare hereditary disease in which excessive loss of phosphate in the urine leads to poorly formed bones , bone pain, and tooth abscesses. ADHR is caused by a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor 23...
or X-linked hypophosphatemia
X-linked hypophosphatemia
X-linked hypophosphatemia , also called X-linked dominant hypophosphatemic rickets, X-linked vitamin d-resistant rickets or hypophosphatemic vitamin d-resistant rickets , is an X-linked dominant form of rickets that differs from most cases of rickets in that ingestion of vitamin D is relatively...
and associated with consanguineous
Consanguinity
Consanguinity refers to the property of being from the same kinship as another person. In that respect, consanguinity is the quality of being descended from the same ancestor as another person...
marriage, and possibly founder effect
Founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using existing theoretical work by those such as Sewall...
. In Kashmir, India patients with pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets had grossly raised 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. Skin colour has also been associated with low 25(OH)D, especially in Africans living in countries with a temperate climate. For example 25-OHD under 10 ng/mL (25 nmol/l) in 44% of asymptomatic East African children living in Melbourne However a study of healthy young Ethiopians living in Addis Ababa (10 degrees N) found average 25(OH)D levels of 23.5nmol/L. A review of Vitamin D in Africa gives the median levels for equatorial countries: Kenya 65.5 nmol/L and Congo-Kinshasa 65nmol/L, concluding that it remains to be established if associations between vitamin D status and health outcomes identified in Western countries can be replicated in African countries.
Vitamin D levels are approximately 30% higher in northern Europe than in central and southern Europe; higher vitamin D concentrations in northern countries may have a genetic basis. In a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies on serum 25(OH)D concentrations globally the levels averaged 54 nmol/l and were higher in women than men, and higher in Caucasians than in non-Caucasians. There was no trend in serum 25(OH)D level with latitude. African Americans often have a very low circulating 25(OH)D level. However, those of African descent have higher parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone , parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids...
and 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol associated with lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D than other ethnic groups; moreover, they have the greatest bone density
Bone density
Bone density is a medical term normally referring to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones. Bone density is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteoporosis and fracture risk.This medical bone density is not the true physical "density" of the bone, which...
and lowest risk of fragility fractures compared to other populations. Deficiency results in impaired bone mineralization, and leads to bone softening diseases
Diagnosis
The serum concentration of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D is typically used to determine vitamin D status. It reflects vitamin D produced in the skin as well as that acquired from the diet, and has a fairly long circulating half-life of 15 days. It does not, however, reveal the amount of vitamin D stored in other body tissues. The level of serum 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D is not usually used to determine vitamin D status because it has a short half-life of 15 hours and is tightly regulated by parathyroid hormone, calcium, and phosphate, such that it does not decrease significantly until vitamin D deficiency is already well advanced.One study found that vitamin D3 raised 25-hydroxy-vitamin D blood levels more than did vitamin D2, but this difference has been adequately disproved to allow reasonable assumption that D2 and D3 are equal for maintaining 25-hydroxy-vitamin D status.
There has been variability in results of laboratory analyses of the level of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D. Falsely low or high values have been obtained depending on the particular test or laboratory used. Beginning in July 2009 a standard reference material became available which should allow laboratories to standardise their procedures.
There is some disagreement concerning the exact levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D needed for good health. A level lower than 10 ng/mL (25 nmol/L) is associated with the most severe deficiency diseases: rickets in infants and children, and osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is the softening of the bones caused by defective bone mineralization secondary to inadequate amounts of available phosphorus and calcium, or because of overactive resorption of calcium from the bone as a result of hyperparathyroidism...
in adults. A concentration above 15 ng/ml (37.5 nmol/L) is generally considered adequate for those in good health. Levels above 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/L) are proposed by some as desirable for achieving optimum health, but there is not yet enough evidence to support this.
Levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D that are consistently above 200 ng/mL (500 nmol/L) are thought to be potentially toxic, although data from humans are sparse. In animal studies levels up to 400 ng/mL (1,000 nmol/L) were not associated with toxicity. Vitamin D toxicity usually results from taking supplements in excess. Hypercalcemia is typically the cause of symptoms, and levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D above 150 ng/mL (375 nmol/L) are usually found, although in some cases 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels may appear to be normal. It is recommended to periodically measure serum calcium in individuals receiving large doses of vitamin D.
In overweight persons increased fat mass is inversely associated with 25(OH)D levels. This association may confound the reported relationships between low vitamin D status and conditions which occur more commonly in obesity as the circulating 25(OH)D underestimates their total body stores. However, as vitamin D is fat-soluble, excess amounts can be stored in fat tissue and used during winter months, when sun exposure is limited.
A study of highly sun exposed (tanned) healthy young skateboarders and surfers in Hawaii found levels below the proposed higher minimum of 30 ng/ml in 51% of the subjects. The highest 25(OH)D concentration was around 60 ng/ml (150nmol/L). A similar
Another study of African Americans found that blood levels of 25(OH)D decreased linearly with increasing African ancestry, the decrease being 2.5-2.75 nmol/L per 10% increase in African ancestry. Sunlight and diet were 46% less effective in raising these levels among subjects with high African ancestry than among those with low/medium African ancestry. It could be possible that vitamin-D metabolism differs by ethnicity.
