
Kliment Voroshilov tank
Encyclopedia
The Kliment Voroshilov (KV) tank
s were a series of Soviet heavy tank
s, named after the Soviet defense commissar and politician Kliment Voroshilov
. The KV series were known for their extremely heavy armour protection during the early war, especially during the first year of the invasion
of the Soviet Union
in World War II
. Almost completely immune to the 7.5 cm KwK 37
and 3.7 cm KwK 36
guns mounted on the early Panzer III
and Panzer IV
tanks, until better guns were developed often the only way to defeat a KV was a point-blank shot to the rear. Prior to the invasion, about 500 of the over 22,000 tanks in Soviet service at the time were of the KV-1 type. When the KV-1 appeared, it outclassed the French Char B1
, the only heavy tank used in the world at that time. Yet in the end it turned out that there was little sense in producing the expensive KV tanks, as the T-34
medium tank performed better (or at least equally) in all practical respects. Later in the war, the KV series became a base of development of the Iosif Stalin tank
s.
heavy tank, Soviet tank designers started drawing up replacements. The T-35 conformed to the 1920s notion of a 'breakthrough tank' with very heavy firepower and armour protection, but suffered from poor mobility. The Spanish Civil War
demonstrated the need for much heavier armor on tanks, and was the main influence on Soviet tank design just prior to World War II.
Several competing designs were offered, and even more were drawn up prior to reaching prototype stage. All had heavy armour, torsion-bar suspension, wide tracks, and were of welded and cast construction. One of the main competing designs was the SMK
, which in its final form had two turrets, mounting the same combination of 76.2 mm and 45 mm weapons. The designers of the SMK independently drew up a single-turreted variant and this received approval at the highest level. Two of these, named after the People's Defence Commissioner were ordered alongside a single SMK. The smaller hull and single turret enabled the designer to install heavy frontal and turret armour while keeping the weight within manageable limits.
 When the Soviets entered the Winter War
When the Soviets entered the Winter War
, the SMK, KV and a third design, the T-100
, were sent to be tested in combat conditions. The SMK and T-100 performed worse than the KV. The heavy armour of the KV proved highly resistant to Finnish
anti-tank weapons, making it more effective than the other designs. In 1939 production of 50 KV was ordered. During the War, the Soviets found it difficult to deal with the concrete bunkers used by the Finns and a request was made for a tank with a large howitzer. One of the rush projects to meet the request put the howitzer in a new turret on one of the KV tanks.
Initially known as Little Turret and Big turret, the 76-mm-armed tank was designated as the KV-1 Heavy Tank and the 152 mm howitzer
one as KV-2 Heavy Artillery Tank.
The KV's strengths included armor that was impenetrable by any tank-mounted weapon then in service except at point-blank range, that it had good firepower, and that it had good traction on soft ground. It also had serious flaws: it was difficult to steer, the transmission (which was a twenty year old Caterpillar
design) was unreliable (and was known to have to be shifted with a hammer), and the ergonomics were poor, with limited visibility and no turret basket. Furthermore, at 45 tons, it was simply too heavy. This severely impacted the maneuverability, not so much in terms of maximum speed, as through inability to cross many bridges medium tanks could cross. The KV outweighed most other tanks of the era, being about twice as heavy as the heaviest contemporary German tank. KVs were never equipped with snorkeling system to ford river on the bottom, so they had to be left to travel to an adequate bridge. As applique armor and other improvements were added without increasing engine power, later models were less capable of keeping up to speed with medium tanks and had more trouble with difficult terrain. In addition, its firepower was no better than the T-34
. It took field reports from senior commanders "and certified heroes", who could be honest without risk of punishment, to reveal "what a dog the KV-1 really was."
, requiring the installation of additional field-expedient appliqué armour. The KV-1's 76.2 mm gun also came in for criticism. While adequate against all German tanks, it was the same gun as carried by smaller, faster, and cheaper T-34
medium tanks. In 1943, it was determined that this gun could not penetrate the frontal armour of the new Tiger
, the first German heavy tank, fortunately captured near Leningrad. The KV-1 was also much more difficult to manufacture and thus more expensive than the T-34. In short, its advantages no longer outweighed its drawbacks.
Nonetheless, because of its initial superior performance, the KV-1 was chosen as one of the few tanks to continue being built following the Soviet reorganization of tank production. Due to the new standardization, it shared the similar engine (the KV used a 600 hp V-2K modification of the T-34's V-2 diesel engine) and gun (the KV had a ZiS-5 main gun, while the T-34 had a similar F-34 main gun) as the T-34, was built in large quantities, and received frequent upgrades.
When production shifted to the Ural Mountains 'Tankograd' complex, the KV-2 was dropped. While impressive on paper, it had been designed as a slow-moving bunker-buster. It was less useful in highly mobile, fluid warfare that developed in World War II. The turret was so heavy it was difficult to traverse on non-level terrain, and it was expensive to produce. Only about 300 KV-2s were made, all in 1940-41, making it one of the rarer Soviet tanks.
 As the war continued, the KV-1 continued to get more armour to compensate for the increasing effectiveness of German weapons. This culminated in the KV-1 model 1942 (German designation KV-1C), which had very heavy armour, but lacked a corresponding improvement to the engine. Tankers complained that although they were well-protected, their mobility was poor and they had no firepower advantage over the T-34 medium tank.
As the war continued, the KV-1 continued to get more armour to compensate for the increasing effectiveness of German weapons. This culminated in the KV-1 model 1942 (German designation KV-1C), which had very heavy armour, but lacked a corresponding improvement to the engine. Tankers complained that although they were well-protected, their mobility was poor and they had no firepower advantage over the T-34 medium tank.
