
Montacute
Encyclopedia
Montacute is a small village
and civil parish in Somerset
, England, 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Yeovil
. The village has a population
of 680 (2002 estimate). The name Montacute is thought by some to derive from the Latin
"Mons Acutus", referring to the small but still quite acute hill
dominating the village to the west.
The village is built almost entirely of the local hamstone
. From the 15th century until the beginning of the 20th century it formed the heart of the estate
of the Phelips family of Montacute House
. The village has a fine medieval church, and a former Cluniac priory
, the gatehouse
of which is now a private house.
At the centre of the village is a large square
known as the 'Borough' around which are grouped picturesque cottage
s and a public house
, the Phelips Arms; there is a second public house and hotel
situated in the village, called the King's Arms.
hill fort
of Ham Hill, a large tribal fort of the Durotriges
. The fort was conquered by the Roman Legio II Augusta
sometime around 45 AD
. The Romans briefly occupied the fort, then moved to a more permanent garrison at nearby Ilchester
(Lindinis
), and constructed the Fosse Way
Roman Road
a few miles west of the village.
A Roman villa
was excavated near Batemoor Barn early in the twentieth century and an extensive mosaic
documented. However this was never adequately protected and has – probably – been damaged by deep ploughing in the last 20 years.
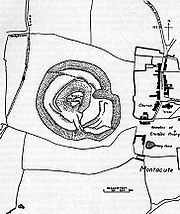 Variously called Logaresburgh by the Saxons
Variously called Logaresburgh by the Saxons
,later Bishoptone or Biscepstone the estate was owned by a Dane called Tofig; who is said to have been Harold Godwinson
's royal standard-bearer
. Montacute is reputed to have been named by Robert, Count of Mortain
, who built the motte-and-bailey
Montacute Castle
as his English seat in 1068 and founded the Cluniac priory. The site of the castle was a deliberate affront to the defeated English because a black flint cross (the "Holy Rood") was said to have been discovered atop the hill earlier in the eleventh century by the village blacksmith. This was supposedly placed in a wagon by Tofig, and he named a series of possible destinations owned by him. The oxen pulling the wagon (six red and six white in one version of the tale) refused to move until he said "Waltham". They then started, and continued non-stop until they reached Waltham
. When they stopped, Tofig decided to build an abbey at the site – this became Waltham Abbey
. This relic had become an object of veneration, pilgrimage and celebration. "Holy Cross" was the battle-cry of Harold's armies at the battles of Stamford Bridge
and Hastings
. The Holy Rood is said to have foretold Harold's defeat at Hastings: on the way there from the Battle of Stamford Bridge he stopped off at Waltham Abbey to pray, and the legend is that the cross "bowed down" off the wall as he did so. This was taken as a portent of doom.
The parish of Montacute was part of the Tintinhull
Hundred.
Castle Montacute was besieged by English rebels from Somerset, Dorset
and neighbouring areas in 1069 and its relief required the assembly of a considerable force, drawn chiefly from the Norman garrisons of London
, Winchester
and Salisbury
. This army was led by the Norman bishop, Geoffrey of Coutances
, whose large landholdings were also threatened. The rebels were taken by surprise and bloodily defeated, putting an end to the revolt. Joseph Bettey has suggested that "the devastation in the surrounding area which followed the English defeat may explain why so many manors in south Somerset are recorded in the Domesday Survey as having decreased in value". The English dead were buried in a mass grave to the West of the village in a sloping field now known as "Under Warren". Village tradition has it that two hilltop fortifications were built: first a wooden clamshell fort with motte & bailey, later replaced by a stone castle. However little evidence to prove the existence of the stone structure exists, except a note in the Parish records that two loads of stone were taken from the site by the neighbouring parish of Martock
. A church or chapel dedicated to St Michael later replaced the castle. Excavations of the hilltop have been limited and inconclusive.
 A folly
A folly
tower, built in 1760 by Edward Phelips V now occupies the hill-top. Known as St Michael's tower it stands on Mons Acutus which was the site of the former castle. The Hamstone
tower is about 5 metres (16.4 ft) in diameter, and rises 15 metres (49.2 ft) before curving inwards to a viewing platform which reached via a 52 step spiral staircase. It has been designated as a Grade II listed building and Scheduled Ancient Monument
.
