
Isis
Encyclopedia

Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world
Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman culture, or the term Greco-Roman , when used as an adjective, as understood by modern scholars and writers, refers to those geographical regions and countries that culturally were directly, protractedly and intimately influenced by the language, culture,...
. She was worshipped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the friend of slaves, sinners, artisan
Artisan
An artisan is a skilled manual worker who makes items that may be functional or strictly decorative, including furniture, clothing, jewellery, household items, and tools...
s, and the downtrodden, and she listened to the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats, and rulers. Isis is the goddess of motherhood, magic
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
and fertility
Fertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
.
The goddess Isis (mother of Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
) was the first daughter of Geb
Geb
Geb was the Egyptian god of the Earth and a member of the Ennead of Heliopolis. It was believed in ancient Egypt that Geb's laughter was earthquakes and that he allowed crops to grow. The name was pronounced as such from the Greek period onward,...
, god of the Earth, and Nut
Nut (goddess)
In the Ennead of Egyptian mythology, Nut was the goddess of the sky.-Goddess of the sky:...
, the goddess of the Overarching Sky, and was born on the fourth intercalary day. At some time Isis and Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
had the same headdress. In later myths about Isis, she had a brother, Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
, who became her husband, and she then was said to have conceived Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
. Isis was instrumental in the resurrection of Osiris when he was murdered by Set
Set (mythology)
Set was in Ancient Egyptian religion, a god of the desert, storms, and foreigners. In later myths he was also the god of darkness, and chaos...
. Her magical skills restored his body to life after she gathered the body parts that had been strewn about the earth by Set. This myth became very important in later Egyptian religious beliefs.
Isis is also known as protector of the dead and goddess of children from whom all beginnings arose. In later times, the ancient Egyptians
Egyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
believed that the Nile River flooded every year because of her tears of sorrow for her dead husband, Osiris. This occurrence of his death and rebirth was relived each year through rituals. The worship of Isis eventually spread throughout the Greco-Roman world, continuing until the suppression of paganism
Paganism
Paganism is a blanket term, typically used to refer to non-Abrahamic, indigenous polytheistic religious traditions....
in the Christian era.
Origin of the name
The name Isis is an anglicized version of the GreekGreek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
version of her name, which itself changed the original Egyptian name spelling by the addition of a last -s because of the grammatical requirements of Greek endings.
The Egyptian name was recorded as or and meant "(She of the) Throne". The true Egyptian
Egyptian language
Egyptian is the oldest known indigenous language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Written records of the Egyptian language have been dated from about 3400 BC, making it one of the oldest recorded languages known. Egyptian was spoken until the late 17th century AD in the...
pronunciation remains uncertain, however, because hieroglyphs
Hieroglyphs
Hieroglyph or hieroglyphics may refer to:*Anatolian hieroglyphs*Chinese character*Cretan hieroglyphs*Cursive hieroglyphs*Dongba script*Egyptian hieroglyphs*Hieroglyphic Luwian*Mayan hieroglyphs...
do not have vowels. Based on recent studies which present us with approximations based on contemporary languages (specifically, Greek) and Coptic
Coptic language
Coptic or Coptic Egyptian is the current stage of the Egyptian language, a northern Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Egypt until at least the 17th century. Egyptian began to be written using the Greek alphabet in the 1st century...
evidence, the reconstructed pronunciation of her name is *Usat *ˈʔyːsəʔ. Osiris's name—that is, *Usir "Osiris" (ws-ỉr) also starts with the throne glyph (-s). The name survived in Coptic
Coptic language
Coptic or Coptic Egyptian is the current stage of the Egyptian language, a northern Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Egypt until at least the 17th century. Egyptian began to be written using the Greek alphabet in the 1st century...
dialects as Ēse or Ēsi, as well as in compound words surviving in names of later people such as "Har-si-Ese
Harsiese
Harsiese, or Har-Si-Ese, was an ancient Egyptian name, literally meaning "Horus, son of Isis". Some people by this name include:* Harsiese A, an independent king in Upper Egypt during the 22nd Dynasty...
", which means "Horus, son of Isis".
For convenience, Egyptologists arbitrarily choose to pronounce her name as "ee-set". Sometimes they may also say "ee-sa" because the final "t" in her name was a feminine suffix
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs...
, which is known to have been dropped in speech during the last stages of the Egyptian language.
The name Isis means "Throne". Her headdress is a throne. As the personification of the throne, she was an important representation of the pharaoh's power, as the pharaoh was depicted as her child, who sat on the throne she provided. Her cult was popular throughout Egypt, but the most important sanctuaries were at Behbeit El-Hagar in the Nile delta
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta is the delta formed in Northern Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers some 240 km of Mediterranean coastline—and is a rich...
, in Lower Egypt and, beginning in the reign with Nectanebo I (380-362 BCE), on the Upper Egyptian island of Philae.
Early history
Her origins are uncertain, but are believed to have come from the Nile Delta. Like other Egyptian deities she did have a centralized Cult of IsisHellenistic religion
Hellenistic religion is any of the various systems of beliefs and practices of the people who lived under the influence of ancient Greek culture during the Hellenistic period and the Roman Empire . There was much continuity in Hellenistic religion: the Greek gods continued to be worshiped, and the...
(New cults) in the Hellenistic Civilization. First mentions of Isis date back to the Fifth dynasty of Egypt
Fifth dynasty of Egypt
The fifth dynasty of ancient Egypt is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and VI under the group title the Old Kingdom. Dynasty V dates approximately from 2494 to 2345 BC.-Rulers:...
which is when the first literary inscriptions are found, but her cult became prominent late in Egyptian history, when it began to absorb the cults of many other goddess
Goddess
A goddess is a female deity. In some cultures goddesses are associated with Earth, motherhood, love, and the household. In other cultures, goddesses also rule over war, death, and destruction as well as healing....
es with strong cult centers. This is when the cult of Osiris arose and she became such an important figure in those beliefs. Her cult eventually spread outside Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
.