In response to criticisms, the lighter KV-1S (Russian language: КВ-1С) was released, with thinner armour and a smaller, lower turret in order to reclaim some speed. Importantly, the KV-1S also had a commander's cupola with all-around vision blocks, a first for a Soviet heavy tank. However, the thinning-out of the armor called into question why the tank was being produced at all, when the T-34 could seemingly do everything the KV could do and much more cheaply. The Soviet heavy tank program was close to cancellation in mid-1943.
The appearance of the German Panther tank
in the summer of 1943 convinced the Red Army to make a serious upgrade of its tank force for the first time since 1941. Soviet tanks needed bigger guns to take on the growing numbers of Panthers and the few Tigers.
A stopgap upgrade to the KV series was the short-lived KV-85 or Objekt 239. This was a KV-1S with a new turret designed for the IS-85, mounting the same 85 mm D-5T gun as the SU-85
and early versions of the T-34-85. Already-high demand for the gun slowed production of the KV-85 tremendously, and only 148 were built before the KV design was replaced. The KV-85 was produced in the fall and winter of 1943-44; they were sent to the front as of September 1943, and production of the KV-85 was stopped by the spring of 1944 once the IS-2 entered full scale production.
, after Iosif (Joseph) Stalin. The KV-13 program's IS-85 prototype was accepted for production as the IS-1 (or IS-85, Object 237) heavy tank. After testing with both 100 mm
and 122 mm guns, the D-25T 122 mm gun was selected as the main armament of the new tank, primarily because of its ready availability and the effect of its large high-explosive shell when attacking German fortifications. The 122mm D-25T used a separate shell and powder charge, resulting in a lower rate of fire and reduced ammunition capacity. While the 122mm armour piercing shell had a lower muzzle velocity than similar late German 7.5 cm and 8.8 cm guns, proving-ground tests showed that the 122mm AP shell could defeat the frontal armour of the German Panther tank, and the HE shell would easily blow off the drive sprocket and tread of the heaviest German tank or self-propelled gun. The IS-122 replaced the IS-85, and began mass production as the IS-2. The 85 mm gun saw service in the lighter SU-85 and T-34-85.
 Some KVs remained in service right up to the end of the war, although in greatly diminishing numbers as they wore out or were knocked out. The 260th Guards Heavy Breakthrough Tank Regiment, based on the Leningrad front, operated a number of 1941-vintage KV-1s at least as late as the summer of 1944 before re-equipping with IS-2s. A regiment
Some KVs remained in service right up to the end of the war, although in greatly diminishing numbers as they wore out or were knocked out. The 260th Guards Heavy Breakthrough Tank Regiment, based on the Leningrad front, operated a number of 1941-vintage KV-1s at least as late as the summer of 1944 before re-equipping with IS-2s. A regiment
of KVs saw service in Manchuria in August 1945, and a few KV-85s were used in the Crimea in the summer of 1944. The Finnish forces had two KVs, nicknamed Klimi, a Model 1940 and Model 1941, both of which received minor upgrades in their service, and both of which survived the war. A single captured KV-2 was used by German forces in 1945 against US forces in the Ruhr.

All tanks in the series were heavily based on the KV-1 technology.

 When Operation Barbarossa
When Operation Barbarossa
began, the Red Army
was equipped with 508 new KV tanks. So effective was its armour that the Germans
were incapable of destroying it with their tanks or anti-tank weapons and had to rely on 88 mm anti-aircraft guns
(flak) or 105 mm guns to knock them out. Only a few of these tanks were used to good effect, but one event of the Battle of Raseiniai
was a notable example. On 23–24 June, a single KV-2 effectively pinned down elements of the 6th Panzer Division – the spearhead of Panzergruppe 4 – for a full day at the bridgeheads of the Dubysa
river near Raseiniai
, Lithuania
, playing a prominent role in delaying the German advance on Leningrad.
) near Leningrad
(St Petersburg), and the only Soviet force available at the time to attempt to stop the German advance consisted of five well-hidden KV-1 tanks, dug in within a grove at the edge of a swamp. KV-1 tank no. 864 was commanded by the leader of this small force, Lieutenant
Zinoviy Kolobanov
.
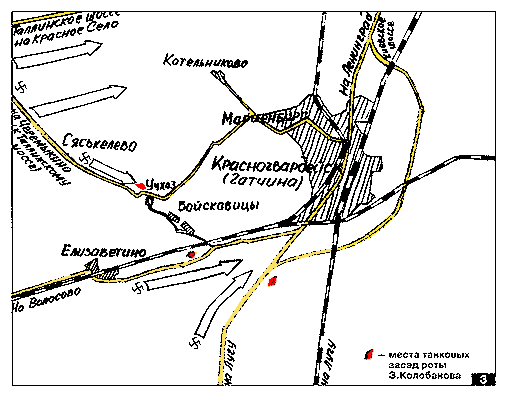
 German forces attacked Krasnogvardeysk from three directions. Near Noviy Uchkhoz settlement the geography favoured the Soviet defenders as the only road in the region passed the swamp, and the defenders commanded this choke point from their hidden position. Lieutenant Kolobanov had carefully studied the situation and readied his detachment the day before. Each KV-1 tank carried twice the normal amount of ammunition, two-thirds being armour-piercing rounds. Kolobanov ordered his other commanders to hold their fire and await orders. He did not want to reveal the total force, so only one exposed tank at a time would engage the enemy.
German forces attacked Krasnogvardeysk from three directions. Near Noviy Uchkhoz settlement the geography favoured the Soviet defenders as the only road in the region passed the swamp, and the defenders commanded this choke point from their hidden position. Lieutenant Kolobanov had carefully studied the situation and readied his detachment the day before. Each KV-1 tank carried twice the normal amount of ammunition, two-thirds being armour-piercing rounds. Kolobanov ordered his other commanders to hold their fire and await orders. He did not want to reveal the total force, so only one exposed tank at a time would engage the enemy.
