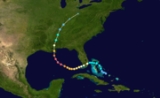
Meteorological history of Hurricane Katrina
Encyclopedia
The meteorological history of Hurricane Katrina
, an extremely destructive Category 5
hurricane
, began on August 23, 2005 when it originated as Tropical Depression Twelve near the Bahamas. The next day, the tropical depression strengthened to a tropical storm, and was named Katrina; it proceeded to make landfall
on the southern tip of the U.S. state
of Florida
as a minimal hurricane.
In passing across Florida, Katrina
weakened to a tropical storm; however, the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico
allowed it to rapidly intensify
to the sixth strongest Atlantic hurricane in recorded history. Afterward, Katrina made landfall as a Category 3 storm near Buras-Triumph, Louisiana
, and once more near the Mississippi
/Louisiana
border. Katrina progressed northward through the central United States and finally dissipated near the Great Lakes
, when it was absorbed by a cold front
.
(2100 UTC
) on August 23, 2005, partially from the remains of Tropical Depression Ten
, which had dissipated due to the effects of a nearby upper tropospheric
trough
. While the normal standards for numbering tropical depressions in the Atlantic
indicate that the old name/number is retained when a depression dissipates and regenerates, satellite data indicated that a second tropical wave
combined with Tropical Depression Ten north of Puerto Rico
to form a new, much more advanced system, which was then designated as Tropical Depression Twelve. Simultaneously, the trough in the upper troposphere weakened, causing the wind shear
in the area to relax, thereby allowing the new tropical depression to develop. In a later re-analysis, it was determined that the low-level circulation of Ten had completely detached and dissipated, with only the remnant mid-level circulation moving on and merging with the aforementioned second tropical wave. As a result, the criteria for keeping the same name and identity were not met.
 As the atmospheric conditions surrounding Tropical Depression Twelve were favorable for tropical development
As the atmospheric conditions surrounding Tropical Depression Twelve were favorable for tropical development
, the system began to intensify and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Katrina on the morning of August 24. A burst of convection
allowed Katrina to become the fifth hurricane of the 2005 season on August 25, only two hours before it made landfall around 6:30 p.m. EST
(2230 UTC) between Hallandale Beach
and Aventura
, Florida
. Katrina struck the peninsula with 80 mph (130 km/h) winds, and had a well-defined eye
on NEXRAD
weather radar
, which remained intact throughout its passage over Florida. The storm weakened over land on August 26 to a tropical storm, but regained strength to hurricane status at 2:00 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC), approximately one hour after ending its passage through Florida and entering the Gulf of Mexico
. Parts of the Florida Keys
experienced tropical storm winds throughout August 26, with the Dry Tortugas
briefly experiencing hurricane-force winds.
forecasts predicted that Katrina would begin turning northward after landfall, eventually to hit the Florida Panhandle
approximately three to four days later. Katrina, however, continued a westerly and west-southwesterly track, which eventually shifted the forecast track westward to New Orleans.
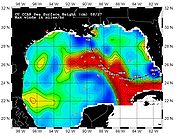 Immediately after the storm entered the Gulf of Mexico, the low wind shear
Immediately after the storm entered the Gulf of Mexico, the low wind shear
, good upper-level outflow, and the warm sea surface temperatures of the Gulf Loop Current
caused Katrina to intensify rapidly
. On August 27, the storm was upgraded to Category 3 intensity, becoming the third major hurricane of the season. An eyewall replacement cycle
disrupted the intensification of maximum winds for about 18 hours, but almost doubled the radius of the storm. A second period of rapid intensification started by 7:00 p.m. CDT on August 27, and by 12:40 a.m. CDT on August 28, Katrina was upgraded to a Category 4 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 145 mph (233 km/h). It became a Category 5 (the first in the Gulf of Mexico since Hurricane Allen
25 years prior) storm by 7:00 a.m. CDT, twelve hours after the beginning of the second round of rapid intensification, and reached its peak intensity at 1:00 p.m. CDT with maximum sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h), gusts of 215 mph (344 km/h) and a central pressure of 902 mbar (26.64 inHg). The minimum pressure made Katrina, at the time, the fourth most intense Atlantic hurricane on record (Hurricanes Rita
and Wilma
would later surpass Katrina that same year). As the hurricane approached New Orleans, the Weather Forecast Office in Slidell, Louisiana issued two strongly worded warnings
of the storm's danger.
