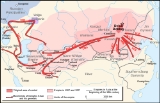
Mongol invasion of Rus
Encyclopedia
The Mongol invasion of Russia' was resumed on 21 December 1237 marking the resumption of the Mongol invasion of Europe
, during which the Mongols
attacked the medieval powers of Poland
, Kiev
, Hungary
, and miscellaneous tribes of less organized peoples. The European invasion, heralded by the Battle of the Kalka River
(1223) was fought between the scout forces of just the two Mongolian generals Subutai
and Jebe
, whose reconnaissance unit met in battle with the combined force of several Rus' princes.
After fifteen years of peace, the Rus' invasion was followed by Batu Khan
's full-scale invasion of Rus' and points east during 1237 to 1240, which only ended with a Mongol succession crisis.
The invasion, facilitated by the breakup of Kievan Rus'
in the 12th century, had incalculable ramifications for the history of Eastern Europe
, including the division of the East Slavic people into three separate nations (modern day Russia
, Ukraine
, and Belarus
). and the rise of the Grand Duchy of Moscow
.
. "For our sins", writes the Rus'
chronicler of the time, "unknown nations arrived. No one knew their origin or whence they came, or what religion they practiced. That is known only to God, and perhaps to wise men learned in books".
The princes of Rus' first heard of the coming Mongol warriors from the nomadic Cumans
. Previously known for pillaging settlers on the frontier, the nomads now preferred peaceful relations, warning their neighbors: "These terrible strangers have taken our country, and tomorrow they will take yours if you do not come and help us". In response to this call, Mstislav the Bold
and Mstislav Romanovich the Old
joined forces and set out eastward to meet the foe, only to be routed in 1223 at the Battle of the Kalka River
, a defeat remembered to this day in Russia
and Ukraine
.
Although this defeat left the Kievan principality at the mercy of invaders, the Mongol forces retreated and did not reappear for thirteen years, during which time the princes of Rus' went on quarreling and fighting as before, until they were startled by a new and much more formidable invading force.
 The vast Mongol hordes of around 35,000 mounted archers, commanded by Batu Khan
The vast Mongol hordes of around 35,000 mounted archers, commanded by Batu Khan
and Subutai
, crossed the Volga River
and invaded Volga Bulgaria
in the autumn of 1236. It took them a year to extinguish the resistance of the Volga Bulgaria
ns, the Kipchaks/Cumans and the Alani
.
In November 1237, Batu Khan sent his envoys to the court of Yuri II
of Vladimir
and demanded his submission. A month later, the hordes besieged Ryazan
. After six days of bloody battle, the city was totally annihilated. Alarmed by the news, Yuri II sent his sons to detain the invaders, but they were soundly defeated. Having burnt down Kolomna
and Moscow
, the horde laid siege to Vladimir on February 4, 1238. Three days later, the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal
was taken and burnt to the ground. The royal family perished in the fire, while the grand prince retreated northward. Crossing the Volga, he mustered a new army, which was totally annihilated by the Mongols in the Battle of the Sit River
on March 4.
Thereupon Batu Khan divided his army into smaller units, which ransacked fourteen cities of modern-day Russia: Rostov
, Uglich
, Yaroslavl
, Kostroma
, Kashin
, Ksnyatin, Gorodets
, Galich
, Pereslavl-Zalessky
, Yuriev-Polsky, Dmitrov
, Volokolamsk
, Tver
, and Torzhok
. The most difficult to take was the small town of Kozelsk
, whose boy-prince Vasily, son of Titus, and inhabitants resisted the Mongols for seven weeks, killing 4,000. As the story goes, at the news of the Mongol approach, the whole town of Kitezh
with all its inhabitants was submerged into a lake, where, as legend has it, it may be seen to this day. The only major cities to escape destruction were Novgorod and Pskov
. Refugees from southern Rus' moved mostly to the northeast, in the forest region with poor soils between the northern Volga and Oka River
s.
In the summer of 1238, Batu Khan devastated the Crimea
and pacified Mordovia
. In the winter of 1239, he sacked Chernigov
and Pereyaslav
. After many days of siege, the horde stormed Kiev
in December 1240. Despite the resistance of Danylo of Halych, Batu Khan managed to take two of his principal cities, Halych
and Volodymyr-Volynskyi
. The Mongols then resolved to "reach the ultimate sea", where they could proceed no further, and invaded Hungary
and Poland
.
Chinese siege engines were used by the Mongols under Tului to raze the walls of Russian cities.