During the formative centuries of Christianity, the religion of Isis drew converts from every corner of the Roman Empire. In Italy itself, the Egyptian faith was a dominant force. At Pompeii, archaeological evidence reveals that Isis played a major role. In Rome, temples were built and obelisks erected in her honour. In Greece, traditional centres of worship in Delos, Delphi, and Eleusis were taken over by followers of Isis, and this occurred in northern Greece and Athens as well. Harbours of Isis were to be found on the Arabian Sea and the Black Sea. Inscriptions show followers in Gaul, Spain, Pannonia, Germany, Arabia, Asia Minor, Portugal and many shrines even in Britain.
Temples
_-_pompei_-_tempio_diside_-_n._5038_-_ca._1870.jpg)
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
retained those local centres of worship, with most major cities and town
Town
A town is a human settlement larger than a village but smaller than a city. The size a settlement must be in order to be called a "town" varies considerably in different parts of the world, so that, for example, many American "small towns" seem to British people to be no more than villages, while...
s widely known as the home of these deities. Isis originally was an independent and popular deity established in predynastic times, prior to 3100 BC, at Sebennytos
Sebennytos
Sebennytos or Sebennytus or Egyptian: Tjebnutjer Arabic: سمنود Samannud was an ancient city of Lower Egypt, located on the Damietta branch of the Nile in the delta...
in the northern delta.
Eventually temples to Isis began to spread outside of Egypt. In many locations, devotees of Isis considered a number of the local goddesses to be Isis, but under different names. The worship of Isis was joined to that of other Mediterranean goddesses, such as Demeter, Astarte, Aphrodite, and more. During the Hellenic era, due to her attributes as a protector and mother, as well as a lusty aspect gained when she absorbed some aspects of Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
, she became the patron goddess of sailor
Sailor
A sailor, mariner, or seaman is a person who navigates water-borne vessels or assists in their operation, maintenance, or service. The term can apply to professional mariners, military personnel, and recreational sailors as well as a plethora of other uses...
s, who spread her worship with the trading ships circulating the Mediterranean Sea.
Likewise, the Arabian goddess Al-Ozza or Al-Uzza العُزّى (al ȝozza), whose name is close to that of Isis, is believed to be a manifestation of her. This, however, is thought to be based on the similarity in the name.
Throughout the Graeco-Roman world, Isis became one of the most significant of the mystery religion
Greco-Roman mysteries
Mystery religions, sacred Mysteries or simply mysteries, were religious cults of the Greco-Roman world, participation in which was reserved to initiates....
s, and many classical
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
writers refer to her temples, cults, and rite
Rite
A rite is an established, ceremonious, usually religious act. Rites in this sense fall into three major categories:* rites of passage, generally changing an individual's social status, such as marriage, baptism, or graduation....
s.
Temples to Isis were built in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
and Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, with a well preserved example discovered in Pompeii
Temple of Isis at Pompeii
The Temple of Isis is a Roman temple dedicated to the Egyptian goddess Isis. This small and almost completely intact temple was among one of the first discoveries during the excavation of Pompeii in 1764. Its role as a Hellenized Egyptian temple in a Roman colony was fully confirmed with an...
. On the Greek island of Delos
Delos
The island of Delos , isolated in the centre of the roughly circular ring of islands called the Cyclades, near Mykonos, is one of the most important mythological, historical and archaeological sites in Greece...
a Doric
Doric order
The Doric order was one of the three orders or organizational systems of ancient Greek or classical architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian.-History:...
Temple of Isis was built on a high over-looking hill at the beginning of the Roman period to venerate the familiar trinity of Isis, the Alexandrian Serapis
Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Graeco-Egyptian name of God. Serapis was devised during the 3rd century BC on the orders of Ptolemy I of Egypt as a means to unify the Greeks and Egyptians in his realm. The god was depicted as Greek in appearance, but with Egyptian trappings, and combined iconography...
and Harpocrates
Harpocrates
In late Greek mythology as developed in Ptolemaic Alexandria, Harpocrates is the god of silence. Harpocrates was adapted by the Greeks from the Egyptian child god Horus. To the ancient Egyptians, Horus represented the new-born Sun, rising each day at dawn...
. The creation of this temple is significant as Delos is particularly known as the birthplace of the Greek gods Artemis
Artemis
Artemis was one of the most widely venerated of the Ancient Greek deities. Her Roman equivalent is Diana. Some scholars believe that the name and indeed the goddess herself was originally pre-Greek. Homer refers to her as Artemis Agrotera, Potnia Theron: "Artemis of the wildland, Mistress of Animals"...
and Apollo
Apollo
Apollo is one of the most important and complex of the Olympian deities in Greek and Roman mythology...
who had temples of their own on the island long before the temple to Isis was built. At Philae
Philae
Philae is an island in the Nile River and the previous site of an Ancient Egyptian temple complex in southern Egypt...
her worship persisted until the 6th century, long after the rise of Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
and the subsequent suppression of paganism.
The cult of Isis and Osiris continued up until the 6th century AD on the island of Philae in Upper Nile. The Theodosian decree (in about 380 AD) to destroy all pagan temples was not enforced there until the time of Justinian. This toleration was due to an old treaty made between the Blemyes-Nobadae and Diocletian
Diocletian
Diocletian |latinized]] upon his accession to Diocletian . c. 22 December 244 – 3 December 311), was a Roman Emperor from 284 to 305....
