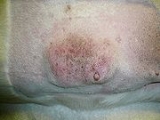
Mammary tumor
Encyclopedia
A mammary tumor is a tumor originating in the mammary gland
. It is a common finding in older female dog
s and cat
s that are not spayed, but they are found in other animals as well. The mammary glands in dogs and cats are associated with their nipple
s and extend from the underside of the chest to the groin on both sides of the midline. There are many differences between mammary tumors in animals and breast cancer
in humans, including tumor
type, malignancy
, and treatment options. The prevalence
in dogs is about three times that of women. In dogs, mammary tumors are the second most common tumor (after skin tumors) over all and the most common tumor in female dogs with a reported incidence of 3.4%. Multiple studies have documented that spaying bitches when young greatly decreases their risk of developing mammary neoplasia when aged. Compared with bitches left intact, those spayed before puberty have 0.5% of the risk, those spayed after one estrous cycle have 8.0% of the risk, and dogs spayed after two estrous cycles have 26.0% of the risk of developing mammary neoplasia later in life. Overall, unspayed bitches have a seven times greater risk of developing mammary neoplasia than do those that are spayed. While the benefit of spaying decreases with each estrous cycle, some benefit has been demonstrated in bitches even up to 9 years of age. There is a much lower risk (about 1 percent) in male dogs and a risk in cats about half that of dogs.


at one year of age and eating red meat
have also been associated with an increased risk for these tumors, as has the feeding of high fat homemade diets.
There are several hypotheses on the molecular mechanisms involved in the development of canine mammary tumors but a specific genetic mutation has not been identified.
s and fibroadenoma
s make up the benign
types. Malignant mammary tumors are divided into sarcoma
s, carcinosarcoma
s, inflammatory carcinomas (usually anaplastic carcinoma
s), and carcinoma
s (including adenocarcinoma
s), which are the most common. Inflammatory carcinomas describe tumors that are fast growing and have bruising, edema
, and pain, and can also cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
. They are the most malignant type of canine mammary tumor.
Malignant tumors are also subdivided histopathologically
into those showing blood vessel
wall invasion and those that do not. Without blood vessel wall invasion there is a better prognosis
. Dogs with noninvasive adenocarcinomas have an average survival time of two years, while dogs with invasive adenocarcinomas have an average survival time of one year. Tumor size also affects the prognosis, in that dogs with tumors greater than five centimeters have a greater chance of lymph node
metastasis
. Tumor type is also important. Sarcomas and carcinosarcomas carry an average survival time of nine to twelve months. Inflammatory carcinomas have a very poor prognosis, and have usually metastasized by the time of diagnosis. Metastasis for any malignant mammary tumor is usually to the regional lymph nodes and lung
s.
The molecular carcinogenesis of canine mammary tumors are not completely understand. However, the increasing information on molecular pathways involved in the carcinogenesis of this canine tumor has potential to complement and refine the current diagnostic and therapeutic approach to this tumor type. Furthermore, current data show that significant similarities and differences exist between canine and human mammary tumors at the molecular level.
will give type and invasiveness of the tumor. In addition, newer studies showed that certain gene expression patterns are associated with malignant behaviour of canine mammary tumors.
Surgical removal is the treatment of choice, but chest x-ray
s should be taken first to rule out metastasis. Removal should be with wide margins to prevent recurrence, taking the whole mammary gland if necessary. Because 40 to 50 percent of dog mammary tumors have estrogen receptor
s, spaying is recommended by many veterinarian
s. A recent study showed a better prognosis in dogs that are spayed at the time of surgery or that had been recently spayed. However, several other studies found no improvement of disease outcome when spaying was performed after the tumor had developed. Chemotherapy
is rarely used.
has shown some promise in treatment.
s. Appearance tends to be a soft, dark colored lump. Most seem to be benign and occur most frequently in neutered males. Surgery is recommended.
s occur in males and females. Most are benign, but 30 percent are adenocarcinomas. They usually do not metastasize, but aggressive surgery is necessary to prevent recurrence.
are adenocarcinomas. They can be caused by viral infection. Recurrence rates are high, and therefore there is a poor prognosis. There is frequently local tissue invasion and metastasis to the lungs. A well known tumor virus of the mouse is the mouse mammary tumor virus MMTV, which may be the most common cause of this tumor in mice.
s are benign fibroadenomas, which are also the most common tumor in the rat. Less than 10 percent are adenocarcinomas. They occur in male and female rats. The tumors can be large and occur anywhere on the trunk. There is a good prognosis with surgery. Spayed rats have a decreased risk of developing mammary tumors.
