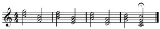
Mediant
Encyclopedia
In music
, the mediant (Latin: to be in the middle) is the third scale degree
of the diatonic scale
, being the note halfway between the tonic
and the dominant
. Similarly, the submediant
is halfway between the tonic and subdominant
. The fifth note is almost always a perfect fifth, while the third note can equally be a minor or major third.
In Roman numeral analysis
, the mediant chord can take several forms. In major scale
s, the mediant chord is minor and is noted with the Roman numeral iii. In a natural minor scale, the mediant occurs as a major chord
, noted with the Roman numeral III. In harmonic minor scales and ascending melodic minor scales, the seventh scale degree is raised by a half-step from a subtonic
to a leading tone, creating an augmented mediant chord, noted with the Roman numeral III+.
For example, in the C major scale
(white keys on a piano, starting on C), the mediant is the note E; and the mediant chord
is E-minor consisting of the notes E, G, and B. Therefore, Em is the iii chord in the C major scale. Also, in the A natural minor scale
(same white keys, but now starting on A), the mediant is the note C; and the mediant chord is C (or C-major) consisting of the notes C, E, and G. Therefore, C is the III chord in the A (natural) minor scale. However, if the harmonic minor scale is used, G would be raised to G, changing the C chord to Caug, consisting of the notes C, E, and G. Therefore, Caug is the III+ chord in the A harmonic minor scale.
"Mediant" also refers to a relationship of musical keys
. For example, relative to the key of A (natural) minor, the key of C major is the mediant, and often serves as a mid-way point between I and V (hence the name). Tonicization
or modulation
to the mediant is quite common in pieces written in the minor mode, and usually serves as the second theme group in sonata form
s, since it is very easy to tonicize III in minor (no need to alternate notes). Tonicization of III in major is quite rare in classical harmony, compared with, say, modulation to the V
in major, but mediant tonicization in major is an important feature of late romantic music
.
In German theory derived from Hugo Riemann
the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel
, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel
, tP.
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, the mediant (Latin: to be in the middle) is the third scale degree
Degree (music)
In music theory, a scale degree or scale step is the name of a particular note of a scale in relation to the tonic...
of the diatonic scale
Diatonic scale
In music theory, a diatonic scale is a seven note, octave-repeating musical scale comprising five whole steps and two half steps for each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps...
, being the note halfway between the tonic
Tonic (music)
In music, the tonic is the first scale degree of the diatonic scale and the tonal center or final resolution tone. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord...
and the dominant
Dominant (music)
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree of the diatonic scale, called "dominant" because it is next in importance to the tonic,and a dominant chord is any chord built upon that pitch, using the notes of the same diatonic scale...
. Similarly, the submediant
Submediant
In music, the submediant is the sixth scale degree of the diatonic scale, the 'lower mediant' halfway between the tonic and the subdominant or 'lower dominant'...
is halfway between the tonic and subdominant
Subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the technical name for the fourth tonal degree of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance "below" the tonic as the dominant is above the tonic - in other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdominant. It is also the note immediately...
. The fifth note is almost always a perfect fifth, while the third note can equally be a minor or major third.
In Roman numeral analysis
Roman numeral analysis
In music, roman numeral analysis is the use of roman numeral symbols in the musical analysis of chords. In music theory related to or derived from the common practice period, arabic numerals with carets are used to designate scale degrees themselves , whereas in theory related to or derived from...
, the mediant chord can take several forms. In major scale
Major scale
In music theory, the major scale or Ionian scale is one of the diatonic scales. It is made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth which duplicates the first an octave higher. In solfege these notes correspond to the syllables "Do, Re, Mi, Fa, Sol, La, Ti/Si, ", the "Do" in the parenthesis at...
s, the mediant chord is minor and is noted with the Roman numeral iii. In a natural minor scale, the mediant occurs as a major chord
Major chord
In music theory, a major chord is a chord having a root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord has these three notes alone, it is called a major triad...
