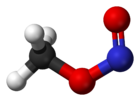
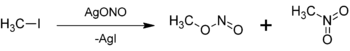Methyl nitrite
Encyclopedia
In organic chemistry
, methyl nitrite is the simplest alkyl nitrite.
to rotation of 45.3 kJ mol−1.
nitrite
with a iodomethane
: Silver nitrite (AgNO2) exists in solution as the silver ion
, Ag+ and the nitrite ion, NO2−. One of the lone pair
s on an oxygen from nitrite ion attacks the methyl group (—CH3), releasing the iodide
ion into solution. Unlike silver nitrite, silver iodide is highly insoluble in water and thus forms a solid. Note that nitrogen
is a better nucleophile than oxygen
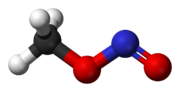
and most nitrites would react via an SN2-like mechanism and the major product would be nitromethane
. For example, sodium
and potassium nitrite
reacting with iodomethane would produce mostly nitromethane, with methyl nitrite as the minor product. However, the presence of the silver ion in solution has a stabilizing effect on the formation of carbocation
intermediates
, increasing the percent yield of methyl nitrite. In either case, some nitromethane and methyl nitrite are both formed.
This compound is produced by the combustion of unleaded petrol, and might be a cause of the decline of insect
s, and hence that of the House Sparrow
and other songbird
s in Europe
.
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, methyl nitrite is the simplest alkyl nitrite.
Structure
At room temperature, methyl nitrite exists as a mixture of cis and trans conformers. The cis conformer is 3.13 kJ mol−1 more stable than the trans form, with an energy barrierActivation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
to rotation of 45.3 kJ mol−1.
 |
 |
Synthesis
Methyl nitrite can be prepared by the reaction of silverSilver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
nitrite
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO2−. The anion is symmetric with equal N-O bond lengths and a O-N-O bond angle of ca. 120°. On protonation the unstable weak acid nitrous acid is produced. Nitrite can be oxidised or reduced, with product somewhat dependent on the oxidizing/reducing agent...
with a iodomethane
Iodomethane
Methyl iodide, also called iodomethane, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally...
: Silver nitrite (AgNO2) exists in solution as the silver ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
, Ag+ and the nitrite ion, NO2−. One of the lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
s on an oxygen from nitrite ion attacks the methyl group (—CH3), releasing the iodide
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. This page is for the iodide ion and its salts. For information on organoiodides, see organohalides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt,...
ion into solution. Unlike silver nitrite, silver iodide is highly insoluble in water and thus forms a solid. Note that nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
is a better nucleophile than oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
and most nitrites would react via an SN2-like mechanism and the major product would be nitromethane
Nitromethane
Nitromethane is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a slightly viscous, highly polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent...
. For example, sodium
Sodium nitrite
Sodium nitrite is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slight yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic...
and potassium nitrite
Potassium nitrite
Potassium nitrite is a salt with chemical formula 2.It is a strong oxidizer and may accelerate the combustion of other materials. Like other nitrite salts such as sodium nitrite, potassium nitrite is toxic if swallowed, and laboratory tests suggest that it may be mutagenic or teratogenic...
reacting with iodomethane would produce mostly nitromethane, with methyl nitrite as the minor product. However, the presence of the silver ion in solution has a stabilizing effect on the formation of carbocation
Carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively-charged carbon atom. The charged carbon atom in a carbocation is a "sextet", i.e. it has only six electrons in its outer valence shell instead of the eight valence electrons that ensures maximum stability . Therefore carbocations are often reactive,...
intermediates
Reaction intermediate
A reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants and reacts further to give the directly observed products of a chemical reaction. Most chemical reactions are stepwise, that is they take more than one elementary step to complete...
, increasing the percent yield of methyl nitrite. In either case, some nitromethane and methyl nitrite are both formed.
This compound is produced by the combustion of unleaded petrol, and might be a cause of the decline of insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
s, and hence that of the House Sparrow
House Sparrow
The House Sparrow is a bird of the sparrow family Passeridae, found in most parts of the world. One of about 25 species in the genus Passer, the House Sparrow occurs naturally in most of Europe, the Mediterranean region, and much of Asia...
and other songbird
Songbird
A songbird is a bird belonging to the suborder Passeri of the perching birds . Another name that is sometimes seen as scientific or vernacular name is Oscines, from Latin oscen, "a songbird"...
s in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.