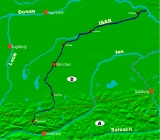
Isar
Encyclopedia
The Isar is a river in Tyrol
, Austria
and Bavaria
, Germany
. Its source is in the Karwendel
range of the Alps
in Tyrol; it enters Germany near Mittenwald
, and flows through Bad Tölz
, Munich
, and Landshut
before reaching the Danube
near Deggendorf
. At 295 km in length, it is the fourth largest river in Bavaria, after the Danube
, Inn, and Main. It is Germany's second most important tributary of the Danube after the Inn.
It may be possible that the ancient name of the lower part of the river Danube, Ister, has the same source. Newer interpretations relate it to the Old Basque particle *(w)its-, 'water', also seen in similar but otherwise unexplained river names, such as Vézère
, Vizela
, Weser and Vistula
.
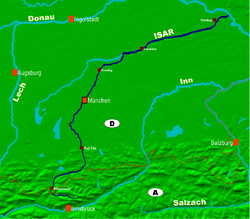
 The Isar drains a substantial part of the Alps
The Isar drains a substantial part of the Alps
and parts of the Karwendel
mountains northeast towards the Danube river and thus finally towards the Black Sea
. The drainage basin
contains some 9,000 square kilometers (3,500 square miles). During the winter most of the precipitation
in the Alps falls as snow. This results in an increased water flow during the spring meltdown. It has an average discharge of 175 cubic meters (6,200 cubic feet) per second. This makes it comparable to other medium-sized rivers in Germany, like the Moselle
, Lech
or Main.
Apart from the larger tributaries Amper
and Loisach
many smaller rivers empty into the Isar, such as the Leutasch
, the Jachen
, the Dürrach, the Dorfen
, the Sempt
and the Pfettrach
.
The official head of the Isar is located in the Hinterau valley east of the village Scharnitz
in the Karwendel mountains in Tyrol
, Austria at a sea level
of 1,160 meters ( 3,500 feet). In 2003 the Isar spring was “developed”, however, this move has been discussed due to enviroinmental reasons. The Lavatsch, which is the Isar’s longest headstream, has its source farther to the southeast near a mountain cabin named Hallangerhaus. It is also sometimes called the Isar’s head. Further on the young Isar is supplied water by the Birkkarbach, which has its source at the foot of the highest mountain of the Karwendel, the Birkkarspitze
and the Moserkarbach. Between Mittenwald and Krün
the Isar is dammed for the first time. Its waters are led into the lake Walchensee
where electricity is generated. To make more energy generation possible and also to avoid flooding farther down the river a large reservoir called Sylvensteinsee was created between 1954 and 1959. It is located some 12 km (7.5 mi) south of Lenggries
. It has prevented some bad floods in Munich, for example in 1979, 1999 and most important, in 2005. In that year for the first time ever water had to be released from the lake because its capacity was exhausted. Flooding was barely avoided in Munich. After leaving the Bavarian Alps at Bad Tölz
, the Isar first flows through the glacial morainic landscape and then through the Munich plain. It continues from Freising
on through the tertiary hills all the way into the Danube valley. Its mouth at the Danube is at 312 meters (950 ft) above sea level, thus the Isar descends some 848 meters (2,600 ft) from its head to its mouth.
is located; formerly this island was called Kohleninsel (coal island), the Praterinsel (both located in Munich) and the Mühleninsel in Landshut
.
 It is quite likely that the Isar was used as a trade route, even in prehistoric times, to transport wares from the Alps and even Italy
It is quite likely that the Isar was used as a trade route, even in prehistoric times, to transport wares from the Alps and even Italy
towards the Danube with rafts. An existing trade road from the Inn valley
across Seefelder Pass
into the northern foothills of the alps was built up and called Via Raetia by the Romans
. The town of Mittenwald
thus became an important trade post in the Werdenfelser Land
.
