
Iatrogenesis
Encyclopedia
Adverse effect (medicine)
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
or complication
Complication (medicine)
Complication, in medicine, is an unfavorable evolution of a disease, a health condition or a medical treatment. The disease can become worse in its severity or show a higher number of signs, symptoms or new pathological changes, become widespread throughout the body or affect other organ systems. A...
resulting from medical
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
treatment or advice, including that of psychologist
Psychologist
Psychologist is a professional or academic title used by individuals who are either:* Clinical professionals who work with patients in a variety of therapeutic contexts .* Scientists conducting psychological research or teaching psychology in a college...
s, therapists, pharmacist
Pharmacist
Pharmacists are allied health professionals who practice in pharmacy, the field of health sciences focusing on safe and effective medication use...
s, nurses, physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
s and dentist
Dentist
A dentist, also known as a 'dental surgeon', is a doctor that specializes in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the oral cavity. The dentist's supporting team aides in providing oral health services...
s. Iatrogenesis is not restricted to conventional medicine: It can also result from complementary and alternative medicine treatments.
Some iatrogenic artifacts are clearly defined and easily recognized, such as a complication following a surgical procedure. Some less obvious ones can require significant investigation to identify, such as complex drug interaction
Drug interaction
A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
s. Furthermore, some conditions have been described for which it is unknown, unproven, or even controversial whether they are iatrogenic or not; this has been encountered in particular with regard to various psychological and chronic-pain conditions. Research in these areas continues.
Causes of iatrogenesis include chance, medical error
Medical error
A medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
, negligence
Negligence
Negligence is a failure to exercise the care that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in like circumstances. The area of tort law known as negligence involves harm caused by carelessness, not intentional harm.According to Jay M...
, social control
Social control
Social control refers generally to societal and political mechanisms or processes that regulate individual and group behavior, leading to conformity and compliance to the rules of a given society, state, or social group. Many mechanisms of social control are cross-cultural, if only in the control...
, unexamined instrument design, anxiety or annoyance related to medical procedures, and the adverse effect
Adverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
s or interactions
Drug interaction
A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
of medications. In the United States, an estimated 44,000 to 98,000 deaths per year may be attributed in some part to iatrogenesis..
History
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
iatros, healer); as such, in its earlier forms, it could refer to good or bad effects.
Since at least the time of Hippocrates
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
, people have recognized the potential damaging effects of a healer's actions. The old mandate "first do no harm" (primum non nocere
Primum non nocere
is a Latin phrase that means "First, do no harm". The phrase is sometimes recorded as .Nonmaleficence, which derives from the maxim, is one of the principal precepts of medical ethics that all medical students are taught in medical school and is a fundamental principle for emergency medical...
) is an important clause of medical ethics
Bioethics
Bioethics is the study of controversial ethics brought about by advances in biology and medicine. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, and philosophy....
, and iatrogenic illness or death caused purposefully or by avoidable error or negligence on the healer's part became a punishable offense in many civilizations.
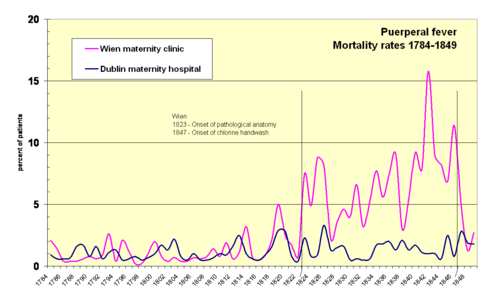
The transfer of pathogens from the autopsy room to maternity patients, leading to shocking historical mortality rates of puerperal fever
Historical mortality rates of puerperal fever
Dr. Ignaz Semmelweis worked at the Vienna General Hospital's maternity clinic on a 3-year contract from 1846-1849. There, as elsewhere in European and North American hospitals, puerperal fever, or childbed fever, was rampant, sometimes climbing to 40 percent of admitted patients...
(a.k.a. "childbed fever") at maternity institutions in the 19th century, was a major iatrogenic catastrophe of that time. The infection mechanism was first identified by Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis was a Hungarian physician now known as an early pioneer of antiseptic procedures. Described as the "savior of mothers", Semmelweis discovered that the incidence of puerperal fever could be drastically cut by the use of hand disinfection in obstetrical clinics...
.
With the development of scientific medicine
Scientific medicine
Scientific medicine, as a descriptive term, applies to "the form of medicine derived from the Flexnerian reformation of medical education and the germ theory in the early 1900s"....
in the 20th century, it could be expected that iatrogenic illness or death would be more easily avoided. Antiseptic
Antiseptic
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction...
s, anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
, antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and better surgical techniques have been developed to decrease iatrogenic mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
.
