Noise, Vibration, and Harshness
Encyclopedia
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), also known as noise and vibration (N&V), is the study and modification of the noise and vibration characteristics of vehicles, particularly cars and trucks. While noise and vibration can be readily measured, Harshness is a subjective quality, and is measured either via "jury" evaluations, or with analytical tools that provide results reflecting human subjective impressions. These latter tools belong to the field known as "psychoacoustics."
Interior NVH deals with noise and vibration experienced by the occupants of the cabin, while exterior NVH is largely concerned with the noise radiated by the vehicle, and includes drive-by noise testing.
NVH is mostly engineering, but often objective measurements fail to predict or correlate well with the subjective impression on human observers. This is partly because the human body has its own frequency response, e.g. the ear's response at moderate noise levels is approximated by A-weighting
, but this does not mean that two noises with the same A-weighted level are equally disturbing. The field of psychoacoustics
is partly concerned with this correlation.
In some cases the NVH engineer is asked to change the sound quality, i.e. adding or subtracting particular harmonics, rather than making the car quieter.
and road surface, brakes, and wind. Noise from cooling fans, or the HVAC
, alternator, and other engine accessories is also fairly common. Many problems are generated as either vibration or noise, transmitted via a variety of paths, and then radiated acoustically into the cabin. These are classified as "structure-borne" noise. Others are generated acoustically and propagated by airborne paths. Structure-borne noise is attenuated by isolation, while airborne noise is reduced by absorption or through the use of barrier materials. Vibrations are sensed at the steering wheel, the seat, armrests, or the floor and pedals. Some problems are sensed visually - such as the vibration of the header rail or rear view mirror on open topped cars.
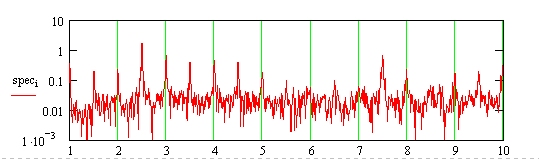
Tonal noises often have harmonic
s. Here is the noise spectrum of Michael Schumacher's Ferrari at 16680 rpm, showing the various harmonics. The x axis is given in terms of multiples of engine speed. The y axis is logarithmic, and uncalibrated.
s, accelerometer
s and force gauges, or load cells. Many NVH facilities will have semi-anechoic chamber
s, and rolling road dynamometer
s. Typically signals are recorded direct to hard disk via an Analog-to-digital converter
. In the past magnetic or DAT tape recorders were used. The integrity of the signal chain is very important, typically each of the instruments used are fully calibrated in a lab once per year, and any given setup is calibrated as a whole once per day.
Scanning Vibrometry is an essential tool for effective NVH optimization. The vibrational characteristics of a sample is acquired full field under operational or excited conditions. The results represent the actual vibrations. No added mass is influencing the measurement, as the sensor is light itself.
, rig tests, lead cladding, acoustic intensity, transfer path analysis, and partial coherence. Most NVH work is done in the frequency domain, using fast Fourier transform
s to convert the time domain signals into the frequency domain. Wavelet
analysis, order analysis, statistical energy analysis
, and subjective evaluation of signals modified in real time are also used.
One example is the modelling works for structure borne noise and vibration analysis. When the phenomenon being considered occurs below, say, 25-30 Hz, for example the idle shaking of the powertrain, a multi-body model can be used. In contrast, when the phenomenon being considered occurs at relatively high frequency, for example above 1 kHz, a Statistical Energy Analysis
(SEA) model may be a better approach.
Deciding which of these (or what combination) to use in solving a particular problem is one of the challenges facing the NVH engineer.
Specific methods for improving NVH include the use of Tuned mass damper
s, Subframe
s, balancing
, modifying the stiffness or mass of structures, retuning exhausts
and Intake
s, modifying the characteristics of elastomeric isolators, adding sound deadening or absorbing materials, or using active noise control
. In some circumstances, substantial changes in vehicle architecture may be the only way to cure some problems cost effectively.
Interior NVH deals with noise and vibration experienced by the occupants of the cabin, while exterior NVH is largely concerned with the noise radiated by the vehicle, and includes drive-by noise testing.
NVH is mostly engineering, but often objective measurements fail to predict or correlate well with the subjective impression on human observers. This is partly because the human body has its own frequency response, e.g. the ear's response at moderate noise levels is approximated by A-weighting
A-weighting
A Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
, but this does not mean that two noises with the same A-weighted level are equally disturbing. The field of psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the scientific study of sound perception. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological and physiological responses associated with sound...
is partly concerned with this correlation.
In some cases the NVH engineer is asked to change the sound quality, i.e. adding or subtracting particular harmonics, rather than making the car quieter.