At a few places the Romans built wooden bridges across the Isara so they could cross the river with its strong currents more easily. One of these could have been along the Roman street from Salzburg
to Augsburg
south of contemporary Munich. Thus trade traffic could easily be controlled and income from tolls was frequent and regular. The medieval foundation of the cities of Munich and Landshut
are directly connected with the building of bridges and the resulting conflicts concerning power and influence on the economy. Due to the continuing growth of the cities there was a constant demand for timber and lime, which resulted in an increase of commercial rafting
. Beginning in the 17th century wares like Mediterranean fruit, spices, cotton and silk from the Venetian Market in Mittenwald were transported down the Isar and Danube all the way to Vienna
and Budapest
. During the 19th century when commercial rafting was at its peak, some 8,000 rafts arrived in Munich each year.
Since the Middle Ages
water mills were working at the banks of the Isar by hydro mechanical power. To ensure a more constant flow for the mills the water in Munich was led into small canals. The canals were also used to provide freshwater to the population of the city and also the numerous tanneries
of the city and to fill the protecting ditches located outside the medieval town wall. During the annual floodings cities along the Isar were flooded again and again, causing severe damage and even killing people. In 1813 a bridge in Munich collapsed during a flood, killing more than 100 people who were watching the flooding from the bridge. From 1806 on, the banks of the river were fixed and the river was canalized. This led to its deeper digging into the river bed due to its flowing faster. Further extensive measures have been taken since the 1920s to install hydroelectric power plants. From 1954 to 1959 the then much-disputed Sylvensteinspeicher
was built for the generation of electricity and for protection against floodings. The village of Fall was drowned in the reservoir. When the water level in the reservoir is very low the church tower can still be seen sticking out of the water. Only over the last few years the Isar was partly turned back from a canal into a more natural river.
At the lower Isar between Moosburg
and Plattling
gold
was washed from the river’s sediments during the 16th and 17th century. However, there was no big economic revenue in this due to the minor amounts of the metal found in the river.
Following their executions on October 16, 1946, the ashes of the Nazi war criminals Joachim von Ribbentrop
, Hans Frank
, Wilhelm Keitel
, Alfred Jodl
, Alfred Rosenberg
, Ernst Kaltenbrunner
, Wilhelm Frick
, Arthur Seyss-Inquart
, Fritz Sauckel
and Julius Streicher
were scattered in the Isar, as were those of Hermann Göring
who had committed suicide the previous night.

 Since the 1920s the water of the Isar has been used for the generation of electricity. This has had far-reaching consequences not only for the local fauna and flora but also for people. To provide the 28 hydroelectric power plants with enough water power the river’s water is diverted several times and almost the whole river was canalized. For example, just north of Mittenwald
Since the 1920s the water of the Isar has been used for the generation of electricity. This has had far-reaching consequences not only for the local fauna and flora but also for people. To provide the 28 hydroelectric power plants with enough water power the river’s water is diverted several times and almost the whole river was canalized. For example, just north of Mittenwald
all the river’s water was diverted to the lake Walchensee
in 1923 for the Walchensee hydroelectric plant. Since 1990 a small portion of the water, 4 cubic meters per second (1100 U.S. gallons per second) is allowed to remain in the river to keep the area from being dry. The construction of the Sylvenstein Dam and numerous regulations relating to the river (pushed through in the early 19th century) have strongly enhanced its character. The construction of the Sylvenstein dam has prevented the river from overflowing its banks.
Lately, there have been attempts to bring the Isar closer back to a natural character. For example, since May, 2000, the river is being re-naturalized in the southern part of the river’s passage through the city of Munich, between Großhesseloher Brücke and Reichenbachbrücke. To achieve this the riverbed is being widened, the banks are flattened and small gravel islands are built along with near-natural ramps to slow the waterflow. Also, the dams are enlarged in width and height.
Besides an improved protection against flooding the river was, thus, brought into an almost natural state and this resulted in an improved quality of the recreational area within the city of Munich. The quality of the water has also improved due to the upgrading of the sewage plants along the river. The number of germs, however, is still relatively high. Together with other cities and communities along the Isar, Munich has set a goal to reduce the number of germs until the water quality is good enough to allow bathing in the river. If this is achieved, Munich would be one of the few big cities in Europe with a river with water of good enough quality to allow swimming in it. The sewer plants on the upper river are now treating the sewage with ultraviolet
light, which greatly reduces the number of germs, but still the Isar cannot be guaranteed safe to bathe in because of the entrance of polluted rainwater into the river, especially during strong precipitation.
