Outline of Estonia
Encyclopedia
Estonia
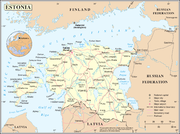
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
is a sovereign country located in the Baltic region
Baltic region
The terms Baltic region, Baltic Rim countries, and Baltic Rim refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea.- Etymology :...
of Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. Estonia is bordered to the north by Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
across the Gulf of Finland
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn...
, to the west by Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, to the south by Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
(343 km), and to the east by the Russian Federation
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(338,6 km). The territory of Estonia covers 45,227 km² and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate.
The Estonians
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns, with the Estonian language
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
sharing many similarities to Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
. The modern name of Estonia is thought to originate from the Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
historian Tacitus
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
, who in his book Germania
Germania (book)
The Germania , written by Gaius Cornelius Tacitus around 98, is an ethnographic work on the Germanic tribes outside the Roman Empire.-Contents:...
(ca. AD 98) described a people called the Aestii. Similarly, ancient Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
n sagas
Sagàs
Sagàs is a small town and municipality located in Catalonia, in the comarca of Berguedà. It is located in the geographical area of the pre-Pyrenees.-Population:...
refer to a land called Eistland. Early Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
and other ancient versions of the name are Estia and Hestia. Until the late 1930s, the name was often written as Esthonia in most English speaking countries.
Estonia is a democratic parliamentary republic
Parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic or parliamentary constitutional republic is a type of republic which operates under a parliamentary system of government - meaning a system with no clear-cut separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches. There are a number of variations of...
and is divided into fifteen counties. The capital and largest city is Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
. Estonia has been a member of the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
since 17 September 1991 of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
since 1 May 2004 and of NATO since 29 March 2004. Estonia has also signed the Kyoto protocol
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change , aimed at fighting global warming...
. With only 1.3 million inhabitants, it comprises one of the smallest populations of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
countries.
The settlement of modern day Estonia began around 8500 BC, immediately after the Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Over the centuries, the Estonians were subjected to Danish
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, Teutonic, Swedish
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n rule. Foreign rule in Estonia began in 1227, when as a consequence of the Northern Crusades
Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Christian kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea...
the area was conquered by Danes and Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
. From 1228–1562, parts or most of Estonia were incorporated into the loosely organized Livonian Confederation
Livonian Confederation
Terra Mariana was the official name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia which was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade in the territories comprising present day Estonia and Latvia...
of Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
, during which time economic activity centered around the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
. In the 16th century, Estonia passed to Swedish
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire refers to the Kingdom of Sweden between 1561 and 1721 . During this time, Sweden was one of the great European powers. In Swedish, the period is called Stormaktstiden, literally meaning "the Great Power Era"...
rule until 1721, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. The Estophile Enlightenment Period (1750–1840) led to a national awakening
Estonian national awakening
The Estonian Age of Awakening is a period in history where Estonians came to acknowledge themselves as a nation deserving the right to govern themselves. This period is considered to begin in 1850s with greater rights being granted to commoners and to end with the declaration of the Republic of...
in the mid-19th century. In 1918 the Estonian Declaration of Independence
Estonian Declaration of Independence
The Estonian Declaration of Independence, also known as the Manifesto to the Peoples of Estonia , is the founding act of the Republic of Estonia from 1918. It is celebrated on 24 February, the National Day or Estonian Independence Day....
was issued, to be followed by the Estonian War of Independence, which resulted in the Tartu Peace Treaty
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)
Tartu Peace Treaty or Treaty of Tartu was a peace treaty between Estonia and Russian SFSR signed on February 2, 1920 ending the Estonian War of Independence. The terms of the treaty stated that "Russia unreservedly recognises" the independence of Republic of Estonia de jure and renounced in...
recognizing Estonian independence in perpetuity. During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Estonia was occupied and annexed first by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and subsequently by Third Reich, only to be re-occupied by the Soviet Union in 1944.
Estonia regained its independence on 20 August 1991. It has since embarked on a rapid program of social and economic reform. Today, the country has gained recognition for its economic freedom its adaptation of new technologies and as one of the world's fastest growing economies.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Estonia:
General reference
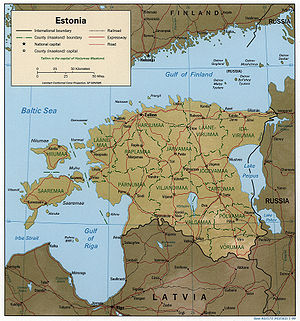
- Pronunciation: ɛˈstoʊniə
- Common English country name: EstoniaEstoniaEstonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Estonia
- Common endonym(s): Eesti, Eestimaa
- Official endonym(s): Eesti Vabariik
- Adjectival(s): Estonian
- Demonym(s): EstoniansEstoniansEstonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Estonia - International rankings of EstoniaInternational rankings of Estonia-International rankings:...