. Every year they visited Elaphantine and at certain intervals took the image of Isis up river to the land of the Blemyes for oracular purposes before returning it. Justinian sent Narses
Narses
Narses was, with Belisarius, one of the great generals in the service of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I during the "Reconquest" that took place during Justinian's reign....
to destroy the sanctuaries, with the priests being arrested and the divine images taken to Constantinople. Philae
Philae
Philae is an island in the Nile River and the previous site of an Ancient Egyptian temple complex in southern Egypt...
was the last of the ancient Egyptian temples to be closed.
Priesthood
Little information on Egyptian rituals for Isis survives, however, it is clear there were both priests and priestesses officiating at her cult rituals throughout its entire history. By the Greco-Roman era, many of them were healerFaith Healer
Faith Healer is a play by Brian Friel about the life of faith healer Francis Hardy as monologued through the shifting memories of Hardy, his wife, Grace, and stage manager, Teddy.-Synopsis:...
s, and were said to have many other special powers, including dream interpretation and the ability to control the weather
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
, which they did by braiding or not combing their hair. The latter was believed because the Egyptians
Egyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
considered knot
Knot
A knot is a method of fastening or securing linear material such as rope by tying or interweaving. It may consist of a length of one or several segments of rope, string, webbing, twine, strap, or even chain interwoven such that the line can bind to itself or to some other object—the "load"...
s to have magical powers.
Associations
Due to the association between knots and magical power, a symbol of Isis was the tiet or tyetTyet
The tyet is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the goddess Isis; its exact origin is unknown. In many respects the tyet resembles an ankh, except that its arms curve down...
(meaning welfare/life), also called the Knot of Isis, Buckle of Isis, or the Blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
of Isis, which is shown to the right. In many respects the tyet resembles an ankh
Ankh
The ankh , also known as key of life, the key of the Nile or crux ansata, was the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic character that read "eternal life", a triliteral sign for the consonants ʻ-n-ḫ...
, except that its arms point downward, and when used as such, seems to represent the idea of eternal life
Eternal Life
"Eternal Life" is a song composed by Jeff Buckley and is track #9 on his album Grace. It also has a video. It is believed to have been influenced by a long-time love for Led Zeppelin's music and a wish to emulate them in this song...
or resurrection
Resurrection
Resurrection refers to the literal coming back to life of the biologically dead. It is used both with respect to particular individuals or the belief in a General Resurrection of the dead at the end of the world. The General Resurrection is featured prominently in Jewish, Christian, and Muslim...
. The meaning of Blood of Isis is more obscure, but the tyet often was used as a funerary amulet
Amulet
An amulet, similar to a talisman , is any object intended to bring good luck or protection to its owner.Potential amulets include gems, especially engraved gems, statues, coins, drawings, pendants, rings, plants and animals; even words said in certain occasions—for example: vade retro satana—, to...
made of red wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
, stone
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
, or glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
, so this may simply have been a description of the appearance of the materials used.
The star Sopdet
Sopdet
In Egyptian mythology, Sopdet was the deification of Sothis, a star considered by almost all Egyptologists to be Sirius. The name Sopdet means sharp in Egyptian, a reference to the brightness of Sirius, which is the brightest star in the night sky...
(Sirius
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
) is associated with Isis. The appearance of the star signified the advent of a new year and Isis was likewise considered the goddess of rebirth and reincarnation, and as a protector of the dead. The Book of the Dead outlines a particular ritual that would protect the dead, enabling travel anywhere in the underworld, and most of the titles Isis holds signify her as the goddess of protection of the dead.
Probably due to assimilation with the goddesses Aphrodite
Aphrodite
Aphrodite is the Greek goddess of love, beauty, pleasure, and procreation.Her Roman equivalent is the goddess .Historically, her cult in Greece was imported from, or influenced by, the cult of Astarte in Phoenicia....
and Venus
Venus (mythology)
Venus is a Roman goddess principally associated with love, beauty, sex,sexual seduction and fertility, who played a key role in many Roman religious festivals and myths...
, during the Roman period, the rose
Rose
A rose is a woody perennial of the genus Rosa, within the family Rosaceae. There are over 100 species. They form a group of erect shrubs, and climbing or trailing plants, with stems that are often armed with sharp prickles. Flowers are large and showy, in colours ranging from white through yellows...
was used in her worship. The demand for roses throughout the empire turned rose production into an important industry.
Depictions
Nymphaea caerulea
Nymphaea caerulea, also known as the Blue Egyptian water lily or sacred blue lily, is a water-lily in the genus Nymphaea.-Distribution:Its original habitat may have been along the Nile and other locations in East Africa...
, or, as a Sycamore tree. One pharaoh, Thutmose III
Thutmose III
Thutmose III was the sixth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. During the first twenty-two years of Thutmose's reign he was co-regent with his stepmother, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh...
, was depicted in his tomb as nursing from a sycamore tree that had a breast.
After she assimilated many of the roles of Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
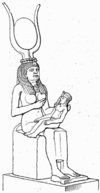
, Isis's headdress is replaced with that of Hathor: the horns of a cow on her head, with the solar disk between them. Sometimes she also was represented as a cow, or a cow's head. Usually, however, she was depicted with her young child, Horus (the pharaoh), with a crown
Crown (headgear)
A crown is the traditional symbolic form of headgear worn by a monarch or by a deity, for whom the crown traditionally represents power, legitimacy, immortality, righteousness, victory, triumph, resurrection, honour and glory of life after death. In art, the crown may be shown being offered to...
, and a vulture
Vulture
Vulture is the name given to two groups of convergently evolved scavenging birds, the New World Vultures including the well-known Californian and Andean Condors, and the Old World Vultures including the birds which are seen scavenging on carcasses of dead animals on African plains...
. Occasionally she was represented as a kite
Kite (bird)
Kites are raptors with long wings and weak legs which spend a great deal of time soaring. Most feed mainly on carrion but some take various amounts of live prey.They are birds of prey which, along with hawks and eagles, are from the family Accipitridae....
flying above the body of Osiris or with the dead Osiris across her lap as she worked her magic to bring him back to life.
