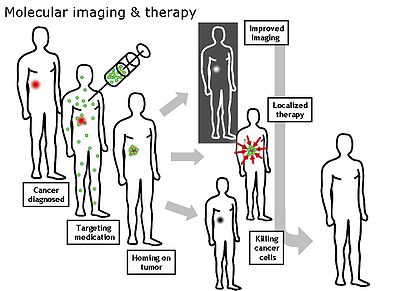
Nanomedicine
Encyclopedia
Nanomedicine is the medical
application of nanotechnology
. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials
, to nanoelectronic
biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology
. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity
and environmental impact
of nanoscale materials
. One nanometer is one-millionth of a millimeter.
Nanomedicine research is receiving funding from the US National Institute of Health. Of note is the funding in 2005 of a five-year plan to set up four nanomedicine centers. In April 2006, the journal Nature Materials
estimated that 130 nanotech-based drugs and delivery systems were being developed worldwide.
expects new commercial applications in the pharmaceutical industry that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and in vivo
imaging. Neuro-electronic interfaces and other nanoelectronics
-based sensors are another active goal of research. Further down the line, the speculative field of molecular nanotechnology
believes that cell repair machines
could revolutionize medicine and the medical field.
Nanomedicine is a large industry, with nanomedicine sales reaching 6.8 billion dollars in 2004, and with over 200 companies and 38 products worldwide, a minimum of 3.8 billion dollars in nanotechnology R&D is being invested every year. As the nanomedicine industry continues to grow, it is expected to have a significant impact on the economy.
and are awaiting human trials are using gold nanoshells to help diagnose and treat cancer
, and using liposomes as vaccine
adjuvants and as vehicles for drug transport. Similarly, drug detoxification is also another application for nanomedicine which has shown promising results in rats. A benefit of using nanoscale for medical technologies is that smaller devices are less invasive and can possibly be implanted inside the body, plus biochemical reaction times are much shorter. These devices are faster and more sensitive than typical drug delivery.
center on developing nanoscale particles
or molecules to improve drug bioavailability
. Bioavailability refers to the presence of drug molecules where they are needed in the body and where they will do the most good. Drug delivery focuses on maximizing bioavailability both at specific places in the body and over a period of time. This can potentially be achieved by molecular targeting by nanoengineered devices. It is all about targeting the molecules and delivering drugs with cell precision. More than $65 billion are wasted each year due to poor bioavailability. In vivo imaging is another area where tools and devices are being developed. Using nanoparticle
contrast agents, images such as ultrasound and MRI have a favorable distribution and improved contrast. The new methods of nanoengineered materials that are being developed might be effective in treating illnesses and diseases such as cancer. What nanoscientists will be able to achieve in the future is beyond current imagination. This might be accomplished by self assembled biocompatible nanodevices that will detect, evaluate, treat and report to the clinical doctor automatically.
Drug delivery systems, lipid- or polymer-based nanoparticles, can be designed to improve the pharmacological and therapeutic properties of drugs. The strength of drug delivery systems is their ability to alter the pharmacokinetics
and biodistribution
of the drug. When designed to avoid the body's defence mechanisms, nanoparticles have beneficial properties that can be used to improve drug delivery. Where larger particles would have been cleared from the body, cells take up these nanoparticles because of their size. Complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, including the ability to get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm
. Efficiency is important because many diseases depend upon processes within the cell and can only be impeded by drugs that make their way into the cell. Triggered response is one way for drug molecules to be used more efficiently. Drugs are placed in the body and only activate on encountering a particular signal. For example, a drug with poor solubility will be replaced by a drug delivery system where both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments exist, improving the solubility. Also, a drug may cause tissue damage, but with drug delivery, regulated drug release can eliminate the problem. If a drug is cleared too quickly from the body, this could force a patient to use high doses, but with drug delivery systems clearance can be reduced by altering the pharmacokinetics of the drug. Poor biodistribution is a problem that can affect normal tissues through widespread distribution, but the particulates
from drug delivery systems lower the volume of distribution and reduce the effect on non-target tissue. Potential nanodrugs will work by very specific and well-understood mechanisms; one of the major impacts of nanotechnology and nanoscience will be in leading development of completely new drugs with more useful behavior and less side effects.
like nanoparticles and Dendrimers is an emerging field called nanobiopharmaceutics
, and these products are called nanobiopharmaceuticals.
 The small size of nanoparticles endows them with properties that can be very useful in oncology
The small size of nanoparticles endows them with properties that can be very useful in oncology
, particularly in imaging. Quantum dots (nanoparticles with quantum confinement properties, such as size-tunable light emission), when used in conjunction with MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), can produce exceptional images of tumor sites. These nanoparticles are much brighter than organic dyes and only need one light source for excitation. This means that the use of fluorescent quantum dots could produce a higher contrast image and at a lower cost than today's organic dyes used as contrast media. The downside, however, is that quantum dots are usually made of quite toxic elements.