On August 14, the German 8th Panzer Division's vanguard ventured directly into the well-prepared Soviet ambush, with Kolobanov's tank knocking out the lead German tank with its first shot. The Germans falsely assumed that their lead tank had hit an anti-tank mine
, and failed to realize that they had been ambushed. The German column stopped, giving Kolobanov the opportunity to destroy the second tank. Only then did the Germans realize they were under attack, but they failed to find the source of the shots. While the German tanks were firing blindly, Kolobanov knocked out the trailing German tank, thus boxing in the entire column.
Although the Germans correctly guessed the direction of fire, they could only spot Lieutenant Kolobanov's tank, and now attempted to engage an unseen enemy. German tanks moving off the road bogged down in the surrounding soft ground, becoming easy targets. 22 German tanks and 2 towed artillery
pieces fell victim to Kolobanov's No. 864 before it ran out of ammunition. Kolobanov ordered in another KV-1, and 21 more German tanks were destroyed before the half-hour battle ended. A total of 43 German tanks were destroyed by just five Soviet KV-1s (two more remained in reserve).
After the battle, the crew of No. 864 counted a total of 135 hits on their tank, none of which had penetrated the KV-1's armour. Lieutenant Kolobanov was awarded the Order of Lenin
, while his driver Usov was awarded the Order of the Red Banner
. Later on, former Captain Zinoviy Kolobanov was again decorated by Soviet authorities, despite having been convicted and downgraded after the Winter War for "fraternizing with the enemy." After the end of World War II, Lieutenant Kolobanov served in the Soviet occupation zone in East Germany, where he was convicted again when a subordinate escaped to the British occupation zone, and was transferred to the reserves.
The battle for Krasnogvardeysk was covered up by Soviet propaganda. A monument dedicated to this battle was installed in the village of Noviy Uchkhoz in 1980, at the place where Kolobanov's KV-1 was dug in, due solely to the demands of the villagers. Unfortunately it was impossible to find a KV-1 tank, so an IS-2 heavy tank was installed there instead.
The Soviet victory was the result of a well-planned ambush in advantageous ground and of technical superiority. Most of the German tanks in this battle were Panzer II
s, armed with 20 mm guns, and a few Panzer III
s armed with 37 mm KwK 36 L/46.5
guns. The German tank guns had neither the range nor the power of the 76 mm main gun of a KV-1, and the narrower track width of the German tanks caused them to become trapped in the swampy ground.
Tank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
s were a series of Soviet heavy tank
Heavy tank
A heavy tank was a subset of tank that filled the heavy direct-fire role of many armies.Heavy tanks have usually been deployed to breakthrough enemy lines, though in practice have been more useful in the defensive role than in the attack...
s, named after the Soviet defense commissar and politician Kliment Voroshilov
Kliment Voroshilov
Kliment Yefremovich Voroshilov , popularly known as Klim Voroshilov was a Soviet military officer, politician, and statesman...
. The KV series were known for their extremely heavy armour protection during the early war, especially during the first year of the invasion
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
in World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. Almost completely immune to the 7.5 cm KwK 37
7.5 cm KwK 37
The 7.5 cm KwK 37 L/24 was a German 75 mm tank gun used during World War II, primarily as the chief weapon of the Panzer IV tank....
and 3.7 cm KwK 36
3.7 cm KwK 36
The 3.7 cm KwK 36 L/45 was a German 3.7 cm cannon used primarily as the chief weapon of variants of the German medium tank the SdKfz.141 Panzerkampfwagen III...
guns mounted on the early Panzer III
Panzer III
Panzer III was the common name of a medium tank that was developed in the 1930s by Germany and was used extensively in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen III translating as "armoured battle vehicle". It was intended to fight other armoured fighting vehicles and...
and Panzer IV
Panzer IV
The Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
tanks, until better guns were developed often the only way to defeat a KV was a point-blank shot to the rear. Prior to the invasion, about 500 of the over 22,000 tanks in Soviet service at the time were of the KV-1 type. When the KV-1 appeared, it outclassed the French Char B1
Char B1
The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II.The Char B1 was a specialised heavy break-through vehicle, originally conceived as a self-propelled gun with a 75 mm howitzer in the hull; later a 47 mm gun in a turret was added, to allow it to function also as a Char...
, the only heavy tank used in the world at that time. Yet in the end it turned out that there was little sense in producing the expensive KV tanks, as the T-34
T-34
The T-34 was a Soviet medium tank produced from 1940 to 1958. Although its armour and armament were surpassed by later tanks of the era, it has been often credited as the most effective, efficient and influential design of World War II...
medium tank performed better (or at least equally) in all practical respects. Later in the war, the KV series became a base of development of the Iosif Stalin tank
Iosif Stalin tank
The Iosif Stalin tank , was a heavy tank developed by the Soviet Union during World War II and first used in the Kursk area in September 1943...
s.
Development history
After disappointing results with the multi-turreted T-35T-35
The T-35 was a Soviet multi-turreted heavy tank of the interwar period and early Second World War that saw limited production and service with the Red Army. It was the only five-turreted heavy tank in the world to reach production but proved to be slow and mechanically unreliable...
heavy tank, Soviet tank designers started drawing up replacements. The T-35 conformed to the 1920s notion of a 'breakthrough tank' with very heavy firepower and armour protection, but suffered from poor mobility. The Spanish Civil War
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil WarAlso known as The Crusade among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War among Carlists, and The Rebellion or Uprising among Republicans. was a major conflict fought in Spain from 17 July 1936 to 1 April 1939...
demonstrated the need for much heavier armor on tanks, and was the main influence on Soviet tank design just prior to World War II.