Most often Isis is seen holding only the generic ankh
Ankh
The ankh , also known as key of life, the key of the Nile or crux ansata, was the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic character that read "eternal life", a triliteral sign for the consonants ʻ-n-ḫ...
sign and a simple staff, but in late images she is seen sometimes with items usually associated only with Hathor, the sacred sistrum
Sistrum
A sistrum is a musical instrument of the percussion family, chiefly associated with ancient Iraq and Egypt. It consists of a handle and a U-shaped metal frame, made of brass or bronze and between 76 and 30 cm in width...
rattle and the fertility-bearing menat
Menat
Menat was a name used for the goddess Hathor. With a slightly different hieroglyphic spelling, it referred to an ancient Egyptian artifact which, like the sistrum, was closely connected with the goddess Hathor. It was held in the hand by its counterpoise and used as a rattle by Hathor's priestesses...
necklace
Necklace
A necklace is an article of jewellery which is worn around the neck. Necklaces are frequently formed from a metal jewellery chain. Others are woven or manufactured from cloth using string or twine....
. In The Book of Coming Forth By Day Isis is depicted standing on the prow of the Solar Bark with her arms outstretched.
Isis in literature
PlutarchPlutarch
Plutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
, a Greek scholar who lived from 46 AD
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
to 120 AD, wrote Isis and Osiris, which is considered a main source about the very late myths about Isis. In it he writes of Isis, describing her as: "a goddess exceptionally wise and a lover of wisdom, to whom, as her name at least seems to indicate, knowledge and understanding are in the highest degree appropriate..." and that the statue of Athena (Plutarch says "whom they believe to be Isis" in Sais
SAIS
SAIS can refer to:* Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies, part of The Johns Hopkins University.* Sharjah American International School* Southern Association of Independent Schools...
carried the inscription "I am all that has been, and is, and shall be, and my robe no mortal has yet uncovered." At Sais, however, the patron goddess of its ancient cult was Neith
Neith
In Egyptian mythology, Neith was an early goddess in the Egyptian pantheon. She was the patron deity of Sais, where her cult was centered in the Western Nile Delta of Egypt and attested as early as the First Dynasty...
, many of whose traits had begun to be attributed to Isis during the Greek occupation. In The Golden Ass
The Golden Ass
The Metamorphoses of Apuleius, which St. Augustine referred to as The Golden Ass , is the only Latin novel to survive in its entirety....
the Roman writer Apuleius
Apuleius
Apuleius was a Latin prose writer. He was a Berber, from Madaurus . He studied Platonist philosophy in Athens; travelled to Italy, Asia Minor and Egypt; and was an initiate in several cults or mysteries. The most famous incident in his life was when he was accused of using magic to gain the...
later gives us his understanding of Isis in the 2nd century, and describes the Navigium Isidis
Navigium Isidis
The Navigium Isidis or Isidis Navigium was an annual ancient Roman religious festival in honor of the goddess Isis. The festival outlived Christian persecution by Theodosius and Arcadius' persecution against the Roman religion.In the Roman Empire, it was still celebrated in Italy at least until...
festival. The following paragraph is particularly significant:
Mythology
When seen as the deification of the wife of the pharaoh in later myths, the prominent role of Isis was as the assistant to the deceased pharaoh. Thus she gained a funerary association, her name appearing over eighty times in the Pyramid TextsPyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian religious texts from the time of the Old Kingdom. The pyramid texts are possibly the oldest known religious texts in the world. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved on the walls and sarcophagi of the pyramids at Saqqara during...
, and she was said to be the mother of the four deities who protected the canopic jar
Canopic jar
Canopic jars were used by the Ancient Egyptians during the mummification process to store and preserve the viscera of their owner for the afterlife. They were commonly either carved from limestone or were made of pottery...
s—more specifically, Isis was viewed as protector of the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
-jar-deity, Imsety. This association with the pharaoh's wife also brought the idea that Isis was considered the spouse of Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
(once seen as her child), who was protector, and later the deification of the pharaoh. By the Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the establishment of the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Fourteenth Dynasty, between 2055 BC and 1650 BC, although some writers include the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties in the Second Intermediate...
, the 11th
Eleventh dynasty of Egypt
The eleventh dynasty of ancient Egypt was one group of rulers, whose earlier members are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, while the later members are considered part of the Middle Kingdom...
through 14th dynasties
Fourteenth dynasty of Egypt
The Eleventh , Twelfth, Thirteenth and Fourteenth Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group title, Middle Kingdom, though this dynasty overlaps partially with either the Thirteenth Dynasty or the Fifteenth Dynasty, during the Second Intermediate Period.It is associated with the...
between 2040 and 1640 BC, as the funeral texts began to be used by more members of Egyptian society, other than the royal family, her role also grows to protect the nobles and even the commoners.
By the New Kingdom
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom of Egypt, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt....
, the 18th
Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt
The eighteenth dynasty of ancient Egypt is perhaps the best known of all the dynasties of ancient Egypt...
, 19th
Nineteenth dynasty of Egypt
The Nineteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt was one of the periods of the Egyptian New Kingdom. Founded by Vizier Ramesses I, whom Pharaoh Horemheb chose as his successor to the throne, this dynasty is best known for its military conquests in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria.The warrior kings of the...
, and 20th dynasties
Twentieth dynasty of Egypt
The Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group title, New Kingdom. This dynasty is considered to be the last one of the New Kingdom of Egypt, and was followed by the Third Intermediate Period....
between 1570 and 1070 BC, Isis gained prominence as the mother and protector of the pharaoh. During this period, she is said to breastfeed the pharaoh and often is depicted doing so.