, on the lower Volga. Here the commander of the Golden Horde
, as the western section of the Mongol empire
was called, fixed his golden headquarters and represented the majesty of his sovereign the grand khan who lived with the Great Horde in the Orkhon Valley
of the Amur. Here they had their headquarters and held parts of Rus in subjection for nearly three centuries. All of Russian states submitted to the Mongol rule, including Novgorod, Smolensk
, Galich
and Pskov
.
The term by which this subjection is commonly designated, the Mongol or Tatar yoke, suggests ideas of terrible oppression, but in reality these nomadic invaders from Mongolia
were not such cruel, oppressive taskmasters as is generally supposed. In the first place, they never settled in the country, and they had little direct dealing with the inhabitants. In accordance with the admonitions of Genghis to his children and grandchildren, they retained their pastoral mode of life, so that the subject races, agriculturists, and dwellers in towns, were not disturbed in their ordinary avocations.
In religious matters they were extremely tolerant. When they first appeared in Europe, they were Shamanists
, and as such they had naturally no religious fanaticism. Thus, after they adopted Islam
they remained as tolerant as before, and the khan of the Golden Horde, who first became a Muslim, allowed the Rus to found a Christian bishopric
in his capital. Nogai Khan
, half a century later, married a daughter of the Byzantine
emperor, and gave his own daughter in marriage to a Rus prince, Theodor the Black. Some modern Russian historians (most notably, the Soviet era historian and "Neo-Eurasianist" ideologist Lev Gumilev
) even postulate there was no invasion at all. According to them, the Rus princes concluded a defensive alliance with the Horde in order to repel attacks of the fanatical Teutonic Knights
, which posed a much greater threat to Rus religion and culture.
These represent the bright side of Tatar rule. It had its dark side also. So long as a great horde of nomads was encamped on the frontier, the country was liable to be invaded by an overwhelming force. Fortunately, these invasions were not frequent but when they occurred they caused an incalculable amount of devastation and suffering. In the intervals the people had to pay a fixed tribute. At first it was collected in a rough-and-ready fashion by Tatar tax-gatherers, by about 1259 it was regulated by a census of the population, and finally its collection was entrusted to the native princes, so that the people were no longer brought into direct contact with the Tatar officials.
(Atlas of World Population History, 1978) estimates the population of European Russia
dropped from 7.5 million prior to the invasion to 7 million afterwards. Centers such as Kiev never recovered from the devastation of the initial attack. The Novgorod Republic
continued to prosper, however, and new entities, the rival cities of Moscow and Tver, began to flourish under the Mongols. Indeed, Moscow's eventual dominance of northern and eastern Rus was in large part attributable to the Mongols. After the prince of Tver joined a rebellion against the Mongols 1327, his rival prince Ivan I of Moscow joined the Mongols in crushing Tver and devastating its lands. By doing so he eliminated his rival, allowed the Russian Orthodox Church
to move its headquarters to Moscow, and was granted the title of Grand prince
by the Mongols. As such, the Muscovite prince became the chief intermediary between the Mongol overlords and the Rus lands, which paid further dividends to Moscow's rulers. While the Mongols often raided other areas of Rus, they tended to respect the lands controlled by their principal collaborator. This, in turn, attracted nobles and their servants who sought to settle in the relatively secure and peaceful Moscow lands.
Although Russia
n forces defeated the Golden Horde at the Battle of Kulikovo
in 1380, Mongol domination of parts of Rus territories, with the requisite demands of tribute, continued until the Great stand on the Ugra river in 1480.
Certainly, it can be (and often is) argued that without the Mongol destruction of Kievan Rus' that Moscow, and subsequently the Russian Empire
, would not have risen. Trade routes with the East came through the Rus lands, making them a center for trade from both worlds. In short, the Mongol influence, while destructive in the extreme to their enemies, had a significant long term effect on the rise of modern Russia
, Ukraine
and Belarus
.
" into Russia. Historians also credit the Mongol regime with an important role in the development of Muscovy as a state. Under Mongol occupation, for example, Muscovy developed its mestnichestvo
hierarchy, postal
road network, census
, fiscal system, and military organization.
A significant number of historians consider the oppression of Rus' by the Mongols to be the major cause of what is sometimes called "the East-West gap" - approximately 200 years delay in introducing major social, political and economical reforms and scientific innovations in Russia compared to Western Europe
. Specifically, the isolation from the West may have caused Russia's later non-involvement in the Renaissance
, the Protestant Reformation
, and failure to develop a middle class
.