Sources of NVH
The sources of noise in a vehicle are many, including the engine, driveline, tire contact patchContact patch
Contact patch is the portion of a vehicle's tire that is in actual contact with the road surface. It is most commonly used in the discussion of pneumatic tires, , where the term is strictly used to describe the portion of the tire’s tread that touches the road surface...
and road surface, brakes, and wind. Noise from cooling fans, or the HVAC
HVAC
HVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
, alternator, and other engine accessories is also fairly common. Many problems are generated as either vibration or noise, transmitted via a variety of paths, and then radiated acoustically into the cabin. These are classified as "structure-borne" noise. Others are generated acoustically and propagated by airborne paths. Structure-borne noise is attenuated by isolation, while airborne noise is reduced by absorption or through the use of barrier materials. Vibrations are sensed at the steering wheel, the seat, armrests, or the floor and pedals. Some problems are sensed visually - such as the vibration of the header rail or rear view mirror on open topped cars.
Tonal versus broadband
NVH can be tonal, such as engine noise, or broadband, such as road noise or wind noise, normally. Some resonant systems respond at characteristic frequencies, but in response to random excitation. Therefore, although they look like tonal problems on any one spectrum, their amplitude varies considerably. Other problems are self resonant, such as whistles from antennas.Tonal noises often have harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s. Here is the noise spectrum of Michael Schumacher's Ferrari at 16680 rpm, showing the various harmonics. The x axis is given in terms of multiples of engine speed. The y axis is logarithmic, and uncalibrated.

Instrumentation
Typical instrumentation used to measure NVH include microphoneMicrophone
A microphone is an acoustic-to-electric transducer or sensor that converts sound into an electrical signal. In 1877, Emile Berliner invented the first microphone used as a telephone voice transmitter...
s, accelerometer
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures proper acceleration, also called the four-acceleration. This is not necessarily the same as the coordinate acceleration , but is rather the type of acceleration associated with the phenomenon of weight experienced by a test mass that resides in the frame...
s and force gauges, or load cells. Many NVH facilities will have semi-anechoic chamber
Anechoic chamber
An anechoic chamber is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves.They are also insulated from exterior sources of noise...
s, and rolling road dynamometer
Dynamometer
A dynamometer or "dyno" for short, is a device for measuring force, moment of force , or power. For example, the power produced by an engine, motor or other rotating prime mover can be calculated by simultaneously measuring torque and rotational speed .A dynamometer can also be used to determine...
s. Typically signals are recorded direct to hard disk via an Analog-to-digital converter
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
. In the past magnetic or DAT tape recorders were used. The integrity of the signal chain is very important, typically each of the instruments used are fully calibrated in a lab once per year, and any given setup is calibrated as a whole once per day.
Scanning Vibrometry is an essential tool for effective NVH optimization. The vibrational characteristics of a sample is acquired full field under operational or excited conditions. The results represent the actual vibrations. No added mass is influencing the measurement, as the sensor is light itself.
Investigative techniques
Techniques used to help identify NVH include part substitution, modal analysisModal analysis
Modal analysis is the study of the dynamic properties of structures under vibrational excitation.Modal analysis is the field of measuring and analysing the dynamic response of structures and or fluids when excited by an input...
, rig tests, lead cladding, acoustic intensity, transfer path analysis, and partial coherence. Most NVH work is done in the frequency domain, using fast Fourier transform
Fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform is an efficient algorithm to compute the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. "The FFT has been called the most important numerical algorithm of our lifetime ." There are many distinct FFT algorithms involving a wide range of mathematics, from simple...
s to convert the time domain signals into the frequency domain. Wavelet
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
analysis, order analysis, statistical energy analysis
Statistical Energy Analysis
Statistical energy analysis is a method for predicting resonant sound and vibration transmission in dynamical systems made up of coupled acoustic cavities and structural parts. The vibrational behavior of the system is defined in terms of energy...
, and subjective evaluation of signals modified in real time are also used.
Computer-based modelling
NVH needs good representative prototypes of the production vehicle, for testing. These are needed early in the design process as the solutions often need substantial modification to the design, forcing in engineering changes which are much cheaper when made early. These early prototypes are very expensive, so there has been great interest in computer aided predictive techniques for NVH. Sometimes these work. Back-of-envelope calculations are very useful.One example is the modelling works for structure borne noise and vibration analysis. When the phenomenon being considered occurs below, say, 25-30 Hz, for example the idle shaking of the powertrain, a multi-body model can be used. In contrast, when the phenomenon being considered occurs at relatively high frequency, for example above 1 kHz, a Statistical Energy Analysis
Statistical Energy Analysis
Statistical energy analysis is a method for predicting resonant sound and vibration transmission in dynamical systems made up of coupled acoustic cavities and structural parts. The vibrational behavior of the system is defined in terms of energy...