Sources
Examples of iatrogenesis:- RiskComplication (medicine)Complication, in medicine, is an unfavorable evolution of a disease, a health condition or a medical treatment. The disease can become worse in its severity or show a higher number of signs, symptoms or new pathological changes, become widespread throughout the body or affect other organ systems. A...
associated with medical interventions- Adverse effectAdverse effectIn medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
s of prescription drugs - Over-use of drugs, (causing - for example - antibiotic resistanceAntibiotic resistanceAntibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
in bacteriaBacteriaBacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
) - Prescription drug interactionDrug interactionA drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
- Adverse effect
- Medical errorMedical errorA medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
- Wrong prescriptionMedical prescriptionA prescription is a health-care program implemented by a physician or other medical practitioner in the form of instructions that govern the plan of care for an individual patient. Prescriptions may include orders to be performed by a patient, caretaker, nurse, pharmacist or other therapist....
, perhaps due to illegible handwritingHandwritingHandwriting is a person's particular & individual style of writing with pen or pencil, which contrasts with "Hand" which is an impersonal and formalised writing style in several historical varieties...
, typos on computer. - NegligenceNegligenceNegligence is a failure to exercise the care that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in like circumstances. The area of tort law known as negligence involves harm caused by carelessness, not intentional harm.According to Jay M...
- Faulty procedures, techniques, information, methods, or equipment.
Medical error and negligence
Iatrogenic conditions do not necessarily result from medical errorMedical error
A medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
s, such as mistakes made in surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, or the prescription or dispensing of the wrong therapy, such as a drug
Medication
A pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine, medication or medicament, can be loosely defined as any chemical substance intended for use in the medical diagnosis, cure, treatment, or prevention of disease.- Classification :...
. In fact, intrinsic and sometimes adverse effects
Adverse effect (medicine)
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
of a medical treatment are iatrogenic. For example, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
and chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
, due to the needed aggressiveness of the therapeutic agents, frequently produce iatrogenic effects such as hair loss, anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
, vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
, lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
, infertility, etc. The loss of functions resulting from the required removal of a diseased organ also counts as iatrogenesis, thus we find, for example, iatrogenic diabetes brought on by removal of all or part of the pancreas.
Other situations may involve actual negligence
Negligence
Negligence is a failure to exercise the care that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in like circumstances. The area of tort law known as negligence involves harm caused by carelessness, not intentional harm.According to Jay M...
or faulty procedures, such as when pharmacotherapist
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is the treatment of disease through the administration of drugs. As such, it is considered part of the larger category of therapy....
s produce handwritten prescriptions for drugs.
Adverse effects
A very common iatrogenic effect is caused by drug interactionDrug interaction
A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
, i.e., when pharmacotherapists fail to check for all medications a patient is taking and prescribe new ones that interact agonistically or antagonistically (potentiate or decrease the intended therapeutic effect). Such situations can cause significant morbidity and mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
. Adverse reactions, such as allergic reactions
Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
to drugs, even when unexpected by pharmacotherapists, are also classified as iatrogenic.
The evolution of antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
in bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
is iatrogenic as well. Bacteria strains resistant to antibiotics have evolved in response to the overprescription of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
drugs.
Certain drugs are toxic in their own right in therapeutic doses because of their mechanism of action. Alkylating antineoplastic agent
Alkylating antineoplastic agent
An alkylating antineoplastic agent is an alkylating agent used in cancer treatment that attaches an alkyl group to DNA.The alkyl group is attached to the guanine base of DNA, at the number 7 nitrogen atom of the purine ring....
s, for example, cause DNA damage, which is more harmful to cancer cells than regular cells. However, alkylation causes severe side-effects and is actually carcinogenic in its own right, with potential to lead to the development of secondary tumors. In similar manner, arsenic-based medications like melarsoprol
Melarsoprol
Melarsoprol is a medicinal drug used in the treatment of human African trypanosomiasis. It is also sold under the trade names “Mel B” and “Melarsen Oxide-BAL.”...
for trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus Trypanosoma. Approximately 500,000 men, women and children in 36 countries of sub-Saharan Africa suffer from human African trypanosomiasis which is caused by...
cause arsenic poisoning
Arsenic poisoning
Arsenic poisoning is a medical condition caused by increased levels of the element arsenic in the body. Arsenic interferes with cellular longevity by allosteric inhibition of an essential metabolic enzyme...
.