There are a number of natural reservations along the Isar, including special protection areas for birds, for example the natural reserve Vogelfreistätte Mittlere Isarstauseen northeast of Moosburg. This area is an important resting place for migrating water birds. There has been evidence for more than 260 different species of birds, among them rare species like the Common Tern
and the Bluethroat
.
To preserve the beauty of the Isar valley Gabriel von Seidl founded the Isartalverein in 1902. This first civil initiative from Munich purchased 90 hectares (220 acres) of land, and today maintains more than 330 km (205.1 mi) of hiking trails.
Tyrol (state)
Tyrol is a state or Bundesland, located in the west of Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical region of Tyrol.The state is split into two parts–called North Tyrol and East Tyrol–by a -wide strip of land where the state of Salzburg borders directly on the Italian province of...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
and Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. Its source is in the Karwendel
Karwendel
The Karwendel is the largest range of the Northern Limestone Alps. Four chains stretch from west to east; in addition, there are a number of fringe ranges and an extensive promontory in the north....
range of the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
in Tyrol; it enters Germany near Mittenwald
Mittenwald
Mittenwald is a German municipality in the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, in Bavaria.-Geography:Mittenwald is located approx. 16 kilometers to the south-east of Garmisch-Partenkirchen...
, and flows through Bad Tölz
Bad Tölz
Bad Tölz is a town in Bavaria, Germany, and administrative center of the district of Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen.- History :Since the retreat of the glaciers at the end of the Ice Age, archaeology has shown continuous occupation of the site of Bad Tölz...
, Munich
Munich
Munich The city's motto is "" . Before 2006, it was "Weltstadt mit Herz" . Its native name, , is derived from the Old High German Munichen, meaning "by the monks' place". The city's name derives from the monks of the Benedictine order who founded the city; hence the monk depicted on the city's coat...
, and Landshut
Landshut
Landshut is a city in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany, belonging to both Eastern and Southern Bavaria. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also the seat of the...
before reaching the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
near Deggendorf
Deggendorf
Deggendorf is a town in Bavaria, capital of the district Deggendorf.The earliest traces of settlement in the area are found near the Danube, about 8,000 years ago. Both Bronze Age and Celtic era archeological finds indicate continuous habitation through the years...
. At 295 km in length, it is the fourth largest river in Bavaria, after the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
, Inn, and Main. It is Germany's second most important tributary of the Danube after the Inn.
Etymology
According to the most common interpretation the name Isar is a construction of the Celtic words ys (fast, torrential) and ura (water, river). According to another interpretation ys may mean “high” as well as “low”, referring to the rapidly changing water level in the river Isar. In the ancient settlement area of the Celts several related river names can be found:- JizeraJizera RiverThe Jizera is a river that begins on the border between Poland and the Czech Republic and ends in Central Bohemia. Like some other names in Bohemia, the name Jizera is of Celtic origin, as the Celts lived in the area during Roman times .-Geography:It develops from the confluence of the Great Jizera...
(Czech Republic) - IsèreIsère RiverThe Isère is a 286 km long river in southeastern France, in the Rhône-Alpes région. Its source is in the Alps on the border with Italy, near the ski resort Val d'Isère. It flows into the Rhône River in Pont-de-l'Isère, a few km north of Valence...
(France) - IselISELISEL can refer to:*Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, a Portuguese school of engineering*Industrial Syndicalist Education League, a British syndicalist organisation*Institut supérieur d'études logistiques, a French school of engineering...
(Austria) - IJsselIJsselRiver IJssel , sometimes called Gelderse IJssel to avoid confusion with its Hollandse IJssel namesake in the west of the Netherlands, is a branch of the Rhine in the Dutch provinces of Gelderland and Overijssel...
(Netherlands) - IJzer (Belgium)
- EisackEisackThe Eisack is a river in Northern Italy, the second largest river in South Tyrol. Its source is near the Brenner Pass, at an altitude of about 1990 m above sea level. The river draws water from an area of about 4,200 km². After about 96 km, it joins the Adige river south of Bolzano. At first the...
(Italy) - Isar (Spanish town, in the province of BurgosBurgosBurgos is a city of northern Spain, historic capital of Castile. It is situated at the edge of the central plateau, with about 178,966 inhabitants in the city proper and another 20,000 in its suburbs. It is the capital of the province of Burgos, in the autonomous community of Castile and León...