Considerable earthworks are built into St Michaels Hill, and the common belief is that these are the remains of an extensive Motte & Bailey, however a report by the Somerset County Archeologist unit favours their view that these are in fact wine-growing terraces.
Montacute is much visited by tourists who come to the area, attracted by the nearby Ham Hill Country Park, and Montacute House
(now owned by the National Trust
) which is one of the finest examples of an Elizabethan
house in England, and several other mansion
s open to the public in the immediate vicinity.
In 2009 Montacute was identified as having England's longest life expectancy in a report compiled by Watson Wyatt Worldwide
.
groups on matters of crime, security, and traffic. The parish council's role also includes initiating projects for the maintenance and repair of parish facilities, as well as consulting with the district council on the maintenance, repair, and improvement of highways, drainage, footpaths, public transport, and street cleaning. Conservation matters (including trees and listed buildings) and environmental issues are also the responsibility of the council.
The village falls within the Non-metropolitan district
of South Somerset
, which was formed on April 1, 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972
, having previously been part of Yeovil Rural District
. The district council is responsible for local planning
and building control, local roads, council housing, environmental health
, market
s and fairs, refuse collection and recycling
, cemeteries and crematoria, leisure services, parks, and tourism
.
Somerset County Council
is responsible for running the largest and most expensive local services such as education
, social services, libraries
, main roads, public transport
, policing
and fire services, trading standards
, waste disposal and strategic planning.
It is also part of a county constituency represented in the House of Commons
of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP)
by the first past the post system of election, and part of the South West England constituency
of the European Parliament
which elects seven MEPs using the d'Hondt method
of party-list proportional representation
.
. To the south of the village, bounded by Woodhouse Lane, and the Roman roads of Park Lane and Hollow Lane lies the older Deer Park: this is divided into High Park and Low Park by the woodland path known as Ladies Walk. The oldest extant known road in the village is a track leading from the front of the Abbey Gatehouse to Ham Hill, via the defensive ramparts of Ham Hill. This track crosses another presumed Roman Road which runs on the line of Stanchester (site of a Roman Villa and the Stanchester Hoard
found there) - Under Warren (abandoned settlement) Batemore (Roman Villa) - Witcombe (abandoned settlement) - Norton Lane — High Wood. Another ancient track struck northeast from the Borough toward Ilchester, and is revealed by the housing layout but the route across the Park has been lost. This and the track to Ham Hill may possibly mark a Roman route between the fortifications of Ilchester and Ham Hill, but are probably older.
In addition to being a Scheduled Ancient Monument
, Iron Age
hill fort
and Roman
site, Ham Hill itself is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), Local Nature Reserve
and country park
. The geology supports a wide range of Fauna including mammals, birds, invertebrates, reptiles and amphibians living on lichens, fungi, ferns and flowering plants.
, Montacute has a temperate climate which is generally wetter and milder than the rest of the country. The annual mean temperature is approximately 10 °C (50 °F). Seasonal temperature variation is less extreme than most of the United Kingdom because of the adjacent sea temperatures. The summer months of July and August are the warmest with mean daily maxima of approximately 21 °C (69.8 °F). In winter mean minimum temperatures of 1 °C (33.8 °F) or 2 °C (35.6 °F) are common. In the summer the Azores
high pressure affects the south-west of England, however convective cloud sometimes forms inland, reducing the number of hours of sunshine. Annual sunshine rates are slightly less than the regional average of 1,600 hours. In December 1998 there were 20 days without sun recorded at Yeovilton. Most the rainfall in the south-west is caused by Atlantic depressions or by convection
. Most of the rainfall in autumn and winter is caused by the Atlantic depressions, which is when they are most active. In summer, a large proportion of the rainfall is caused by sun heating the ground leading to convection and to showers and thunderstorms. Average rainfall is around 700 mm (27.6 in). About 8–15 days of snowfall is typical. November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, and June to August have the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.