Adverse effects can appear mechanically. The design of some surgical instruments may be decades old, hence certain adverse effects (such as tissue trauma) may have never been characterized. Some instruments that are long-standing parts of surgical kit would be unlikely to succeed if they were introduced anew; the collateral damage one "expects" to see with their use would be unacceptable if associated with a *new* product.
Psychology
In psychology, iatrogenesis can occur due to misdiagnosisMedical error
A medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
(including diagnosis with a false condition as was the case of hystero-epilepsy
Hystero-epilepsy
Hystero-epilepsy is an alleged disease "discovered" by 19th-century French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot. It is considered a famous example of iatrogenic artifact, or a disease created by doctors....
). Conditions hypothesized as partially or completely iatrogenic include bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder or bipolar affective disorder, historically known as manic–depressive disorder, is a psychiatric diagnosis that describes a category of mood disorders defined by the presence of one or more episodes of abnormally elevated energy levels, cognition, and mood with or without one or...
,
dissociative identity disorder
Dissociative identity disorder
Dissociative identity disorder is a psychiatric diagnosis and describes a condition in which a person displays multiple distinct identities , each with its own pattern of perceiving and interacting with the environment....
,
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a medical disorder characterized by chronic widespread pain and allodynia, a heightened and painful response to pressure. It is an example of a diagnosis of exclusion...
,
somatoform disorder
Somatoform disorder
In psychology, a somatoform disorder is a mental disorder characterized by physical symptoms that suggest physical illness or injury - symptoms that cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, direct effect of a substance, or attributable to another mental disorder . The symptoms that...
,
chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome is the most common name used to designate a significantly debilitating medical disorder or group of disorders generally defined by persistent fatigue accompanied by other specific symptoms for a minimum of six months, not due to ongoing exertion, not substantially...
,
posttraumatic stress disorder,
substance abuse
Substance abuse
A substance-related disorder is an umbrella term used to describe several different conditions associated with several different substances .A substance related disorder is a condition in which an individual uses or abuses a...
,
antisocial youths
and others,
though research is equivocal for each condition. The degree of association of any particular condition with iatrogenesis is unclear and in some cases controversial. The over-diagnosis of psychological conditions (with the assignment of mental illness terminology) may relate primarily to clinician dependence on subjective criteria. The assignment of pathological nomenclature is rarely a benign process and can easily rise to the level of emotional iatrogenesis, especially when no alternatives outside of the diagnostic naming process have been considered.
Iatrogenic poverty
Meessen et al. used the term “iatrogenic poverty” to describe impoverishment induced by medical care. Impoverishment is described for households exposed to catastrophic health expenditure or to hardship financing. Every year, worldwide, over 100,000 households fall into poverty due to health care expenses. In the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, medical debt is the leading cause of bankruptcy
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal status of an insolvent person or an organisation, that is, one that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors. In most jurisdictions bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor....
. Especially in countries in economic transition
Transition economy
A transition economy or transitional economy is an economy which is changing from a centrally planned economy to a free market. Transition economies undergo economic liberalization, where market forces set prices rather than a central planning organization and trade barriers are removed,...
, the willingness to pay
Willingness to pay
In economics, the willingness to pay is the maximum amount a person would be willing to pay, sacrifice or exchange in order to receive a good or to avoid something undesired, such as pollution...
for health care
Health care
Health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. Health care is delivered by practitioners in medicine, chiropractic, dentistry, nursing, pharmacy, allied health, and other care providers...
is increasing, and the supply side does not stay behind and develops very fast. But the regulatory and protective capacity in those countries is often lagging behind. Patients easily fall in a vicious cycle of illness, ineffective therapies, consumption of savings, indebtedness, sale of productive assets, and eventually poverty.
Incidence and importance
Iatrogenesis is a major phenomenon, and a severe risk to patients.A study carried out in 1981 more than one-third of illnesses of patients in a university hospital were iatrogenic, nearly one in ten was considered major, and, in 2% of the patients, the iatrogenic disorder ended in death. Complications were most strongly associated with exposure to drugs and medications. In another study, the main factors leading to problems were inadequate patient evaluation, lack of monitoring and follow-up, and failure to perform necessary tests.
In the United States, figures suggest estimated deaths per year of:
- 12,000 due to unnecessary surgery
- 7,000 due to medication errors in hospitals
- 20,000 due to other errors in hospitals
- 80,000 due to nosocomial infections in hospitals
- 106,000 due to non-error, negative effects of drugs
Based on these figures, iatrogenesis may cause 225,000 deaths per year in the United States (excluding recognizable error).