)
It may be possible that the ancient name of the lower part of the river Danube, Ister, has the same source. Newer interpretations relate it to the Old Basque particle *(w)its-, 'water', also seen in similar but otherwise unexplained river names, such as Vézère
Vézère
The Vézère is a 211 km long river in south-western France, right tributary of the Dordogne River. Its source is in the north-western Massif Central...
, Vizela
Vizela
Vizela is a municipality in Portugal with a total area of 24.7 km² and a total population of 23,528 inhabitants.The municipality is composed of 7 parishes, and is located in the Braga District....
, Weser and Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
.
Geography


Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
and parts of the Karwendel
Karwendel
The Karwendel is the largest range of the Northern Limestone Alps. Four chains stretch from west to east; in addition, there are a number of fringe ranges and an extensive promontory in the north....
mountains northeast towards the Danube river and thus finally towards the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. The drainage basin
Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
contains some 9,000 square kilometers (3,500 square miles). During the winter most of the precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
in the Alps falls as snow. This results in an increased water flow during the spring meltdown. It has an average discharge of 175 cubic meters (6,200 cubic feet) per second. This makes it comparable to other medium-sized rivers in Germany, like the Moselle
Moselle
Moselle is a department in the east of France named after the river Moselle.- History :Moselle is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790...
, Lech
Lech River
The Lech is a river in Austria and Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube in length with a drainage basin of .Its source is located in the Austrian state of Vorarlberg, where the river rises from lake Formarinsee in the Alps at an altitude of...
or Main.
Apart from the larger tributaries Amper
Amper
The Amper is a river located in southern Bavaria, Germany and is the largest tributary to the Isar river. The Amper flows into the Isar in Moosburg, 185 km from the headwater of the river and at a speed of 45 m³/s. It runs out of the Ammersee and its upper course, upstream from the...
and Loisach
Loisach
The Loisach is a river that flows through Tyrol, Austria and Bavaria, Germany. Its name is Celtic in origin, from Proto-Celtic *lawo and *iskā, both of which mean "water."...
many smaller rivers empty into the Isar, such as the Leutasch
Leutasch
Leutasch is a municipality in the northern part of the district Innsbruck-Land and is located approximately 30 km northwest of Innsbruck. The beautiful valley lies within a 16 km long high-lying valley and possesses 2073 inhabitants and 26 hamlets....
, the Jachen
Jachen
Jachen is a river of Bavaria, Germany.-See also:*List of rivers of Bavaria...
, the Dürrach, the Dorfen
Dorfen
Dorfen is a town in the district of Erding, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated 18 km east of Erding and 29 km south of Landshut....
, the Sempt
Sempt
Sempt is a river of Bavaria, Germany.-See also:*List of rivers of Bavaria...
and the Pfettrach
Pfettrach
Pfettrach is a river of Bavaria, Germany.-See also:*List of rivers of Bavaria...
.
The official head of the Isar is located in the Hinterau valley east of the village Scharnitz
Scharnitz
Scharnitz is a municipality in the district of Innsbruck-Land and is located 16,40 km north of Innsbruck as well as 9 km above Seefeld in Tirol at the border to Germany. It has one of the biggest area size and possesses 12 parts. The village was founded in the early middle age and was once an...
in the Karwendel mountains in Tyrol
Tyrol (state)
Tyrol is a state or Bundesland, located in the west of Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical region of Tyrol.The state is split into two parts–called North Tyrol and East Tyrol–by a -wide strip of land where the state of Salzburg borders directly on the Italian province of...
