
Octadecagon
Encyclopedia
| Regular octadecagon | |
|---|---|
| Edge Edge (geometry) In geometry, an edge is a one-dimensional line segment joining two adjacent zero-dimensional vertices in a polygon. Thus applied, an edge is a connector for a one-dimensional line segment and two zero-dimensional objects.... s and vertices Vertex (geometry) In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:... |
18 |
| Schläfli symbol | {18} |
| Coxeter–Dynkin diagram | |
| Symmetry group Symmetry group The symmetry group of an object is the group of all isometries under which it is invariant with composition as the operation... |
Dihedral (D18) |
| Area Area Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat... (with t=edge length) |
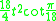 |
| Internal angle Internal angle In geometry, an interior angle is an angle formed by two sides of a polygon that share an endpoint. For a simple, convex or concave polygon, this angle will be an angle on the 'inner side' of the polygon... (degree Degree (angle) A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians... s) |
160° |
| Properties | convex Convex polygon In geometry, a polygon can be either convex or concave .- Convex polygons :A convex polygon is a simple polygon whose interior is a convex set... , cyclic, equilateral Equilateral In geometry, an equilateral polygon is a polygon which has all sides of the same length.For instance, an equilateral triangle is a triangle of equal edge lengths... , isogonal, isotoxal |
An octadecagon is a polygon
Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
with 18 sides
Edge (geometry)
In geometry, an edge is a one-dimensional line segment joining two adjacent zero-dimensional vertices in a polygon. Thus applied, an edge is a connector for a one-dimensional line segment and two zero-dimensional objects....
and 18 vertices
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
. Another name for an octadecagon is octakaidecagon.
Construction
A regular octadecagon cannot be constructedConstructible polygon
In mathematics, a constructible polygon is a regular polygon that can be constructed with compass and straightedge. For example, a regular pentagon is constructible with compass and straightedge while a regular heptagon is not....
using compass and straightedge
Compass and straightedge
Compass-and-straightedge or ruler-and-compass construction is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an idealized ruler and compass....
.
Petrie polygons
The regular octadecagon is the Petrie polygonPetrie polygon
In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of n dimensions is a skew polygon such that every consecutive sides belong to one of the facets...
for a number of higher dimensional polytopes, shown in these skew orthogonal projections from Coxeter planes:
| A17 | 17-simplex |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC9 | 9-orthoplex |
Rectified 9-orthoplex Rectified 9-orthoplex In nine-dimensional geometry, a rectified 9-simplex is a convex uniform 9-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 9-orthoplex.There are 9 rectifications of the 9-orthoplex. Vertices of the rectified 9-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 9-orthoplex. Vertices of the birectified... |
Birectified 9-orthoplex |
Trirectified 9-orthoplex |
Quadrirectified 9-cube |
Trirectified 9-cube |
Birectified 9-cube |
Rectified 9-cube Rectified 9-cube In nine-dimensional geometry, a rectified 9-cube is a convex uniform 9-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 9-cube.There are 9 rectifications of the 9-cube. The zeroth is the 9-cube itself, and the 8th is the dual 9-orthoplex. Vertices of the rectified 9-cube are located at the... |
9-cube |
| D10 | t8(171) |
t7(171) Rectified 10-orthoplex In ten-dimensional geometry, a rectified 10-orthoplex is a convex uniform 10-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 10-orthoplex.There are 10 rectifications of the 10-orthoplex. Vertices of the rectified 10-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 9-orthoplex. Vertices of the... |
t6(171) |
t5(171) |
t4(171) |
t3(171) |
t2(171) |
t1(171) |
10-demicube 10-demicube In geometry, a demidekeract or 10-demicube is a uniform 10-polytope, constructed from the 10-cube with alternated vertices deleted. It is part of a dimensionally infinite family of uniform polytopes called demihypercubes.... (171) |
| E7 | (321) |
t1(321) |
t2(321) |
(231) Gosset 2 31 polytope In 7-dimensional geometry, 231 is a uniform polytope, constructed from the E7 group.Coxeter named it 231 by its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of one of the 2-node sequences.... |
t1(231) Gosset 2 31 polytope In 7-dimensional geometry, 231 is a uniform polytope, constructed from the E7 group.Coxeter named it 231 by its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of one of the 2-node sequences.... |
t1(132) Gosset 1 32 polytope In 7-dimensional geometry, 132 is a uniform polytope, constructed from the E7 group.Coxeter named it 132 by its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of one of the 1-node sequences.... |
(132) Gosset 1 32 polytope In 7-dimensional geometry, 132 is a uniform polytope, constructed from the E7 group.Coxeter named it 132 by its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of one of the 1-node sequences.... |