Another nanoproperty, high surface area to volume ratio, allows many functional groups to be attached to a nanoparticle, which can seek out and bind to certain tumor cells. Additionally, the small size of nanoparticles (10 to 100 nanometers), allows them to preferentially accumulate at tumor sites (because tumors lack an effective lymphatic drainage system). A very exciting research question is how to make these imaging nanoparticles do more things for cancer. For instance, is it possible to manufacture multifunctional nanoparticles that would detect, image, and then proceed to treat a tumor? This question is under vigorous investigation; the answer to which could shape the future of cancer treatment. A promising new cancer treatment that may one day replace radiation and chemotherapy is edging closer to human trials. Kanzius RF
therapy attaches microscopic nanoparticles to cancer cells and then "cooks" tumors inside the body with radio waves that heat only the nanoparticles and the adjacent (cancerous) cells.
Sensor test chips containing thousands of nanowires, able to detect proteins and other biomarkers left behind by cancer cells, could enable the detection and diagnosis of cancer in the early stages from a few drops of a patient's blood.
The basic point to use drug delivery is based upon three facts: a) efficient encapsulation of the drugs, b) successful delivery of said drugs to the targeted region of the body, and c) successful release of that drug there.
Researchers at Rice University
under Prof. Jennifer West, have demonstrated the use of 120 nm diameter nanoshell
s coated with gold to kill cancer tumors in mice. The nanoshells can be targeted to bond to cancerous cells by conjugating antibodies or peptides to the nanoshell surface. By irradiating the area of the tumor with an infrared laser, which passes through flesh without heating it, the gold is heated sufficiently to cause death to the cancer cells.
Nanoparticle
s of cadmium selenide
(quantum dots) glow when exposed to ultraviolet light. When injected, they seep into cancer
tumors. The surgeon can see the glowing tumor, and use it as a guide for more accurate tumor removal.
In photodynamic therapy
, a particle is placed within the body and is illuminated with light from the outside. The light gets absorbed by the particle and if the particle is metal, energy from the light will heat the particle and surrounding tissue. Light may also be used to produce high energy oxygen molecules which will chemically react with and destroy most organic molecules that are next to them (like tumors). This therapy is appealing for many reasons. It does not leave a “toxic trail” of reactive molecules throughout the body (chemotherapy) because it is directed where only the light is shined and the particles exist. Photodynamic therapy has potential for a noninvasive procedure for dealing with diseases, growth and tumors.
, medical imaging
, and as diagnostic sensors. However, the biodistribution of these nanoparticles is still imperfect due to the complex host's reactions to nano- and microsized materials[14] and the difficulty in targeting specific organs in the body. Nevertheless, a lot of work is still ongoing to optimize and better understand the potential and limitations of nanoparticulate systems. For example, current research in the excretory systems of mice shows the ability of gold composites to selectively target certain organs based on their size and charge. These composites are encapsulated by a dendrimer and assigned a specific charge and size. Positively-charged gold nanoparticles were found to enter the kidneys while negatively-charged gold nanoparticles remained in the liver and spleen. It is suggested that the positive surface charge of the nanoparticle decreases the rate of opsonization of nanoparticles in the liver, thus affecting the excretory pathway. Even at a relatively small size of 5 nm , though, these particles can become compartmentalized in the peripheral tissues, and will therefore accumulate in the body over time. While advancement of research proves that targeting and distribution can be augmented by nanoparticles, the dangers of nanotoxicity become an important next step in further understanding of their medical uses.
One limitation to this innovation is the fact that electrical interference is a possibility. Electric fields, electromagnetic pulses (EMP)
, and stray fields from other in vivo electrical devices can all cause interference. Also, thick insulators are required to prevent electron leakage, and if high conductivity of the in vivo medium occurs there is a risk of sudden power loss and “shorting out.” Finally, thick wires are also needed to conduct substantial power levels without overheating. Little practical progress has been made even though research is happening. The wiring of the structure is extremely difficult because they must be positioned precisely in the nervous system so that it is able to monitor and respond to nervous signals. The structures that will provide the interface must also be compatible with the body’s immune system so that they will remain unaffected in the body for a long time. In addition, the structures must also sense ionic currents and be able to cause currents to flow backward. While the potential for these structures is amazing, there is no timetable for when they will be available.