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
have found that lavender oil
may have played a role in the reduction of advanced mammary tumors in lab rats. Research is on-going for potential breast
, ovarian
, pancreatic
, liver
, and prostate
cancer treatments in humans.
s and malignant in gerbil
s.
.
Mammary gland
A mammary gland is an organ in mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word "mammary". In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in their udders...
. It is a common finding in older female dog
Dog
The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s and cat
Cat
The cat , also known as the domestic cat or housecat to distinguish it from other felids and felines, is a small, usually furry, domesticated, carnivorous mammal that is valued by humans for its companionship and for its ability to hunt vermin and household pests...
s that are not spayed, but they are found in other animals as well. The mammary glands in dogs and cats are associated with their nipple
Nipple
In its most general form, a nipple is a structure from which a fluid emanates. More specifically, it is the projection on the breasts or udder of a mammal by which breast milk is delivered to a mother's young. In this sense, it is often called a teat, especially when referring to non-humans, and...
s and extend from the underside of the chest to the groin on both sides of the midline. There are many differences between mammary tumors in animals and breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
in humans, including tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
type, malignancy
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
, and treatment options. The prevalence
Prevalence
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a health-related state in a statistical population is defined as the total number of cases of the risk factor in the population at a given time, or the total number of cases in the population, divided by the number of individuals in the population...
in dogs is about three times that of women. In dogs, mammary tumors are the second most common tumor (after skin tumors) over all and the most common tumor in female dogs with a reported incidence of 3.4%. Multiple studies have documented that spaying bitches when young greatly decreases their risk of developing mammary neoplasia when aged. Compared with bitches left intact, those spayed before puberty have 0.5% of the risk, those spayed after one estrous cycle have 8.0% of the risk, and dogs spayed after two estrous cycles have 26.0% of the risk of developing mammary neoplasia later in life. Overall, unspayed bitches have a seven times greater risk of developing mammary neoplasia than do those that are spayed. While the benefit of spaying decreases with each estrous cycle, some benefit has been demonstrated in bitches even up to 9 years of age. There is a much lower risk (about 1 percent) in male dogs and a risk in cats about half that of dogs.

Mammary tumors in dogs


Causes
The exact causes for the development of canine mammary tumors are not fully understood. However, hormones of the estrous cycle seem to be involved. Female dogs who are not spayed or who are spayed later than the first heat cycle are more likely to develop mammary tumors. Dogs have an overall reported incidence of mammary tumors of 3.4 percent. Dogs spayed before their first heat have 0.5 percent of this risk, and dogs spayed after just one heat cycle have 8 percent of this risk. The tumors are often multiple. The average age of dogs with mammary tumors is ten to eleven years old. ObesityObesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
at one year of age and eating red meat
Red meat
Red meat in traditional culinary terminology is meat which is red when raw and not white when cooked. In the nutritional sciences, red meat includes all mammal meat. Red meat includes the meat of most adult mammals and some fowl ....
have also been associated with an increased risk for these tumors, as has the feeding of high fat homemade diets.
There are several hypotheses on the molecular mechanisms involved in the development of canine mammary tumors but a specific genetic mutation has not been identified.
Biology
Historically, about 50 percent of mammary tumors in dogs were found to be malignant, although taking into account tumor behavior, one study has estimated true malignancy in mammary tumors to be 21 to 22 percent. AdenomaAdenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of glandular origin. Adenomas can grow from many organs including the colon, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, etc. Although these growths are benign, over time they may progress to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas...
s and fibroadenoma
Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenomas of the breast, are lumps composed of fibrous and glandular tissue. Because breast cancer can also appear as a lump, doctors may recommend a tissue sample to rule out cancer in older patients...
s make up the benign
Benign
A benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
types. Malignant mammary tumors are divided into sarcoma
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells in one of a number of tissues that develop from embryonic mesoderm. Thus, sarcomas include tumors of bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, vascular, and hematopoietic tissues...
s, carcinosarcoma
Carcinosarcoma
Carcinosarcoma is a malignant tumor that is a mixture of carcinoma and sarcoma ....
s, inflammatory carcinomas (usually anaplastic carcinoma
Anaplastic carcinoma
Anaplastic carcinoma is a general term for a malignant neoplasm arising from the uncontrolled proliferation of transformed cells of epithelial origin, or showing some epithelial characteristics, but that reveal no cytological or architectural features of associated with more differentiated tumors,...
s), and carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
s (including adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is a cancer of an epithelium that originates in glandular tissue. Epithelial tissue includes, but is not limited to, the surface layer of skin, glands and a variety of other tissue that lines the cavities and organs of the body. Epithelium can be derived embryologically from...
s), which are the most common. Inflammatory carcinomas describe tumors that are fast growing and have bruising, edema
Edema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
, and pain, and can also cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation , also known as disseminated intravascular coagulopathy or consumptive coagulopathy, is a pathological activation of coagulation mechanisms that happens in response to a variety of diseases. DIC leads to the formation of small blood clots inside the blood...