The period of Mongol rule over Russia included significant cultural and interpersonal contacts between the Russian and Mongolian ruling classes. By 1450, the Tatar language
had become fashionable in the court of the Grand Prince of Moscow, Vasily II, who was accused of excessive love of the Tatars and their speech, and many Russian noblemen adopted Tatar surnames (for example, a member of the Veliamanov family adopted the Turkic name "Aksak" and his descendents were the Aksakov
s) Many Russian boyar
(noble) families traced their descent from the Mongols or Tatars, including Veliaminov-Zernov, Godunov
, Arseniev, Bakhmetev, Bulgakov
(descendents of Bulgak) and Chaadaev (descendents of Genghis Khan's son Jagatay). In a survey of Russian noble families of the 17th century, over 15% of the Russian noble families had Tatar or Oriental origins.
The Mongols brought about changes in economics power of states and overall trade.
In the religious sphere, St. Paphnutius of Borovsk was the grandson of a Mongol baskak
, or tax collector, while a nephew of khan
Bergai of the Golden Horde
converted to Christianity and became known as the monk St. Peter Tsarevich of the Horde
In the judicial sphere, under Mongol influence capital punishment, which during the times of Kievan Rus had only been applied to slaves, became widespread and the use of torture became a regular part of criminal procedure. Specific punishments introduced in Moscow included beheading for alleged traitors, branding of thieves (with execution for a third arrest). Penal law in western Europe in the Middle Ages was even harsher, however, than Mongol and Russian law.
The Russian language adopted numerous words from Mongol and Turkic. Such words include dengi (money), kazna (treasury), tamozhnia (customhouse), barysh (profit), and bashmak (shoe).
, Astrakhan, Crimean, and Siberian khanate
s, as well as the Nogai Horde
, all of which were eventually conquered by the Russian Empire
.
Mongol invasion of Europe
The resumption of the Mongol invasion of Europe, during which the Mongols attacked medieval Rus' principalities and the powers of Poland and Hungary, was marked by the Mongol invasion of Rus starting in 21 December 1237...
, during which the Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
attacked the medieval powers of Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Kiev
Kiev
Kiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press....
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, and miscellaneous tribes of less organized peoples. The European invasion, heralded by the Battle of the Kalka River
Battle of the Kalka River
The Battle of the Kalka River took place on May 31, 1223, between the Mongol Empire and Kiev, Galich, and several other Rus' principalities and the Cumans, under the command of Mstislav the Bold and Mstislav III of Kiev...
(1223) was fought between the scout forces of just the two Mongolian generals Subutai
Subutai
Subutai was the primary military strategist and general of Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan...
and Jebe
Jebe
Chepe Noyan was one of the prominent Noyans of Genghis Khan. His clan was Besud, which belonged to the Taichud tribe, which was at the time of Genghis Khan under Targudai Khiriltug's leadership....
, whose reconnaissance unit met in battle with the combined force of several Rus' princes.
After fifteen years of peace, the Rus' invasion was followed by Batu Khan
Batu Khan
Batu Khan was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Ulus of Jochi , the sub-khanate of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. His ulus was the chief state of the Golden Horde , which ruled Rus and the Caucasus for around 250 years, after also destroying the armies...
's full-scale invasion of Rus' and points east during 1237 to 1240, which only ended with a Mongol succession crisis.
The invasion, facilitated by the breakup of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
in the 12th century, had incalculable ramifications for the history of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, including the division of the East Slavic people into three separate nations (modern day Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
). and the rise of the Grand Duchy of Moscow
Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia....
.
Background
As it was undergoing fragmentation, Kievan Rus' faced the unexpected eruption of an irresistible foreign foe coming from the mysterious regions of the Far EastFar East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
. "For our sins", writes the Rus'
Rus' (people)
The Rus' were a group of Varangians . According to the Primary Chronicle of Rus, compiled in about 1113 AD, the Rus had relocated from the Baltic region , first to Northeastern Europe, creating an early polity which finally came under the leadership of Rurik...
chronicler of the time, "unknown nations arrived. No one knew their origin or whence they came, or what religion they practiced. That is known only to God, and perhaps to wise men learned in books".
The princes of Rus' first heard of the coming Mongol warriors from the nomadic Cumans
Cumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
. Previously known for pillaging settlers on the frontier, the nomads now preferred peaceful relations, warning their neighbors: "These terrible strangers have taken our country, and tomorrow they will take yours if you do not come and help us". In response to this call, Mstislav the Bold
Mstislav the Bold
Mstislav Mstislavich the Bold was one of the most popular and active princes of Kievan Rus' in the decades preceding Mongol invasion of Rus. He was the maternal grandfather of Alexander Nevsky and the prince Leo of Galicia....
and Mstislav Romanovich the Old
Mstislav III of Kiev
Mstislav Romanovich the Old , Prince of Pskov , Smolensk , Belgorod , Halych and Grand Prince of Kiev...
joined forces and set out eastward to meet the foe, only to be routed in 1223 at the Battle of the Kalka River
Battle of the Kalka River
The Battle of the Kalka River took place on May 31, 1223, between the Mongol Empire and Kiev, Galich, and several other Rus' principalities and the Cumans, under the command of Mstislav the Bold and Mstislav III of Kiev...