The role of her name and her throne-crown is uncertain. Some early Egyptologists believed that being the throne-mother was Isis's original function, however, a more modern view states that aspects of that role came later by association. In many African tribes, the throne is known as the mother of the king, and that concept fits well with either theory, possibly giving insight into the thinking of ancient Egyptians.
Sister-wife to Osiris
In the Old KingdomOld Kingdom
Old Kingdom is the name given to the period in the 3rd millennium BC when Egypt attained its first continuous peak of civilization in complexity and achievement – the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley .The term itself was...
, the 3rd Dynasty
Third dynasty of Egypt
For the Sumerian Renaissance, see Third Dynasty of Ur.The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth...
through to the 6th Dynasty
Sixth dynasty of Egypt
The sixth dynasty of ancient Egypt is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and V under the group title the Old Kingdom.-Pharaohs:...
dated between 2686 to 2134 BC, the pantheons of individual Egyptian cities varied by region. During the 5th dynasty
Fifth dynasty of Egypt
The fifth dynasty of ancient Egypt is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and VI under the group title the Old Kingdom. Dynasty V dates approximately from 2494 to 2345 BC.-Rulers:...
, Isis became one of the Ennead
Ennead
The Ennead was a group ofnine deities in Egyptian mythology. The Ennead were worshipped at Heliopolis and consisted of the god Atum, his children Shu and Tefnut, their children Geb and Nut and their children Osiris, Isis, Horus, Set and Nephthys.-Terminology:Egyptian mythology established multiple...
of the city of Heliopolis
Heliopolis (ancient)
Heliopolis was one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, the capital of the 13th Lower Egyptian nome that was located five miles east of the Nile to the north of the apex of the Nile Delta...
. She was believed to be a daughter of Nut
Nut (goddess)
In the Ennead of Egyptian mythology, Nut was the goddess of the sky.-Goddess of the sky:...
and Geb
Geb
Geb was the Egyptian god of the Earth and a member of the Ennead of Heliopolis. It was believed in ancient Egypt that Geb's laughter was earthquakes and that he allowed crops to grow. The name was pronounced as such from the Greek period onward,...
, and sister to Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
, Nephthys
Nephthys
In Egyptian mythology, Nephthys is a member of the Great Ennead of Heliopolis, a daughter of Nut and Geb. Nephthys was typically paired with her sister Isis in funerary rites because of their role as protectors of the mummy and the god Osiris and as the sister-wife of Seth.Nephthys is regarded as...
, and Set
Set (mythology)
Set was in Ancient Egyptian religion, a god of the desert, storms, and foreigners. In later myths he was also the god of darkness, and chaos...
. The two sisters, Isis and Nephthys, often were depicted on coffins, with wings outstretched, as protectors against evil. As a funerary deity, she was associated with Osiris, lord of the underworld (Duat
Duat
In Egyptian mythology, Duat is the underworld. The Duat is a vast area under the Earth, connected with Nun, the waters of the primordial abyss. The Duat is the realm of the god Osiris and the residence of other gods and supernatural beings...
), and was considered his wife.

Anubis
Anubis is the Greek name for a jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife in ancient Egyptian religion. In the ancient Egyptian language, Anubis is known as Inpu . According to the Akkadian transcription in the Amarna letters, Anubis' name was vocalized as Anapa...
, of the underworld when the cult of Osiris gained more authority), tells us of the birth of Anubis. The tale describes how Nephthys was denied a child by Set and disguised herself as the much more attractive Isis to seduce him. The plot failed, but Osiris now found Nephthys very attractive, as he thought she was Isis. They coupled
Sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse, also known as copulation or coitus, commonly refers to the act in which a male's penis enters a female's vagina for the purposes of sexual pleasure or reproduction. The entities may be of opposite sexes, or they may be hermaphroditic, as is the case with snails...
, resulting in the birth of Anubis
Anubis
Anubis is the Greek name for a jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife in ancient Egyptian religion. In the ancient Egyptian language, Anubis is known as Inpu . According to the Akkadian transcription in the Amarna letters, Anubis' name was vocalized as Anapa...
. Alternatively, Nephthys had intentionally assumed the form of Isis in order to trick Osiris into fathering her son. In fear of Set's retribution upon them, Nephthys persuaded Isis to adopt Anubis, so that Set would not find out and kill the child. The tale describes both why Anubis is seen as an underworld deity (he becomes a son of Osiris), and why he could not inherit Osiris's position (he was not a legitimate heir in this new birth scenario), neatly preserving Osiris's position as lord of the underworld. It should be remembered, however, that this new myth was only a later creation of the Osirian cult who wanted to depict Set in an evil position, as the enemy of Osiris.
In another Osirian myth, Set had a banquet for Osiris in which he brought in a beautiful box and said that whoever could fit in the box perfectly would get to keep it. Set had measured Osiris in his sleep and made sure that he was the only one who could fit the box. Several tried to see whether they fit. Once it was Osiris's turn to see if he could fit in the box, Set closed the lid on him so that the box was now a coffin for Osiris. Set flung the box in the Nile so that it would drift far away. Isis went looking for the box so that Osiris could have a proper burial. She found the box in a tree in Byblos
Byblos
Byblos is the Greek name of the Phoenician city Gebal . It is a Mediterranean city in the Mount Lebanon Governorate of present-day Lebanon under the current Arabic name of Jubayl and was also referred to as Gibelet during the Crusades...
, a city along the Phoenician coast, and brought it back to Egypt, hiding it in a swamp. But Set went hunting that night and found the box. Enraged, Set chopped Osiris's body into fourteen pieces and scattered them all over Egypt to ensure that Isis could never find Osiris again for a proper burial. Isis and her sister Nephthys went looking for these pieces, but could only find thirteen of the fourteen. Fish had swallowed the last piece, his phallus
Phallus
A phallus is an erect penis, a penis-shaped object such as a dildo, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. Any object that symbolically resembles a penis may also be referred to as a phallus; however, such objects are more often referred to as being phallic...