. They are the most malignant type of canine mammary tumor.
Malignant tumors are also subdivided histopathologically
Histopathology
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease...
into those showing blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
wall invasion and those that do not. Without blood vessel wall invasion there is a better prognosis
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
. Dogs with noninvasive adenocarcinomas have an average survival time of two years, while dogs with invasive adenocarcinomas have an average survival time of one year. Tumor size also affects the prognosis, in that dogs with tumors greater than five centimeters have a greater chance of lymph node
Lymph node
A lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
. Tumor type is also important. Sarcomas and carcinosarcomas carry an average survival time of nine to twelve months. Inflammatory carcinomas have a very poor prognosis, and have usually metastasized by the time of diagnosis. Metastasis for any malignant mammary tumor is usually to the regional lymph nodes and lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s.
The molecular carcinogenesis of canine mammary tumors are not completely understand. However, the increasing information on molecular pathways involved in the carcinogenesis of this canine tumor has potential to complement and refine the current diagnostic and therapeutic approach to this tumor type. Furthermore, current data show that significant similarities and differences exist between canine and human mammary tumors at the molecular level.
Diagnosis and treatment
Appearance and location of the tumor is enough to identify it as a mammary tumor. BiopsyBiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
will give type and invasiveness of the tumor. In addition, newer studies showed that certain gene expression patterns are associated with malignant behaviour of canine mammary tumors.
Surgical removal is the treatment of choice, but chest x-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s should be taken first to rule out metastasis. Removal should be with wide margins to prevent recurrence, taking the whole mammary gland if necessary. Because 40 to 50 percent of dog mammary tumors have estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptor refers to a group of receptors that are activated by the hormone 17β-estradiol . Two types of estrogen receptor exist: ER, which is a member of the nuclear hormone family of intracellular receptors, and the estrogen G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 , which is a G protein-coupled...
s, spaying is recommended by many veterinarian
Veterinarian
A veterinary physician, colloquially called a vet, shortened from veterinarian or veterinary surgeon , is a professional who treats disease, disorder and injury in animals....
s. A recent study showed a better prognosis in dogs that are spayed at the time of surgery or that had been recently spayed. However, several other studies found no improvement of disease outcome when spaying was performed after the tumor had developed. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
is rarely used.
Breeds at increased risk
- PoodlePoodleThe Poodle is a breed of dog. The poodle breed is found officially in toy, miniature, and standard sizes, with many coat colors. Originally bred as a type of water dog, the poodle is highly intelligent and skillful in many dog sports, including agility, obedience, tracking, and even herding...
- Brittany Spaniel
- English SetterEnglish SetterThe English Setter is a breed of dog. It is part of the Setter family, which includes red Irish Setters, Irish Red and White Setters, and black-and-tan Gordon Setters. It is a gun dog, bred for a mix of endurance and athleticism.- Appearance :...
- Pointer
- Fox TerrierFox TerrierFox Terrier refers primarily to two different breeds of the terrier dog type: the Smooth Fox Terrier and the Wire Fox Terrier. Both of these breeds originated in the 19th century from a handful of dogs who are descended from earlier varieties of British terriers, and are related to other modern...
- Boston TerrierBoston TerrierThe Boston Terrier is a breed of dog originating in the United States of America. This "American Gentleman" was accepted in 1893 by the American Kennel Club as a non-sporting breed. Color and markings are important when distinguishing this breed to the AKC standard. They should be either black,...
- Cocker Spaniel
- lhasa apsoLhasa ApsoThe Lhasa Apso is a non-sporting dog breed originating in Tibet. It was bred as an interior sentinel in the Buddhist monasteries, who alerted the monks to any intruders who entered...
Mammary tumors in cats
Mammary tumors are the third most common neoplasia in cats, following lymphoid and skin cancers. The incidence of mammary tumors in cats is reduced by 91 percent in cats spayed prior to six months of age and by 86 percent in cats spayed prior to one year, according to one study. Siamese cats and Japanese breeds seem to have increased risk, and obesity also appears to be a factor in tumor development. Malignant tumors make up 80 to 96 percent of mammary tumors in cats, almost all adenocarcinomas. Male cats may also develop mammary adenocarcinoma, albeit rarely, and the clinical course is similar to female cats. As in dogs, tumor size is an important prognostic factor, although for tumors less than three centimeters the individual size is less predictive. According to one study, cats with tumors less than three cm had an average survival time of 21 months, and cats with tumors greater than three cm had an average survival of 12 months. About 10 percent of cat mammary tumors have estrogen receptors, so spaying at the time of surgery has little effect on recurrence or survival time. Metastasis tends to be to the lungs and lymph nodes, and rarely to bone. Diagnosis and treatment is similar to the dog. There is a better prognosis with bilateral radical surgery (removing the both mammary chains) than with more conservative surgery. DoxorubicinDoxorubicin
Doxorubicin INN is a drug used in cancer chemotherapy. It is an anthracycline antibiotic, closely related to the natural product daunomycin, and like all anthracyclines, it works by intercalating DNA....
has shown some promise in treatment.
Mammary tumors in ferrets
Mammary tumors are rare in ferretFerret
The ferret is a domesticated mammal of the type Mustela putorius furo. Ferrets are sexually dimorphic predators with males being substantially larger than females. They typically have brown, black, white, or mixed fur...
s. Appearance tends to be a soft, dark colored lump. Most seem to be benign and occur most frequently in neutered males. Surgery is recommended.
Mammary tumors in guinea pigs
Mammary tumors in guinea pigGuinea pig
The guinea pig , also called the cavy, is a species of rodent belonging to the family Caviidae and the genus Cavia. Despite their common name, these animals are not in the pig family, nor are they from Guinea...
s occur in males and females. Most are benign, but 30 percent are adenocarcinomas. They usually do not metastasize, but aggressive surgery is necessary to prevent recurrence.
Mammary tumors in mice
Most mammary tumors in miceMouse
A mouse is a small mammal belonging to the order of rodents. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse . It is also a popular pet. In some places, certain kinds of field mice are also common. This rodent is eaten by large birds such as hawks and eagles...
are adenocarcinomas. They can be caused by viral infection. Recurrence rates are high, and therefore there is a poor prognosis. There is frequently local tissue invasion and metastasis to the lungs. A well known tumor virus of the mouse is the mouse mammary tumor virus MMTV, which may be the most common cause of this tumor in mice.
Mammary tumors in rats
Most mammary tumors in ratRat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents of the superfamily Muroidea. "True rats" are members of the genus Rattus, the most important of which to humans are the black rat, Rattus rattus, and the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus...
s are benign fibroadenomas, which are also the most common tumor in the rat. Less than 10 percent are adenocarcinomas. They occur in male and female rats. The tumors can be large and occur anywhere on the trunk. There is a good prognosis with surgery. Spayed rats have a decreased risk of developing mammary tumors.
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
University of Wisconsin–Madison
The University of Wisconsin–Madison is a public research university located in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1848, UW–Madison is the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. It became a land-grant institution in 1866...
have found that lavender oil
Lavender oil
Lavender oil is an essential oil obtained by distillation from the flower spikes of certain species of lavender. Two forms are distinguished, lavender flower oil, a colorless oil, insoluble in water, having a density of 0.885 g/mL; and lavender spike oil, a distillate from the herb Lavandula...
may have played a role in the reduction of advanced mammary tumors in lab rats. Research is on-going for potential breast
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
, ovarian
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
, pancreatic
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
, liver
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. Most cases of HCC are secondary to either a viral hepatitide infection or cirrhosis .Compared to other cancers, HCC is quite a rare tumor in the United States...
, and prostate
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
cancer treatments in humans.
Mammary tumors in hamsters and gerbils
Mammary tumors tend to be benign in hamsterHamster
Hamsters are rodents belonging to the subfamily Cricetinae. The subfamily contains about 25 species, classified in six or seven genera....
s and malignant in gerbil
Gerbil
A gerbil is a small mammal of the order Rodentia. Once known simply as "desert rats", the gerbil subfamily includes about 110 species of African, Indian, and Asian rodents, including sand rats and jirds, all of which are adapted to arid habitats...
s.
Mammary tumors in hedgehogs
Mammary gland adenocarcinoma is the most common tumor of the hedgehogHedgehog
A hedgehog is any of the spiny mammals of the subfamily Erinaceinae and the order Erinaceomorpha. There are 17 species of hedgehog in five genera, found through parts of Europe, Asia, Africa, and New Zealand . There are no hedgehogs native to Australia, and no living species native to the Americas...
.