(SEA) model may be a better approach.
Typical solutions
There are three principal means of improving NVH:- reducing the source strength, as in making a noise source quieter with a muffler, or improving the balance of a rotating mechanism;
- interrupting the noise or vibration path, with barriers (for noise) or isolators (for vibration); or
- absorption of the noise or vibration energy, as for example with foam noise absorbers, or tuned vibration dampers.
Deciding which of these (or what combination) to use in solving a particular problem is one of the challenges facing the NVH engineer.
Specific methods for improving NVH include the use of Tuned mass damper
Tuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper, also known as an active mass damper or harmonic absorber, is a device mounted in structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. Their application can prevent discomfort, damage, or outright structural failure...
s, Subframe
Subframe
A subframe is a structural component of a vehicle, such as an automobile or an aircraft, that uses a discrete, separate structure within a larger body-on-frame or unit body to carry certain components, such as the engine, drivetrain, or suspension. The subframe is bolted and/or welded to the vehicle...
s, balancing
Engine balance
Engine balance is the design, construction and tuning of an engine to run smoothly. Improving engine balance reduces vibration and other stresses and can improve the overall performance, efficiency, cost of ownership and reliability of the engine, as well as reducing the stress on other machinery...
, modifying the stiffness or mass of structures, retuning exhausts
Exhaust system
An exhaust system is usually tubing used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes...
and Intake
Intake
An intake , or especially for aircraft inlet, is an air intake for an engine. Because the modern internal combustion engine is in essence a powerful air pump, like the exhaust system on an engine, the intake must be carefully engineered and tuned to provide the greatest efficiency and power...
s, modifying the characteristics of elastomeric isolators, adding sound deadening or absorbing materials, or using active noise control
Active noise control
Active noise control is a method for reducing unwanted sound.- Explanation :...
. In some circumstances, substantial changes in vehicle architecture may be the only way to cure some problems cost effectively.
See also
- Acoustical measurements and instrumentationAcoustical measurements and instrumentationAnalysis of sound and acoustics plays a role in such engineering tasks as product design, production test, machine performance, and process control. For instance, product design can require modification of sound level or noise for compliance with standards from ANSI, IEC, and ISO. The work might...
- AcousticsAcousticsAcoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
- Acoustic quietingAcoustic quietingOne of the major reasons for the development of acoustic quieting techniques was for making submarines difficult to detect by sonar. This military goal of the mid- and late-twentieth century allowed the technology to be adapted to many industries and products, such as computers , automobiles , and...
- Noise controlNoise controlNoise control is an active or passive means of reducing sound emissions, often incentivised by personal comfort, environmental considerations or legal compliance. Practical and efficient noise control is wholly reliant on an accurate diagnosis of what is causing the noise, which first involves...
- Noise mitigationNoise mitigationNoise mitigation is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution. The main areas of noise mitigation or abatement are: transportation noise control, architectural design, and occupational noise control...
- Noise health effectsNoise health effectsNoise health effects are the health consequences of elevated sound levels. Elevated workplace or other noise can cause hearing impairment, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, annoyance and sleep disturbance. Changes in the immune system and birth defects have been attributed to noise exposure...
- SoundproofingSoundproofingSoundproofing is any means of reducing the sound pressure with respect to a specified sound source and receptor. There are several basic approaches to reducing sound: increasing the distance between source and receiver, using noise barriers to reflect or absorb the energy of the sound waves, using...
- Vibration isolationVibration isolationVibration isolation is the process of isolating an object, such as a piece of equipment, from the source of vibrations.-Passive isolation:Passive vibration isolation systems consist essentially of a mass, spring and damper ....
- Sound maskingSound maskingSound masking is the addition of natural or artificial sound into an environment to cover up unwanted sound by using auditory masking. This is in contrast to the technique of active noise control...
- ResonanceResonanceIn physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
- Sound pressure level
- VibrationVibrationVibration refers to mechanical oscillations about an equilibrium point. The oscillations may be periodic such as the motion of a pendulum or random such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road.Vibration is occasionally "desirable"...
- Whole body vibrationWhole body vibrationWhole body vibration , as a therapy, was explored by Russian scientist Vladimir Nazarov, who tested vibration on cosmonauts in an effort to decrease the loss of muscle and bone mass in space. As there is minimal gravitational force in space, muscles and bones are not loaded as they normally are on...
External links
- Structural Dynamics Testing/Modal Analysis
- Animating Vibration Test Results
- Some NVH application examples from HEAD acoustics
- Bruel and Kjaer's introductory notes for noise and vibration analysis
- Agilent's Fundamentals of Signal Analysis
- The Dirac Delta Science & Engineering Encyclopedia NVH Section
- Noise and Vibration Introduction
- An introduction to Transfer Path Analysis