By the afternoon of August 28, the storm was large enough that some areas of the Gulf Coast were already experiencing tropical storm-force winds. The center of Katrina was about 180 statute miles (290 km) from the mouth of the Mississippi River
, but tropical storm-force winds extended 230 mi (370 km) from the center of the storm, and hurricane-force winds extended about 105 miles (170 km) away. Overnight on August 29, and into the morning of the next day, Katrina quickly weakened (in terms of maximum sustained winds) as it began to enter another eyewall replacement cycle. The inner eyewall deteriorated before an outer eyewall had fully formed, playing an important role in the weakening. In 18 hours, the hurricane's maximum sustained winds decreased from 170 mph (280 km/h) to 125 mph (205 km/h). However, storm surge remained high at landfall because large waves greater than 30 feet (9.1 m) in height were generated beforehand (with a buoy
recording a 55 ft/16.7 m wave at sea), when Katrina was at Categories 4 and 5 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
. The waves then combined with the storm surge of the large Category 3 hurricane.
. Because Katrina had just weakened from Category 4 and due to the shape of the coastline, sustained Category 4 winds likely existed on land while the eye was over water. At landfall, hurricane-force winds extended 120 miles (190 km) from the center, the storm's pressure was 920 mbar (27.17 inHg), and its forward speed was 15 mph (24 km/h). As it made its way up the eastern Louisiana coastline, most communities in Plaquemines, St. Bernard Parish, and Slidell
in St. Tammany Parish were severely damaged by storm surge and the strong winds of the eyewall, which also grazed eastern New Orleans, causing in excess of $1 billion worth of damage to the city (see Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans
).
Original estimates indicated that Katrina had made this landfall as a Category 4 hurricane, with 135 mph (220 km/h) winds; however, as indicated above, the storm weakened just before landfall to Category 3 intensity. The reasons for this weakening are not completely known yet; while the eye-wall replacement cycle played a part, slightly increasing shear
, dropping sea-surface temperatures, dry air on the western semicircle
of the storm and interaction with the continental landmass also may have played a role in weakening the cyclone. This follows the trend of previous strong cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico
: all cyclones with minimum central pressures
of 973 mbar (28.73 inHg) or less have weakened over the 12 hours before making landfall
in the Gulf Coast of the United States
.
A few hours later, after weakening slightly, Katrina made its third landfall near the Louisiana–Mississippi border with 120 mph (195 km/h) sustained winds and 928 mbar (27.37 inHg) pressure, still at Category 3 intensity. Its minimum pressure at its second landfall was 920 mbar (27.17 inHg), making Katrina the third strongest hurricane on record to make landfall on the United States, behind Hurricane Camille
's 909 mbar (26.85 inHg) reading in 1969, and the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane's 892 mbar (26.35 inHg) record.
 Because the storm was so large, highly destructive eye-wall winds and the strong northeastern quadrant of the storm pushed record storm surge
Because the storm was so large, highly destructive eye-wall winds and the strong northeastern quadrant of the storm pushed record storm surge
s onshore, smashing the entire Mississippi Gulf Coast, including towns in Mississippi such as Waveland
, Bay St. Louis
, Pass Christian
, Long Beach
, Gulfport
, Biloxi
, Ocean Springs
, Gautier
and Pascagoula
, and, in Alabama, Bayou La Batre
. The surges peaked at 28 feet (8.5 m) in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi
, and at 13 feet (4.0 m) as far away as Mobile, Alabama
, which saw its highest storm surge since 1917. Storm surge was particularly high due to the hydrology
of the region, the hurricane's extreme size, and the fact that it weakened only shortly before landfall. As Katrina moved inland diagonally over Mississippi, high winds cut a swath of damage that affected almost the entire state.