, a defeat remembered to this day in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
.
Although this defeat left the Kievan principality at the mercy of invaders, the Mongol forces retreated and did not reappear for thirteen years, during which time the princes of Rus' went on quarreling and fighting as before, until they were startled by a new and much more formidable invading force.
Invasion of Batu Khan

Batu Khan
Batu Khan was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Ulus of Jochi , the sub-khanate of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. His ulus was the chief state of the Golden Horde , which ruled Rus and the Caucasus for around 250 years, after also destroying the armies...
and Subutai
Subutai
Subutai was the primary military strategist and general of Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan...
, crossed the Volga River
Volga River
The Volga is the largest river in Europe in terms of length, discharge, and watershed. It flows through central Russia, and is widely viewed as the national river of Russia. Out of the twenty largest cities of Russia, eleven, including the capital Moscow, are situated in the Volga's drainage...
and invaded Volga Bulgaria
Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria
The Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria lasted from 1223 to 1236.-The Mongol campaigns:In 1223, after defeating Russian and Cuman/Kipchak armies at the Battle of Kalka, a Mongol army under the generals Subutai and Jebe was sent to subdue Volga Bulgaria. At that point in history Genghis Khan's troops...
in the autumn of 1236. It took them a year to extinguish the resistance of the Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria, or Volga–Kama Bolghar, is a historic Bulgar state that existed between the seventh and thirteenth centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers in what is now Russia.-Origin:...
ns, the Kipchaks/Cumans and the Alani
Alans
The Alans, or the Alani, occasionally termed Alauni or Halani, were a group of Sarmatian tribes, nomadic pastoralists of the 1st millennium AD who spoke an Eastern Iranian language which derived from Scytho-Sarmatian and which in turn evolved into modern Ossetian.-Name:The various forms of Alan —...
.
In November 1237, Batu Khan sent his envoys to the court of Yuri II
Yuri II
Yuri II , also known as George II of Vladimir or Georgy II Vsevolodovich , was the fourth Grand Prince of Vladimir who presided over Vladimir-Suzdal at the time of the Mongol invasion of Russia.He was the third and best-loved son of Vsevolod III and Maria Shvarnovna.He first...
of Vladimir
Vladimir
Vladimir is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, to the east of Moscow along the M7 motorway. Population:...
and demanded his submission. A month later, the hordes besieged Ryazan
Ryazan
Ryazan is a city and the administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Oka River southeast of Moscow. Population: The strategic bomber base Dyagilevo is just west of the city, and the air base of Alexandrovo is to the southeast as is the Ryazan Turlatovo Airport...
. After six days of bloody battle, the city was totally annihilated. Alarmed by the news, Yuri II sent his sons to detain the invaders, but they were soundly defeated. Having burnt down Kolomna
Kolomna
Kolomna is an ancient city and the administrative center of Kolomensky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva and Oka Rivers, southeast of Moscow. The area of the city is about . The city was founded in 1177...
and Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, the horde laid siege to Vladimir on February 4, 1238. Three days later, the capital of Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal
The Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
was taken and burnt to the ground. The royal family perished in the fire, while the grand prince retreated northward. Crossing the Volga, he mustered a new army, which was totally annihilated by the Mongols in the Battle of the Sit River
Battle of the Sit River
The Battle of the Sit River was fought in the northern part of the present-day Yaroslavl Oblast of Russia on March 4, 1238 between the Mongol Hordes of Batu Khan and the Rus' people under Grand Prince Yuri II of Vladimir-Suzdal during the Mongol invasion of Rus...
on March 4.
Thereupon Batu Khan divided his army into smaller units, which ransacked fourteen cities of modern-day Russia: Rostov
Rostov
Rostov is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population:...
, Uglich
Uglich
Uglich is a historic town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, which stands on the Volga River. Population: A local tradition dates the town's origins to 937. It was first documented in 1148 as Ugliche Pole...
, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historical part of the city, a World Heritage Site, is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl Rivers. It is one of the Golden Ring cities, a group of historic cities...
, Kostroma
Kostroma
Kostroma is a historic city and the administrative center of Kostroma Oblast, Russia. A part of the Golden Ring of Russian towns, it is located at the confluence of the Volga and Kostroma Rivers...