, noted with the Roman numeral III. In harmonic minor scales and ascending melodic minor scales, the seventh scale degree is raised by a half-step from a subtonic
Subtonic
In music, the subtonic or flattened seventh is the lowered or minor seventh degree of the scale, a whole step below the tonic, as opposed to the leading tone...
to a leading tone, creating an augmented mediant chord, noted with the Roman numeral III+.
For example, in the C major scale
Major scale
In music theory, the major scale or Ionian scale is one of the diatonic scales. It is made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth which duplicates the first an octave higher. In solfege these notes correspond to the syllables "Do, Re, Mi, Fa, Sol, La, Ti/Si, ", the "Do" in the parenthesis at...
(white keys on a piano, starting on C), the mediant is the note E; and the mediant chord
Chord (music)
A chord in music is any harmonic set of two–three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may for many practical and theoretical purposes be understood as chords...
is E-minor consisting of the notes E, G, and B. Therefore, Em is the iii chord in the C major scale. Also, in the A natural minor scale
Minor scale
A minor scale in Western music theory includes any scale that contains, in its tonic triad, at least three essential scale degrees: 1) the tonic , 2) a minor-third, or an interval of a minor third above the tonic, and 3) a perfect-fifth, or an interval of a perfect fifth above the tonic, altogether...
(same white keys, but now starting on A), the mediant is the note C; and the mediant chord is C (or C-major) consisting of the notes C, E, and G. Therefore, C is the III chord in the A (natural) minor scale. However, if the harmonic minor scale is used, G would be raised to G, changing the C chord to Caug, consisting of the notes C, E, and G. Therefore, Caug is the III+ chord in the A harmonic minor scale.
"Mediant" also refers to a relationship of musical keys
Key (music)
In music theory, the term key is used in many different and sometimes contradictory ways. A common use is to speak of music as being "in" a specific key, such as in the key of C major or in the key of F-sharp. Sometimes the terms "major" or "minor" are appended, as in the key of A minor or in the...
. For example, relative to the key of A (natural) minor, the key of C major is the mediant, and often serves as a mid-way point between I and V (hence the name). Tonicization
Tonicization
In music, tonicization is the treatment of a pitch other than the overall tonic as a temporary tonic in a composition. Tonicization is achieved through the use of the scale and harmonies of the tonicized key. The most common method of tonicization uses leading tones, dominant-tonic chord...
or modulation
Modulation (music)
In music, modulation is most commonly the act or process of changing from one key to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature. Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest...
to the mediant is quite common in pieces written in the minor mode, and usually serves as the second theme group in sonata form
Sonata form
Sonata form is a large-scale musical structure used widely since the middle of the 18th century . While it is typically used in the first movement of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement...
s, since it is very easy to tonicize III in minor (no need to alternate notes). Tonicization of III in major is quite rare in classical harmony, compared with, say, modulation to the V
Dominant (music)
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree of the diatonic scale, called "dominant" because it is next in importance to the tonic,and a dominant chord is any chord built upon that pitch, using the notes of the same diatonic scale...
in major, but mediant tonicization in major is an important feature of late romantic music
Romantic music
Romantic music or music in the Romantic Period is a musicological and artistic term referring to a particular period, theory, compositional practice, and canon in Western music history, from 1810 to 1900....
.
In German theory derived from Hugo Riemann
Hugo Riemann
Karl Wilhelm Julius Hugo Riemann was a German music theorist.-Biography:Riemann was born at Grossmehlra, Schwarzburg-Sondershausen. He was educated in theory by Frankenberger, studied the piano with Barthel and Ratzenberger, studied law, and finally philosophy and history at Berlin and Tübingen...
the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel
Dominant parallel
In music theory, the dominant parallel is terminology used in German theory derived mainly from Hugo Riemann. The dominant parallel is abbreviated Dp, in major, and dP, in minor, where a capital letter denotes a major chord and a lowercase letter denotes a minor chord...
, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel
Tonic parallel
In music theory, the tonic parallel is a diatonic function and chord, relative to the tonic, and thus considered to have or fulfill the function of the tonic. The term is used in German theory and derives from the work of Hugo Riemann. It is abbreviated "Tp" in major and "tP" in minor.In C major:*...
, tP.