, so Isis made him a new one with magic, putting his body back together after which they conceived Horus. The number of pieces is described on temple walls variously as fourteen and sixteen, and occasionally forty-two
42 (number)
42 is the natural number immediately following 41 and directly preceding 43. The number has received considerable attention in popular culture as a result of its central appearance in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy as the "Answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and...
, one for each nome
Nome (Egypt)
A nome was a subnational administrative division of ancient Egypt. Today's use of the Greek nome rather than the Egyptian term sepat came about during the Ptolemaic period. Fascinated with Egypt, Greeks created many historical records about the country...
or district.
Assimilation of Hathor
When the cult of RaRa
Ra is the ancient Egyptian sun god. By the Fifth Dynasty he had become a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun...
rose to prominence he became associated with the similar deity, Horus. Hathor had been paired with Ra in some regions and when Isis began to be paired with Ra, soon Hathor and Isis began to be merged in some regions also as, Isis-Hathor.
Mother of Horus

Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
, Isis became the mother of Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
, rather than his wife, and thus, when beliefs of Ra absorbed Atum
Atum
Atum, sometimes rendered as Atem or Tem, is an important deity in Egyptian mythology.- Name :Atum's name is thought to be derived from the word 'tem' which means to complete or finish. Thus he has been interpreted as being the 'complete one' and also the finisher of the world, which he returns to...
into Atum-Ra, it also had to be taken into account that Isis was one of the Ennead
Ennead
The Ennead was a group ofnine deities in Egyptian mythology. The Ennead were worshipped at Heliopolis and consisted of the god Atum, his children Shu and Tefnut, their children Geb and Nut and their children Osiris, Isis, Horus, Set and Nephthys.-Terminology:Egyptian mythology established multiple...
, as the wife of Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
. It had to be explained how Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
, however, who (as lord of the dead) being dead, could be considered a father to Horus, who was not considered dead. This conflict in themes led to the evolution of the idea that Osiris needed to be resurrected, and therefore, to the Legend of Osiris and Isis
Legend of Osiris and Isis
The Myth of Osiris and Isis, concerning the deities of Egyptian mythology Osiris, Isis, Horus, and Set, became one of the most important and powerful in Egyptian mythology during the New Kingdom...
, of which Plutarch's Greek description written in the 1st century AD, De Iside et Osiride, contains the most extensive account known today.
Yet another set of late myths detail the adventures of Isis after the birth of Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
's posthumous son, Horus. Isis was said to have given birth to Horus at Khemmis, thought to be located on the Nile Delta. Many dangers faced Horus after birth, and Isis fled with the newborn to escape the wrath of Set
Set (mythology)
Set was in Ancient Egyptian religion, a god of the desert, storms, and foreigners. In later myths he was also the god of darkness, and chaos...
, the murderer of her husband. In one instance, Isis heals Horus from a lethal scorpion sting; she also performs other miracles in relation to the cippi, or the plaques of Horus. Isis protected and raised Horus until he was old enough to face Set, and subsequently, became the pharaoh of Egypt.
Magic
In order to resurrect Osiris for the purpose of having the child Horus, it was necessary for Isis to "learn" magic (which long had been her domain before the cult of Ra arose), and so it was said that Isis tricked RaRa
Ra is the ancient Egyptian sun god. By the Fifth Dynasty he had become a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun...
(i.e. Amun-Ra/Atum-Ra) into telling her his "secret name," by causing a snake
Serpent (symbolism)
Serpent in Latin means: Rory Collins :&, in turn, from the Biblical Hebrew word of: "saraf" with root letters of: which refers to something burning-as, the pain of poisonous snake's bite was likened to internal burning.This word is commonly used in a specifically mythic or religious context,...
to bite him, for which only Isis had the cure. The names of deities were secret and not divulged to any but the religious leaders. Knowing the secret name of a deity enabled one to have power of the deity. That he would use his "secret name" to "survive" implies that the serpent had to be a more powerful deity than Ra. The oldest deity known in Egypt was Wadjet
Wadjet
In Egyptian mythology, Wadjet, or the Green One , was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep , which became part of the city that the Egyptians named Per-Wadjet, House of...
, the Egyptian cobra
Egyptian cobra
The Egyptian cobra is a species in the genus Naja found in Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. It is one of the largest Naja species in Africa.- Description :...
, whose cult never was eclipsed in Ancient Egyptian religion. As a deity from the same region, she would have been a benevolent resource for Isis. The use of secret names became central in late Egyptian magic spells, and Isis often is implored to "use the true name of Ra" in the performance of rituals. By the late Egyptian historical period, after the occupations by the Greeks and the Romans, Isis became the most important and most powerful deity of the Egyptian pantheon because of her magical skills. Magic
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
is central to the entire mythology of Isis, arguably more so than any other Egyptian deity.
Prior to this late change in the nature of Egyptian religion, the rule of Ma'at had governed the correct actions for most of the thousands of years of Egyptian religion, with little need for magic. Thoth
Thoth
Thoth was considered one of the more important deities of the Egyptian pantheon. In art, he was often depicted as a man with the head of an ibis or a baboon, animals sacred to him. His feminine counterpart was Seshat...
had been the deity who resorted to magic when it was needed. The goddess
which held the quadruple roles of healer, protector of the canopic jars, protector of marriage, and goddess of magic previously had been Serket
Serket
In Egyptian mythology, Serket is the goddess of healing stings and bites who originally was the deification of the scorpion....