, Kashin
Kashin
Kashin is a town and the administrative center of Kashinsky District of Tver Oblast, Russia, located around a rural agricultural area on the Kashinka River from Moscow and from Kalyazin...
, Ksnyatin, Gorodets
Gorodets
Gorodets is a town and the administrative center of Gorodetsky District of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Volga River, northwest of Nizhny Novgorod...
, Galich
Galich
Galich may refer to:*Alexander Ivanovich Galich , Russian philosopher and Latin scholar*Alexander Galich , Russian dissident bard*Galich, Russia, a town in Kostroma Oblast, Russia...
, Pereslavl-Zalessky
Pereslavl-Zalessky
Pereslavl-Zalessky or Pereyaslavl-Zalessky , is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow on the main Moscow Yaroslavl road and on the shores of Pleschevo Lake. It was called Pereyaslavl until the 15th century. The town is located on the southeastern shore of the Lake...
, Yuriev-Polsky, Dmitrov
Dmitrov
Dmitrov is a town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Moscow Canal. Population: -History:...
, Volokolamsk
Volokolamsk
Volokolamsk is a town and the administrative center of Volokolamsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Gorodenka River, not far from its confluence with the Lama River, northwest of Moscow. Population: -History:...
, Tver
Tver
Tver is a city and the administrative center of Tver Oblast, Russia. Population: 403,726 ; 408,903 ;...
, and Torzhok
Torzhok
Torzhok is a town in Tver Oblast, Russia, famous for its folk craft of goldwork embroidery. Population: Torzhok has twenty-two large and medium-sized industrial enterprises. Two of them are especially significant...
. The most difficult to take was the small town of Kozelsk
Kozelsk
Kozelsk is a town in Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the Zhizdra River , southwest of Kaluga. Population: -History:The town of Kozelsk was first mentioned in a chronicle under the year of 1146 as a part of Principality of Chernigov...
, whose boy-prince Vasily, son of Titus, and inhabitants resisted the Mongols for seven weeks, killing 4,000. As the story goes, at the news of the Mongol approach, the whole town of Kitezh
Kitezh
Kitezh was a mythical city on the shores of the Svetloyar lake in the Voskresensky District of the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast in central Russia. It appears for the first time in "Kitezh Chronicle", an anonymous book from the late 18th century, believed to have originated among the Old believers.-The...
with all its inhabitants was submerged into a lake, where, as legend has it, it may be seen to this day. The only major cities to escape destruction were Novgorod and Pskov
Pskov
Pskov is an ancient city and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, Russia, located in the northwest of Russia about east from the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population: -Early history:...
. Refugees from southern Rus' moved mostly to the northeast, in the forest region with poor soils between the northern Volga and Oka River
Oka River
Oka is a river in central Russia, the largest right tributary of the Volga. It flows through the regions of Oryol, Tula, Kaluga, Moscow, Ryazan, Vladimir, and Nizhny Novgorod and is navigable over a large part of its total length, as far upstream as to the town of Kaluga. Its length exceeds...
s.
In the summer of 1238, Batu Khan devastated the Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
and pacified Mordovia
Mordovia
The Republic of Mordovia , also known as Mordvinia, is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the city of Saransk. Population: -Geography:The republic is located in the eastern part of the East European Plain of Russia...
. In the winter of 1239, he sacked Chernigov
Chernihiv
Chernihiv or Chernigov is a historic city in northern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Chernihiv Oblast , as well as of the surrounding Chernihivskyi Raion within the oblast...
and Pereyaslav
Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi
Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi is a town located where Alta River flows into Trubizh River in the Kiev Oblast in central Ukraine. Serving as the administrative center of the Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi Raion , the town itself is also designated as a separate raion within the oblast...
. After many days of siege, the horde stormed Kiev
Kiev
Kiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press....
in December 1240. Despite the resistance of Danylo of Halych, Batu Khan managed to take two of his principal cities, Halych
Halych
Halych is a historic city on the Dniester River in western Ukraine. The town gave its name to the historic province and kingdom of Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, of which it was the capital until the early 14th century, when the seat of the local princes was moved to Lviv...
and Volodymyr-Volynskyi
Volodymyr-Volynskyi
Volodymyr-Volynsky is a city located in Volyn Oblast, in north-western Ukraine. Serving as the administrative centre of the Volodymyr-Volynsky District, the city itself is also designated as a separate raion within the oblast...
. The Mongols then resolved to "reach the ultimate sea", where they could proceed no further, and invaded Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
and Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
.