 Katrina maintained hurricane strength well into Mississippi
Katrina maintained hurricane strength well into Mississippi
, but weakened thereafter, losing hurricane strength more than 150 miles (240 km) inland, near Meridian, Mississippi
. It was downgraded to a tropical depression near Clarksville, Tennessee
and broke in half. One half continued to race northward, affecting the Central United States
along its path, and was last distinguishable in the eastern Great Lakes
region on August 31. On August 31, Katrina was absorbed by a frontal boundary and became a powerful extratropical low, causing 1.97–6.69 inches (50–170 mm) of rain in 12 hours, as well as gale-force wind gusts from 31 to 61 mph (50 to 98 km/h) in southeastern Quebec
and northern New Brunswick
. In the region of Saguenay
and Côte-Nord
, rain caused breakdowns and failure in roads. The Côte-Nord region was isolated from the rest of Quebec for at least 1 week. The other half of Katrina broke off in the eastern part of the Appalachians, primarily leading to a significant tornado outbreak
in the area from central Georgia
to central Pennsylvania
, killing two people and causing millions of dollars in additional damage.
At 11:00 p.m. EDT on August 31, the center of the remnant low of what was Katrina had been completely absorbed by a frontal boundary in southeastern Canada, with no discernible circulation.
Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a powerful Atlantic hurricane. It is the costliest natural disaster, as well as one of the five deadliest hurricanes, in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall...
, an extremely destructive Category 5
Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
The Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale , or the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale , classifies hurricanes — Western Hemisphere tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms — into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds...
hurricane
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
, began on August 23, 2005 when it originated as Tropical Depression Twelve near the Bahamas. The next day, the tropical depression strengthened to a tropical storm, and was named Katrina; it proceeded to make landfall
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
on the southern tip of the U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
as a minimal hurricane.
In passing across Florida, Katrina
Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a powerful Atlantic hurricane. It is the costliest natural disaster, as well as one of the five deadliest hurricanes, in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall...
weakened to a tropical storm; however, the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
allowed it to rapidly intensify
Rapid deepening
Rapid deepening, also known as rapid intensification, is a meteorological condition that occurs when the minimum sea-level atmospheric pressure of a tropical cyclone decreases drastically in a short period of time. The National Weather Service describes rapid deepening as a decrease of...
to the sixth strongest Atlantic hurricane in recorded history. Afterward, Katrina made landfall as a Category 3 storm near Buras-Triumph, Louisiana
Buras-Triumph, Louisiana
Buras-Triumph is a census-designated place in Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 3,358 at the 2000 census. On the peninsula, Buras has been located higher, with Triumph located southeast of Buras.-History:...
, and once more near the Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
/Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
border. Katrina progressed northward through the central United States and finally dissipated near the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
, when it was absorbed by a cold front
Cold front
A cold front is defined as the leading edge of a cooler mass of air, replacing a warmer mass of air.-Development of cold front:The cooler and denser air wedges under the less-dense warmer air, lifting it...
.
Formation
Tropical Depression Twelve formed over the southeastern Bahamas at 5:00 p.m. EDTEastern Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone of the United States and Canada is a time zone that falls mostly along the east coast of North America. Its UTC time offset is −5 hrs during standard time and −4 hrs during daylight saving time...
(2100 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
) on August 23, 2005, partially from the remains of Tropical Depression Ten
Tropical Depression Ten (2005)
Tropical Depression Ten was the tenth tropical cyclone of the record-breaking 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. It formed on August 13 from a tropical wave that emerged from the west coast of Africa on August 8. As a result of strong wind shear, the depression remained weak and did not strengthen...
, which had dissipated due to the effects of a nearby upper tropospheric
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 80% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols....
trough
Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts.Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a weather chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked...
. While the normal standards for numbering tropical depressions in the Atlantic
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
indicate that the old name/number is retained when a depression dissipates and regenerates, satellite data indicated that a second tropical wave
Tropical wave
Tropical waves, easterly waves, or tropical easterly waves, also known as African easterly waves in the Atlantic region, are a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which move from east to west across the tropics causing areas of...
combined with Tropical Depression Ten north of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
to form a new, much more advanced system, which was then designated as Tropical Depression Twelve. Simultaneously, the trough in the upper troposphere weakened, causing the wind shear
Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
in the area to relax, thereby allowing the new tropical depression to develop. In a later re-analysis, it was determined that the low-level circulation of Ten had completely detached and dissipated, with only the remnant mid-level circulation moving on and merging with the aforementioned second tropical wave. As a result, the criteria for keeping the same name and identity were not met.