Several competing designs were offered, and even more were drawn up prior to reaching prototype stage. All had heavy armour, torsion-bar suspension, wide tracks, and were of welded and cast construction. One of the main competing designs was the SMK
SMK tank
SMK was an armored vehicle prototype developed by the Soviet Union prior to the Second World War...
, which in its final form had two turrets, mounting the same combination of 76.2 mm and 45 mm weapons. The designers of the SMK independently drew up a single-turreted variant and this received approval at the highest level. Two of these, named after the People's Defence Commissioner were ordered alongside a single SMK. The smaller hull and single turret enabled the designer to install heavy frontal and turret armour while keeping the weight within manageable limits.

Winter War
The Winter War was a military conflict between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet offensive on 30 November 1939 – three months after the start of World War II and the Soviet invasion of Poland – and ended on 13 March 1940 with the Moscow Peace Treaty...
, the SMK, KV and a third design, the T-100
T-100 tank
The T-100 was a twin-turreted Soviet heavy tank prototype, designed in 1938–39 as a possible replacement for the T-35.The T-100 was designed to by N. Barykov's OKMO design team at S.M. Kirov Factory No. 185 in Leningrad...
, were sent to be tested in combat conditions. The SMK and T-100 performed worse than the KV. The heavy armour of the KV proved highly resistant to Finnish
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
anti-tank weapons, making it more effective than the other designs. In 1939 production of 50 KV was ordered. During the War, the Soviets found it difficult to deal with the concrete bunkers used by the Finns and a request was made for a tank with a large howitzer. One of the rush projects to meet the request put the howitzer in a new turret on one of the KV tanks.
Initially known as Little Turret and Big turret, the 76-mm-armed tank was designated as the KV-1 Heavy Tank and the 152 mm howitzer
Howitzer
A howitzer is a type of artillery piece characterized by a relatively short barrel and the use of comparatively small propellant charges to propel projectiles at relatively high trajectories, with a steep angle of descent...
one as KV-2 Heavy Artillery Tank.
The KV's strengths included armor that was impenetrable by any tank-mounted weapon then in service except at point-blank range, that it had good firepower, and that it had good traction on soft ground. It also had serious flaws: it was difficult to steer, the transmission (which was a twenty year old Caterpillar
Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc. , also known as "CAT", designs, manufactures, markets and sells machinery and engines and sells financial products and insurance to customers via a worldwide dealer network. Caterpillar is the world's largest manufacturer of construction and mining equipment, diesel and natural gas...
design) was unreliable (and was known to have to be shifted with a hammer), and the ergonomics were poor, with limited visibility and no turret basket. Furthermore, at 45 tons, it was simply too heavy. This severely impacted the maneuverability, not so much in terms of maximum speed, as through inability to cross many bridges medium tanks could cross. The KV outweighed most other tanks of the era, being about twice as heavy as the heaviest contemporary German tank. KVs were never equipped with snorkeling system to ford river on the bottom, so they had to be left to travel to an adequate bridge. As applique armor and other improvements were added without increasing engine power, later models were less capable of keeping up to speed with medium tanks and had more trouble with difficult terrain. In addition, its firepower was no better than the T-34
T-34
The T-34 was a Soviet medium tank produced from 1940 to 1958. Although its armour and armament were surpassed by later tanks of the era, it has been often credited as the most effective, efficient and influential design of World War II...
. It took field reports from senior commanders "and certified heroes", who could be honest without risk of punishment, to reveal "what a dog the KV-1 really was."
Further development
By 1942, when the Germans were fielding large numbers of long-barrelled 50 mm and 75 mm guns, the KV's armor was no longer invincible. The KV-1's side, top, and turret armor could also be penetrated by the high-velocity MK 101 carried by German ground attack aircraft such as the Henschel Hs 129Henschel Hs 129
The Henschel Hs 129 was a World War II ground-attack aircraft fielded by the German Luftwaffe. Its nickname, the Panzerknacker , is a deliberate pun—in German, it also means "safe cracker"...
, requiring the installation of additional field-expedient appliqué armour. The KV-1's 76.2 mm gun also came in for criticism. While adequate against all German tanks, it was the same gun as carried by smaller, faster, and cheaper T-34
T-34
The T-34 was a Soviet medium tank produced from 1940 to 1958. Although its armour and armament were surpassed by later tanks of the era, it has been often credited as the most effective, efficient and influential design of World War II...
medium tanks. In 1943, it was determined that this gun could not penetrate the frontal armour of the new Tiger
Tiger I
Tiger I is the common name of a German heavy tank developed in 1942 and used in World War II. The final official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen Tiger Ausf. E, often shortened to Tiger. It was an answer to the unexpectedly formidable Soviet armour encountered in the initial months of...
, the first German heavy tank, fortunately captured near Leningrad. The KV-1 was also much more difficult to manufacture and thus more expensive than the T-34. In short, its advantages no longer outweighed its drawbacks.
Nonetheless, because of its initial superior performance, the KV-1 was chosen as one of the few tanks to continue being built following the Soviet reorganization of tank production. Due to the new standardization, it shared the similar engine (the KV used a 600 hp V-2K modification of the T-34's V-2 diesel engine) and gun (the KV had a ZiS-5 main gun, while the T-34 had a similar F-34 main gun) as the T-34, was built in large quantities, and received frequent upgrades.