Chinese siege engines were used by the Mongols under Tului to raze the walls of Russian cities.
The age of the Tatar yoke
This time the invaders came to stay, and they built for themselves a capital, called SaraiSarai (city)
Sarai was the name of two cities, which were successively capital cities of the Golden Horde, the Mongol kingdom which ruled Russia and much of central Asia in the 13th and 14th centuries...
, on the lower Volga. Here the commander of the Golden Horde
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde was a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate that formed the north-western sector of the Mongol Empire...
, as the western section of the Mongol empire
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire , initially named as Greater Mongol State was a great empire during the 13th and 14th centuries...
was called, fixed his golden headquarters and represented the majesty of his sovereign the grand khan who lived with the Great Horde in the Orkhon Valley
Orkhon Valley
Orkhon Valley Cultural Landscape sprawls along the banks of the Orkhon River in Central Mongolia, some 360 km west from the capital Ulaanbaatar. It was inscribed by UNESCO in the World Heritage List as representing evolution of nomadic pastoral traditions spanning more than two millennia...
of the Amur. Here they had their headquarters and held parts of Rus in subjection for nearly three centuries. All of Russian states submitted to the Mongol rule, including Novgorod, Smolensk
Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River. Situated west-southwest of Moscow, this walled city was destroyed several times throughout its long history since it was on the invasion routes of both Napoleon and Hitler. Today, Smolensk...
, Galich
Galich
Galich may refer to:*Alexander Ivanovich Galich , Russian philosopher and Latin scholar*Alexander Galich , Russian dissident bard*Galich, Russia, a town in Kostroma Oblast, Russia...
and Pskov
Pskov
Pskov is an ancient city and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, Russia, located in the northwest of Russia about east from the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population: -Early history:...
.
The term by which this subjection is commonly designated, the Mongol or Tatar yoke, suggests ideas of terrible oppression, but in reality these nomadic invaders from Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
were not such cruel, oppressive taskmasters as is generally supposed. In the first place, they never settled in the country, and they had little direct dealing with the inhabitants. In accordance with the admonitions of Genghis to his children and grandchildren, they retained their pastoral mode of life, so that the subject races, agriculturists, and dwellers in towns, were not disturbed in their ordinary avocations.
In religious matters they were extremely tolerant. When they first appeared in Europe, they were Shamanists
Shamanism
Shamanism is an anthropological term referencing a range of beliefs and practices regarding communication with the spiritual world. To quote Eliade: "A first definition of this complex phenomenon, and perhaps the least hazardous, will be: shamanism = technique of ecstasy." Shamanism encompasses the...
, and as such they had naturally no religious fanaticism. Thus, after they adopted Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
they remained as tolerant as before, and the khan of the Golden Horde, who first became a Muslim, allowed the Rus to found a Christian bishopric
Krutitsy
Krutitsy Metochion , full name: Krutitsy Patriarchal Metochion is an operating ecclesiastical estate of Russian Orthodox Church, located in Tagansky District of Moscow, Russia, 3 kilometers south-east from the Kremlin. The name Krutitsy , i.e. steep river banks, originally meant the hills...
in his capital. Nogai Khan
Nogai Khan
Nogai , also called Isa Nogai, was a general and de facto ruler of the Golden Horde and a great-great-grandson of Genghis Khan. His grandfather was Baul/Teval Khan, the 7th son of Jochi...
, half a century later, married a daughter of the Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
emperor, and gave his own daughter in marriage to a Rus prince, Theodor the Black. Some modern Russian historians (most notably, the Soviet era historian and "Neo-Eurasianist" ideologist Lev Gumilev
Lev Gumilev
Lev Nikolayevich Gumilev , was a Soviet historian, ethnologist and anthropologist. His unorthodox ideas on the birth and death of ethnic groups have given rise to the political and cultural movement known as "Neo-Eurasianism".-Life:His parents were two prominent poets Nikolay Gumilev and Anna...
) even postulate there was no invasion at all. According to them, the Rus princes concluded a defensive alliance with the Horde in order to repel attacks of the fanatical Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
, which posed a much greater threat to Rus religion and culture.
These represent the bright side of Tatar rule. It had its dark side also. So long as a great horde of nomads was encamped on the frontier, the country was liable to be invaded by an overwhelming force. Fortunately, these invasions were not frequent but when they occurred they caused an incalculable amount of devastation and suffering. In the intervals the people had to pay a fixed tribute. At first it was collected in a rough-and-ready fashion by Tatar tax-gatherers, by about 1259 it was regulated by a census of the population, and finally its collection was entrusted to the native princes, so that the people were no longer brought into direct contact with the Tatar officials.