 The Church of St Catherine has 12th century origins, and is a Grade II* listed building. The church underwent alterations in the 13th and 15th centuries and was extensively restored
The Church of St Catherine has 12th century origins, and is a Grade II* listed building. The church underwent alterations in the 13th and 15th centuries and was extensively restored
in 1870 by Henry Hall. The church contains monuments to the Phelips family including David and Ann, who died in 1484, and Bridget, died 1508. There are canopied effigies of Thomas, died 1588, and Elizabeth, died 1598. On the west wall is a marble monument to Edward, who died in 1690. An Anglo-Saxon Hamstone font
lay unidentified in the churchyard for many years, but has now been reinstated in place of its Tudor successor.
Little now remains of the Cluniac Montacute Priory
, which was a victim of the Reformation. The incorrectly named "Abbey Gatehouse
" remains as a private dwelling (it was a Priory — not an Abbey) as does the Monk's Pigeon Loft and Stewpond. The former infirmary for the Priory — the Grade II thatched "Monk's House" dating from the 15th century — is likewise a private dwelling.
of Montacute between 1885 and 1918 was the Reverend Charles Francis Powys (1843–1923), father of the writers John Cowper Powys
, Llewelyn Powys
and Theodore Francis Powys. Philippa Powys
, their sister, and another notable author, was born in Montacute.
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet with the population ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand , Though often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighbourhoods, such as the West Village in Manhattan, New...
and civil parish in Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
, England, 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Yeovil
Yeovil
Yeovil is a town and civil parish in south Somerset, England. The parish had a population of 27,949 at the 2001 census, although the wider urban area had a population of 42,140...
. The village has a population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
of 680 (2002 estimate). The name Montacute is thought by some to derive from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
"Mons Acutus", referring to the small but still quite acute hill
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. Hills often have a distinct summit, although in areas with scarp/dip topography a hill may refer to a particular section of flat terrain without a massive summit A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. Hills...
dominating the village to the west.
The village is built almost entirely of the local hamstone
Hamstone
Hamstone is the colloquial name given to stone from Ham Hill, Somerset, England. Hamstone is a Jurassic limestone from the Toarcian, or Upper Lias, stage. It is a well cemented medium to coarse grained limestone characterised by its honey-gold colour and marked bedding planes. The stone contains...
. From the 15th century until the beginning of the 20th century it formed the heart of the estate
Estate (house)
An estate comprises the houses and outbuildings and supporting farmland and woods that surround the gardens and grounds of a very large property, such as a country house or mansion. It is the modern term for a manor, but lacks the latter's now abolished jurisdictional authority...
of the Phelips family of Montacute House
Montacute House
Montacute House is a late Elizabethan country house situated in the South Somerset village of Montacute. This house is a textbook example of English architecture during a period that was moving from the medieval Gothic to the Renaissance Classical; this has resulted in Montacute being regarded as...
. The village has a fine medieval church, and a former Cluniac priory
Priory
A priory is a house of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or religious sisters , or monasteries of monks or nuns .The Benedictines and their offshoots , the Premonstratensians, and the...
, the gatehouse
Gatehouse
A gatehouse, in architectural terminology, is a building enclosing or accompanying a gateway for a castle, manor house, fort, town or similar buildings of importance.-History:...
of which is now a private house.
At the centre of the village is a large square
Town square
A town square is an open public space commonly found in the heart of a traditional town used for community gatherings. Other names for town square are civic center, city square, urban square, market square, public square, and town green.Most town squares are hardscapes suitable for open markets,...
known as the 'Borough' around which are grouped picturesque cottage
Cottage
__toc__In modern usage, a cottage is usually a modest, often cozy dwelling, typically in a rural or semi-rural location. However there are cottage-style dwellings in cities, and in places such as Canada the term exists with no connotations of size at all...
s and a public house
Public house
A public house, informally known as a pub, is a drinking establishment fundamental to the culture of Britain, Ireland, Australia and New Zealand. There are approximately 53,500 public houses in the United Kingdom. This number has been declining every year, so that nearly half of the smaller...
, the Phelips Arms; there is a second public house and hotel
Hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. The provision of basic accommodation, in times past, consisting only of a room with a bed, a cupboard, a small table and a washstand has largely been replaced by rooms with modern facilities, including en-suite bathrooms...
situated in the village, called the King's Arms.