- ISO country codes: EE, EST, 233
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:EEISO 3166-2:EEISO 3166-2:EE is the entry for Estonia in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Estonia, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .ee.ee.ee is the Internet country code top-level domain of Estonia, operated by Estonian Internet Foundation.-Second-Level Domain Names:* .com.ee -- companies as defined in the Commercial Code* .pri.ee -- individuals...
Geography of Estonia
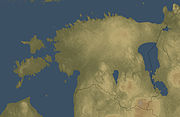
- Estonia is: a country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Northern EuropeNorthern EuropeNorthern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
- Eastern EuropeEastern EuropeEastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
- Northern Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern European TimeEastern European TimeEastern European Time is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in some European countries that also use Eastern European Summer Time as a summer daylight saving time.- Usage :...
(UTC+02), Eastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer Time is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone, 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries...
(UTC+03) - Extreme points of Estonia
- High: Suur MunamägiSuur MunamägiSuur Munamägi is the highest peak in Estonia , reaching above sea level. It is located near the village of Haanja, in Võru County in the south-eastern corner of Estonia, close to the borders of both Latvia and Russia...
318 m (1,043 ft) - Low: Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
0 m
- High: Suur Munamägi
- Land boundaries: 633 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Latvia 343 km
Latvia 343 km Russia 290 km
Russia 290 km
- Coastline: Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
3,794 km - Population of Estonia: 1,340,600 (January 1, 2008) - 148th most populous country
- Area of Estonia: 45,228 km2
- Atlas of Estonia
- Coastline: Baltic Sea
Environment of Estonia

- Climate of EstoniaClimate of EstoniaEstonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat content of the northern Atlantic Ocean, it has a milder climate despite its northern...
- Environmental issues in Estonia
- Ecoregions in Estonia
- Renewable energy in Estonia
- Geology of Estonia
- Protected areas of EstoniaProtected areas of EstoniaProtected areas of Estonia are regulated by the Nature Conservation Act , which was passed by the Estonian parliament on April 21, 2004 and entered into force May 10, 2004.-Protected areas:...
- Biosphere reserves in Estonia
- National parks of Estonia
- Fauna of EstoniaFauna of EstoniaEstonia is a small, heavily forested country situated on the Baltic Sea. It is a partof Palearctic ecozone and Temperate Northern Atlantic marine ecoregion....
- Birds of Estonia
- Mammals of Estonia
- Flora of Estonia
Natural geographic features of Estonia
- Glaciers of Estonia
- Islands of Estonia
- Lakes of Estonia
- Mountains of Estonia
- Volcanoes in Estonia
- Rivers of Estonia
- Waterfalls of Estonia
- Valleys of Estonia
- World Heritage Sites in Estonia
Administrative divisions of Estonia
- Main article: Administrative divisions of Estonia
- Counties of EstoniaCounties of EstoniaA county is an administrative subdivision of Estonia.Estonia is divided into 15 counties. The government of each county is led by a county governor , who represents the national government at the regional level...
- Municipalities of EstoniaMunicipalities of EstoniaA Municipality is the smallest administrative subdivision of Estonia. Each municipality is a unit of self-government with its representative and executive bodies. The municipalities in Estonia cover the entire territory of the country....
- Municipalities of Estonia
Municipalities of Estonia
- Capital of Estonia: Tallinn
- Cities of Estonia
Government and politics of Estonia
- Main article: Government of Estonia and Politics of EstoniaPolitics of EstoniaPolitics in Estonia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the Estonian parliament. Executive power is exercised by the Government...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: parliamentaryParliamentary systemA parliamentary system is a system of government in which the ministers of the executive branch get their democratic legitimacy from the legislature and are accountable to that body, such that the executive and legislative branches are intertwined....
representative democraticRepresentative democracyRepresentative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
republicRepublicA republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of... - Capital of Estonia: Tallinn
- Elections in EstoniaElections in EstoniaEstonia elects a legislature on the national level. The Riigikogu has 101 members, elected for a four year term by proportional representation. A head of state - the president - is elected for a five year term by parliament or an electoral college...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Estonia
- Political scandals of Estonia
- Taxation in Estonia
Executive branch of the government of Estonia
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of EstoniaPresident of EstoniaThe President of the Republic is the head of state of the Republic of Estonia.Estonia is a parliamentary republic, therefore President is mainly a symbolic figure and holds no executive power. The President has to suspend his membership in any political party for his term in office...
, Toomas Hendrik IlvesToomas Hendrik IlvesToomas Hendrik Ilves is the fourth and current President of Estonia. He is a former diplomat and journalist, was the leader of the Social Democratic Party in the 1990s and later a member of the European Parliament... - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of EstoniaPrime Minister of EstoniaThe Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government of the Republic of Estonia. The prime minister is nominated by the President after appropriate consultations with the parliamentary factions and confirmed by the Parliament. In case of disagreement, the Parliament can reject the President's...
, Andrus AnsipAndrus AnsipAndrus Ansip is the current Prime Minister of Estonia, and chairman of the market liberal Estonian Reform Party .-Early life and career:... - Cabinet of Estonia
Judicial branch of the government of Estonia
- Supreme Court of EstoniaSupreme Court of EstoniaThe Supreme Court of Estonia is the court of last resort in Estonia. It is both a court of cassation and a constitutional court. The courthouse is in Tartu.Chief justices=* Kaarel Parts * Rait Maruste...
Foreign relations of Estonia
- Diplomatic missions in Estonia
- Diplomatic missions of Estonia
International organization membership
The Republic of Estonia is a member of:- Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Baltic AssemblyBaltic AssemblyThe Baltic Assembly is an international organisation which aims to promote co-operation between the parliaments of the Republics of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues...
(BA) - Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Council of the Baltic Sea StatesCouncil of the Baltic Sea StatesThe Council of the Baltic Sea States is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension, including trafficking in human...
(CBSS) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Investment BankEuropean Investment BankThe European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
(EIB) - European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) (correspondent) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU)
- International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nordic Investment BankNordic Investment BankThe Nordic Investment Bank is an international financial institution founded in the mid-1970s by the five Nordic countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. In 2005, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland...
(NIB) - North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (accession state)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Schengen Convention
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesUnited Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesThe Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees , also known as The UN Refugee Agency is a United Nations agency mandated to protect and support refugees at the request of a government or the UN itself and assists in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to...
(UNHCR) - United Nations Institute for Training and ResearchUnited Nations Institute for Training and ResearchThe United Nations Institute for Training and Research was established in 1965 following a "for the training of personnel, particularly from developing Member States, for administrative and operational assignments with the United Nations and the specialized agencies, both at Headquarters and in...
(UNITAR) - United Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationUnited Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationThe United Nations Truce Supervision Organization is an organization founded on 29 May 1948 for peacekeeping in the Middle East. Its primary task was providing the military command structure to the peace keeping forces in the Middle East to enable the peace keepers to observe and maintain the...
(UNTSO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) (associate partner) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Estonia
- Main article: Law of EstoniaLaw of EstoniaAccording to the Constitution of Estonia the supreme power of the state is vested in the people. The people exercise their supreme power of the state on the elections of the Riigikogu through citizens who have the right to vote. The supreme judicial power is vested in the Supreme Court or...
- Capital punishment in EstoniaCapital punishment in EstoniaIn Estonia the last execution took place on the 11th of September 1991 when Rein Oruste was shot with a bullet to the back of the head for the crime of murder. The death penalty was completely abolished in Estonia on the 18th of March 1998 when Protocol No...
- Constitution of EstoniaConstitution of EstoniaThe Constitution of Estonia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Estonia and establishes the state order as that of a democratic republic where the supreme power is vested in its citizens. It was adopted in a freely elected Estonian Constituent Assembly on 15 June 1920 and came into force on...
- Crime in EstoniaCrime in EstoniaCrime in Estonia includes both private and public sector crime.-Private sector crime:According to statistics published in Britain in 2008 about the period 1991–2001, the number of crimes increased by 84% from 1991 to 2001...
- Human rights in EstoniaHuman rights in EstoniaHuman rights in Estonia are generally respected by the government, according to US Department of State. Estonia is ranked above-average in democracy, press freedom, privacy and human development...
- LGBT rights in Estonia
- Freedom of religion in Estonia
- Law enforcement in Estonia
Military of Estonia
- Main article: Military of EstoniaMilitary of EstoniaThe Estonian Defence Forces is the name of the unified armed forces of the Republic of Estonia. The Estonian military is a defence force consisting of Maavägi , Merevägi , Õhuvägi and a paramilitary organization Kaitseliit...
