Molecular logic gate
Encyclopedia
A molecular logic gate is a molecule that performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. Much academic research is dedicated to the development of these systems and several prototypes now exist. Because of their potential utility in simple arithmetic
these molecular machine
s are also called moleculators.
Molecular logic gates work with input signals based on chemical process
es and with output signals based on spectroscopy
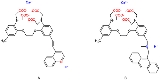
. One of the earlier water solution-based systems exploits the chemical behavior of compounds A and B in scheme 1 .
Compound A is a push-pull olefin
with the top receptor containing four carboxylic acid
anion groups (and non-disclosed counter cations) capable of binding to calcium
. The bottom part is a quinoline
molecule which is a receptor for hydrogen ions. The logic gate operates as follows.
Without any chemical input of Ca2+ or H+, the chromophore
shows a maximum absorbance in UV/VIS spectroscopy at 390 nm. When calcium is introduced a blue shift
takes place and the absorbance at 390 nm decreases. Likewise addition of protons causes a red shift
and when both cations are in the water the net result is absorption at the original 390 nm. This system represents a XNOR logic gate in absorption and a XOR logic gate in transmittance
.
In compound B the bottom section now contains a tertiary amino group also capable of binding to protons. In this system fluorescence
only takes place when both cations are present and therefore the system represents an AND logic gate
.
With both systems run in parallel and with monitoring of transmittance for system A and fluorescence for system B the result is a half-adder capable of reproducing the equation 1+1=2.
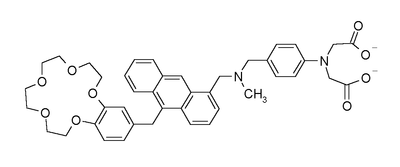
In a modification of system B not two but three chemical inputs are simultaneously processed in an AND logic gate . An enhanced fluorescence
signal from the compound depicted below is obtained only in the presence of hydrogen, zinc and sodium ions through interaction with respectively the amine
, carboxylate and crown ether
receptors and this system can be potentially applied in disease screening (lab-on-a-molecule) because these ions are all physiologically
relevant.
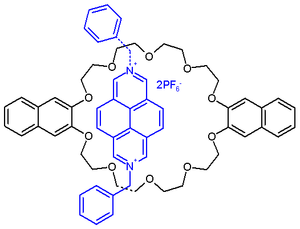
 In another XOR logic gate system the chemistry is based on the pseudorotaxane depicted in scheme 3. In organic solution the electron deficient diazapyrenium
In another XOR logic gate system the chemistry is based on the pseudorotaxane depicted in scheme 3. In organic solution the electron deficient diazapyrenium
salt (rod) and the electron rich 2,3-dioxynaphthalene
units of the crown ether
(ring) self-assemble
by formation of a charge transfer complex
.
An added tertiary amine like tributylamine forms a 1:2 adduct with the diazapyrene and the complex gets dethreaded. This process is accompanied by an increase in emission intensity at 343 nm resulting from freed crown ether. Added trifluoromethanesulfonic acid
reacts with the amine and the process is reverted. Excess acid locks the crown ether by protonation
and again the complex is dethreaded.
 A full adder system based on fluorescein
A full adder system based on fluorescein
is able to compute 1+1+1=3.
Arithmetic
Arithmetic or arithmetics is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple day-to-day counting to advanced science and business calculations. It involves the study of quantity, especially as the result of combining numbers...
these molecular machine
Molecular machine
A molecular machine, or nanomachine, is any discrete number of molecular components that produce quasi-mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli . The expression is often more generally applied to molecules that simply mimic functions that occur at the macroscopic level...
s are also called moleculators.
Molecular logic gates work with input signals based on chemical process
Chemical process
In a "scientific" sense, a chemical process is a method or means of somehow changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds. Such a chemical process can occur by itself or be caused by somebody. Such a chemical process commonly involves a chemical reaction of some sort...
es and with output signals based on spectroscopy
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
. One of the earlier water solution-based systems exploits the chemical behavior of compounds A and B in scheme 1 .