History
To the west of the village is the Iron AgeIron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
hill fort
Hill fort
A hill fort is a type of earthworks used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze and Iron Ages. Some were used in the post-Roman period...
of Ham Hill, a large tribal fort of the Durotriges
Durotriges
The Durotriges were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset, south Wiltshire and south Somerset...
. The fort was conquered by the Roman Legio II Augusta
Legio II Augusta
Legio secunda Augusta , was a Roman legion, levied by Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus in 43 BC, and still operative in Britannia in the 4th century...
sometime around 45 AD
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
. The Romans briefly occupied the fort, then moved to a more permanent garrison at nearby Ilchester
Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parish, situated on the River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. The parish, which includes the village of Sock Dennis and the old parish of Northover, has a population of 2,021...
(Lindinis
Lindinis
Lindinis was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Ilchester, located in the English county of Somerset....
), and constructed the Fosse Way
Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road in England that linked Exeter in South West England to Lincoln in Lincolnshire, via Ilchester , Bath , Cirencester and Leicester .It joined Akeman Street and Ermin Way at Cirencester, crossed Watling Street at Venonis south...
Roman Road
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
a few miles west of the village.
A Roman villa
Villa
A villa was originally an ancient Roman upper-class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity,...
was excavated near Batemoor Barn early in the twentieth century and an extensive mosaic
Mosaic
Mosaic is the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. It may be a technique of decorative art, an aspect of interior decoration, or of cultural and spiritual significance as in a cathedral...
documented. However this was never adequately protected and has – probably – been damaged by deep ploughing in the last 20 years.

Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
,later Bishoptone or Biscepstone the estate was owned by a Dane called Tofig; who is said to have been Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson was the last Anglo-Saxon King of England.It could be argued that Edgar the Atheling, who was proclaimed as king by the witan but never crowned, was really the last Anglo-Saxon king...
's royal standard-bearer
Standard-bearer
A standard-bearer is a person who bears an emblem called an ensign or standard, i.e. either a type of flag or an inflexible but mobile image, which is used as a formal, visual symbol of a state, prince, military unit, etc.This can either be an occasional duty, often seen as an honour , or a...
. Montacute is reputed to have been named by Robert, Count of Mortain
Robert, Count of Mortain
Robert, Count of Mortain, 1st Earl of Cornwall was a Norman nobleman and the half-brother of William I of England. Robert was the son of Herluin de Conteville and Herleva of Falaise and was full brother to Odo of Bayeux. The exact year of Robert's birth is unknown Robert, Count of Mortain, 1st...
, who built the motte-and-bailey
Motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey is a form of castle, with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised earthwork called a motte, accompanied by an enclosed courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade...
Montacute Castle
Montacute Castle
Montacue Castle was a castle built on a hill overlooking the village of Montacute, Somerset, England.-Details:Montacute Castle was built after the Norman Conquest of England in 1066 by Robert of Mortain...
as his English seat in 1068 and founded the Cluniac priory. The site of the castle was a deliberate affront to the defeated English because a black flint cross (the "Holy Rood") was said to have been discovered atop the hill earlier in the eleventh century by the village blacksmith. This was supposedly placed in a wagon by Tofig, and he named a series of possible destinations owned by him. The oxen pulling the wagon (six red and six white in one version of the tale) refused to move until he said "Waltham". They then started, and continued non-stop until they reached Waltham
Waltham Abbey, Essex
Waltham Abbey is a market town of about 20,400 people in the south west of the county of Essex, in the East of England region. It is about 24 km north of London on the Greenwich Meridian and lies between the River Lea in the west and Epping Forest in the east. It takes its name from The Abbey...
. When they stopped, Tofig decided to build an abbey at the site – this became Waltham Abbey
Waltham Abbey (abbey)
The Abbey Church of Waltham Abbey has been a place of worship since at least 1030, and is in the town of Waltham Abbey, Essex, England. The Prime Meridian passes through its grounds. Harold Godwinson is said to be buried just outside the present abbey...