When production shifted to the Ural Mountains 'Tankograd' complex, the KV-2 was dropped. While impressive on paper, it had been designed as a slow-moving bunker-buster. It was less useful in highly mobile, fluid warfare that developed in World War II. The turret was so heavy it was difficult to traverse on non-level terrain, and it was expensive to produce. Only about 300 KV-2s were made, all in 1940-41, making it one of the rarer Soviet tanks.

In response to criticisms, the lighter KV-1S (Russian language: КВ-1С) was released, with thinner armour and a smaller, lower turret in order to reclaim some speed. Importantly, the KV-1S also had a commander's cupola with all-around vision blocks, a first for a Soviet heavy tank. However, the thinning-out of the armor called into question why the tank was being produced at all, when the T-34 could seemingly do everything the KV could do and much more cheaply. The Soviet heavy tank program was close to cancellation in mid-1943.
The appearance of the German Panther tank
Panther tank
Panther is the common name of a medium tank fielded by Nazi Germany in World War II that served from mid-1943 to the end of the European war in 1945. It was intended as a counter to the T-34, and to replace the Panzer III and Panzer IV; while never replacing the latter, it served alongside it as...
in the summer of 1943 convinced the Red Army to make a serious upgrade of its tank force for the first time since 1941. Soviet tanks needed bigger guns to take on the growing numbers of Panthers and the few Tigers.
A stopgap upgrade to the KV series was the short-lived KV-85 or Objekt 239. This was a KV-1S with a new turret designed for the IS-85, mounting the same 85 mm D-5T gun as the SU-85
SU-85
The SU-85 was a Soviet self-propelled gun used during World War II, based on the chassis of the T-34 medium tank. Earlier Soviet self-propelled guns were meant to serve as either assault guns, such as the SU-122, or as mobile anti-tank weapons; the SU-85 fell into the latter category...
and early versions of the T-34-85. Already-high demand for the gun slowed production of the KV-85 tremendously, and only 148 were built before the KV design was replaced. The KV-85 was produced in the fall and winter of 1943-44; they were sent to the front as of September 1943, and production of the KV-85 was stopped by the spring of 1944 once the IS-2 entered full scale production.
Successor
A new heavy tank design entered production late in 1943 based on the work done on the KV-13. Because Kliment Voroshilov had fallen out of political favour, the new heavy tank series was named the Iosif Stalin tankIosif Stalin tank
The Iosif Stalin tank , was a heavy tank developed by the Soviet Union during World War II and first used in the Kursk area in September 1943...
, after Iosif (Joseph) Stalin. The KV-13 program's IS-85 prototype was accepted for production as the IS-1 (or IS-85, Object 237) heavy tank. After testing with both 100 mm
D-10 tank gun
The D-10 is a Soviet antitank gun developed in late World War II, and installed in tank destroyers and tanks. Versions of the 100 mm gun were installed on new T-55 tanks as late as 1979, and continue to be in active service in many countries.- History :...
and 122 mm guns, the D-25T 122 mm gun was selected as the main armament of the new tank, primarily because of its ready availability and the effect of its large high-explosive shell when attacking German fortifications. The 122mm D-25T used a separate shell and powder charge, resulting in a lower rate of fire and reduced ammunition capacity. While the 122mm armour piercing shell had a lower muzzle velocity than similar late German 7.5 cm and 8.8 cm guns, proving-ground tests showed that the 122mm AP shell could defeat the frontal armour of the German Panther tank, and the HE shell would easily blow off the drive sprocket and tread of the heaviest German tank or self-propelled gun. The IS-122 replaced the IS-85, and began mass production as the IS-2. The 85 mm gun saw service in the lighter SU-85 and T-34-85.

Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
of KVs saw service in Manchuria in August 1945, and a few KV-85s were used in the Crimea in the summer of 1944. The Finnish forces had two KVs, nicknamed Klimi, a Model 1940 and Model 1941, both of which received minor upgrades in their service, and both of which survived the war. A single captured KV-2 was used by German forces in 1945 against US forces in the Ruhr.
Models
The Soviets did not recognize different production models of KV-1 during the war; designations like model 1939 (M1939, Russian: Obr. 1939) were introduced later in military publications. These designations however are not strict and describe leading changes, while other changes might be adapted earlier or later in specific production batches. Designations like KV-1A were applied by the Germans during the war.
- KV-1
- Model 1939 – First production models, these tanks were prone to frequent breakdowns, but were highly resistant to anti-tank weapons during the Winter WarWinter WarThe Winter War was a military conflict between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet offensive on 30 November 1939 – three months after the start of World War II and the Soviet invasion of Poland – and ended on 13 March 1940 with the Moscow Peace Treaty...
. These tanks were armed with the 76 mm L-11 tank gun, recognizable due to a recuperatorRecuperatorA recuperator is a special purpose counter-flow energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air handling system, or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the waste heat...
above a barrel. Most tanks were lacking the hull machine gun. 141 were built. - Model 1940 (German designation: KV-1A) – Used the F-32 76 mm gun and a new mantlet. The main production model by the time of the German invasion.
- Model 1940 s ekranami ("with screens") or KV1-E – with additional bolted-on appliqué armour and F-32 gun.
- Model 1941 (KV-1B) – Up-armoured with 25 to 35 mm added to the turret, hull front and sides. Turret was now cast instead of welded. This tank was armed with the longer-barrelled F-34, and later ZiS-5ZIS-5ZiS-5 may refer to:* F-34 tank gun, used on the T-34 tank* ZiS-5 , produced at Zavod imeni Stalina; see also ZiS-6...
76.2 mm tank guns. - Model 1942 (KV-1C) – Fully cast turret with thicker armour or welded turret with thicker armour, again up-armoured and used an improved engine and the 76 mm ZiS-5 tank gun.