First landfall

Tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the term that describes the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which mid-latitude cyclogenesis occurs...
, the system began to intensify and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Katrina on the morning of August 24. A burst of convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
allowed Katrina to become the fifth hurricane of the 2005 season on August 25, only two hours before it made landfall around 6:30 p.m. EST
North American Eastern Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone of the United States and Canada is a time zone that falls mostly along the east coast of North America. Its UTC time offset is −5 hrs during standard time and −4 hrs during daylight saving time...
(2230 UTC) between Hallandale Beach
Hallandale Beach, Florida
Hallandale Beach is a city in Broward County, Florida, United States. The city is named after Luther Halland, a worker for Henry Flagler's Florida East Coast Railroad. As of the 2010 census, the population was 37,113...
and Aventura
Aventura, Florida
Aventura is a planned, suburban city located in northeastern Miami-Dade County, Florida. The city name is from the Spanish word for "adventure", and was named "Aventura" after one of the developers of the original group of condominiums in the area remarked to the others, "What an adventure this is...
, Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
. Katrina struck the peninsula with 80 mph (130 km/h) winds, and had a well-defined eye
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather found at the center of strong tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area and typically 30–65 km in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, a ring of towering thunderstorms where the second most severe weather of a cyclone...
on NEXRAD
NEXRAD
NEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 159 high-resolution Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service, an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration within the United States Department of Commerce...
weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
, which remained intact throughout its passage over Florida. The storm weakened over land on August 26 to a tropical storm, but regained strength to hurricane status at 2:00 a.m. EDT (0600 UTC), approximately one hour after ending its passage through Florida and entering the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. Parts of the Florida Keys
Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral archipelago in southeast United States. They begin at the southeastern tip of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and extend in a gentle arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry...
experienced tropical storm winds throughout August 26, with the Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas
The Dry Tortugas are a small group of islands, located at the end of the Florida Keys, USA, about west of Key West, and west of the Marquesas Keys, the closest islands. Still further west is the Tortugas Bank, which is completely submerged. The first Europeans to discover the islands were the...
briefly experiencing hurricane-force winds.
Gulf of Mexico
The initial National Hurricane CenterNational Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
forecasts predicted that Katrina would begin turning northward after landfall, eventually to hit the Florida Panhandle
Florida Panhandle
The Florida Panhandle, an informal, unofficial term for the northwestern part of Florida, is a strip of land roughly 200 miles long and 50 to 100 miles wide , lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia also on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is...
approximately three to four days later. Katrina, however, continued a westerly and west-southwesterly track, which eventually shifted the forecast track westward to New Orleans.

Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
, good upper-level outflow, and the warm sea surface temperatures of the Gulf Loop Current
Loop Current
A parent to the Florida Current, the Loop Current is a warm ocean current in the Gulf of Mexico that flows northward between Cuba and the Yucatán peninsula, moves north into the Gulf of Mexico, loops east and south before exiting to the east through the Florida Straits and joining the Gulf Stream.A...
caused Katrina to intensify rapidly
Rapid deepening
Rapid deepening, also known as rapid intensification, is a meteorological condition that occurs when the minimum sea-level atmospheric pressure of a tropical cyclone decreases drastically in a short period of time. The National Weather Service describes rapid deepening as a decrease of...
. On August 27, the storm was upgraded to Category 3 intensity, becoming the third major hurricane of the season. An eyewall replacement cycle
Eyewall replacement cycle
Eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones, generally with winds greater than 185 km/h , or major hurricanes...
disrupted the intensification of maximum winds for about 18 hours, but almost doubled the radius of the storm. A second period of rapid intensification started by 7:00 p.m. CDT on August 27, and by 12:40 a.m. CDT on August 28, Katrina was upgraded to a Category 4 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 145 mph (233 km/h). It became a Category 5 (the first in the Gulf of Mexico since Hurricane Allen
Hurricane Allen
Hurricane Allen was the first and strongest hurricane of the 1980 Atlantic hurricane season. It was one of the strongest hurricanes in recorded history, one of the few hurricanes to reach Category 5 status on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale on three separate occasions, and spent more time...
