
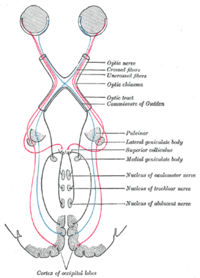
Optic tract
Encyclopedia
The optic tract is a part of the visual system
in the brain
.
It is a continuation of the optic nerve
and runs from the optic chiasm
(where half of the information from each eye crosses sides, and half stays on the same side) to the lateral geniculate nucleus
.
In split-brain
patients whom have undergone a corpus callosotomy
(usually to treat severe epilepsy
) the information from one optic tract does not get transmitted to both hemispheres. In carefully controlled experiments, split brain patients shown an image in his or her left left visual field (that is, the left half of what both eyes see), will be unable to vocally name what he or she has seen as the speech-control center is in the left brain hemisphere in most people. See the main article, split-brain
.
Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
in the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
.
It is a continuation of the optic nerve
Optic nerve
The optic nerve, also called cranial nerve 2, transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. Derived from the embryonic retinal ganglion cell, a diverticulum located in the diencephalon, the optic nerve doesn't regenerate after transection.-Anatomy:The optic nerve is the second of...
and runs from the optic chiasm
Optic chiasm
The optic chiasm or optic chiasma is the part of the brain where the optic nerves partially cross...
(where half of the information from each eye crosses sides, and half stays on the same side) to the lateral geniculate nucleus
Lateral geniculate nucleus
The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary relay center for visual information received from the retina of the eye. The LGN is found inside the thalamus of the brain....
.
Right vs. left
The relationships of the retinal fibers to the optic tracts are illustrated below, with the nasal retinal fibers in blue and the temporal retinal fibers in red.
| optic tract | temporal retinal fibers | nasal retinal fiber >- | right optic tract |
from the right eye | >- | from the left eye | from the right eye |
In split-brain
Split-brain
Split-brain is a lay term to describe the result when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. The surgical operation to produce this condition is called corpus callosotomy and is usually used as a last resort to treat otherwise intractable epilepsy...
patients whom have undergone a corpus callosotomy
Corpus callosotomy
Corpus callosotomy is a surgical procedure that disconnects the cerebral hemispheres, resulting in a condition called split-brain....
(usually to treat severe epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
) the information from one optic tract does not get transmitted to both hemispheres. In carefully controlled experiments, split brain patients shown an image in his or her left left visual field (that is, the left half of what both eyes see), will be unable to vocally name what he or she has seen as the speech-control center is in the left brain hemisphere in most people. See the main article, split-brain
Split-brain
Split-brain is a lay term to describe the result when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. The surgical operation to produce this condition is called corpus callosotomy and is usually used as a last resort to treat otherwise intractable epilepsy...
.