is a speculative subfield of nanotechnology regarding the possibility of engineering molecular assembler
s, machines which could re-order matter at a molecular or atomic scale. Molecular nanotechnology is highly theoretical, seeking to anticipate what inventions nanotechnology might yield and to propose an agenda for future inquiry. The proposed elements of molecular nanotechnology, such as molecular assemblers and nanorobots
are far beyond current capabilities.
in medicine, advocates say, would totally change the world of medicine
once it is realized. Nanomedicine would make use of these nanorobots (e.g., Computational Genes
), introduced into the body, to repair or detect damages and infections. According to Robert Freitas
of the Institute for Molecular Manufacturing, a typical blood
borne medical nanorobot would be between 0.5-3 micrometres in size, because that is the maximum size possible due to capillary
passage requirement. Carbon
could be the primary element used to build these nanorobots due to the inherent strength and other characteristics of some forms of carbon (diamond
/fullerene
composites), and nanorobots would be fabricated in desktop nanofactories specialized for this purpose.
Nanodevices could be observed at work inside the body using MRI, especially if their components were manufactured using mostly 13C atoms rather than the natural 12C isotope of carbon, since 13C has a nonzero nuclear magnetic moment. Medical nanodevices would first be injected into a human body, and would then go to work in a specific organ or tissue mass. The doctor will monitor the progress, and make certain that the nanodevices have gotten to the correct target treatment region. The doctor will also be able to scan a section of the body, and actually see the nanodevices congregated neatly around their target (a tumor mass, etc.) so that he or she can be sure that the procedure was successful.
The healthcare possibilities of these cell repair machines are impressive. Comparable to the size of viruses or bacteria, their compact parts would allow them to be more complex. The early machines will be specialized. As they open and close cell membranes or travel through tissue and enter cells and viruses, machines will only be able to correct a single molecular disorder like DNA damage or enzyme deficiency. Later, cell repair machines will be programmed with more abilities with the help of advanced AI systems.
Nanocomputers will be needed to guide these machines. These computers will direct machines to examine, take apart, and rebuild damaged molecular structures. Repair machines will be able to repair whole cells by working structure by structure. Then by working cell by cell and tissue by tissue, whole organs can be repaired. Finally, by working organ by organ, health is restored to the body. Cells damaged to the point of inactivity can be repaired because of the ability of molecular machines to build cells from scratch. Therefore, cell repair machines will free medicine from reliance on self repair alone.
is a branch of nanomedicine and nanotechnology that seeks to use nano-materials and nano-devices for the diagnosis, therapy, and management of renal diseases. It includes the following goals:
Advances in Nanonephrology are expected to be based on discoveries in the above areas that can provide nano-scale information on the cellular molecular machinery involved in normal kidney processes and in pathological states. By understanding the physical and chemical properties of proteins and other macromolecules at the atomic level in various cells in the kidney, novel therapeutic approaches can be designed to combat major renal diseases.
The nano-scale artificial kidney is a goal that many physicians dream of. Nano-scale engineering advances will permit programmable and controllable nano-scale robots to execute curative and reconstructive procedures in the human kidney at the cellular and molecular levels. Designing nanostructures compatible with the kidney cells and that can safely operate in vivo is also a future goal. The ability to direct events in a controlled fashion at the cellular nano-level has the potential of significantly improving the lives of patients with kidney diseases.
Journals
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
application of nanotechnology
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of manipulating matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally, nanotechnology deals with developing materials, devices, or other structures possessing at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres...
. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials is a field that takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology. It studies materials with morphological features on the nanoscale, and especially those that have special properties stemming from their nanoscale dimensions...
, to nanoelectronic
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refer to the use of nanotechnology on electronic components, especially transistors. Although the term nanotechnology is generally defined as utilizing technology less than 100 nm in size, nanoelectronics often refer to transistor devices that are so small that inter-atomic...
biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials...
. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity
Nanotoxicology
Nanotoxicology is the study of the toxicity of nanomaterials. Because of quantum size effects and large surface area to volume ratio, nanomaterials have unique properties compared with their larger counterparts....
and environmental impact
Implications of nanotechnology
The impact of nanotechnology extend from its medical, ethical, mental, legal and environmental applications, to fields such as engineering, biology, chemistry, computing, materials science, military applications, and communications....
of nanoscale materials
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials is a field that takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology. It studies materials with morphological features on the nanoscale, and especially those that have special properties stemming from their nanoscale dimensions...
. One nanometer is one-millionth of a millimeter.
Nanomedicine research is receiving funding from the US National Institute of Health. Of note is the funding in 2005 of a five-year plan to set up four nanomedicine centers. In April 2006, the journal Nature Materials
Nature Materials
Nature Materials, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Publishing Group. It was launched in September 2002. Vincent Dusastre is the launching and current chief editor...
estimated that 130 nanotech-based drugs and delivery systems were being developed worldwide.