. She then became considered an aspect of Isis. Thus it is not surprising that Isis had a central role in Egyptian magic spells and ritual, especially those of protection
Safety
Safety is the state of being "safe" , the condition of being protected against physical, social, spiritual, financial, political, emotional, occupational, psychological, educational or other types or consequences of failure, damage, error, accidents, harm or any other event which could be...
and healing
Healing
Physiological healing is the restoration of damaged living tissue, organs and biological system to normal function. It is the process by which the cells in the body regenerate and repair to reduce the size of a damaged or necrotic area....
. In many spells, she also is completely merged even with Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
, where invocations of Isis are supposed to involve Horus's powers automatically as well. In Egyptian history the image of a wounded Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
became a standard feature of Isis's healing spells, which typically invoked the curative powers of the milk of Isis. (Silverman, Ancient Egypt, 135)
In Egypt
Isis was venerated first in Egypt. Isis was the only goddess worshiped by all Egyptians alike, and whose influence was so widespread that she had become completely syncreticSyncretism
Syncretism is the combining of different beliefs, often while melding practices of various schools of thought. The term means "combining", but see below for the origin of the word...
with the Greek goddess Demeter
Demeter
In Greek mythology, Demeter is the goddess of the harvest, who presided over grains, the fertility of the earth, and the seasons . Her common surnames are Sito as the giver of food or corn/grain and Thesmophoros as a mark of the civilized existence of agricultural society...
. After the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great, and the Hellenization
Hellenization
Hellenization is a term used to describe the spread of ancient Greek culture, and, to a lesser extent, language. It is mainly used to describe the spread of Hellenistic civilization during the Hellenistic period following the campaigns of Alexander the Great of Macedon...
of the Egyptian culture initiated by Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter I , also known as Ptolemy Lagides, c. 367 BC – c. 283 BC, was a Macedonian general under Alexander the Great, who became ruler of Egypt and founder of both the Ptolemaic Kingdom and the Ptolemaic Dynasty...
, Isis eventually became known as Queen of Heaven
Queen of heaven (antiquity)
Queen of Heaven was a title given to a number of ancient goddesses in the ancient Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Anat, Isis, Innana, Astarte. Hera and possibly Asherah . Elsewhere, Nordic Frigg also bore this title. In Greco-Roman times Hera, and her Roman aspect Juno bore this title....
.
Greco-Roman world

Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
writes that after Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
's assassination, a temple in honour of Isis had been decreed; Augustus suspended this, and tried to turn Romans back to the Roman deities who were closely associated with the state. Eventually the Roman emperor Caligula
Caligula
Caligula , also known as Gaius, was Roman Emperor from 37 AD to 41 AD. Caligula was a member of the house of rulers conventionally known as the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Caligula's father Germanicus, the nephew and adopted son of Emperor Tiberius, was a very successful general and one of Rome's most...
abandoned the Augustan wariness toward what was described as oriental cults, and it was in his reign that the Isiac festival of the Navigium Isidis
Navigium Isidis
The Navigium Isidis or Isidis Navigium was an annual ancient Roman religious festival in honor of the goddess Isis. The festival outlived Christian persecution by Theodosius and Arcadius' persecution against the Roman religion.In the Roman Empire, it was still celebrated in Italy at least until...
was established in Rome. According to Josephus
Josephus
Titus Flavius Josephus , also called Joseph ben Matityahu , was a 1st-century Romano-Jewish historian and hagiographer of priestly and royal ancestry who recorded Jewish history, with special emphasis on the 1st century AD and the First Jewish–Roman War, which resulted in the Destruction of...
, Caligula donned female garb and took part in the mysteries he instituted, and in the Hellenistic age Isis acquired a "new rank as a leading goddess of the Mediterranean world." Vespasian
Vespasian
Vespasian , was Roman Emperor from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian was the founder of the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for a quarter century. Vespasian was descended from a family of equestrians, who rose into the senatorial rank under the Emperors of the Julio-Claudian dynasty...
, along with Titus
Titus
Titus , was Roman Emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, thus becoming the first Roman Emperor to come to the throne after his own father....
, practised incubation in the Roman Iseum
Iseum
An Iseum, also spelled Isaeum, is a sanctuary for the worshippers of the Greco-Roman god Isis. Isis was originally an Egyptian goddess who became hellenised. Many Iseums still exist today. They include the temple of Isis at Pompeii, a dedication at the Egyptian complex at Philae, and a scattering...
. Domitian
Domitian
Domitian was Roman Emperor from 81 to 96. Domitian was the third and last emperor of the Flavian dynasty.Domitian's youth and early career were largely spent in the shadow of his brother Titus, who gained military renown during the First Jewish-Roman War...
built another Iseum along with a Serapeum
Serapeum
A serapeum is a temple or other religious institution dedicated to the syncretic Hellenistic-Egyptian god Serapis, who combined aspects of Osiris and Apis in a humanized form that was accepted by the Ptolemaic Greeks of Alexandria...
. Trajan
Trajan
Trajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
appears before Isis and Horus, presenting them with votive offerings of wine, in a bas-relief on his triumphal arch in Rome.
Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
decorated his villa at Tibur with Isiac scenes. Galerius
Galerius
Galerius , was Roman Emperor from 305 to 311. During his reign he campaigned, aided by Diocletian, against the Sassanid Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across the Danube against the Carpi, defeating them in 297 and 300...
regarded Isis as his protectress.
Roman perspectives on cults were syncretic
Syncretism
Syncretism is the combining of different beliefs, often while melding practices of various schools of thought. The term means "combining", but see below for the origin of the word...
, seeing in new deities, merely local aspects of a familiar one. For many Romans, Egyptian Isis was an aspect of Phrygia
Phrygia
In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now modern-day Turkey. The Phrygians initially lived in the southern Balkans; according to Herodotus, under the name of Bryges , changing it to Phruges after their final migration to Anatolia, via the...
n Cybele
Cybele
Cybele , was a Phrygian form of the Earth Mother or Great Mother. As with Greek Gaia , her Minoan equivalent Rhea and some aspects of Demeter, Cybele embodies the fertile Earth...