Impact on development
The influence of the Mongol invasion on the territories of Kievan Rus' was uneven. Colin McEvedyColin McEvedy
Colin Peter McEvedy , was a British psychiatrist, historian, demographer and non-fiction author. He was born in Salford, Lancashire and died in London....
(Atlas of World Population History, 1978) estimates the population of European Russia
European Russia
European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with...
dropped from 7.5 million prior to the invasion to 7 million afterwards. Centers such as Kiev never recovered from the devastation of the initial attack. The Novgorod Republic
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...
continued to prosper, however, and new entities, the rival cities of Moscow and Tver, began to flourish under the Mongols. Indeed, Moscow's eventual dominance of northern and eastern Rus was in large part attributable to the Mongols. After the prince of Tver joined a rebellion against the Mongols 1327, his rival prince Ivan I of Moscow joined the Mongols in crushing Tver and devastating its lands. By doing so he eliminated his rival, allowed the Russian Orthodox Church
Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church or, alternatively, the Moscow Patriarchate The ROC is often said to be the largest of the Eastern Orthodox churches in the world; including all the autocephalous churches under its umbrella, its adherents number over 150 million worldwide—about half of the 300 million...
to move its headquarters to Moscow, and was granted the title of Grand prince
Grand Prince
The title grand prince or great prince ranked in honour below emperor and tsar and above a sovereign prince .Grand duke is the usual and established, though not literal, translation of these terms in English and Romance languages, which do not normally use separate words for a "prince" who reigns...
by the Mongols. As such, the Muscovite prince became the chief intermediary between the Mongol overlords and the Rus lands, which paid further dividends to Moscow's rulers. While the Mongols often raided other areas of Rus, they tended to respect the lands controlled by their principal collaborator. This, in turn, attracted nobles and their servants who sought to settle in the relatively secure and peaceful Moscow lands.
Although Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n forces defeated the Golden Horde at the Battle of Kulikovo
Battle of Kulikovo
The Battle of Kulikovo was a battle between Tatar Mamai and Muscovy Dmitriy and portrayed by Russian historiography as a stand-off between Russians and the Golden Horde. However, the political situation at the time was much more complicated and concerned the politics of the Northeastern Rus'...
in 1380, Mongol domination of parts of Rus territories, with the requisite demands of tribute, continued until the Great stand on the Ugra river in 1480.
Certainly, it can be (and often is) argued that without the Mongol destruction of Kievan Rus' that Moscow, and subsequently the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, would not have risen. Trade routes with the East came through the Rus lands, making them a center for trade from both worlds. In short, the Mongol influence, while destructive in the extreme to their enemies, had a significant long term effect on the rise of modern Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
.
Influence on Rus' society
Historians have debated the long-term influence of Mongol rule on Rus society. The Mongols have been blamed for the destruction of Kievan Rus', the breakup of the ancient Rus nationality into three components, and the introduction of the concept of "oriental despotismOriental despotism
Oriental despotism is a term used to describe a despotic form of government that opposes the western tradition. Historically, the term's meaning has varied and today it is hardly ever used at all, largely because of all the issues surrounding the concept of orientalism.- Origins in Ancient Greece...
" into Russia. Historians also credit the Mongol regime with an important role in the development of Muscovy as a state. Under Mongol occupation, for example, Muscovy developed its mestnichestvo
Mestnichestvo
In Russian history, Mestnichestvo was a feudal hierarchical system in Russia from the 15th to 17th centuries. Mestnichestvo revolved around a simple principle: the boyar who estimated that his origins were more ancient and his personal services to the tsar more valuable could claim a higher state...
hierarchy, postal
Mail
Mail, or post, is a system for transporting letters and other tangible objects: written documents, typically enclosed in envelopes, and also small packages are delivered to destinations around the world. Anything sent through the postal system is called mail or post.In principle, a postal service...
road network, census
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population. It is a regularly occurring and official count of a particular population. The term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common...
, fiscal system, and military organization.
A significant number of historians consider the oppression of Rus' by the Mongols to be the major cause of what is sometimes called "the East-West gap" - approximately 200 years delay in introducing major social, political and economical reforms and scientific innovations in Russia compared to Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
. Specifically, the isolation from the West may have caused Russia's later non-involvement in the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, and failure to develop a middle class
Middle class
The middle class is any class of people in the middle of a societal hierarchy. In Weberian socio-economic terms, the middle class is the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the working class and upper class....
.