25 years prior) storm by 7:00 a.m. CDT, twelve hours after the beginning of the second round of rapid intensification, and reached its peak intensity at 1:00 p.m. CDT with maximum sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h), gusts of 215 mph (344 km/h) and a central pressure of 902 mbar (26.64 inHg). The minimum pressure made Katrina, at the time, the fourth most intense Atlantic hurricane on record (Hurricanes Rita
Hurricane Rita
Hurricane Rita was the fourth-most intense Atlantic hurricane ever recorded and the most intense tropical cyclone ever observed in the Gulf of Mexico. Rita caused $11.3 billion in damage on the U.S. Gulf Coast in September 2005...
and Wilma
Hurricane Wilma
Hurricane Wilma was the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Atlantic basin. Wilma was the twenty-second storm , thirteenth hurricane, sixth major hurricane, and fourth Category 5 hurricane of the record-breaking 2005 season...
would later surpass Katrina that same year). As the hurricane approached New Orleans, the Weather Forecast Office in Slidell, Louisiana issued two strongly worded warnings
National Weather Service bulletin for New Orleans region
The National Weather Service bulletin for the New Orleans region of 10:11 a.m., August 28, 2005 was a vividly worded release issued by the local Weather Forecast Office in Slidell, Louisiana, warning of the devastation that the Gulf Coast of the United States could experience as a result of...
of the storm's danger.
By the afternoon of August 28, the storm was large enough that some areas of the Gulf Coast were already experiencing tropical storm-force winds. The center of Katrina was about 180 statute miles (290 km) from the mouth of the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
, but tropical storm-force winds extended 230 mi (370 km) from the center of the storm, and hurricane-force winds extended about 105 miles (170 km) away. Overnight on August 29, and into the morning of the next day, Katrina quickly weakened (in terms of maximum sustained winds) as it began to enter another eyewall replacement cycle. The inner eyewall deteriorated before an outer eyewall had fully formed, playing an important role in the weakening. In 18 hours, the hurricane's maximum sustained winds decreased from 170 mph (280 km/h) to 125 mph (205 km/h). However, storm surge remained high at landfall because large waves greater than 30 feet (9.1 m) in height were generated beforehand (with a buoy
Buoy
A buoy is a floating device that can have many different purposes. It can be anchored or allowed to drift. The word, of Old French or Middle Dutch origin, is now most commonly in UK English, although some orthoepists have traditionally prescribed the pronunciation...
recording a 55 ft/16.7 m wave at sea), when Katrina was at Categories 4 and 5 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale
The Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale , or the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale , classifies hurricanes — Western Hemisphere tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms — into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds...
. The waves then combined with the storm surge of the large Category 3 hurricane.
Second and third landfalls
Katrina made its second landfall at 6:10 a.m. CDT on August 29 as a Category 3 hurricane with sustained winds of 125 mph (205 km/h) near Buras-Triumph, LouisianaBuras-Triumph, Louisiana
Buras-Triumph is a census-designated place in Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 3,358 at the 2000 census. On the peninsula, Buras has been located higher, with Triumph located southeast of Buras.-History:...
. Because Katrina had just weakened from Category 4 and due to the shape of the coastline, sustained Category 4 winds likely existed on land while the eye was over water. At landfall, hurricane-force winds extended 120 miles (190 km) from the center, the storm's pressure was 920 mbar (27.17 inHg), and its forward speed was 15 mph (24 km/h). As it made its way up the eastern Louisiana coastline, most communities in Plaquemines, St. Bernard Parish, and Slidell
Slidell, Louisiana
Slidell is a city situated on the northeast shore of Lake Pontchartrain in St. Tammany Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 25,695 at the 2000 census. The Greater Slidell Community has a population of about 90,000...
in St. Tammany Parish were severely damaged by storm surge and the strong winds of the eyewall, which also grazed eastern New Orleans, causing in excess of $1 billion worth of damage to the city (see Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans
Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans
The effects of Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans have been long-lasting. As the center of Katrina passed South-east of New Orleans on August 29, 2005, winds downtown were in the Category 3 range with frequent intense gusts and tidal surge. Hurricane force winds were experienced throughout the...
