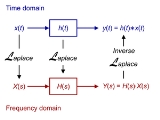
LTI system theory
Overview
Applied mathematics
Applied mathematics is a branch of mathematics that concerns itself with mathematical methods that are typically used in science, engineering, business, and industry. Thus, "applied mathematics" is a mathematical science with specialized knowledge...
and has direct applications in NMR spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained...
, seismology
Seismology
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake effects, such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic,...
, circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
s, signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, and other technical areas. It investigates the response of a linear
Linear system
A linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator.Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the general, nonlinear case....
and time-invariant system
Time-invariant system
A time-invariant system is one whose output does not depend explicitly on time.This property can be satisfied if the transfer function of the system is not a function of time except expressed by the input and output....
to an arbitrary input signal. Trajectories of these systems are commonly measured and tracked as they move through time (e.g., an acoustic waveform), but in applications like image processing
Image processing
In electrical engineering and computer science, image processing is any form of signal processing for which the input is an image, such as a photograph or video frame; the output of image processing may be either an image or, a set of characteristics or parameters related to the image...
and field theory
Classical field theory
A classical field theory is a physical theory that describes the study of how one or more physical fields interact with matter. The word 'classical' is used in contrast to those field theories that incorporate quantum mechanics ....
, the LTI systems also have trajectories in spatial dimensions.

