
Molar conductivity
Encyclopedia
Molar conductivity is defined as the conductivity
of an electrolyte
solution
divided by the molar concentration of the electrolyte, and so measures the efficiency with which a given electrolyte conducts electricity in solution. Its units are siemens
per meter per molarity, or siemens meter-squared per mole. The usual symbol is a capital lambda, Λ, or Λm.
established that to a high accuracy in dilute solutions, molar conductivity is composed of individual contributions of ions. This is known as the law of independent migration of ions.
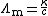
where:
For strong electrolyte
s, such as salt
s, strong acid
s and strong bases, molar conductivity is only weakly dependent on concentration and, to a good approximation, fits into the Debye - Huckel - Onsager equation :
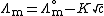
where:
In contrast, Friedrich Kohlrausch
showed that the molar conductivity is strongly concentration dependent for weak (incompletely dissociated) electrolytes; the more dilute a solution, the greater its molar conductivity, due to increased ionic dissociation. (This, for example, is the case of SDS-coated proteins in the stacking gel of an SDS-PAGE
.)
The limiting molar conductivity can be decomposed into contributions from the different ions (law of independent migration of ions):
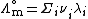
where:
Conductivity (electrolytic)
The conductivity of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is siemens per meter ....
of an electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
divided by the molar concentration of the electrolyte, and so measures the efficiency with which a given electrolyte conducts electricity in solution. Its units are siemens
Siemens (unit)
The siemens is the SI derived unit of electric conductance and electric admittance. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance and impedance respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term...
per meter per molarity, or siemens meter-squared per mole. The usual symbol is a capital lambda, Λ, or Λm.
History
Friedrich KohlrauschFriedrich Kohlrausch
Friedrich Wilhelm Georg Kohlrausch was a German physicist who investigated the conductive properties of electrolytes and contributed to knowledge of their behaviour...
established that to a high accuracy in dilute solutions, molar conductivity is composed of individual contributions of ions. This is known as the law of independent migration of ions.
Description
From its definition, the molar conductivity is given by: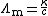
where:
- κ is the measured conductivity
- c is the electrolyte concentration.
For strong electrolyte
Strong electrolyte
A strong electrolyte is a solute that completely, or almost completely, ionizes or dissociates in a solution. These ions are good conductors of electric current in the solution....
s, such as salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
s, strong acid
Strong acid
A strong acid is an acid that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution by losing one proton, according to the equationFor sulfuric acid which is diprotic, the "strong acid" designation refers only to dissociation of the first protonMore precisely, the acid must be stronger in aqueous solution than...
s and strong bases, molar conductivity is only weakly dependent on concentration and, to a good approximation, fits into the Debye - Huckel - Onsager equation :
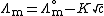
where:
-
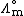 is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution (or limiting molar conductivityLimiting molar conductivitySee Kohlrausch's Law for details this is the conductivity of an ionic substance which has been extrapolated to an infinite dilution. It is normally the case thatMolar conductivity = Limiting molar conductivity - Kc1/2...
is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution (or limiting molar conductivityLimiting molar conductivitySee Kohlrausch's Law for details this is the conductivity of an ionic substance which has been extrapolated to an infinite dilution. It is normally the case thatMolar conductivity = Limiting molar conductivity - Kc1/2...
) - K is the Kohlrausch coefficient, which depends on the nature of the specific salt in solution.
In contrast, Friedrich Kohlrausch
Friedrich Kohlrausch
Friedrich Wilhelm Georg Kohlrausch was a German physicist who investigated the conductive properties of electrolytes and contributed to knowledge of their behaviour...
showed that the molar conductivity is strongly concentration dependent for weak (incompletely dissociated) electrolytes; the more dilute a solution, the greater its molar conductivity, due to increased ionic dissociation. (This, for example, is the case of SDS-coated proteins in the stacking gel of an SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, describes a collection of related techniques widely used in biochemistry, forensics, genetics and molecular biology to separate proteins according to their electrophoretic mobility...
.)
The limiting molar conductivity can be decomposed into contributions from the different ions (law of independent migration of ions):
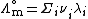
where:
-
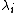 is the molar ionic conductivity of ion i.
is the molar ionic conductivity of ion i. -
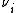 is the number of ions i in the formula unit of the electrolyte (e.g. 2 and 1 for Na+ and SO42- respectively in Na2SO4)
is the number of ions i in the formula unit of the electrolyte (e.g. 2 and 1 for Na+ and SO42- respectively in Na2SO4)