. This relic had become an object of veneration, pilgrimage and celebration. "Holy Cross" was the battle-cry of Harold's armies at the battles of Stamford Bridge
Battle of Stamford Bridge
The Battle of Stamford Bridge took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire in England on 25 September 1066, between an English army under King Harold Godwinson and an invading Norwegian force led by King Harald Hardrada of Norway and the English king's brother Tostig...
and Hastings
Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings occurred on 14 October 1066 during the Norman conquest of England, between the Norman-French army of Duke William II of Normandy and the English army under King Harold II...
. The Holy Rood is said to have foretold Harold's defeat at Hastings: on the way there from the Battle of Stamford Bridge he stopped off at Waltham Abbey to pray, and the legend is that the cross "bowed down" off the wall as he did so. This was taken as a portent of doom.
The parish of Montacute was part of the Tintinhull
Tintinhull (hundred)
The Hundred of Tintinhull is one of the 40 historical Hundreds in the ceremonial county of Somerset, England, dating from before the Norman conquest during the Anglo-Saxon era although exact dates are unknown. Each hundred had a 'fyrd', which acted as the local defence force and a court which was...
Hundred.
Castle Montacute was besieged by English rebels from Somerset, Dorset
Dorset
Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
and neighbouring areas in 1069 and its relief required the assembly of a considerable force, drawn chiefly from the Norman garrisons of London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, Winchester
Winchester
Winchester is a historic cathedral city and former capital city of England. It is the county town of Hampshire, in South East England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government district, and is located at the western end of the South Downs, along the course of...
and Salisbury
Salisbury
Salisbury is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England and the only city in the county. It is the second largest settlement in the county...
. This army was led by the Norman bishop, Geoffrey of Coutances
Geoffrey de Montbray
Geoffrey de Montbray , bishop of Coutances , a right-hand man of William the Conqueror, was a type of the great feudal prelate, warrior and administrator at need....
, whose large landholdings were also threatened. The rebels were taken by surprise and bloodily defeated, putting an end to the revolt. Joseph Bettey has suggested that "the devastation in the surrounding area which followed the English defeat may explain why so many manors in south Somerset are recorded in the Domesday Survey as having decreased in value". The English dead were buried in a mass grave to the West of the village in a sloping field now known as "Under Warren". Village tradition has it that two hilltop fortifications were built: first a wooden clamshell fort with motte & bailey, later replaced by a stone castle. However little evidence to prove the existence of the stone structure exists, except a note in the Parish records that two loads of stone were taken from the site by the neighbouring parish of Martock
Martock
Martock is a large village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated on the edge of the Somerset Levels north west of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The parish includes Hurst, approximately one mile south of the village, and Bower Hinton, which is located at the western end of the...
. A church or chapel dedicated to St Michael later replaced the castle. Excavations of the hilltop have been limited and inconclusive.

Folly
In architecture, a folly is a building constructed primarily for decoration, but either suggesting by its appearance some other purpose, or merely so extravagant that it transcends the normal range of garden ornaments or other class of building to which it belongs...
tower, built in 1760 by Edward Phelips V now occupies the hill-top. Known as St Michael's tower it stands on Mons Acutus which was the site of the former castle. The Hamstone
Hamstone
Hamstone is the colloquial name given to stone from Ham Hill, Somerset, England. Hamstone is a Jurassic limestone from the Toarcian, or Upper Lias, stage. It is a well cemented medium to coarse grained limestone characterised by its honey-gold colour and marked bedding planes. The stone contains...
tower is about 5 metres (16.4 ft) in diameter, and rises 15 metres (49.2 ft) before curving inwards to a viewing platform which reached via a 52 step spiral staircase. It has been designated as a Grade II listed building and Scheduled Ancient Monument
Scheduled Ancient Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a 'nationally important' archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorized change. The various pieces of legislation used for legally protecting heritage assets from damage and destruction are grouped under the term...
.
Considerable earthworks are built into St Michaels Hill, and the common belief is that these are the remains of an extensive Motte & Bailey, however a report by the Somerset County Archeologist unit favours their view that these are in fact wine-growing terraces.
Montacute is much visited by tourists who come to the area, attracted by the nearby Ham Hill Country Park, and Montacute House
Montacute House
Montacute House is a late Elizabethan country house situated in the South Somerset village of Montacute. This house is a textbook example of English architecture during a period that was moving from the medieval Gothic to the Renaissance Classical; this has resulted in Montacute being regarded as...