Overview
Nanomedicine seeks to deliver a valuable set of research tools and clinically useful devices in the near future. The National Nanotechnology InitiativeNational Nanotechnology Initiative
The National Nanotechnology Initiative is a United States federal nanoscale science, engineering, and technology research and development program...
expects new commercial applications in the pharmaceutical industry that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and in vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
imaging. Neuro-electronic interfaces and other nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refer to the use of nanotechnology on electronic components, especially transistors. Although the term nanotechnology is generally defined as utilizing technology less than 100 nm in size, nanoelectronics often refer to transistor devices that are so small that inter-atomic...
-based sensors are another active goal of research. Further down the line, the speculative field of molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials...
believes that cell repair machines
Nanorobotics
Nanorobotics is the emerging technology field of creating machines or robots whose components are at or close to the scale of a nanometer . More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots, with devices ranging in size from...
could revolutionize medicine and the medical field.
Nanomedicine is a large industry, with nanomedicine sales reaching 6.8 billion dollars in 2004, and with over 200 companies and 38 products worldwide, a minimum of 3.8 billion dollars in nanotechnology R&D is being invested every year. As the nanomedicine industry continues to grow, it is expected to have a significant impact on the economy.
Medical use of nanomaterials
Two forms of nanomedicine that have already been tested in miceMICE
-Fiction:*Mice , alien species in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy*The Mice -Acronyms:* "Meetings, Incentives, Conferencing, Exhibitions", facilities terminology for events...
and are awaiting human trials are using gold nanoshells to help diagnose and treat cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, and using liposomes as vaccine
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
adjuvants and as vehicles for drug transport. Similarly, drug detoxification is also another application for nanomedicine which has shown promising results in rats. A benefit of using nanoscale for medical technologies is that smaller devices are less invasive and can possibly be implanted inside the body, plus biochemical reaction times are much shorter. These devices are faster and more sensitive than typical drug delivery.
Drug delivery
Nanomedical approaches to drug deliveryDrug delivery
Drug delivery is the method or process of administering a pharmaceutical compound to achieve a therapeutic effect in humans or animals. Drug delivery technologies modify drug release profile, absorption, distribution and elimination for the benefit of improving product efficacy and safety, as well...
center on developing nanoscale particles
Nanoparticle
In nanotechnology, a particle is defined as a small object that behaves as a whole unit in terms of its transport and properties. Particles are further classified according to size : in terms of diameter, coarse particles cover a range between 10,000 and 2,500 nanometers. Fine particles are sized...
or molecules to improve drug bioavailability
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
. Bioavailability refers to the presence of drug molecules where they are needed in the body and where they will do the most good. Drug delivery focuses on maximizing bioavailability both at specific places in the body and over a period of time. This can potentially be achieved by molecular targeting by nanoengineered devices. It is all about targeting the molecules and delivering drugs with cell precision. More than $65 billion are wasted each year due to poor bioavailability. In vivo imaging is another area where tools and devices are being developed. Using nanoparticle
Nanoparticle
In nanotechnology, a particle is defined as a small object that behaves as a whole unit in terms of its transport and properties. Particles are further classified according to size : in terms of diameter, coarse particles cover a range between 10,000 and 2,500 nanometers. Fine particles are sized...
contrast agents, images such as ultrasound and MRI have a favorable distribution and improved contrast. The new methods of nanoengineered materials that are being developed might be effective in treating illnesses and diseases such as cancer. What nanoscientists will be able to achieve in the future is beyond current imagination. This might be accomplished by self assembled biocompatible nanodevices that will detect, evaluate, treat and report to the clinical doctor automatically.
Drug delivery systems, lipid- or polymer-based nanoparticles, can be designed to improve the pharmacological and therapeutic properties of drugs. The strength of drug delivery systems is their ability to alter the pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to the determination of the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism...
and biodistribution
Biodistribution
Biodistribution is a method of tracking where compounds of interest travel in an experimental animal or human subject. For example, in the development of new compounds for PET scanning, a radioactive isotope is chemically joined with a peptide...
