
Megaspore
Encyclopedia
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s. These types of plants have two spore types, megaspores and microspore
Microspore
In biology, a microspore is a small spore as contrasted to the larger megaspore.In botany, microspores develop into male gametophytes, whereas megaspores develop into female gametophytes. The combination of megaspores and microspores is found only in heterosporous organisms...
s. Generally speaking, the megaspore, or large spore, germinates into a female (egg-producing) gametophyte, which is fertilized by sperm produced by the male gametophyte developing from the microspore. Plants which are known to do this include those in the following genera:
- Selaginella: the spikemosses, included within the lycopod, or clubmoss group
- MarsileaceaeMarsileaceaeThe Marsileaceae are a small family of heterosporous aquatic and semi-aquatic ferns, though at first sight they do not physically resemble other ferns. The group is commonly known as the "pepperwort family" or as the "water-clover family" because the leaves of the genus Marsilea superficially...
: the water-clovers, MarsileaMarsileaMarsilea is a genus of approximately 65 species of aquatic ferns of the family Marsileaceae.These small plants are of unusual appearance and do not resemble common ferns...
, PilulariaPilulariaPilularia is a genus of unusual ferns of family Marsileaceae distributed in North Temperate regions, Ethiopian mountains, and the southern hemisphere in Australia, New Zealand, and western South America....
, and RegnellidiumRegnellidiumRegnellidium is a monotypic genus of ferns of family Marsileaceae.The single living species, Regnellidium diphyllum, Two-leaf Water Fern, is native to South Eastern Brazil and adjacent regions of Argentina. It resembles its relatives from the genus Marsilea, but has 2-lobed leaves . This fern is... - Azolla: in the Azollaceae, within the fernFernA fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s - SalviniaSalviniaSalvinia, a genus in the family Salviniaceae, is a floating fern named in honor of Antonio Maria Salvini, a 17th Century Italian scientist. The genus was published by Séguier, in Pl. Veron. 3: 52. 1754. About ten species exist....
: in the SalviniaceaeSalviniaceaeSalviniaceae , is a family of ferns....
, within the fernFernA fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s - gymnospermGymnospermThe gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s and flowering plantFlowering plantThe flowering plants , also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies...
s
Megasporogenesis
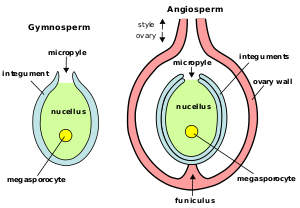
In gymnosperms and flowering plants, the megaspore is produced inside the nucellus or embryo sac of the ovuleOvule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
. During megasporogenesis, a diploid precursor cell, the megasporocyte or megaspore mother cell, undergoes meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
to produce initially four haploid cells (the megaspores). Angiosperms exhibit three patterns of megasporogenesis: monosporic, bisporic, and tetrasporic, also known as the Polygonum type, the Alisma type, and the Drusa type, respectively. The monosporic pattern occurs most frequently (>70% of angiosperms) and is found in many economically and biologically important groups such as Brassicaceae (e.g., Arabidopsis, Capsella, Brassica), Gramineae (e.g., maize, rice, wheat), Malvaceae (e.g., cotton), Leguminoseae (e.g., beans, soybean), and Solanaceae (e.g., pepper, tobacco, tomato, potato, petunia).
This pattern is characterized by cell plate formation after meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
1 & 2, which results in four one-nucleate megaspores, of which three degenerate. The bisporic pattern is characterized by cell plate formation only after meiosis 1, and results in two two-nucleate megaspores, of which one degenerates. The tetrasporic pattern is characterized by cell plates failing to form after either meiosis 1 or 2, and results in one four-nucleate megaspore. Therefore, each pattern gives rise to a single functional megaspore which contains one, two, or four meiotic nuclei, respectively. The megaspore then undergoes megagametogenesis to give rise to the female gametophyte
Gametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
.
Megagametogenesis
After megasporogenesis, the megaspore develops into the female gametophyteGametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
(the embryo sac) in a process called megagametogenesis. The process of megagametogenesis varies depending on which pattern of megasporogenesis occurred. Some species, such as Tridax trilobata, Ehretia laevis, and Alectra thomsoni, can undergo different patterns of megasporogenesis and therefore different patterns of megagametogenesis.
If the monosporic pattern occurred, the single nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
undergoes mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
three times, producing an eight-nucleate cell. These eight nuclei are arranged into two groups of four. These groups both send a nucleus to the center of the cell; these become the polar nuclei. Depending on the species, these nuclei fuse together before or upon fertilization of the central cell. The three nuclei at the end of the cell near the micropylar become the egg apparatus, with an egg cell in the center and two synergids. At the other end of the cell, a cell wall forms around the nuclei and forms the antipodals. Therefore the resulting embryo sac is a seven-celled structure consisting of one central cell, one egg cell, two synergid cells, and three antipodal cells.
The bisporic and tetrasporic patterns undergo varying processes and result in varying embryo sacs as well. In Lilium which has a tetrasporic pattern, the central cell of the embryo sac is 4N. Therefore, upon fertilization the endosperm will be 5N rather than the typical 3N.