These estimates are lower than those in an earlier IOM
Institute of Medicine
The Institute of Medicine is a not-for-profit, non-governmental American organization founded in 1970, under the congressional charter of the National Academy of Sciences...
report, which would suggest from 230,000 to 284,000 iatrogenic deaths.
These figures are likely exaggerated, however, as they are based on recorded deaths in hospitals rather than in the general population. Even so, the large gap separating these estimates, deaths from cerebrovascular disease would still suggest that iatrogenic illness constitutes the third-leading cause of death in the United States; heart disease and cancer are the first- and second-leading causes of death, respectively.
See also
- Adverse drug reactionAdverse drug reactionAn adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
- Adverse effect (medicine)Adverse effect (medicine)In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
- BedsoreBedsoreBedsores, more properly known as pressure ulcers or decubitus ulcers, are lesions caused by many factors—such as unrelieved pressure, friction, humidity, shearing forces, temperature, age, continence, and medication—to any part of the body, especially portions over bony or cartilaginous areas such...
- BioethicsBioethicsBioethics is the study of controversial ethics brought about by advances in biology and medicine. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, and philosophy....
- Cascade effectCascade effectA Cascade Effect is an unforeseen chain of events due to an act affecting a system. If there is a possibility that the cascade effect will have a negative impact on the system, it is possible to analyze the effects with a consequence/impact analysis...
- Classification of Pharmaco-Therapeutic ReferralsClassification of Pharmaco-Therapeutic ReferralsThe Classification of Pharmaco-Therapeutic Referrals is a taxonomy focused to define and group together situations requiring a referral from pharmacists to physicians regarding the pharmacotherapy used by the patients. It has been published in 2008...
- Complication (medicine)Complication (medicine)Complication, in medicine, is an unfavorable evolution of a disease, a health condition or a medical treatment. The disease can become worse in its severity or show a higher number of signs, symptoms or new pathological changes, become widespread throughout the body or affect other organ systems. A...
- Fatal Care: Survive in the U.S. Health SystemFatal Care: Survive in the U.S. Health SystemFatal Care: Survive in the U.S. Health System is a book about preventable medical errors written by Sanjaya Kumar, president and chief medical officer of Quantros, Milpitas, California. Fatal Care was published in April 2008 by IGI Publishing, Minneapolis, Minnesota.Fatal Care: Survive in the U.S...
(book) - Ivan Illich — Medical NemesisIvan IllichIvan Illich was an Austrian philosopher, Roman Catholic priest, and "maverick social critic" of the institutions of contemporary western culture and their effects on the provenance and practice of education, medicine, work, energy use, transportation, and economic development.- Personal life...
(book) - Journal of Negative Results in BiomedicineJournal of Negative Results in BiomedicineThe Journal of Negative Results in Biomedicine is an open access peer-reviewed medical journal. It publishes papers that promote a discussion of unexpected, controversial, provocative and/or negative results in the context of current tenets....
'’ - List of medicine contamination incidents
- Medical errorMedical errorA medical error may be defined as a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.-Definitions:As a general...
- NoceboNoceboIn medicine, a nocebo reaction or response refers to harmful, unpleasant, or undesirable effects a subject manifests after receiving an inert dummy drug or placebo...
- Patient safetyPatient safetyPatient safety is a new healthcare discipline that emphasizes the reporting, analysis, and prevention of medical error that often leads to adverse healthcare events. The frequency and magnitude of avoidable adverse patient events was not well known until the 1990s, when multiple countries reported...
- PlaceboPlaceboA placebo is a simulated or otherwise medically ineffectual treatment for a disease or other medical condition intended to deceive the recipient...
- PolypharmacyPolypharmacyPolypharmacy is the use of multiple medications by a patient, especially when too many forms of medication are used by a patient, when more drugs are prescribed than is clinically warranted, or even when all prescribed medications are clinically indicated but there are too many pills to take ....
- Quaternary preventionQuaternary preventionThe quaternary prevention, concept coined by the Belgian general practitioner , are the action taken to identify patient at risk of overmedicalisation, to protect him from new medical invasion, and to suggest to him interventions, which are ethically acceptable...
- Medical harmMedical harmMedical harm refers to any systemic failure in the health care system that results in a negative psychological or physical consequence. Medical harm is not limited to iatrogenic illness....
- Nosocomial infectionNosocomial infectionA nosocomial infection , also known as a hospital-acquired infection or HAI, is an infection whose development is favoured by a hospital environment, such as one acquired by a patient during a hospital visit or one developing among hospital staff...