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
: Lieutenant GeneralLieutenant GeneralLieutenant General is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a Captain General....
Ants LaaneotsAnts LaaneotsKindral Ants Laaneots, in Kilingi-Nõmme in Pärnumaa, is the current Commander-in-Chief of the Estonian Defence Forces. General Laaneots previously served as the Commandant of the Estonian National Defence College from 2001 to 2006...
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Estonia
- Navy of Estonia
- Air Force of Estonia
- Special forces of Estonia
- Military history of Estonia
- Military ranks of EstoniaMilitary ranks of EstoniaPresent Estonian system of rank insignia is a direct descendant of various systems used in the past in the Estonian Army. Some of the grades trace their name back to period of World Wars, for instance the rank of aspirant literally means an officers in training in military academies or...
History of Estonia
- Main article: History of EstoniaHistory of EstoniaEstonia was settled near the end of the last glacial era, beginning from around 8500 BC. Before the German invasions in the 13th century proto-Estonians of the Ancient Estonia worshipped the spirits of nature...
, Timeline of the history of EstoniaTimeline of the history of Estonia-Pre-11th century:*c. 680 BC - A meteor disaster in Saaremaa forms the Kaali crater.*98 - Roman historian Tacitus writes in the book Germania about aesti tribes....
, and Current events of Estonia
- Economic history of Estonia
- Military history of Estonia
Culture of Estonia
- Main article: Culture of EstoniaCulture of EstoniaEstonian culture combines an indigenous heritage, represented by the country's Uralic national language Estonian, with Nordic cultural aspects. Due to its history and geography, Estonia's culture has been influenced by the traditions of the adjacent area's various Finnic, Baltic, Slavic and...
- Architecture of EstoniaArchitecture of EstoniaArchitecture of Estonia today represents a travel through time. The old town of Tallinn, a historic Hanseatic town called Reval, the capital of Estonia is one of the world's best preserved medieval architectural ensembles, UNESCO's World Heritage Site site since 1997...
- Cuisine of EstoniaCuisine of EstoniaTraditional Estonian cuisine has substantially been based on meat and potatoes, and on fish in coastal and lakeside areas, but is influenced by many other cuisines by now. In the present day it includes a variety of international foods and dishes, with a number of contributions from the traditions...
- Ethnic minorities in Estonia
- Estonian Jews
- Estonian SwedesEstonian SwedesThe Estonian Swedes, Estonia-Swedes, or Coastal Swedes are a Swedish-speaking linguistic minority traditionally residing in the coastal areas and islands of what is now western and northern Estonia...
- Estonian Russians
- Baltic Germans
- Festivals in Estonia
- Humor in Estonia
- Languages of EstoniaLanguages of EstoniaThe official language of Estonia is Estonian, a Uralic language closely related to Finnish but unrelated to nearby Russian or Latvian. Standard Estonian is mainly based on the North Estonian language, while South Estonian includes several unrecognised dialects, specifically Võro, Mulgi and Tartu...
- Media in Estonia
- National symbols of EstoniaNational symbols of Estonia- Estonian flag :The current coat of arms of Estonia is a golden shield which includes three slim, blue leopards in the middle, with oak branches along the side of the shield....
- Coat of arms of EstoniaCoat of arms of EstoniaThe coat of arms of Estonia is a golden shield which includes three slim blue passant gardant lions in the middle, with oak branches along the side of the shield. The three lions derive from the arms of Danish king Valdemar II who had conquered northern Estonia in 1219...
- Flag of EstoniaFlag of EstoniaThe national flag of Estonia is a tricolour featuring three equal horizontal bands of blue , black, and white. The normal size is 105 × 165 cm...
- National anthem of Estonia
- Coat of arms of Estonia
- People of Estonia
- Prostitution in EstoniaProstitution in EstoniaProstitution in Estonia is, in itself, legal but organized prostitution is illegal. Since prostitution is a sensitive indicator that develops with changes in the social environment and the state, it is useful to divide the history of this phenomenon from Estonia's first independence according to...
- Public holidays in EstoniaPublic holidays in EstoniaAll official holidays in Estonia are established by acts of Parliament.-Public holidays:The following are holidays that mean days off:-National Holidays:The following holidays do not give a day off:- References :* *...
