
Organorhodium chemistry
Encyclopedia
Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry
of organometallic compounds containing a carbon
to rhodium
chemical bond
, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reaction
s.
Organometallic rhodium compounds share many characteristics with those of cobalt (see organocobalt compounds) in the same group 9
. Rhodium can exist in oxidation states +IV to -III but +I and +III are the most common. Rhodium(I) compounds (d8 configuration) can occur with square planar geometries and with trigonal bipyramidal geometries. Important homoleptic rhodium compounds are tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl
Rh4(CO)10 and hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium
Rh6(CO)16. The hexarhodium compound is less preferred due to poor solubility. Both are important catalysts in hydroformylation
of alkenes often accompanied by a phosphine ligand:
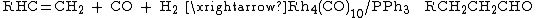
Nitrobenzene
reduction is another reaction catalysed by this compound type:
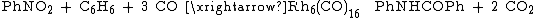
Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer [RhCl(COD)]2 is investigated for its use in C-H bond activation
. Sandwich compound
s of rhodium, such as rhodocene
, and half-sandwich compounds like [(η5-Cp
)Rh(CO)2] are well known.
compounds constitute an important class of organometallic chemistry. Although such compounds are well documented in the literature rhodium(III) cyclometalates with azo
function are spare. A typical example of this category viz. novel hexacoordinated orthometalated rhodium(III) thiolato complex trans-[Rh(C∧N∧S)Cl(PPh3)2] was synthesized from benzyl 2-(phenylazo)phenyl thioether and RhCl3·3H2O in the presence of excess PPh3 via in situ C(sp2)−H and C(sp3)−S bond scissions. This is the first example for a coordination compound of (phenylazo)thiolate ligand. The mechanism of formation of orthometalated azobenzene
derivative was described to proceed via initial coordination of azo-nitrogen followed by electrophilic substitution at the pendant phenyl ring. PPh3 plays a crucial role in the C(sp3)−S cleavage process. Reductive cleavage by single electron transfer (SET) mechanism is likely to be operative for the C−S bond cleavage. Unlike analogous (phenylazo)phenolato compound the orthometalated thiolato complex exhibits a fully reversible oxidative wave at 0.82 V vs Ag/AgCl and this response is supposed to be primarily centered on the thiolato sulfur atom .
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
of organometallic compounds containing a carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
to rhodium
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed...
chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reaction
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
s.
Organometallic rhodium compounds share many characteristics with those of cobalt (see organocobalt compounds) in the same group 9
Group 9 element
In modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 9 of the periodic table contains the elements cobalt , rhodium , iridium , and meitnerium . These are all d-block transition metals...
. Rhodium can exist in oxidation states +IV to -III but +I and +III are the most common. Rhodium(I) compounds (d8 configuration) can occur with square planar geometries and with trigonal bipyramidal geometries. Important homoleptic rhodium compounds are tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl
Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl
Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl is the chemical compound with the formula Rh412. This dark-red crystalline solid is the smallest stable binary rhodium carbonyl. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis.-Structure, synthesis, reactions:...
Rh4(CO)10 and hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium
Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium
Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium is a metal carbonyl cluster with the formula Rh616. It exists as black crystals that are soluble in organic solvents.-Discovery and synthesis:...
Rh6(CO)16. The hexarhodium compound is less preferred due to poor solubility. Both are important catalysts in hydroformylation
Hydroformylation
Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond...
of alkenes often accompanied by a phosphine ligand:
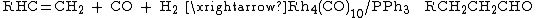
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to aniline. Although occasionally used as a flavoring or perfume...
reduction is another reaction catalysed by this compound type:
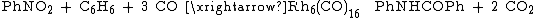
Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer [RhCl(COD)]2 is investigated for its use in C-H bond activation
C-H bond activation
Carbon–hydrogen bond activation or C−H activation may be defined as a reaction that cleaves a carbon–hydrogen bond. Often the term is restricted to reactions involving organometallic complexes and proceeding by coordination of a hydrocarbon to the inner-sphere of metal, either via an...
. Sandwich compound
Sandwich compound
In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic covalent bonds to two arene ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives...
s of rhodium, such as rhodocene
Rhodocene
Rhodocene, formally known as bisrhodium, is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has covalent...
, and half-sandwich compounds like [(η5-Cp
Cyclopentadienyl
In organic chemistry, cyclopentadienyl is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C5H5. Cyclopentadienyl are closely related to cyclopentadiene. Cyclopentadienyl have five carbon atoms bonded together in a pentagonal planar ring, all five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms...
)Rh(CO)2] are well known.
| Name | Molecular formula | CAS |
|---|---|---|
| (Acetylacetonato)dicarbonylrhodium(I) | Rh(CO)2(C5H7O2) | 14874-82-9 |
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-diene-rhodium(I) chloride dimer |
C14H16Cl2Rh2 | 12257-42-0 |
| Chloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)rhodium(I) dimer |
C16H24Cl2Rh2 | 12092-47-6 |
| (Acetylacetonato)(norbornadiene)rhodium(I) |
C12H15O22Rh | 32354-50-0 |
| Chloro(1,5-hexadiene)rhodium(I),dimer |
C12H24Rh2Cl2 | 32965-49-4 |
| Acetylacetonatobis(ethylene)rhodium(I) |
C9H15O2Rh | 12082-47-2 |
| [1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane](1,5-cyclooctadiene)rhodium(I) tetrafluoroborate |
C36H40BF4P2Rh | 79255-71-3 |
Cyclometallation
Cyclometalated rhodiumRhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed...
compounds constitute an important class of organometallic chemistry. Although such compounds are well documented in the literature rhodium(III) cyclometalates with azo
Azo
Azo may refer to:* Azo compound, chemistry functional group and class of compounds, also used for CDs and DVDs* A urinary tract analgesic also known as phenazopyridine* the medieval Italian jurist, see Azo of Bologna...
function are spare. A typical example of this category viz. novel hexacoordinated orthometalated rhodium(III) thiolato complex trans-[Rh(C∧N∧S)Cl(PPh3)2] was synthesized from benzyl 2-(phenylazo)phenyl thioether and RhCl3·3H2O in the presence of excess PPh3 via in situ C(sp2)−H and C(sp3)−S bond scissions. This is the first example for a coordination compound of (phenylazo)thiolate ligand. The mechanism of formation of orthometalated azobenzene
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the best known example of an azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of molecules that share the core azobenzene structure, with different chemical...
derivative was described to proceed via initial coordination of azo-nitrogen followed by electrophilic substitution at the pendant phenyl ring. PPh3 plays a crucial role in the C(sp3)−S cleavage process. Reductive cleavage by single electron transfer (SET) mechanism is likely to be operative for the C−S bond cleavage. Unlike analogous (phenylazo)phenolato compound the orthometalated thiolato complex exhibits a fully reversible oxidative wave at 0.82 V vs Ag/AgCl and this response is supposed to be primarily centered on the thiolato sulfur atom .
See also
- Chemical bonds of carbon with other elements in the periodic table:

