
Maui Nui
Encyclopedia
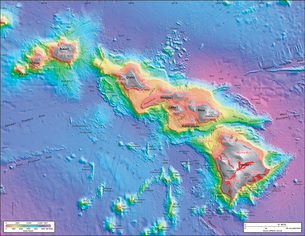
Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
built from seven shield volcano
Shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from more explosive volcanoes...
es. Nui means "great/large" in the Hawaiian language
Hawaiian language
The Hawaiian language is a Polynesian language that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the state of Hawaii...
.
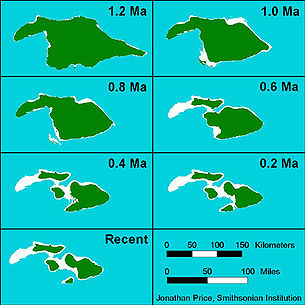
1.2 million years ago, Maui Nui was 14600 square kilometres (5,637.1 sq mi), 50% larger than the present-day island of Hawaii
Hawaii (island)
The Island of Hawaii, also called the Big Island or Hawaii Island , is a volcanic island in the North Pacific Ocean...
. Sea levels were lower than today's due to distant glaciation locking up the Earth's water during ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
s, thus exposing more land. As the volcanoes slowly settled by subsidence due to the weight of the shield volcanoes and erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
, the saddles between them slowly flooded, forming four separate islands: Maui
Maui
The island of Maui is the second-largest of the Hawaiian Islands at and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is part of the state of Hawaii and is the largest of Maui County's four islands, bigger than Lānai, Kahoolawe, and Molokai. In 2010, Maui had a population of 144,444,...
, Molokai
Molokai
Molokai or Molokai is an island in the Hawaiian archipelago. It is 38 by 10 miles in size with a land area of , making it the fifth largest of the main Hawaiian Islands and the 27th largest island in the United States. It lies east of Oahu across the 25-mile wide Kaiwi Channel and north of...
, Lānai
Lanai
Lānai or Lanai is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is also known as the Pineapple Island because of its past as an island-wide pineapple plantation. The only town is Lānai City, a small settlement....
and Kahoolawe
Kahoolawe
Kahoolawe is the smallest of the eight main volcanic islands in the Hawaiian Islands. Kahoolawe is located about seven miles southwest of Maui and also southeast of Lanai, and it is long by wide, with a total land area of . The highest point on Kahoolawe is the crater of Lua Makika at the...
by about 200,000 years ago. Another former volcanic island lying west of Molokai was completely submerged and covered with a cap of coral
Coral
Corals are marine animals in class Anthozoa of phylum Cnidaria typically living in compact colonies of many identical individual "polyps". The group includes the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.A coral "head" is a colony of...
; it is now known as Penguin Bank
Penguin Bank
Penguin Bank is the name given to a now-submerged shield volcano of the Hawaiian Islands. Its coral-capped remains lay west of the island of Molokai under relatively shallow water...
.
The sea floor between these four islands is relatively shallow, about 500 metres (1,640.4 ft) deep, and all of the islands except Kahoolawe were joined during the low sea levels of the last glacial maximum
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
, about 20,000 years ago. But at the outer edges of former Maui Nui, as with the edges of all Hawaiian Islands, the floor plummets to the abyssal ocean floor
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 metres. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest...
of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. The steep slopes can result in massive landslide
Landslide
A landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rockfalls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments...
s due to flank collapse, including one which removed most of the northern half of East Molokai.
Administratively, the current islands remaining from Maui Nui comprise Maui County
Maui County, Hawaii
-National protected areas:* Haleakala National Park* Kakahaia National Wildlife Refuge* Kealia Pond National Wildlife Refuge- Demographics :As of the 2000 Census, there were 128,094 people, 43,507 households, and 29,889 families residing in the county. The population density was 110 people per...
(with the minor exception of a tiny part of Molokai which comprises Kalawao County
Kalawao County, Hawaii
-Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 147 people, 115 households, and 21 families residing in the county. The population density was 11 people per square mile . There were 172 housing units at an average density of 13 per square mile...
).

