
Lydersen method
Encyclopedia
The Lydersen method is a group contribution method
for the estimation of critical properties temperature (Tc), pressure (Pc) and volume (Vc). The Lydersen method is the prototype for and ancestor of many new models like Joback
, Klincewicz
,
Ambrose,
Gani-Constantinou and others.
The Lydersen method is based in case of the critical temperature on the Guldberg rule which establishes a relation between the normal boiling point
and the critical temperature.
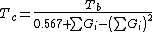
Guldberg has found that a rough estimate of the normal boiling point Tb, when expressed in kelvins (i.e., as an absolute temperature), is approximately two-thirds of the critical temperature Tc. Lydersen uses this basic idea but calculates more accurate values.
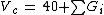
M is the molar mass
and Gi are the group contributions (different for all three properties) for functional group
s of a molecule
.
Acetone
is fragmented in two different groups, one carbonyl group and two methyl groups. For the critical volume the following calculation results:
Vc = 40 + 60.0 + 2 * 55.0 = 210 cm3
In the literature the values 215.90 cm3 , 230.5 cm3 and 209.0 cm3 are published.
Group contribution method
A group contribution method is a technique to estimate and predict thermodynamic and other properties from molecular structures.- Introduction :In today's chemical processes hundreds of thousands of components are used...
for the estimation of critical properties temperature (Tc), pressure (Pc) and volume (Vc). The Lydersen method is the prototype for and ancestor of many new models like Joback
Joback method
The Joback method predicts eleven important and commonly used pure component thermodynamic properties from molecular structure only.- Group Contribution Method :The Joback method is a group contribution method...
, Klincewicz
Klincewicz method
In thermodynamic theory, the Klincewicz method is a predictive method based both on group contributions and on a correlation with some basic molecular properties...
,
Ambrose,
Gani-Constantinou and others.
The Lydersen method is based in case of the critical temperature on the Guldberg rule which establishes a relation between the normal boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
and the critical temperature.
Critical temperature
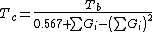
Guldberg has found that a rough estimate of the normal boiling point Tb, when expressed in kelvins (i.e., as an absolute temperature), is approximately two-thirds of the critical temperature Tc. Lydersen uses this basic idea but calculates more accurate values.
Critical volume
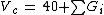
M is the molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
and Gi are the group contributions (different for all three properties) for functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s of a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
.
Group contributions
| Group | Gi (Tc) | Gi (Pc) | Gi (Vc) | Group | Gi (Tc) | Gi (Pc) | Gi (Vc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -CH3,-CH2- | 0.020 | 0.227 | 55.0 | >CH | 0.012 | 0.210 | 51.0 |
| -C< | |||||||
| 0,210 | 41.0 | =CH2,#CH | 0.018 | 0,198 | 45.0 | ||
| =C<,=C= | |||||||
| 0.198 | 36.0 | =C-H,#C- | 0.005 | 0.153 | 36.0 | ||
| -CH2-(Ring) | 0.013 | 0.184 | 44.5 | >CH-(Ring) | 0.012 | 0.192 | 46.0 |
| >C<(Ring) | |||||||
| 0.154 | 31.0 | =CH-,=C<,=C=(Ring) | 0.011 | 0.154 | 37.0 | ||
| -F | 0.018 | 0.224 | 18.0 | -Cl | 0.017 | 0.320 | 49.0 |
| -Br | 0.010 | 0.500 | 70.0 | -I | 0.012 | 0.830 | 95.0 |
| -OH | 0.082 | 0.060 | 18.0 | -OH(Aromat) | 0.031 | ||
| 3.0 | |||||||
| -O- | 0.021 | 0.160 | 20.0 | -O-(Ring) | 0.014 | 0.120 | 8.0 |
| >C=O | 0.040 | 0.290 | 60.0 | >C=O(Ring) | 0.033 | 0.200 | 50.0 |
| HC=O- | 0.048 | 0.330 | 73.0 | -COOH | 0.085 | 0.400 | 80.0 |
| -COO- | 0.047 | 0.470 | 80.0 | -NH2 | 0.031 | 0.095 | 28.0 |
| >NH | 0.031 | 0.135 | 37.0 | >NH(Ring) | 0.024 | 0.090 | 27.0 |
| >N | 0.014 | 0.170 | 42.0 | >N-(Ring) | 0.007 | 0.130 | 32.0 |
| -CN | 0.060 | 0.360 | 80.0 | -NO2 | 0.055 | 0.420 | 78.0 |
| -SH,-S- | 0.015 | 0.270 | 55.0 | -S-(Ring) | 0.008 | 0.240 | 45.0 |
| =S | 0.003 | 0.240 | 47.0 | >Si< | 0.030 | 0.540 | |
| -B< | 0.030 | ||||||
Example calculation

Acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
is fragmented in two different groups, one carbonyl group and two methyl groups. For the critical volume the following calculation results:
Vc = 40 + 60.0 + 2 * 55.0 = 210 cm3
In the literature the values 215.90 cm3 , 230.5 cm3 and 209.0 cm3 are published.