of the drug. When designed to avoid the body's defence mechanisms, nanoparticles have beneficial properties that can be used to improve drug delivery. Where larger particles would have been cleared from the body, cells take up these nanoparticles because of their size. Complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, including the ability to get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
. Efficiency is important because many diseases depend upon processes within the cell and can only be impeded by drugs that make their way into the cell. Triggered response is one way for drug molecules to be used more efficiently. Drugs are placed in the body and only activate on encountering a particular signal. For example, a drug with poor solubility will be replaced by a drug delivery system where both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments exist, improving the solubility. Also, a drug may cause tissue damage, but with drug delivery, regulated drug release can eliminate the problem. If a drug is cleared too quickly from the body, this could force a patient to use high doses, but with drug delivery systems clearance can be reduced by altering the pharmacokinetics of the drug. Poor biodistribution is a problem that can affect normal tissues through widespread distribution, but the particulates
Particulates
Particulates – also known as particulate matter , suspended particulate matter , fine particles, and soot – are tiny subdivisions of solid matter suspended in a gas or liquid. In contrast, aerosol refers to particles and/or liquid droplets and the gas together. Sources of particulate matter can be...
from drug delivery systems lower the volume of distribution and reduce the effect on non-target tissue. Potential nanodrugs will work by very specific and well-understood mechanisms; one of the major impacts of nanotechnology and nanoscience will be in leading development of completely new drugs with more useful behavior and less side effects.
Protein and peptide delivery
Protein and peptides exert multiple biological actions in human body and they have been identified as showing great promise for treatment of various diseases and disorders. These macromolecules are called biopharmaceuticals. Targeted and/or controlled delivery of these biopharmaceuticals using nanomaterialsNanomaterials
Nanomaterials is a field that takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology. It studies materials with morphological features on the nanoscale, and especially those that have special properties stemming from their nanoscale dimensions...
like nanoparticles and Dendrimers is an emerging field called nanobiopharmaceutics
Nanobiopharmaceutics
Nanobiopharmaceutics is an inter-disciplinary field involving delivery of biopharmaceutical products through nanobiotechnology applications like nanoparticles, liposomes. It involves knowledge from nanobiotechnology, biotechnology and biopharmaceutics....
, and these products are called nanobiopharmaceuticals.
Cancer

Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with cancer...
, particularly in imaging. Quantum dots (nanoparticles with quantum confinement properties, such as size-tunable light emission), when used in conjunction with MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), can produce exceptional images of tumor sites. These nanoparticles are much brighter than organic dyes and only need one light source for excitation. This means that the use of fluorescent quantum dots could produce a higher contrast image and at a lower cost than today's organic dyes used as contrast media. The downside, however, is that quantum dots are usually made of quite toxic elements.
Another nanoproperty, high surface area to volume ratio, allows many functional groups to be attached to a nanoparticle, which can seek out and bind to certain tumor cells. Additionally, the small size of nanoparticles (10 to 100 nanometers), allows them to preferentially accumulate at tumor sites (because tumors lack an effective lymphatic drainage system). A very exciting research question is how to make these imaging nanoparticles do more things for cancer. For instance, is it possible to manufacture multifunctional nanoparticles that would detect, image, and then proceed to treat a tumor? This question is under vigorous investigation; the answer to which could shape the future of cancer treatment. A promising new cancer treatment that may one day replace radiation and chemotherapy is edging closer to human trials. Kanzius RF
John Kanzius
John S. Kanzius was an American inventor, radio and TV engineer, one-time station owner and ham radio operator from Erie, Pennsylvania. He invented a method that has the potential to treat virtually all forms of cancer, with no side effects, and without the need for surgery or medication...
therapy attaches microscopic nanoparticles to cancer cells and then "cooks" tumors inside the body with radio waves that heat only the nanoparticles and the adjacent (cancerous) cells.
Sensor test chips containing thousands of nanowires, able to detect proteins and other biomarkers left behind by cancer cells, could enable the detection and diagnosis of cancer in the early stages from a few drops of a patient's blood.
The basic point to use drug delivery is based upon three facts: a) efficient encapsulation of the drugs, b) successful delivery of said drugs to the targeted region of the body, and c) successful release of that drug there.
Researchers at Rice University
Rice University
William Marsh Rice University, commonly referred to as Rice University or Rice, is a private research university located on a heavily wooded campus in Houston, Texas, United States...
under Prof. Jennifer West, have demonstrated the use of 120 nm diameter nanoshell
Nanoshell
A nanoshell is a type of spherical nanoparticle consisting of a dielectric core which is covered by a thin metallic shell . These nanoshells involve a quasiparticle called plasmon which is a collective excitation or quantum plasma oscillation where the electrons simultaneously oscillate with...
s coated with gold to kill cancer tumors in mice. The nanoshells can be targeted to bond to cancerous cells by conjugating antibodies or peptides to the nanoshell surface. By irradiating the area of the tumor with an infrared laser, which passes through flesh without heating it, the gold is heated sufficiently to cause death to the cancer cells.