).
Original estimates indicated that Katrina had made this landfall as a Category 4 hurricane, with 135 mph (220 km/h) winds; however, as indicated above, the storm weakened just before landfall to Category 3 intensity. The reasons for this weakening are not completely known yet; while the eye-wall replacement cycle played a part, slightly increasing shear
Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
, dropping sea-surface temperatures, dry air on the western semicircle
Semicircle
In mathematics , a semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that forms half of a circle. Being half of a circle's 360°, the arc of a semicircle always measures 180° or a half turn...
of the storm and interaction with the continental landmass also may have played a role in weakening the cyclone. This follows the trend of previous strong cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
: all cyclones with minimum central pressures
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
of 973 mbar (28.73 inHg) or less have weakened over the 12 hours before making landfall
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
in the Gulf Coast of the United States
Gulf Coast of the United States
The Gulf Coast of the United States, sometimes referred to as the Gulf South, South Coast, or 3rd Coast, comprises the coasts of American states that are on the Gulf of Mexico, which includes Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida and are known as the Gulf States...
.
A few hours later, after weakening slightly, Katrina made its third landfall near the Louisiana–Mississippi border with 120 mph (195 km/h) sustained winds and 928 mbar (27.37 inHg) pressure, still at Category 3 intensity. Its minimum pressure at its second landfall was 920 mbar (27.17 inHg), making Katrina the third strongest hurricane on record to make landfall on the United States, behind Hurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille was the third and strongest tropical cyclone and second hurricane during the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season. The second of three catastrophic Category 5 hurricanes to make landfall in the United States during the 20th century , which it did near the mouth of the Mississippi River...
's 909 mbar (26.85 inHg) reading in 1969, and the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane's 892 mbar (26.35 inHg) record.

Storm surge
A storm surge is an offshore rise of water associated with a low pressure weather system, typically tropical cyclones and strong extratropical cyclones. Storm surges are caused primarily by high winds pushing on the ocean's surface. The wind causes the water to pile up higher than the ordinary sea...
s onshore, smashing the entire Mississippi Gulf Coast, including towns in Mississippi such as Waveland
Waveland, Mississippi
Waveland is a city located in Hancock County, Mississippi, on the Gulf of Mexico. It is part of the Gulfport–Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. The City of Waveland was incorporated in 1972. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 6,674...
, Bay St. Louis
Bay St. Louis, Mississippi
Bay Saint Louis is a city located in Hancock County, Mississippi. It is part of the Gulfport–Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 8,209. It is the county seat of Hancock County...
, Pass Christian
Pass Christian, Mississippi
Pass Christian , nicknamed The Pass, is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States, along the Gulf of Mexico. It is part of the Gulfport–Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area...
, Long Beach
Long Beach, Mississippi
Long Beach is a city located in Harrison County, Mississippi, USA. It is part of the Gulfport–Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area...
, Gulfport
Gulfport, Mississippi
Gulfport is the second largest city in Mississippi after the state capital Jackson. It is the larger of the two principal cities of the Gulfport-Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Gulfport-Biloxi-Pascagoula, Mississippi Combined Statistical Area. As of the...
, Biloxi
Biloxi, Mississippi
Biloxi is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, in the United States. The 2010 census recorded the population as 44,054. Along with Gulfport, Biloxi is a county seat of Harrison County....
, Ocean Springs
Ocean Springs, Mississippi
Ocean Springs is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States, about east of Biloxi. It is part of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 17,225 at the 2000 census...
, Gautier
Gautier, Mississippi
Gautier is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States, along the Gulf of Mexico west of Pascagoula. It is part of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 11,681 at the 2000 census. In 2002, Gautier annexed land nearly doubling its population to...
and Pascagoula
Pascagoula, Mississippi
Pascagoula is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States. It is the principal city of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area, as a part of the Gulfport–Biloxi–Pascagoula, Mississippi Combined Statistical Area. The population was 26,200 at the 2000 census...