(now owned by the National Trust
National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, usually known as the National Trust, is a conservation organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland...
) which is one of the finest examples of an Elizabethan
Elizabethan era
The Elizabethan era was the epoch in English history of Queen Elizabeth I's reign . Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history...
house in England, and several other mansion
Mansion
A mansion is a very large dwelling house. U.S. real estate brokers define a mansion as a dwelling of over . A traditional European mansion was defined as a house which contained a ballroom and tens of bedrooms...
s open to the public in the immediate vicinity.
In 2009 Montacute was identified as having England's longest life expectancy in a report compiled by Watson Wyatt Worldwide
Watson Wyatt Worldwide
Watson Wyatt Worldwide, Inc. was a global consulting firm, which merged in January 2010 with Towers Perrin to form Towers Watson. The firm's services included managing the cost and effectiveness of employee benefit programs; developing attraction, retention and reward strategies; advising pension...
.
Governance
The parish council has responsibility for local issues, including setting an annual precept (local rate) to cover the council’s operating costs and producing annual accounts for public scrutiny. The parish council evaluates local planning applications and works with the local police, district council officers, and neighbourhood watchNeighbourhood Watch (UK)
The Neighbourhood Watch scheme in the United Kingdom is a partnership where people come together to make their communities safer. It involves the Police, Community Safety departments of local authorities, other voluntary organisations and, above all, individuals and families who want to make their...
groups on matters of crime, security, and traffic. The parish council's role also includes initiating projects for the maintenance and repair of parish facilities, as well as consulting with the district council on the maintenance, repair, and improvement of highways, drainage, footpaths, public transport, and street cleaning. Conservation matters (including trees and listed buildings) and environmental issues are also the responsibility of the council.
The village falls within the Non-metropolitan district
Non-metropolitan district
Non-metropolitan districts, or colloquially shire districts, are a type of local government district in England. As created, they are sub-divisions of non-metropolitan counties in a so-called "two-tier" arrangement...
of South Somerset
South Somerset
South Somerset is a local government district in Somerset, England.The South Somerset district covers and area of ranging from the borders with Devon and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. It has a population of approximately 158,000...
, which was formed on April 1, 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972
Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974....
, having previously been part of Yeovil Rural District
Yeovil Rural District
Yeovil was a rural district in Somerset, England, from 1894 to 1974.It was created in 1894 under the Local Government Act 1894.In 1974 it was abolished under the Local Government Act 1972 when it became part of South Somerset....
. The district council is responsible for local planning
Planning permission
Planning permission or planning consent is the permission required in the United Kingdom in order to be allowed to build on land, or change the use of land or buildings. Within the UK the occupier of any land or building will need title to that land or building , but will also need "planning...
and building control, local roads, council housing, environmental health
Environmental health
Environmental health is the branch of public health that is concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment that may affect human health...
, market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
s and fairs, refuse collection and recycling
Recycling
Recycling is processing used materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials, reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reduce energy usage, reduce air pollution and water pollution by reducing the need for "conventional" waste disposal, and lower greenhouse...
, cemeteries and crematoria, leisure services, parks, and tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".Tourism has become a...
.
Somerset County Council
Somerset County Council
Somerset County Council is the county council of Somerset in the South West of England, an elected local government authority responsible for the most significant local government services in most of the county.-Area covered:...
is responsible for running the largest and most expensive local services such as education
Local Education Authority
A local education authority is a local authority in England and Wales that has responsibility for education within its jurisdiction...
, social services, libraries
Library
In a traditional sense, a library is a large collection of books, and can refer to the place in which the collection is housed. Today, the term can refer to any collection, including digital sources, resources, and services...
, main roads, public transport
Public transport
Public transport is a shared passenger transportation service which is available for use by the general public, as distinct from modes such as taxicab, car pooling or hired buses which are not shared by strangers without private arrangement.Public transport modes include buses, trolleybuses, trams...
, policing
Police
The police is a personification of the state designated to put in practice the enforced law, protect property and reduce civil disorder in civilian matters. Their powers include the legitimized use of force...
and fire services, trading standards
Trading Standards
Trading Standards is the name given to local authority departments in the UK formerly known as Weights and Measures. These departments investigate commercial organisations that carry out trade in unethical ways or outside the scope of the law.-History:...