Nanoparticle
Nanoparticle
In nanotechnology, a particle is defined as a small object that behaves as a whole unit in terms of its transport and properties. Particles are further classified according to size : in terms of diameter, coarse particles cover a range between 10,000 and 2,500 nanometers. Fine particles are sized...
s of cadmium selenide
Cadmium selenide
Cadmium selenide is a solid, binary compound of cadmium and selenium. Common names for this compound are cadmium selenide, cadmium selenide, and cadmoselite ....
(quantum dots) glow when exposed to ultraviolet light. When injected, they seep into cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
tumors. The surgeon can see the glowing tumor, and use it as a guide for more accurate tumor removal.
In photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy is used clinically to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including malignant cancers, and is recognised as a treatment strategy which is both minimally invasive and minimally toxic...
, a particle is placed within the body and is illuminated with light from the outside. The light gets absorbed by the particle and if the particle is metal, energy from the light will heat the particle and surrounding tissue. Light may also be used to produce high energy oxygen molecules which will chemically react with and destroy most organic molecules that are next to them (like tumors). This therapy is appealing for many reasons. It does not leave a “toxic trail” of reactive molecules throughout the body (chemotherapy) because it is directed where only the light is shined and the particles exist. Photodynamic therapy has potential for a noninvasive procedure for dealing with diseases, growth and tumors.
Surgery
At Rice University, a flesh welder is used to fuse two pieces of chicken meat into a single piece. The two pieces of chicken are placed together touching. A greenish liquid containing gold-coated nanoshells is dribbled along the seam. An infrared laser is traced along the seam, causing the two sides to weld together. This could solve the difficulties and blood leaks caused when the surgeon tries to restitch the arteries that have been cut during a kidney or heart transplant. The flesh welder could weld the artery perfectly.Visualization
Tracking movement can help determine how well drugs are being distributed or how substances are metabolized. It is difficult to track a small group of cells throughout the body, so scientists used to dye the cells. These dyes needed to be excited by light of a certain wavelength in order for them to light up. While different color dyes absorb different frequencies of light, there was a need for as many light sources as cells. A way around this problem is with luminescent tags. These tags are quantum dots attached to proteins that penetrate cell membranes. The dots can be random in size, can be made of bio-inert material, and they demonstrate the nanoscale property that color is size-dependent. As a result, sizes are selected so that the frequency of light used to make a group of quantum dots fluoresce is an even multiple of the frequency required to make another group incandesce. Then both groups can be lit with a single light source.Nanoparticle targeting
It is greatly observed that nanoparticles are promising tools for the advancement of drug deliveryDrug delivery
Drug delivery is the method or process of administering a pharmaceutical compound to achieve a therapeutic effect in humans or animals. Drug delivery technologies modify drug release profile, absorption, distribution and elimination for the benefit of improving product efficacy and safety, as well...
, medical imaging
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
, and as diagnostic sensors. However, the biodistribution of these nanoparticles is still imperfect due to the complex host's reactions to nano- and microsized materials[14] and the difficulty in targeting specific organs in the body. Nevertheless, a lot of work is still ongoing to optimize and better understand the potential and limitations of nanoparticulate systems. For example, current research in the excretory systems of mice shows the ability of gold composites to selectively target certain organs based on their size and charge. These composites are encapsulated by a dendrimer and assigned a specific charge and size. Positively-charged gold nanoparticles were found to enter the kidneys while negatively-charged gold nanoparticles remained in the liver and spleen. It is suggested that the positive surface charge of the nanoparticle decreases the rate of opsonization of nanoparticles in the liver, thus affecting the excretory pathway. Even at a relatively small size of 5 nm , though, these particles can become compartmentalized in the peripheral tissues, and will therefore accumulate in the body over time. While advancement of research proves that targeting and distribution can be augmented by nanoparticles, the dangers of nanotoxicity become an important next step in further understanding of their medical uses.
Neuro-electronic interfaces
Neuro-electronic interfacing is a visionary goal dealing with the construction of nanodevices that will permit computers to be joined and linked to the nervous system. This idea requires the building of a molecular structure that will permit control and detection of nerve impulses by an external computer. The computers will be able to interpret, register, and respond to signals the body gives off when it feels sensations. The demand for such structures is huge because many diseases involve the decay of the nervous system (ALS and multiple sclerosis). Also, many injuries and accidents may impair the nervous system resulting in dysfunctional systems and paraplegia. If computers could control the nervous system through neuro-electronic interface, problems that impair the system could be controlled so that effects of diseases and injuries could be overcome. Two considerations must be made when selecting the power source for such applications. They are refuelable and nonrefuelable strategies. A refuelable strategy implies energy is refilled continuously or periodically with external sonic, chemical, tethered, magnetic, or electrical sources. A nonrefuelable strategy implies that all power is drawn from internal energy storage which would stop when all energy is drained.One limitation to this innovation is the fact that electrical interference is a possibility. Electric fields, electromagnetic pulses (EMP)
Electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse is a burst of electromagnetic radiation. The abrupt pulse of electromagnetic radiation usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, especially a nuclear explosion, or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field...