Compound A is a push-pull olefin
Push-pull olefin
A push-pull olefin is a type of olefin characterized by an electron-withdrawing substituent on one side of the double bond and an electron-donating substituent on the other side. This makes the pi bond very polarized...
with the top receptor containing four carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
anion groups (and non-disclosed counter cations) capable of binding to calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
. The bottom part is a quinoline
Quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C9H7N and is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odour. Aged samples, if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown...
molecule which is a receptor for hydrogen ions. The logic gate operates as follows.
Without any chemical input of Ca2+ or H+, the chromophore
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two different molecular orbitals falls...
shows a maximum absorbance in UV/VIS spectroscopy at 390 nm. When calcium is introduced a blue shift
Blue shift
A blueshift is any decrease in wavelength ; the opposite effect is referred to as redshift. In visible light, this shifts the colour from the red end of the spectrum to the blue end...
takes place and the absorbance at 390 nm decreases. Likewise addition of protons causes a red shift
Red shift
-Science:* Redshift, the increase of wavelength of detected electromagnetic radiation with respect to the original wavelength of the emission* Red shift, an informal term for a bathochromic shift...
and when both cations are in the water the net result is absorption at the original 390 nm. This system represents a XNOR logic gate in absorption and a XOR logic gate in transmittance
Transmittance
In optics and spectroscopy, transmittance is the fraction of incident light at a specified wavelength that passes through a sample. A related term is absorptance, or absorption factor, which is the fraction of radiation absorbed by a sample at a specified wavelength...
.
In compound B the bottom section now contains a tertiary amino group also capable of binding to protons. In this system fluorescence
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
only takes place when both cations are present and therefore the system represents an AND logic gate
AND gate
The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements logical conjunction - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results only if both the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH . If neither or only one input to the AND gate is HIGH, a LOW output results...
.
With both systems run in parallel and with monitoring of transmittance for system A and fluorescence for system B the result is a half-adder capable of reproducing the equation 1+1=2.
In a modification of system B not two but three chemical inputs are simultaneously processed in an AND logic gate . An enhanced fluorescence
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
signal from the compound depicted below is obtained only in the presence of hydrogen, zinc and sodium ions through interaction with respectively the amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
, carboxylate and crown ether
Crown ether
Crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups. The most common crown ethers are oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., -CH2CH2O-. Important members of this series are the tetramer , the pentamer , and the hexamer...
receptors and this system can be potentially applied in disease screening (lab-on-a-molecule) because these ions are all physiologically
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
relevant.

Pyrene
Pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of four fused benzene rings, resulting in a flat aromatic system. The chemical formula is . This colourless solid is the smallest peri-fused PAH...
salt (rod) and the electron rich 2,3-dioxynaphthalene
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings...
units of the crown ether
Crown ether
Crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups. The most common crown ethers are oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., -CH2CH2O-. Important members of this series are the tetramer , the pentamer , and the hexamer...
(ring) self-assemble
Molecular self-assembly
Molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly, intramolecular self-assembly and intermolecular self-assembly...
by formation of a charge transfer complex
Charge transfer complex
A charge-transfer complex or electron-donor-acceptor complex is an association of two or more molecules, or of different parts of one very large molecule, in which a fraction of electronic charge is transferred between the molecular entities. The resulting electrostatic attraction provides a...
.
An added tertiary amine like tributylamine forms a 1:2 adduct with the diazapyrene and the complex gets dethreaded. This process is accompanied by an increase in emission intensity at 343 nm resulting from freed crown ether. Added trifluoromethanesulfonic acid
Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid
Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, also known as triflic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification.-Properties:Triflic acid is a hygroscopic, colorless...
reacts with the amine and the process is reverted. Excess acid locks the crown ether by protonation
Protonation
In chemistry, protonation is the addition of a proton to an atom, molecule, or ion. Some classic examples include*the protonation of water by sulfuric acid:*the protonation of isobutene in the formation of a carbocation:2C=CH2 + HBF4 → 3C+ + BF4−*the protonation of ammonia in the...
and again the complex is dethreaded.

Fluorescein
Fluorescein is a synthetic organic compound available as a dark orange/red powder soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications....
is able to compute 1+1+1=3.