, waste disposal and strategic planning.
It is also part of a county constituency represented in the House of Commons
British House of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which also comprises the Sovereign and the House of Lords . Both Commons and Lords meet in the Palace of Westminster. The Commons is a democratically elected body, consisting of 650 members , who are known as Members...
of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP)
Member of Parliament
A Member of Parliament is a representative of the voters to a :parliament. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, the term applies specifically to members of the lower house, as upper houses often have a different title, such as senate, and thus also have different titles for its members,...
by the first past the post system of election, and part of the South West England constituency
South West England (European Parliament constituency)
South West England is a constituency of the European Parliament. For 2009 it elects 6 MEPs using the d'Hondt method of party-list proportional representation, reduced from 7 in 2004.-Boundaries:...
of the European Parliament
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
which elects seven MEPs using the d'Hondt method
D'Hondt method
The d'Hondt method is a highest averages method for allocating seats in party-list proportional representation. The method described is named after Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt who described it in 1878...
of party-list proportional representation
Party-list proportional representation
Party-list proportional representation systems are a family of voting systems emphasizing proportional representation in elections in which multiple candidates are elected...
.
Geography
An area of grass parkland lies to the east of the village; this formed the eastern approach to Montacute House though the drive through the park is now unused. Although associated with the Montacute estate, the park lies mainly within the neighbouring village of OdcombeOdcombe
Odcombe is a village and civil parish in south Somerset, England, west of the town of Yeovil, with a population of 730 in 2002.The upper part of the village, Higher Odcombe, sits on the crest of the hill, while the lower part, Lower Odcombe, is built on its northern slopes...
. To the south of the village, bounded by Woodhouse Lane, and the Roman roads of Park Lane and Hollow Lane lies the older Deer Park: this is divided into High Park and Low Park by the woodland path known as Ladies Walk. The oldest extant known road in the village is a track leading from the front of the Abbey Gatehouse to Ham Hill, via the defensive ramparts of Ham Hill. This track crosses another presumed Roman Road which runs on the line of Stanchester (site of a Roman Villa and the Stanchester Hoard
Stanchester Hoard
The Stanchester Hoard is a hoard of 1,166 Roman coins dating from the fourth to early fifth century found at Wilcot, in the Vale of Pewsey, Wiltshire, England in 2000. The find was considered important because of the large quantity of unclipped silver coins contained within...
found there) - Under Warren (abandoned settlement) Batemore (Roman Villa) - Witcombe (abandoned settlement) - Norton Lane — High Wood. Another ancient track struck northeast from the Borough toward Ilchester, and is revealed by the housing layout but the route across the Park has been lost. This and the track to Ham Hill may possibly mark a Roman route between the fortifications of Ilchester and Ham Hill, but are probably older.
In addition to being a Scheduled Ancient Monument
Scheduled Ancient Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a 'nationally important' archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorized change. The various pieces of legislation used for legally protecting heritage assets from damage and destruction are grouped under the term...
, Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
hill fort
Hill fort
A hill fort is a type of earthworks used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze and Iron Ages. Some were used in the post-Roman period...
and Roman
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
site, Ham Hill itself is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), Local Nature Reserve
Local Nature Reserve
Local nature reserve or LNR is a designation for nature reserves in the United Kingdom. The designation has its origin in the recommendations of the Wild Life Conservation Special Committee which established the framework for nature conservation in the United Kingdom and suggested a national suite...
and country park
Country park
A country park is an area designated for people to visit and enjoy recreation in a countryside environment.-History:In the United Kingdom the term 'Country Park' has a special meaning. There are over 400 Country Parks in England alone . Most Country Parks were designated in the 1970s, under the...
. The geology supports a wide range of Fauna including mammals, birds, invertebrates, reptiles and amphibians living on lichens, fungi, ferns and flowering plants.
Climate
Along with the rest of South West EnglandSouth West England
South West England is one of the regions of England defined by the Government of the United Kingdom for statistical and other purposes. It is the largest such region in area, covering and comprising Bristol, Gloucestershire, Somerset, Dorset, Wiltshire, Devon, Cornwall and the Isles of Scilly. ...