, and, in Alabama, Bayou La Batre
Bayou La Batre, Alabama
Bayou La Batre is a town in Mobile County, Alabama, United States. It is included in the Mobile metropolitan statistical area. At the 2000 census, the population was 2,313. According to the 2005 U.S. Census estimates, the city had a population of 2,725....
. The surges peaked at 28 feet (8.5 m) in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi
Bay St. Louis, Mississippi
Bay Saint Louis is a city located in Hancock County, Mississippi. It is part of the Gulfport–Biloxi, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 8,209. It is the county seat of Hancock County...
, and at 13 feet (4.0 m) as far away as Mobile, Alabama
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile is the third most populous city in the Southern US state of Alabama and is the county seat of Mobile County. It is located on the Mobile River and the central Gulf Coast of the United States. The population within the city limits was 195,111 during the 2010 census. It is the largest...
, which saw its highest storm surge since 1917. Storm surge was particularly high due to the hydrology
Hydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
of the region, the hurricane's extreme size, and the fact that it weakened only shortly before landfall. As Katrina moved inland diagonally over Mississippi, high winds cut a swath of damage that affected almost the entire state.
Demise

Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
, but weakened thereafter, losing hurricane strength more than 150 miles (240 km) inland, near Meridian, Mississippi
Meridian, Mississippi
Meridian is the county seat of Lauderdale County, Mississippi. It is the sixth largest city in the state and the principal city of the Meridian, Mississippi Micropolitan Statistical Area...
. It was downgraded to a tropical depression near Clarksville, Tennessee
Clarksville, Tennessee
Clarksville is a city in and the county seat of Montgomery County, Tennessee, United States, and the fifth largest city in the state. The population was 132,929 in 2010 United States Census...
and broke in half. One half continued to race northward, affecting the Central United States
Central United States
The Central United States is sometimes conceived as between the Eastern United States and Western United States as part of a three-region model, roughly coincident with the Midwestern United States plus the western and central portions of the Southern United States; the term is also sometimes used...
along its path, and was last distinguishable in the eastern Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
region on August 31. On August 31, Katrina was absorbed by a frontal boundary and became a powerful extratropical low, causing 1.97–6.69 inches (50–170 mm) of rain in 12 hours, as well as gale-force wind gusts from 31 to 61 mph (50 to 98 km/h) in southeastern Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
and northern New Brunswick
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area...
. In the region of Saguenay
Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean
Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean is a region in Quebec, Canada. It contains the Saguenay Fjord, the estuary of the Saguenay River, stretching through much of the region...
and Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord is the second largest administrative region by land area in Quebec, Canada, after Nord-du-Québec...
, rain caused breakdowns and failure in roads. The Côte-Nord region was isolated from the rest of Quebec for at least 1 week. The other half of Katrina broke off in the eastern part of the Appalachians, primarily leading to a significant tornado outbreak
Tornado outbreak
While there is no single agreed upon definition, generally at least 6-10 tornadoes produced by the same synoptic scale weather system is considered a tornado outbreak. The tornadoes usually occur within the same day, or continue into the early morning hours of the succeeding day, and within the...
in the area from central Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
to central Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, killing two people and causing millions of dollars in additional damage.
At 11:00 p.m. EDT on August 31, the center of the remnant low of what was Katrina had been completely absorbed by a frontal boundary in southeastern Canada, with no discernible circulation.
See also
- Hurricane Katrina tornado outbreakHurricane Katrina tornado outbreakThe Hurricane Katrina tornado outbreak was a tornado outbreak across the eastern United States from August 29 to August 31, 2005, spawned mostly by the outer bands of Hurricane Katrina . One person was killed and numerous communities suffered damage of varying degrees from central Mississippi to...
- Risk prevention
- Timeline of Hurricane KatrinaTimeline of Hurricane KatrinaThis article contains a historical timeline of the events of Hurricane Katrina.-Tuesday, August 23, 2005:Tropical Depression Twelve formed over the southeastern Bahamas at 5:00 p.m. EDT on August 23, 2005, partially from the remains of Tropical Depression Ten, which had dissipated due to the...