- KV-1S – A lighter variant of late 1942 with higher speed, but thinner armour. A new, smaller, cast turret and redesigned rear hull were used. 1370 were built.
- Panzerkampfwagen KV-IA 753(r) and Panzerkampfwagen KV-IB 755(r) - The KV-1 in German service. Some were fitted with a high-velocity KwK 40 L/43 75-mm gun7.5 cm KwK 40The 7.5 cm KwK 40 was a German 7.5 cm Second World War era vehicle mounted gun, used as the primary anti-tank weapon of the German medium tank the SdKfz.161 Panzerkampfwagen IV and the SdKfz.142 Sturmgeschütz III assault guns ...
, the same gun used in a Panzer IVPanzer IVThe Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
Ausf F2.
- Model 1939 – First production models, these tanks were prone to frequent breakdowns, but were highly resistant to anti-tank weapons during the Winter War
All tanks in the series were heavily based on the KV-1 technology.

- KV-2 (334) – A heavy assault tank with the M-10 152 mm howitzer, the KV-2 was produced at the same time as the KV-1. Due to the size of its heavy turret and gun, the KV-2 was slower and had a much higher profile than the KV-1. Those captured and used by the German Army were known as (Sturm)Panzer kampfwagen KV-II 754(r)
- KV-3 (Object 223) - Experimental tank based on KV-1. Longer chassis (7 rollers per side). New 850 hp V-2SN engine. 130 mm armor. New conic turret. 107mm ZiS-6 cannon. One prototype was constructed and prooved in 1941.
- KV-4KV-4The KV-4 was a proposed Soviet heavy break-through tank, developed during World War II. Part of the Kliment Voroshilov tank design series, it never progressed past a series of feasibility studies.-Design history:...
(Object 224) - A project for a Super-heavy tankSuper-heavy tankSuper-heavy tanks are armored vehicles of very large size, generally over 75 tonnes. Programs have been initiated on several occasions with the aim of creating an invincible vehicle for penetrating enemy formations without fear of being destroyed in combat; however, only a few examples have ever...
. About 20 different designs were proposed, but it was cancelled in favour of the IS series tanksIosif Stalin tankThe Iosif Stalin tank , was a heavy tank developed by the Soviet Union during World War II and first used in the Kursk area in September 1943...
. Different versions would have been between about 85 and 110 tonnes. Armour from about 120 to 150 mm. Armament 107mm ZiS-6 cannon. - KV-5 (Object 225) - A cancelled project for a heavy tankHeavy tankA heavy tank was a subset of tank that filled the heavy direct-fire role of many armies.Heavy tanks have usually been deployed to breakthrough enemy lines, though in practice have been more useful in the defensive role than in the attack...
. Armament was to be a 130 mm gun in a large turret and machine-gun in a small secondary turret. - KV-6 (Object 226) - Experimental flame tank based on KV-1. Flamethrower was mounted inside hull to the right from driver. Visual feature of this tank is armored box on the front of chassis to the right from driver. One vehicle was constructed and prooved in 1941.
- KV-8 (42) – A KV-1 fitted with the ATO-41 flame-thrower in the turret, beside a machine gun. In order to accommodate the new weapon, the 76.2mm gun was replaced with a smaller 45 mm Gun M1932, though it was disguised to look like the standard 76 mm (The cannon was placed inside 76mm tube).
- KV-8S (25) – The same as KV-8, but based on KV-1S. Was equipped with ATO-42 flamethrower (improved version of ATO-41).
- KV-9 (Object 229) - A KV-1 with short 122mm U-11 cannon. One prototype was construcred and prooved in 1941.
- KV-10 (Object 230) - Also known as KV-1K. A KV-1S with 4 rocket launchers on the back of hull. Each launcher contained two 132mm M-13 rockets. One prototype was constucted in 1942. Not taken in service.
- KV-12 (Object 232) - Experimental chemical tank. Was equipped with 4 external toxin tanks on the back of chassis. Tanks surrounded with 30mm armor. Not taken in service.
- KV-13 (Object 233) - Prototype of a medium tank. Designation for an advanced redesign of the KV series, which was resulted in the production of the IS series.
- IS Model 2 - A KV-13, with turret and armanent from KV-9. One prototype was construcred and prooved in 1943. Tank had lost competition to IS Model 1 and was not taken in service.
- KV-14 (Object 236) – Prototype designation for a 152 mm self-propelled gunSelf-propelled gunA self-propelled gun is form of self-propelled artillery, and in modern use is usually used to refer to artillery pieces such as howitzers....
, accepted for service as the SU-152SU-152The SU-152 was a Soviet heavy self-propelled heavy howitzer used during World War II.It mounted a 152 mm gun-howitzer on the chassis of a KV-1S heavy tank. Later production used IS tank chassis and was re-designated as ISU-152...
. - KV-85 – A KV-1S with the 85mm D-5T cannon in a new turret, with the ball mounted hull machine gun removed and the hole welded shut, 148 of these tanks were produced in the second half of 1943 until the spring of 1944 as a stopgap until the IS tank series entered production. This tank had its original turret, but later models were equipped with IS-1 turret.
- KV-85G - KV-1S with 85mm S-18 cannon. Turret and mantlet remained from conventional KV-1S. This variant was a competitor of KV-85 during prooving. It lost competition and was not taken in service.
- KV-152 - A KV-85 with short 152mm S-41 cannon. One prototype was made in 1943. Not taken in service.
- KV-100 - A KV-85 with the 100mm D-10T cannon. One prototype was made in 1944. Not taken in service.
- KV-122 - A KV-85 with the 122mm D-25T cannon. One prototype was made in 1944. Not taken in service.