, Montacute has a temperate climate which is generally wetter and milder than the rest of the country. The annual mean temperature is approximately 10 °C (50 °F). Seasonal temperature variation is less extreme than most of the United Kingdom because of the adjacent sea temperatures. The summer months of July and August are the warmest with mean daily maxima of approximately 21 °C (69.8 °F). In winter mean minimum temperatures of 1 °C (33.8 °F) or 2 °C (35.6 °F) are common. In the summer the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
high pressure affects the south-west of England, however convective cloud sometimes forms inland, reducing the number of hours of sunshine. Annual sunshine rates are slightly less than the regional average of 1,600 hours. In December 1998 there were 20 days without sun recorded at Yeovilton. Most the rainfall in the south-west is caused by Atlantic depressions or by convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
. Most of the rainfall in autumn and winter is caused by the Atlantic depressions, which is when they are most active. In summer, a large proportion of the rainfall is caused by sun heating the ground leading to convection and to showers and thunderstorms. Average rainfall is around 700 mm (27.6 in). About 8–15 days of snowfall is typical. November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, and June to August have the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.
Religious sites

Victorian restoration
Victorian restoration is the term commonly used to refer to the widespread and extensive refurbishment and rebuilding of Church of England churches and cathedrals that took place in England and Wales during the 19th-century reign of Queen Victoria...
in 1870 by Henry Hall. The church contains monuments to the Phelips family including David and Ann, who died in 1484, and Bridget, died 1508. There are canopied effigies of Thomas, died 1588, and Elizabeth, died 1598. On the west wall is a marble monument to Edward, who died in 1690. An Anglo-Saxon Hamstone font
Baptismal font
A baptismal font is an article of church furniture or a fixture used for the baptism of children and adults.-Aspersion and affusion fonts:...
lay unidentified in the churchyard for many years, but has now been reinstated in place of its Tudor successor.
Little now remains of the Cluniac Montacute Priory
Montacute Priory
Montacute Priory was a Cluniac priory of the Benedictine order in Montacute, Somerset, England, founded between 1078 and 1102 by William, Count of Mortain, in face of a threat that if he did not do so, the King would take the land from him. It was the only Somerset dependency of Cluny Abbey until...
, which was a victim of the Reformation. The incorrectly named "Abbey Gatehouse
Abbey Farmhouse, Montacute
Abbey Farmhouse is a detached house in Montacute, Somerset, England, which incorporates the gateway of the medieval Montacute Priory. It was built in the 16th century and has been designated as a Grade I listed building....
" remains as a private dwelling (it was a Priory — not an Abbey) as does the Monk's Pigeon Loft and Stewpond. The former infirmary for the Priory — the Grade II thatched "Monk's House" dating from the 15th century — is likewise a private dwelling.
Notable residents
The vicarVicar
In the broadest sense, a vicar is a representative, deputy or substitute; anyone acting "in the person of" or agent for a superior . In this sense, the title is comparable to lieutenant...
of Montacute between 1885 and 1918 was the Reverend Charles Francis Powys (1843–1923), father of the writers John Cowper Powys
John Cowper Powys
-Biography:Powys was born in Shirley, Derbyshire, in 1872, the son of the Reverend Charles Francis Powys , who was vicar of Montacute, Somerset for thirty-two years, and Mary Cowper Johnson, a descendent of the poet William Cowper. He came from a family of eleven children, many of whom were also...
, Llewelyn Powys
Llewelyn Powys
Llewelyn Powys was a British writer and younger brother of John Cowper Powys and T. F. Powys.-Life:Powys was born in Dorchester, the son of a clergyman, and was educated at Sherborne School and Corpus Christi College, Cambridge. While lecturing in the United States he contracted tuberculosis...
and Theodore Francis Powys. Philippa Powys
Philippa Powys
Catharine Edith Philippa Powys , a novelist and poet, belonged to one of the most distinguished families in modern literature.-Family:Among her brothers were the novelists John Cowper Powys and Theodore Francis Powys and the essayist Llewelyn Powys as well as Littleton Charles Powys , headmaster...
, their sister, and another notable author, was born in Montacute.