, whose orgiastic rites were long-naturalized at Rome, indeed, she was known as Isis of Ten Thousand Names.
Among these names of Roman Isis, Queen of Heaven
Queen of heaven (antiquity)
Queen of Heaven was a title given to a number of ancient goddesses in the ancient Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Anat, Isis, Innana, Astarte. Hera and possibly Asherah . Elsewhere, Nordic Frigg also bore this title. In Greco-Roman times Hera, and her Roman aspect Juno bore this title....
is outstanding for its long and continuous history. Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
identified Isis with the Greek
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
and Roman
Roman mythology
Roman mythology is the body of traditional stories pertaining to ancient Rome's legendary origins and religious system, as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans...
goddesses of agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, Demeter
Demeter
In Greek mythology, Demeter is the goddess of the harvest, who presided over grains, the fertility of the earth, and the seasons . Her common surnames are Sito as the giver of food or corn/grain and Thesmophoros as a mark of the civilized existence of agricultural society...
and Ceres.
In later years, Isis also had temples throughout Europe, Africa and Asia. An alabaster statue of Isis from the 3rd century BC, found in Ohrid
Ohrid
Ohrid is a city on the eastern shore of Lake Ohrid in the Republic of Macedonia. It has about 42,000 inhabitants, making it the seventh largest city in the country. The city is the seat of Ohrid Municipality. Ohrid is notable for having once had 365 churches, one for each day of the year and has...
, in the Republic of Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
, is depicted on the obverse
Obverse and reverse
Obverse and its opposite, reverse, refer to the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags , seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, obverse means the front face of the object and reverse...
of the Macedonian 10 denars
Macedonian denar
The denar is the currency of the Republic of Macedonia. It is subdivided into 100 deni . The name denar comes from the name of the ancient Roman monetary unit, the denarius...
banknote, issued in 1996.
The male first name "Isidore
Isidore
Isidore is a male name of Greek origin, derived from the Greek name Ἰσίδωρος, a combination of Ἶσις δώρον meaning "gift of Isis". The name survived the suppression of the worship of the goddess Isis in the newly Christianized Roman Empire, and is, among others, the name of several Christian saints...
" (also "Isador"), means in Greek "Gift of Isis" (similar to "Theodore", "God's Gift"). The name, which became common in Roman times, survived the suppression of the Isis worship and remains popular up to the present - being among others the name of several Christian saints.
Kenya
Among the Kalenjins tribe of Kenya East Africa, the god name Asis is used to depict the god sun which according to historian Kipkoech Sambu is the same god Isis.Titles
In the Book of the DeadBook of the Dead
The Book of the Dead is the modern name of an ancient Egyptian funerary text, used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw is translated as "Book of Coming Forth by Day". Another translation would be "Book of...
Isis was described as:
- She who gives birth to heavenHeavenHeaven, the Heavens or Seven Heavens, is a common religious cosmological or metaphysical term for the physical or transcendent place from which heavenly beings originate, are enthroned or inhabit...
and earth, - She who knows the orphanOrphanAn orphan is a child permanently bereaved of or abandoned by his or her parents. In common usage, only a child who has lost both parents is called an orphan...
, - She who knows the widow spider,
- She who seeks justice for the poor people,
- She who seeks shelter for the weak people
- She who seeks the righteousness in her people
Some of Isis's many other titles were:
- Queen of HeavenQueen of heaven (antiquity)Queen of Heaven was a title given to a number of ancient goddesses in the ancient Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Anat, Isis, Innana, Astarte. Hera and possibly Asherah . Elsewhere, Nordic Frigg also bore this title. In Greco-Roman times Hera, and her Roman aspect Juno bore this title....
, - Mother of the Gods,
- The One Who is All,
- Lady of Green Crops,
- The Brilliant One in the Sky,
- Star of the SeaOur Lady, Star of the SeaOur Lady, Star of the Sea is an ancient title for the Virgin Mary, mother of Jesus Christ. The words Star of the Sea are a translation of the Latin title Stella Maris, first reliably used with relation to the Virgin Mary in the ninth century...
, - Great Lady of Magic,
- Mistress of the House of Life,
- She Who Knows How To Make Right Use of the Heart,
- LightLightLight or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
-Giver of Heaven, - Lady of the Words of Power,
- MoonMoonThe Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
Shining Over the SeaSeaA sea generally refers to a large body of salt water, but the term is used in other contexts as well. Most commonly, it means a large expanse of saline water connected with an ocean, and is commonly used as a synonym for ocean...
.
See also
- "Isis" of the Suebi"Isis" of the SuebiIn Roman historian Tacitus's first century CE book Germania, Tacitus describes the veneration of what he deems as an "Isis" of the Suebi. Due to Tacitus's usage of interpretatio romana elsewhere in the text, his admitted uncertainty, and his reasoning for referring to the veneration of an Egyptian...
, a goddess identified by Tacitus as venerated by the Suebi, a Germanic people
Primary sources
- Ovid, Metamorphoses i.588–747
- Eusebius, Chronicon 32.9–13, 40.7–9, 43.12–16
Secondary sources
- Ian Shaw (2000) The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt
- Rosalie David (1998) Handbook to Life in Ancient Egypt
- Lewis Spences (1990) Ancient Egyptian Myths and Legends
- Plutarch, (1936) De Iside et Osiride, edited by Frank C. Babbitt
- Richard H. Wilkinson (2003) The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt
- Ian Shaw & Paul T. Nicholson (1995) The British Museum Dictionary of Ancient Egypt
- Kockelmann, Holger, Praising the goddess: a comparative and annotated re-edition of six demotic hymns and praises addressed to Isis (Berlin; New York: Walter de Gruyter, 2008).