, and stray fields from other in vivo electrical devices can all cause interference. Also, thick insulators are required to prevent electron leakage, and if high conductivity of the in vivo medium occurs there is a risk of sudden power loss and “shorting out.” Finally, thick wires are also needed to conduct substantial power levels without overheating. Little practical progress has been made even though research is happening. The wiring of the structure is extremely difficult because they must be positioned precisely in the nervous system so that it is able to monitor and respond to nervous signals. The structures that will provide the interface must also be compatible with the body’s immune system so that they will remain unaffected in the body for a long time. In addition, the structures must also sense ionic currents and be able to cause currents to flow backward. While the potential for these structures is amazing, there is no timetable for when they will be available.
Medical applications of molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnologyMolecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials...
is a speculative subfield of nanotechnology regarding the possibility of engineering molecular assembler
Molecular assembler
A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a "proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision". Some biological molecules such as ribosomes fit this definition. This is because they receive instructions from messenger RNA and...
s, machines which could re-order matter at a molecular or atomic scale. Molecular nanotechnology is highly theoretical, seeking to anticipate what inventions nanotechnology might yield and to propose an agenda for future inquiry. The proposed elements of molecular nanotechnology, such as molecular assemblers and nanorobots
Nanorobotics
Nanorobotics is the emerging technology field of creating machines or robots whose components are at or close to the scale of a nanometer . More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots, with devices ranging in size from...
are far beyond current capabilities.
Nanorobots
The somewhat speculative claims about the possibility of using nanorobotsNanorobotics
Nanorobotics is the emerging technology field of creating machines or robots whose components are at or close to the scale of a nanometer . More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots, with devices ranging in size from...
in medicine, advocates say, would totally change the world of medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
once it is realized. Nanomedicine would make use of these nanorobots (e.g., Computational Genes
Computational Genes
A computational gene is a molecular automaton consisting of a structural part anda functional part; and its design is such that it might work in a cellular environment.The structural part is a naturally occurring gene, which is used as a...
), introduced into the body, to repair or detect damages and infections. According to Robert Freitas
Robert Freitas
Robert A. Freitas Jr. is a Senior Research Fellow, one of four researchers at the nonprofit foundation Institute for Molecular Manufacturing in Palo Alto, California. He holds a 1974 Bachelor's degree majoring in both physics and psychology from Harvey Mudd College, and a 1978 Juris Doctor degree...
of the Institute for Molecular Manufacturing, a typical blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
borne medical nanorobot would be between 0.5-3 micrometres in size, because that is the maximum size possible due to capillary
Capillary
Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels and are parts of the microcirculation. They are only 1 cell thick. These microvessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter, connect arterioles and venules, and enable the exchange of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and many other nutrient and waste...
passage requirement. Carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
could be the primary element used to build these nanorobots due to the inherent strength and other characteristics of some forms of carbon (diamond
Diamond
In mineralogy, diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a variation of the face-centered cubic crystal structure called a diamond lattice. Diamond is less stable than graphite, but the conversion rate from diamond to graphite is negligible at ambient conditions...
/fullerene
Fullerene
A fullerene is any molecule composed entirely of carbon, in the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube. Spherical fullerenes are also called buckyballs, and they resemble the balls used in association football. Cylindrical ones are called carbon nanotubes or buckytubes...
composites), and nanorobots would be fabricated in desktop nanofactories specialized for this purpose.
Nanodevices could be observed at work inside the body using MRI, especially if their components were manufactured using mostly 13C atoms rather than the natural 12C isotope of carbon, since 13C has a nonzero nuclear magnetic moment. Medical nanodevices would first be injected into a human body, and would then go to work in a specific organ or tissue mass. The doctor will monitor the progress, and make certain that the nanodevices have gotten to the correct target treatment region. The doctor will also be able to scan a section of the body, and actually see the nanodevices congregated neatly around their target (a tumor mass, etc.) so that he or she can be sure that the procedure was successful.