The period of Mongol rule over Russia included significant cultural and interpersonal contacts between the Russian and Mongolian ruling classes. By 1450, the Tatar language
Tatar language
The Tatar language , or more specifically Kazan Tatar, is a Turkic language spoken by the Tatars of historical Kazan Khanate, including modern Tatarstan and Bashkiria...
had become fashionable in the court of the Grand Prince of Moscow, Vasily II, who was accused of excessive love of the Tatars and their speech, and many Russian noblemen adopted Tatar surnames (for example, a member of the Veliamanov family adopted the Turkic name "Aksak" and his descendents were the Aksakov
Aksakov
Aksakov and Aksakova is a common Russian last name and may refer to:*Alexandr Aksakov , Russian author, translator, journalist, editor and psychic researcher*Ivan Aksakov , Russian journalist and slavophile...
s) Many Russian boyar
Boyar
A boyar, or bolyar , was a member of the highest rank of the feudal Moscovian, Kievan Rus'ian, Bulgarian, Wallachian, and Moldavian aristocracies, second only to the ruling princes , from the 10th century through the 17th century....
(noble) families traced their descent from the Mongols or Tatars, including Veliaminov-Zernov, Godunov
Godunov
Godunov is a Russian surname.Godunov can refer to the following:Two Tsars of Russia and their kin:** Tsar Boris Fyodorovich Godunov a regent of Russia from 1584 to 1598 and then tsar from 1598 to 1605...
, Arseniev, Bakhmetev, Bulgakov
Bulgakov
Bulgakov is a common Russian family name and may refer to:*Gediminid family of Princes Bulgakov*Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Bulgakov, Soviet politician, USSR Minister of Education 1978 to 1983*Aleksandr Viktorovich Bulgakov Bulgakov is a common Russian family name and may refer to:*Gediminid family...
(descendents of Bulgak) and Chaadaev (descendents of Genghis Khan's son Jagatay). In a survey of Russian noble families of the 17th century, over 15% of the Russian noble families had Tatar or Oriental origins.
The Mongols brought about changes in economics power of states and overall trade.
In the religious sphere, St. Paphnutius of Borovsk was the grandson of a Mongol baskak
Darughachi
Darughachi, which originally designated officials in the Mongol Empire in charge of taxes and administration in a certain province, is the plural form of the Mongolian word darugha. They were sometimes referred to as governors...
, or tax collector, while a nephew of khan
Khan (title)
Khan is an originally Altaic and subsequently Central Asian title for a sovereign or military ruler, widely used by medieval nomadic Turko-Mongol tribes living to the north of China. 'Khan' is also seen as a title in the Xianbei confederation for their chief between 283 and 289...
Bergai of the Golden Horde
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde was a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate that formed the north-western sector of the Mongol Empire...
converted to Christianity and became known as the monk St. Peter Tsarevich of the Horde
In the judicial sphere, under Mongol influence capital punishment, which during the times of Kievan Rus had only been applied to slaves, became widespread and the use of torture became a regular part of criminal procedure. Specific punishments introduced in Moscow included beheading for alleged traitors, branding of thieves (with execution for a third arrest). Penal law in western Europe in the Middle Ages was even harsher, however, than Mongol and Russian law.
The Russian language adopted numerous words from Mongol and Turkic. Such words include dengi (money), kazna (treasury), tamozhnia (customhouse), barysh (profit), and bashmak (shoe).
Successors of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde was succeeded by the KazanKhanate of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan was a medieval Tatar state which occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El,...
, Astrakhan, Crimean, and Siberian khanate
Siberia Khanate
The Khanate of Sibir were the patrilineal descendants of Shayban , the fifth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The Khanate had an ethnically diverse population of Siberian Tatars, Khanty, Mansi, Nenets and Selkup people. Along with the Khanate of Kazan it was the northernmost Muslim state....
s, as well as the Nogai Horde
Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation of about eighteen Turkic and Mongol tribes that occupied the Pontic-Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghits constituted a core of the Horde...
, all of which were eventually conquered by the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
.
See also
- Mongol invasion of Volga BulgariaMongol invasion of Volga BulgariaThe Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria lasted from 1223 to 1236.-The Mongol campaigns:In 1223, after defeating Russian and Cuman/Kipchak armies at the Battle of Kalka, a Mongol army under the generals Subutai and Jebe was sent to subdue Volga Bulgaria. At that point in history Genghis Khan's troops...
- Tatar invasionsTatar invasionsThe Mongol invasion of Europe from the east took place over the course of three centuries, from the Middle Ages to the early modern period.The terms Tatars or Tartars are applied to nomadic Turkic peoples who, themselves, were conquered by Mongols and incorporated into their horde...
- Mongol occupation of Eastern Europe