, Austria at a sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
of 1,160 meters ( 3,500 feet). In 2003 the Isar spring was “developed”, however, this move has been discussed due to enviroinmental reasons. The Lavatsch, which is the Isar’s longest headstream, has its source farther to the southeast near a mountain cabin named Hallangerhaus. It is also sometimes called the Isar’s head. Further on the young Isar is supplied water by the Birkkarbach, which has its source at the foot of the highest mountain of the Karwendel, the Birkkarspitze
Birkkarspitze
The Birkkarspitze is the highest mountain in the Karwendel range, Austria....
and the Moserkarbach. Between Mittenwald and Krün
Krün
Krün is a municipality in the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, in Bavaria, Germany....
the Isar is dammed for the first time. Its waters are led into the lake Walchensee
Walchensee
Walchensee or Lake Walchen is one of the deepest and largest alpine lakes in Germany, with a maximum depth of and an area of . The lake is south of Munich in the middle of the Bavarian Alps. The entire lake, including the island Sassau is part of the municipality of Kochel...
where electricity is generated. To make more energy generation possible and also to avoid flooding farther down the river a large reservoir called Sylvensteinsee was created between 1954 and 1959. It is located some 12 km (7.5 mi) south of Lenggries
Lenggries
Lenggries is a municipality in Bavaria, Germany. Lenggries is the center of the Isarwinkel, the region along the Isar between Bad Tölz and Wallgau...
. It has prevented some bad floods in Munich, for example in 1979, 1999 and most important, in 2005. In that year for the first time ever water had to be released from the lake because its capacity was exhausted. Flooding was barely avoided in Munich. After leaving the Bavarian Alps at Bad Tölz
Bad Tölz
Bad Tölz is a town in Bavaria, Germany, and administrative center of the district of Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen.- History :Since the retreat of the glaciers at the end of the Ice Age, archaeology has shown continuous occupation of the site of Bad Tölz...
, the Isar first flows through the glacial morainic landscape and then through the Munich plain. It continues from Freising
Freising
Freising is a town in Bavaria, Germany, and capital of the district Freising. Total population 48,500.The city is located north of Munich at the Isar river, near the Munich International Airport...
on through the tertiary hills all the way into the Danube valley. Its mouth at the Danube is at 312 meters (950 ft) above sea level, thus the Isar descends some 848 meters (2,600 ft) from its head to its mouth.
Islands
Most of the small islands and gravel banks keep changing shape and size due to the annual floods. Some of the islands within the bigger cities were built up during the 19th century and thus protected against the abrasive powers of the water. Among those are the Museumsinsel (on which the Deutsches MuseumDeutsches Museum
The Deutsches Museum in Munich, Germany, is the world's largest museum of technology and science, with approximately 1.5 million visitors per year and about 28,000 exhibited objects from 50 fields of science and technology. The museum was founded on June 28, 1903, at a meeting of the Association...
is located; formerly this island was called Kohleninsel (coal island), the Praterinsel (both located in Munich) and the Mühleninsel in Landshut
Landshut
Landshut is a city in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany, belonging to both Eastern and Southern Bavaria. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also the seat of the...
.
History

Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
towards the Danube with rafts. An existing trade road from the Inn valley
Inn River
The Inn is a river in Switzerland, Austria and Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube and is approximately 500km long. The highest point of its drainage basin is the summit of Piz Bernina, at 4,049 metres.- Geography :...
across Seefelder Pass
Seefeld, Tirol
Seefeld in Tirol is a municipality of the Innsbruck-Land District in the Austrian state of Tyrol, located about northwest of Innsbruck. With more than one million overnight stays each year, it is one of the most popular Tyrolean tourist destinations especially for skiing in winter, but also for...
into the northern foothills of the alps was built up and called Via Raetia by the Romans
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. The town of Mittenwald
Mittenwald
Mittenwald is a German municipality in the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, in Bavaria.-Geography:Mittenwald is located approx. 16 kilometers to the south-east of Garmisch-Partenkirchen...
thus became an important trade post in the Werdenfelser Land
Werdenfelser Land
The Werdenfelser Land is a region of Upper Bavaria that extends from Mittenwald in the south to Farchant. It includes parts of the Bavarian Alps. From the Middle Ages until the Thirty Years War the Werdenfelser Land was subject to the Prince-Bishop of Freising, not the Duke of Bavaria.The region...
.