- Т-150 (Object 150) - Experimental tank based on KV-1. Armor - 90mm. New 700 hp engine. Turret design and armanent remained from KV-1. One prototype was constructed in 1941.
- KV-220 (Object 220) - Experimental tank based on KV-1. Longer chassis (7 rollers per side). Armor - 100mm. New 850 hp V-2SN engine with turbocharging. New diamond-shaped turret. 85mm F-30 cannon. One prototype was constructed in 1941.
- KV-222 (Object 222) - Experimental tank based on KV-1. Longer chassis (7 rollers per side). Armor - 90mm. New 850 hp V-2SN engine. One prototype was constructed in 1941. Armament - 107mm ZiS-6 cannon.
Table of data, containing several WW2 Soviet heavy tanks
| T-35 T-35 The T-35 was a Soviet multi-turreted heavy tank of the interwar period and early Second World War that saw limited production and service with the Red Army. It was the only five-turreted heavy tank in the world to reach production but proved to be slow and mechanically unreliable... |
T-100 T-100 tank The T-100 was a twin-turreted Soviet heavy tank prototype, designed in 1938–39 as a possible replacement for the T-35.The T-100 was designed to by N. Barykov's OKMO design team at S.M. Kirov Factory No. 185 in Leningrad... |
SMK SMK SMK can refer to:* Statens Museum for Kunst, the Danish National Gallery* SMK tank, a Soviet heavy tank prototype* Slagsmålsklubben, Swedish band* Smacker video computer video file format* Super Mario Kart, the debut title in Nintendo's Mario Kart series.... |
KV-1 M1940 |
KV-1 M1941 |
KV-1 M1942 |
KV-1S M1942 |
KV-85 M1943 |
IS-2 M1945 |
IS-3 M1945 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 11 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Weight | 45 t | 58 t | 55 t | 43 t | 45 t | 47 t | 42.5 t | 46 | 46 t | 46.5 t |
| Gun | 76.2 mm M. 27/32 |
76.2 mm L-11 |
76.2 mm L-11 |
76.2 mm F-32 |
76.2 mm F-34 F-34 tank gun The 76 mm tank gun M1940 F-34 was a 76.2 mm Soviet tank gun used on the T-34/76 tank. A modified version of the gun, the 76 mm tank gun M1941 ZiS-5 was used on KV-1 tanks during World War II... |
76.2 mm ZiS-5 |
76.2 mm ZiS-5 |
85 mm D-5T |
122 mm D-25T |
122 mm D-25T |
| Ammunition | 100 rds. | – | – | 111 | 111 | 114 | 114 | 70 | 28 | 28 |
| Secondary armament | 2×45 mm, 5×7.62 mm |
45 mm | 45 mm | 2×DT | 4×DT | 4×DT | 4×DT | 3×DT | 2×DT, DShK DShK The DShK 1938 is a Soviet heavy machine gun firing the 12.7x108mm cartridge. The weapon was also used as a heavy infantry machine gun, in which case it was frequently deployed with a two-wheeled mounting and a single-sheet armour-plate shield... |
2×DT, DShK |
| Engine | 500 hp M-17M gasoline Gasoline Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain... |
500 hp | 850 hp AM-34 |
600 hp V-2K diesel Diesel engine A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber... |
600 hp V-2 |
600 hp V-2 |
600 hp V-2 |
600 hp V-2 |
600 hp V-2 |
600 hp V-2-IS |
| Fuel | 910 L Litre pic|200px|right|thumb|One litre is equivalent to this cubeEach side is 10 cm1 litre water = 1 kilogram water The litre is a metric system unit of volume equal to 1 cubic decimetre , to 1,000 cubic centimetres , and to 1/1,000 cubic metre... |
– | – | 600 L | 600 L | 600 L | 975 L | 975 L | 820 L | 520 + 270 L |
| Road speed | 30 km/h | 35 km/h | 36 km/h | 35 km/h | 35 km/h | 28 km/h | 45 km/h | 40 km/h | 37 km/h | 37 km/h |
| Road range | 150 km | – | 150 km | 335 km | 335 km | 250 km | 250 km | 250 km | 240 km | 150 (225) km |
| Armour | 11–30 mm | 20–70 mm | 20–60 mm | 25–75 mm | 30–90 mm | 20–130 mm | 30–82 mm | 30–160 mm | 30–160 mm | 20–220 mm |
Raseiniai

Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
began, the Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
was equipped with 508 new KV tanks. So effective was its armour that the Germans
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
were incapable of destroying it with their tanks or anti-tank weapons and had to rely on 88 mm anti-aircraft guns
88 mm gun
The 88 mm gun was a German anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun from World War II. It was widely used by Germany throughout the war, and was one of the most recognizable German weapons of the war...
(flak) or 105 mm guns to knock them out. Only a few of these tanks were used to good effect, but one event of the Battle of Raseiniai
Battle of Raseiniai
The Battle of Raseiniai was a tank battle fought between the elements of the 4th Panzer Group commanded by Gen. Erich Hoepner and the 3rd Mechanized Corps commanded by Major General Kurkin & 12th Mechanised Corps commanded by Major General Shestapolov in Lithuania 75 km northwest of Kaunas...
was a notable example. On 23–24 June, a single KV-2 effectively pinned down elements of the 6th Panzer Division – the spearhead of Panzergruppe 4 – for a full day at the bridgeheads of the Dubysa
Dubysa
Dubysa, at 131 km, is the 15th longest river in Lithuania. It originates just a few kilometers from Lake Rėkyva near Šiauliai city. At first it flows south, but at Lyduvėnai turns southeast and near Ariogala - southwest. Dubysa is a Samogitian river...
river near Raseiniai
Raseiniai
Raseiniai is a city in Lithuania. It is located on the south eastern foothills of the Samogitians highland, some north from the Kaunas–Klaipėda highway.- Grand Duchy of Lithuania :...
, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, playing a prominent role in delaying the German advance on Leningrad.
Krasnogvardeysk
On August 14, 1941, the vanguard of the German 8th Panzer Division approached Krasnogvardeysk (GatchinaGatchina
Gatchina is a town and the administrative center of Gatchinsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located south of St. Petersburg by the road leading to Pskov...
) near Leningrad
Leningrad
Leningrad is the former name of Saint Petersburg, Russia.Leningrad may also refer to:- Places :* Leningrad Oblast, a federal subject of Russia, around Saint Petersburg* Leningrad, Tajikistan, capital of Muminobod district in Khatlon Province...
(St Petersburg), and the only Soviet force available at the time to attempt to stop the German advance consisted of five well-hidden KV-1 tanks, dug in within a grove at the edge of a swamp. KV-1 tank no. 864 was commanded by the leader of this small force, Lieutenant
Lieutenant
A lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer in many nations' armed forces. Typically, the rank of lieutenant in naval usage, while still a junior officer rank, is senior to the army rank...
Zinoviy Kolobanov
Zinoviy Kolobanov
Zinoviy G. Kolobanov was a tank commander and veteran of the German-Soviet War. He commanded a KV-1 tank and is widely considered the second top scoring tanker ace of the Soviet Union.-Service:...
.


On August 14, the German 8th Panzer Division's vanguard ventured directly into the well-prepared Soviet ambush, with Kolobanov's tank knocking out the lead German tank with its first shot. The Germans falsely assumed that their lead tank had hit an anti-tank mine
Anti-tank mine
An anti-tank mine, , is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles....
, and failed to realize that they had been ambushed. The German column stopped, giving Kolobanov the opportunity to destroy the second tank. Only then did the Germans realize they were under attack, but they failed to find the source of the shots. While the German tanks were firing blindly, Kolobanov knocked out the trailing German tank, thus boxing in the entire column.
Although the Germans correctly guessed the direction of fire, they could only spot Lieutenant Kolobanov's tank, and now attempted to engage an unseen enemy. German tanks moving off the road bogged down in the surrounding soft ground, becoming easy targets. 22 German tanks and 2 towed artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
pieces fell victim to Kolobanov's No. 864 before it ran out of ammunition. Kolobanov ordered in another KV-1, and 21 more German tanks were destroyed before the half-hour battle ended. A total of 43 German tanks were destroyed by just five Soviet KV-1s (two more remained in reserve).
After the battle, the crew of No. 864 counted a total of 135 hits on their tank, none of which had penetrated the KV-1's armour. Lieutenant Kolobanov was awarded the Order of Lenin
Order of Lenin
The Order of Lenin , named after the leader of the Russian October Revolution, was the highest decoration bestowed by the Soviet Union...
, while his driver Usov was awarded the Order of the Red Banner
Order of the Red Banner
The Soviet government of Russia established the Order of the Red Banner , a military decoration, on September 16, 1918 during the Russian Civil War...
. Later on, former Captain Zinoviy Kolobanov was again decorated by Soviet authorities, despite having been convicted and downgraded after the Winter War for "fraternizing with the enemy." After the end of World War II, Lieutenant Kolobanov served in the Soviet occupation zone in East Germany, where he was convicted again when a subordinate escaped to the British occupation zone, and was transferred to the reserves.
The battle for Krasnogvardeysk was covered up by Soviet propaganda. A monument dedicated to this battle was installed in the village of Noviy Uchkhoz in 1980, at the place where Kolobanov's KV-1 was dug in, due solely to the demands of the villagers. Unfortunately it was impossible to find a KV-1 tank, so an IS-2 heavy tank was installed there instead.
The Soviet victory was the result of a well-planned ambush in advantageous ground and of technical superiority. Most of the German tanks in this battle were Panzer II
Panzer II
The Panzer II was the common name for a family of German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen II...
s, armed with 20 mm guns, and a few Panzer III
Panzer III
Panzer III was the common name of a medium tank that was developed in the 1930s by Germany and was used extensively in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen III translating as "armoured battle vehicle". It was intended to fight other armoured fighting vehicles and...
s armed with 37 mm KwK 36 L/46.5
3.7 cm KwK 36
The 3.7 cm KwK 36 L/45 was a German 3.7 cm cannon used primarily as the chief weapon of variants of the German medium tank the SdKfz.141 Panzerkampfwagen III...
guns. The German tank guns had neither the range nor the power of the 76 mm main gun of a KV-1, and the narrower track width of the German tanks caused them to become trapped in the swampy ground.
See also
- Comparison of early World War II tanksComparison of early World War II tanksThis table compare the tanks in use by the belligerent nations of Europe at the start of the Second World War, employed in the Polish Campaign , the Fall of France , and Operation Barbarossa ....
- March of the Soviet TankmenMarch of the Soviet TankmenMarch of the Soviet Tankmen is a military march composed in 1939 by the Pokrass brothers with lyrics by Laskin. It was commonly used as a Soviet propaganda song in World War II.- Lyrics :...
External links
- LemaireSoft
- OnWar specifications: KV-1 M39, KV-1e M40, KV-1 M41, KV-1S, KV-85, KV-2
- Russian Battlefield: KV-1, KV-1S, KV-2, KV-8 and KV-8S, KV-85, KV-3, KV-4, KV-5, KV-7, KV-9 and KV-220, Soviet Heavy Tanks Specification
- World War II Vehicles
- Walkaround KV-85 from Avtovo, Saint-Petersburg (Russia)
- KV tanks, KV tanks in museum and monuments

