
Josephson vortex
Encyclopedia
In superconductivity
, a Josephson vortex (after Brian Josephson
from Cambridge University) is a vortex of supercurrent
in a long Josephson junction
(LJJ). The supercurrents circulate around the vortex center which is situated inside the Josephson barrier. In contrast to Abrikosov vortices
in type-II superconductors, a Josephson vortex has no normal core.
Usually the Josephson vortex's supercurrents create a magnetic field with the total flux equal to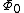 —a single flux quantum
—a single flux quantum
. Such a vortex is therefore called a (Josephson) fluxon
. It has been shown that under certain conditions a propagating Josephson vortex can initiate another Josephson vortex. This effect is called flux cloning (or fluxon cloning). Although a second vortex appears, this does not violate the conservation of the single flux quantum.
Recently it was demonstrated by Hilgenkamp et al. that Josephson vortices in the so-called 0-π LJJ can also carry half of the flux quantum
, and are called semifluxon
s.
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance occurring in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum...
, a Josephson vortex (after Brian Josephson
Brian David Josephson
Brian David Josephson, FRS is a Welsh physicist. He became a Nobel Prize laureate in 1973 for the prediction of the eponymous Josephson effect....
from Cambridge University) is a vortex of supercurrent
Supercurrent
A supercurrent is a superconducting current, that is, electric current which flows without dissipation....
in a long Josephson junction
Long Josephson junction
In superconductivity, a long Josephson junction is a Josephson junction which has one or more dimensions longer than the Josephson penetration depth \lambda_J. This definition is not strict....
(LJJ). The supercurrents circulate around the vortex center which is situated inside the Josephson barrier. In contrast to Abrikosov vortices
Abrikosov vortex
In superconductivity, an Abrikosov vortex is a vortex of supercurrent in a type-II superconductor. The supercurrent circulates around the normal core of the vortex. The core has a size \sim\xi — the superconducting coherence length...
in type-II superconductors, a Josephson vortex has no normal core.
Usually the Josephson vortex's supercurrents create a magnetic field with the total flux equal to
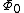 —a single flux quantum
—a single flux quantumMagnetic flux quantum
The magnetic flux quantum Φ0 is the quantum of magnetic flux passing through a superconductor. The phenomenon of flux quantization was discovered B. S. Deaver and W. M. Fairbank and, independently, by R. Doll and M. Nabauer, in 1961...
. Such a vortex is therefore called a (Josephson) fluxon
Fluxon
In physics, a fluxon is a quantum of electromagnetic flux. The term may have any of several related meanings.- Superconductivity :In the context of superconductivity, a fluxon is a small whisker of normal phase surrounded by superconducting phase. Supercurrents circulate around its center...
. It has been shown that under certain conditions a propagating Josephson vortex can initiate another Josephson vortex. This effect is called flux cloning (or fluxon cloning). Although a second vortex appears, this does not violate the conservation of the single flux quantum.
Recently it was demonstrated by Hilgenkamp et al. that Josephson vortices in the so-called 0-π LJJ can also carry half of the flux quantum
Magnetic flux quantum
The magnetic flux quantum Φ0 is the quantum of magnetic flux passing through a superconductor. The phenomenon of flux quantization was discovered B. S. Deaver and W. M. Fairbank and, independently, by R. Doll and M. Nabauer, in 1961...
, and are called semifluxon
Semifluxon
In superconductivity, a Semifluxon is a vortex of supercurrent carrying the magnetic flux equal to the half of the magnetic flux quantum. Semifluxons exist in the so-called 0-π long Josephson junctions at the boundary between 0 and π regions. For a shorter junction length In superconductivity, a...
s.
See also
- FluxonFluxonIn physics, a fluxon is a quantum of electromagnetic flux. The term may have any of several related meanings.- Superconductivity :In the context of superconductivity, a fluxon is a small whisker of normal phase surrounded by superconducting phase. Supercurrents circulate around its center...
- Josephson effectJosephson effectThe Josephson effect is the phenomenon of supercurrent across two superconductors coupled by a weak link...
- Josephson penetration depthJosephson penetration depthIn superconductivity, Josephson penetration depth characterizes the typical length on which an externally-applied magnetic field penetrates into the long Josephson junction...
- Long Josephson junctionLong Josephson junctionIn superconductivity, a long Josephson junction is a Josephson junction which has one or more dimensions longer than the Josephson penetration depth \lambda_J. This definition is not strict....
- Shape wavesShape wavesShape waves are excitations propagating along Josephson vortices or fluxons. In the case of two-dimensional Josephson junctions described by the 2D sine-Gordon equation, shape waves are distortions of a Josephson vortex line of an arbitrary profile...
- Sine-Gordon equationSine-Gordon equationThe sine–Gordon equation is a nonlinear hyperbolic partial differential equation in 1 + 1 dimensions involving the d'Alembert operator and the sine of the unknown function. It was originally considered in the nineteenth century in the course of study of surfaces of constant negative...