At a few places the Romans built wooden bridges across the Isara so they could cross the river with its strong currents more easily. One of these could have been along the Roman street from Salzburg
Salzburg
-Population development:In 1935, the population significantly increased when Salzburg absorbed adjacent municipalities. After World War II, numerous refugees found a new home in the city. New residential space was created for American soldiers of the postwar Occupation, and could be used for...
to Augsburg
Augsburg
Augsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a...
south of contemporary Munich. Thus trade traffic could easily be controlled and income from tolls was frequent and regular. The medieval foundation of the cities of Munich and Landshut
Landshut
Landshut is a city in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany, belonging to both Eastern and Southern Bavaria. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also the seat of the...
are directly connected with the building of bridges and the resulting conflicts concerning power and influence on the economy. Due to the continuing growth of the cities there was a constant demand for timber and lime, which resulted in an increase of commercial rafting
Timber rafting
Timber rafting is a log transportation method in which logs are tied together into rafts and drifted or pulled across a water body or down a flatter river. It is arguably the second cheapest method of transportation of timber, next after log driving...
. Beginning in the 17th century wares like Mediterranean fruit, spices, cotton and silk from the Venetian Market in Mittenwald were transported down the Isar and Danube all the way to Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
and Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
. During the 19th century when commercial rafting was at its peak, some 8,000 rafts arrived in Munich each year.
Since the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
water mills were working at the banks of the Isar by hydro mechanical power. To ensure a more constant flow for the mills the water in Munich was led into small canals. The canals were also used to provide freshwater to the population of the city and also the numerous tanneries
Tanning
Tanning is the making of leather from the skins of animals which does not easily decompose. Traditionally, tanning used tannin, an acidic chemical compound from which the tanning process draws its name . Coloring may occur during tanning...
of the city and to fill the protecting ditches located outside the medieval town wall. During the annual floodings cities along the Isar were flooded again and again, causing severe damage and even killing people. In 1813 a bridge in Munich collapsed during a flood, killing more than 100 people who were watching the flooding from the bridge. From 1806 on, the banks of the river were fixed and the river was canalized. This led to its deeper digging into the river bed due to its flowing faster. Further extensive measures have been taken since the 1920s to install hydroelectric power plants. From 1954 to 1959 the then much-disputed Sylvensteinspeicher
Sylvensteinspeicher
Sylvenstein Dam is an earthen embankment dam in the Isar valley, in the alpine part of Upper Bavaria, Germany which impounds the Sylvenstein Reservoir ....
was built for the generation of electricity and for protection against floodings. The village of Fall was drowned in the reservoir. When the water level in the reservoir is very low the church tower can still be seen sticking out of the water. Only over the last few years the Isar was partly turned back from a canal into a more natural river.
At the lower Isar between Moosburg
Moosburg
Moosburg an der Isar is a town in the Landkreis Freising of Bavaria, Germany.The oldest town between Regensburg and Italy, it lies on the river Isar at an altitude of 421 m . It has 17,275 inhabitants and covers an area of 44 km². It is easily reached by the A 92 autobahn and regional trains on...
and Plattling
Plattling
Plattling is a town in the district of Deggendorf, in Bavaria, Germany.During World War II, a subcamp of Flossenburg concentration camp was located here...
gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
was washed from the river’s sediments during the 16th and 17th century. However, there was no big economic revenue in this due to the minor amounts of the metal found in the river.
Following their executions on October 16, 1946, the ashes of the Nazi war criminals Joachim von Ribbentrop
Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop was Foreign Minister of Germany from 1938 until 1945. He was later hanged for war crimes after the Nuremberg Trials.-Early life:...
, Hans Frank
Hans Frank
Hans Michael Frank was a German lawyer who worked for the Nazi party during the 1920s and 1930s and later became a high-ranking official in Nazi Germany...
, Wilhelm Keitel
Wilhelm Keitel
Wilhelm Bodewin Gustav Keitel was a German field marshal . As head of the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht and de facto war minister, he was one of Germany's most senior military leaders during World War II...
, Alfred Jodl
Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl was a German military commander, attaining the position of Chief of the Operations Staff of the Armed Forces High Command during World War II, acting as deputy to Wilhelm Keitel...
, Alfred Rosenberg
Alfred Rosenberg
' was an early and intellectually influential member of the Nazi Party. Rosenberg was first introduced to Adolf Hitler by Dietrich Eckart; he later held several important posts in the Nazi government...
, Ernst Kaltenbrunner
Ernst Kaltenbrunner
Ernst Kaltenbrunner was an Austrian-born senior official of Nazi Germany during World War II. Between January 1943 and May 1945, he held the offices of Chief of the Reichssicherheitshauptamt , President of Interpol and, as a Obergruppenführer und General der Polizei und Waffen-SS, he was the...