Cancer
A US National Cancer InstituteNational Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute is part of the National Institutes of Health , which is one of 11 agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The NCI coordinates the U.S...
study analyzed data from the third national Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to examine the relationship between levels of circulating vitamin D in the blood and cancer mortality in a group of 16,818 participants aged 17 and older. It found no support for an association between 25(OH)D and total cancer mortality. Unlike other studies, this one was carried out prospectively
Prospective cohort study
A prospective cohort study is a cohort study that follows over time a group of similar individuals who differ with respect to certain factors under study, to determine how these factors affect rates of a certain outcome...
meaning that participants were followed looking forward and the researchers used actual blood tests to measure the amount of vitamin D in blood, rather than trying to infer vitamin D levels from potentially inaccurate predictive models.
The molecular basis for thinking that vitamin D has the potential to prevent cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
lies in its role as a nuclear transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
that regulates cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
and a wide range of cellular mechanisms central to the development of cancer. These effects may be mediated through vitamin D receptors expressed in cancer cells. Polymorphisms
Polymorphism (biology)
Polymorphism in biology occurs when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species — in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph...
of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene have been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, although a study of 78 Turkish breast cancer patients showed that the prevalence of the VDR Taq I and Bsm I alleles and the genotype frequencies in patients with breast cancer was similar to that in the normal population. Impairment of the VDR-mediated gene expression is thought to alter mammary gland
Mammary gland
A mammary gland is an organ in mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word "mammary". In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in their udders...
development or function and may predispose cells to malignant transformation
Malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as malignant degeneration of a previously existing benign tumor....
. Women with homozygous FOK1 mutations in the VDR gene had an increased risk of breast cancer compared with the women who did not. FOK1 mutation has also been associated with decreasing bone mineral density which in turn may be associated with an increase in the risk of breast cancer. Research is also being done on the use of calcitriol in the medical treatment of patients with advanced prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
.
Research has also suggested that cancer patients who have surgery or treatment in the summer — and therefore make more endogenous vitamin D — have a better chance of surviving their cancer than those who undergo treatment in the winter when they are exposed to less sunlight, (however, see flu season
Flu season
Flu season is a annually-recurring time period characterized by the prevalence of outbreaks of influenza . The season occurs during the cold half of the year in each hemisphere. Influenza activity can sometimes be predicted and even tracked geographically...
for the factors apart from vitamin D that influence rates of infection during winter).
Correlation of the vitamin D levels of a population with the solar irradiance to which they are exposed can be confounded by other factors such as age, gender, skin pigmentation, latitude, sunscreen use, and clothing. Moreover, there are genetic factors involved with cancer incidence and mortality which are more common in northern latitudes.
A 2005 metastudy
Meta-analysis
In statistics, a meta-analysis combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses. In its simplest form, this is normally by identification of a common measure of effect size, for which a weighted average might be the output of a meta-analyses. Here the...
found correlations between serum levels of vitamin D and cancer, drawing from a meta-analysis
Meta-analysis
In statistics, a meta-analysis combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses. In its simplest form, this is normally by identification of a common measure of effect size, for which a weighted average might be the output of a meta-analyses. Here the...
of 63 observational studies of vitamin D status. The authors suggested that intake of an additional 1,000 international units (IU) (or 25 micrograms) of vitamin D daily reduced an individual's colon cancer risk by 50%, and breast
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
risks by 30%. Low levels of vitamin D in serum have been correlated with breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
disease progression and bone metastases.
Another 2006 study found that taking the U.S. RDA of vitamin D (400 IU per day) cut the risk of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
by 43% in a sample of more than 120,000 people from two long-term health surveys. However, in male smokers, a 3-fold increased risk for pancreatic cancer in the highest compared to lowest quintile
Quintile
Quintile may refer to:*Income quintiles, a division of households by income into five quantiles*Quintiles, a biotechnology research company based in the United States...
of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration has been found.
A randomized intervention study involving 1,200 women, published in June 2007, reports that vitamin D supplementation (1,100 international units (IU)/day) resulted in a 60% reduction in cancer incidence, during a four-year clinical trial, rising to a 77% reduction for cancers diagnosed after the first year (and therefore excluding those cancers more likely to have originated prior to the vitamin D intervention). The study was criticized on several grounds including lack of data, use of statistical techniques and comparison with a self-selected (i.e. non-randomized) observational study that found long term convergence of breast cancer incidence The author's response provided the required data, explained their statistical usage and commented that even if the vitamin D merely delayed the appearance of cancer (which they did not believe, based on other studies), that that was still a considerable benefit.
A study by Cedric F. Garland and Frank C. Garland
Frank C. Garland
Frank Caldwell Garland was an American epidemiologist whose research led to the conclusion that vitamin D deficiency can be a factor increasing risk for breast cancer and colon cancer.-Biography:...
of the University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego
The University of California, San Diego, commonly known as UCSD or UC San Diego, is a public research university located in the La Jolla neighborhood of San Diego, California, United States...
analyzed the blood from 25,000 volunteers from Washington County, Maryland
Washington County, Maryland
Washington County is a county located in the western part of the U.S. state of Maryland, bordering southern Pennsylvania to the north, northern Virginia to the south, and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia to the south and west. As of the 2010 Census, its population is 147,430...
, finding that those with the highest levels of levels of Calcifediol had one-fifth the risk of colon cancer compared to typical rates.
External links
- VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY - Treatment and diagnosis from UCTV (University of California) (videos)
- Vitamin D Council
- "The Power of D", Nathan Seppa, Science News, July 16, 2011, pages 22–26, a review article.