Cell repair machines
Using drugs and surgery, doctors can only encourage tissues to repair themselves. With molecular machines, there will be more direct repairs. Cell repair will utilize the same tasks that living systems already prove possible. Access to cells is possible because biologists can insert needles into cells without killing them. Thus, molecular machines are capable of entering the cell. Also, all specific biochemical interactions show that molecular systems can recognize other molecules by touch, build or rebuild every molecule in a cell, and can disassemble damaged molecules. Finally, cells that replicate prove that molecular systems can assemble every system found in a cell. Therefore, since nature has demonstrated the basic operations needed to perform molecular-level cell repair, in the future, nanomachine based systems will be built that are able to enter cells, sense differences from healthy ones and make modifications to the structure.The healthcare possibilities of these cell repair machines are impressive. Comparable to the size of viruses or bacteria, their compact parts would allow them to be more complex. The early machines will be specialized. As they open and close cell membranes or travel through tissue and enter cells and viruses, machines will only be able to correct a single molecular disorder like DNA damage or enzyme deficiency. Later, cell repair machines will be programmed with more abilities with the help of advanced AI systems.
Nanocomputers will be needed to guide these machines. These computers will direct machines to examine, take apart, and rebuild damaged molecular structures. Repair machines will be able to repair whole cells by working structure by structure. Then by working cell by cell and tissue by tissue, whole organs can be repaired. Finally, by working organ by organ, health is restored to the body. Cells damaged to the point of inactivity can be repaired because of the ability of molecular machines to build cells from scratch. Therefore, cell repair machines will free medicine from reliance on self repair alone.
Nanonephrology
NanonephrologyNanonephrology
Nanonephrology is a branch of nanomedicine and nanotechnology that deals with:# the study of kidney protein structures at the atomic level;# nano-imaging approaches to study cellular processes in kidney cells; and...
is a branch of nanomedicine and nanotechnology that seeks to use nano-materials and nano-devices for the diagnosis, therapy, and management of renal diseases. It includes the following goals:
- the study of kidney protein structures at the atomic level
- nano-imaging approaches to study cellular processes in kidney cells
- nano medical treatments that utilize nanoparticles to treat various kidney diseases
Advances in Nanonephrology are expected to be based on discoveries in the above areas that can provide nano-scale information on the cellular molecular machinery involved in normal kidney processes and in pathological states. By understanding the physical and chemical properties of proteins and other macromolecules at the atomic level in various cells in the kidney, novel therapeutic approaches can be designed to combat major renal diseases.
The nano-scale artificial kidney is a goal that many physicians dream of. Nano-scale engineering advances will permit programmable and controllable nano-scale robots to execute curative and reconstructive procedures in the human kidney at the cellular and molecular levels. Designing nanostructures compatible with the kidney cells and that can safely operate in vivo is also a future goal. The ability to direct events in a controlled fashion at the cellular nano-level has the potential of significantly improving the lives of patients with kidney diseases.
See also
- NanobiotechnologyNanobiotechnologyBionanotechnology, nanobiotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blanket terms for various related technologies.This...
- Nanotechnology in fictionNanotechnology in fictionThe use of nanotechnology in fiction has attracted scholarly attention. The first use of the distinguishing concepts of nanotechnology was "There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom", a talk given by physicist Richard Feynman in 1959. K. Eric Drexler's 1987 book Engines of Creation introduced the...
- Top-down and bottom-up designTop-down and bottom-up designTop–down and bottom–up are strategies of information processing and knowledge ordering, mostly involving software, but also other humanistic and scientific theories . In practice, they can be seen as a style of thinking and teaching...
- NanosensorNanosensorNanosensors are any biological, chemical, or surgical sensory points used to convey information about nanoparticles to the macroscopic world. Their use mainly include various medicinal purposes and as gateways to building other nanoproducts, such as computer chips that work at the nanoscale and...
- Photodynamic therapyPhotodynamic therapyPhotodynamic therapy is used clinically to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including malignant cancers, and is recognised as a treatment strategy which is both minimally invasive and minimally toxic...
- ImpalefectionImpalefectionImpalefection is a method of gene delivery using nanomaterials, such as carbon nanofibers, carbon nanotubes, nanowires Ref.1. Needle-like nanostructures are synthesized perpendicular to the surface of a substrate. Plasmid DNA containing the gene, intended for intracellular delivery, is attached to...
- NanobiopharmaceuticsNanobiopharmaceuticsNanobiopharmaceutics is an inter-disciplinary field involving delivery of biopharmaceutical products through nanobiotechnology applications like nanoparticles, liposomes. It involves knowledge from nanobiotechnology, biotechnology and biopharmaceutics....
- Monitoring (medicine)Monitoring (medicine)In medicine, monitoring is the evaluation of a disease or condition over time.It can be performed by continuously measuring certain parameters , and/or by repeatedly performing medical tests .Transmitting data from a monitor to a distant...
External links
- Impact of Nanotechnology on Biomedical Sciences
- Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine
- European Technology Platform on Nanomedicine
- NCN Nano-Devices for Medicine and Biology: Tutorials
- NCN Nano-Devices for Medicine and Biology: Simulation Tools for Research
Journals