, Wilhelm Frick
Wilhelm Frick
Wilhelm Frick was a prominent German Nazi official serving as Minister of the Interior of the Third Reich. After the end of World War II, he was tried for war crimes at the Nuremberg Trials and executed...
, Arthur Seyss-Inquart
Arthur Seyss-Inquart
Arthur Seyss-Inquart was a Chancellor of Austria, lawyer and later Nazi official in pre-Anschluss Austria, the Third Reich and for wartime Germany in Poland and the Netherlands...
, Fritz Sauckel
Fritz Sauckel
Ernst Friedrich Christoph "Fritz" Sauckel was a Nazi war criminal, who organized the systematic enslavement of millions from lands occupied by Nazi Germany...
and Julius Streicher
Julius Streicher
Julius Streicher was a prominent Nazi prior to World War II. He was the founder and publisher of Der Stürmer newspaper, which became a central element of the Nazi propaganda machine...
were scattered in the Isar, as were those of Hermann Göring
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring, was a German politician, military leader, and a leading member of the Nazi Party. He was a veteran of World War I as an ace fighter pilot, and a recipient of the coveted Pour le Mérite, also known as "The Blue Max"...
who had committed suicide the previous night.
Environmental issues


Mittenwald
Mittenwald is a German municipality in the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, in Bavaria.-Geography:Mittenwald is located approx. 16 kilometers to the south-east of Garmisch-Partenkirchen...
all the river’s water was diverted to the lake Walchensee
Walchensee
Walchensee or Lake Walchen is one of the deepest and largest alpine lakes in Germany, with a maximum depth of and an area of . The lake is south of Munich in the middle of the Bavarian Alps. The entire lake, including the island Sassau is part of the municipality of Kochel...
in 1923 for the Walchensee hydroelectric plant. Since 1990 a small portion of the water, 4 cubic meters per second (1100 U.S. gallons per second) is allowed to remain in the river to keep the area from being dry. The construction of the Sylvenstein Dam and numerous regulations relating to the river (pushed through in the early 19th century) have strongly enhanced its character. The construction of the Sylvenstein dam has prevented the river from overflowing its banks.
Lately, there have been attempts to bring the Isar closer back to a natural character. For example, since May, 2000, the river is being re-naturalized in the southern part of the river’s passage through the city of Munich, between Großhesseloher Brücke and Reichenbachbrücke. To achieve this the riverbed is being widened, the banks are flattened and small gravel islands are built along with near-natural ramps to slow the waterflow. Also, the dams are enlarged in width and height.
Besides an improved protection against flooding the river was, thus, brought into an almost natural state and this resulted in an improved quality of the recreational area within the city of Munich. The quality of the water has also improved due to the upgrading of the sewage plants along the river. The number of germs, however, is still relatively high. Together with other cities and communities along the Isar, Munich has set a goal to reduce the number of germs until the water quality is good enough to allow bathing in the river. If this is achieved, Munich would be one of the few big cities in Europe with a river with water of good enough quality to allow swimming in it. The sewer plants on the upper river are now treating the sewage with ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light, which greatly reduces the number of germs, but still the Isar cannot be guaranteed safe to bathe in because of the entrance of polluted rainwater into the river, especially during strong precipitation.
There are a number of natural reservations along the Isar, including special protection areas for birds, for example the natural reserve Vogelfreistätte Mittlere Isarstauseen northeast of Moosburg. This area is an important resting place for migrating water birds. There has been evidence for more than 260 different species of birds, among them rare species like the Common Tern
Common Tern
The Common Tern is a seabird of the tern family Sternidae. This bird has a circumpolar distribution, breeding in temperate and sub-Arctic regions of Europe, Asia and east and central North America. It is strongly migratory, wintering in coastal tropical and subtropical regions. It is sometimes...
and the Bluethroat
Bluethroat
The Bluethroat is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World flycatcher, Muscicapidae...
.
To preserve the beauty of the Isar valley Gabriel von Seidl founded the Isartalverein in 1902. This first civil initiative from Munich purchased 90 hectares (220 acres) of land, and today maintains more than 330 km (205.1 mi) of hiking trails.

