Maurice Princet
Encyclopedia
Maurice Princet was a French
mathematician
and actuary
who played a role in the birth of cubism
. He was an associate of Pablo Picasso
, Guillaume Apollinaire
, Max Jacob
, Jean Metzinger
, and Marcel Duchamp
. He is known as "le mathématicien du cubisme" ("the mathematician of cubism").
 Princet is credited with introducing the work of Henri Poincaré
Princet is credited with introducing the work of Henri Poincaré
and the concept of the "fourth dimension" to the cubists at the Bateau-Lavoir
. Princet brought to Picasso's attention a book by Esprit Jouffret
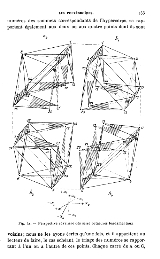
, Traité élémentaire de géométrie à quatre dimensions (Elementary Treatise on the Geometry of Four Dimensions, 1903), a popularization of Poincaré's Science and Hypothesis in which Jouffret described hypercube
s and other complex polyhedra
in four dimension
s and projected them onto the two-dimensional page. Picasso's sketchbooks for Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
illustrate Jouffret's influence on the artist's work.
In 1907, Princet's wife left him for André Derain
, and he drifted away from the circle of artists at the Bateau-Lavoir. But Princet remained close to Metzinger and participated in meetings of the Section d'Or
in Puteaux
. He gave informal lectures to the group, many of whom were passionate about mathematical order.
Princet's influence on the cubists was attested to by his contemporaries. Maurice Vlaminck
wrote, "I witnessed the birth of cubism, its growth, its decline. Picasso was the obstetrician, Guillaume Apollinaire the midwife, Princet the godfather."
In 1910, Metzinger said of him, "[Picasso] lays out a free, mobile perspective, from which that ingenious mathematician Maurice Princet has deduced a whole geometry". Later, Metzinger wrote in his memoirs that:
Louis Vauxcelles
sarcastically dubbed Princet "the father of cubism":
Duchamp told Pierre Cabanne, "We weren't mathematicians at all, but we really did believe in Princet".
French people
The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
and actuary
Actuary
An actuary is a business professional who deals with the financial impact of risk and uncertainty. Actuaries provide expert assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms ....
who played a role in the birth of cubism
Cubism
Cubism was a 20th century avant-garde art movement, pioneered by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture...
. He was an associate of Pablo Picasso
Pablo Picasso
Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso known as Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish expatriate painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and stage designer, one of the greatest and most influential artists of the...
, Guillaume Apollinaire
Guillaume Apollinaire
Wilhelm Albert Włodzimierz Apolinary Kostrowicki, known as Guillaume Apollinaire was a French poet, playwright, short story writer, novelist, and art critic born in Italy to a Polish mother....
, Max Jacob
Max Jacob
Max Jacob was a French poet, painter, writer, and critic.-Life and career:After spending his childhood in Quimper, Brittany, France, he enrolled in the Paris Colonial School, which he left in 1897 for an artistic career...
, Jean Metzinger
Jean Metzinger
Jean Metzinger was a French painter.Metzinger was born in Nantes, France. Initially he was influenced by Fauvism and Impressionism, but from 1908 he was associated with Cubism. Metzinger was a member of the Section d'Or group of artists...
, and Marcel Duchamp
Marcel Duchamp
Marcel Duchamp was a French artist whose work is most often associated with the Dadaist and Surrealist movements. Considered by some to be one of the most important artists of the 20th century, Duchamp's output influenced the development of post-World War I Western art...
. He is known as "le mathématicien du cubisme" ("the mathematician of cubism").

Henri Poincaré
Jules Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and a philosopher of science...
and the concept of the "fourth dimension" to the cubists at the Bateau-Lavoir
Le Bateau-Lavoir
Le Bateau-Lavoir is a name which French painter Max Jacob coined for an area at the top of the steps leading to No. 13 Rue Ravigan, in Montmartre, Paris . The area is famous in art history because around the start of the 20th century a group of outstanding artists lived and rented artistic studios...
. Princet brought to Picasso's attention a book by Esprit Jouffret
Esprit Jouffret
Esprit Jouffret was a French artillery officer, insurance actuary and mathematician, author of Traité élémentaire de géométrie à quatre dimensions , a popularization of Henri Poincaré's Science and Hypothesis in which Jouffret described hypercubes and other complex polyhedra in four dimensions and...
, Traité élémentaire de géométrie à quatre dimensions (Elementary Treatise on the Geometry of Four Dimensions, 1903), a popularization of Poincaré's Science and Hypothesis in which Jouffret described hypercube
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an n-dimensional analogue of a square and a cube . It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length.An...
s and other complex polyhedra
Polyhedron
In elementary geometry a polyhedron is a geometric solid in three dimensions with flat faces and straight edges...
in four dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
s and projected them onto the two-dimensional page. Picasso's sketchbooks for Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
He followed his success by developing into his Rose period from 1904 to 1907, which introduced a strong element of sensuality and sexuality into his work...
illustrate Jouffret's influence on the artist's work.
In 1907, Princet's wife left him for André Derain
André Derain
André Derain was a French artist, painter, sculptor and co-founder of Fauvism with Henri Matisse.-Early years:...
, and he drifted away from the circle of artists at the Bateau-Lavoir. But Princet remained close to Metzinger and participated in meetings of the Section d'Or
Section d'Or
The Section d'Or , also known as Groupe de Puteaux or Puteaux Group, was a collective of painters and critics associated with an offshoot of Cubism known as Orphism...
in Puteaux
Puteaux
Puteaux is a commune in the western suburbs of Paris, France. It is located in the heart of the Hauts-de-Seine department from the center of Paris....
. He gave informal lectures to the group, many of whom were passionate about mathematical order.
Princet's influence on the cubists was attested to by his contemporaries. Maurice Vlaminck
Maurice de Vlaminck
Maurice de Vlaminck was a French painter. Along with André Derain and Henri Matisse he is considered one of the principal figures in the Fauve movement, a group of modern artists who from 1904 to 1908 were united in their use of intense color.-Life:Maurice de Vlaminck was born in Paris to a family...
wrote, "I witnessed the birth of cubism, its growth, its decline. Picasso was the obstetrician, Guillaume Apollinaire the midwife, Princet the godfather."
In 1910, Metzinger said of him, "[Picasso] lays out a free, mobile perspective, from which that ingenious mathematician Maurice Princet has deduced a whole geometry". Later, Metzinger wrote in his memoirs that:
Maurice Princet joined us often. Although quite young, thanks to his knowledge of mathematics he had an important job in an insurance company. But, beyond his profession, it was as an artist that he conceptualized mathematics, as an aesthetician that he invoked n-dimensional continuums. He loved to get the artists interested in the new views on space that had been opened up by Schlegel and some others. He succeeded at that.
Louis Vauxcelles
Louis Vauxcelles
Louis Vauxcelles was an influential French art critic. He is credited with coining the terms Fauvism , and Cubism ....
sarcastically dubbed Princet "the father of cubism":
M. Princet has studied at length non-Euclidean geometry and the theorems of Riemann, of which Gleizes and Metzinger speak rather carelessly. Now then, M. Princet one day met M. Max Jacob and confided him one or two of his discoveries relating to the fourth dimension. M. Jacob informed the ingenious M. Picasso of it, and M. Picasso saw there a possibility of new ornamental schemes. M. Picasso explained his intentions to M. Apollinaire, who hastened to write them up in formularies and codify them. The thing spread and propagated. Cubism, the child of M. Princet, was born.
Duchamp told Pierre Cabanne, "We weren't mathematicians at all, but we really did believe in Princet".