- Records of Estonia
- Religion in Estonia
- Buddhism in Estonia
- Christianity in Estonia
- Estonian Evangelical Lutheran ChurchEstonian Evangelical Lutheran ChurchThe Estonian Evangelical Lutheran Church is a Lutheran church in Estonia. EELC is member of the Lutheran World Federation...
- Roman Catholicism in EstoniaRoman Catholicism in EstoniaThe Catholic Church in Estonia is the national branch of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope and curia in Rome.-The History of Catholicism in Estonia:...
- Estonian Apostolic Orthodox Church
- Estonian Orthodox Church of Moscow PatriarchateEstonian Orthodox Church of Moscow PatriarchateThe Estonian Orthodox Church of Moscow Patriarchate is a semi-autonomous diocese of the Patriarchate of Moscow whose primate is appointed by the Holy Synod of the latter. Its official name in English is the Estonian Orthodox Church of Moscow Patriarchate...
- Estonian Evangelical Lutheran Church
- Hinduism in EstoniaHinduism in EstoniaFrom the religious movements of Eastern origin that reached Estonia, beginning from the end of the 1980s, first and foremost were the ones inspired by Hinduism and Buddhism.Hinduism and Buddhism were registered in the 1990s....
- Islam in EstoniaIslam in EstoniaIn the most recent census, performed in the year 2000, the number of people in Estonia who reported themselves to be Muslims was 1,387. However some sources claim that the number of Muslims is much higher, with estimates given of 10,000 or even 20,000...
- Judaism in Estonia
- Sikhism in Estonia
- World Heritage Sites in Estonia
Art in Estonia
- Art in Estonia
- Cinema of EstoniaCinema of EstoniaCinema in Estonia started in 1896 when the first "moving pictures" were screened in Tallinn. The first movie theater was opened in 1908. First local documentary was made in 1908 with the production of a newsreel about Swedish King Gustav V’s visit to Tallinn...
- Literature of Estonia
- Music of EstoniaMusic of EstoniaThe earliest mentioning of Estonian singing and dancing dates back to Saxo Grammaticus' Gesta Danorum . Saxo speaks of Estonian warriors who sang at night while waiting for an epic battle. The Estonian folk music tradition is broadly divided into 2 periods...
- Television in Estonia
- Theatre in Estonia
Sport in Estonia
- Main article: Sport in EstoniaSport in EstoniaSport plays an important role in Estonian culture. Estonia first competed as a nation at the 1920 Summer Olympics, although the National Olympic Committee was established in 1923. Estonian athletes took part of the Olympic Games until the country was annexed by the Soviet Union in 1940. The 1980...
- Football in EstoniaFootball in EstoniaFootball in Estonia is governed by the Estonian Football Association . The EJL controls the domestic club championships , the Estonian Cup, Estonian SuperCup, Estonian Small Cup and the national teams Football in Estonia is governed by the Estonian Football Association (Eesti Jalgpalli Liit). The...
- Estonia at the OlympicsEstonia at the OlympicsAfter declaring independence from Russia in 1918, Estonia first competed as a nation at the 1920 Summer Olympics, although the National Olympic Committee was established in 1923. The first Winter Olympics were the 1924 Winter Olympics. Estonian athletes took part of the Olympic Games until the...
Economy and infrastructure of Estonia
- Main article: Economy of EstoniaEconomy of EstoniaEstonia is a member of the European Union and the eurozone and is an advanced economy, according to the IMF.Before the Second World War Estonia's economy was based on agriculture, but there was a significant knowledge sector and a growing industrial sector, similar to Finland...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 90th (ninetieth)
- Agriculture in EstoniaAgriculture in EstoniaLike the rest of the economy, agriculture in Estonia has been in great flux since the degeneration of the collective and state farm systems. In 1991 roughly 12 percent of the labor force was employed in agriculture, producing 15.4 percent of Estonia's GDP. Estonia has some 1.3 million hectares of...
- Banking in Estonia
- National Bank of Estonia
- Communications in EstoniaCommunications in EstoniaThe National Telecommunications act in the second period of Estonian independence granted a Monopoly on international and local fixed line telephony to Estonian Telecom . In the process of privatization, a concession was granted to liberalize mobile, CATV and packet-switched telecommunications. ...
- Internet in EstoniaInternet in EstoniaEstonia has one of the highest Internet penetration rates in the world. Computerization and digital connection for people are encouraged and supported by the state...
- Internet in Estonia
- Companies of Estonia
- Currency of EstoniaCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: KroonEstonian kroonIn 1992, coins were introduced in denominations of 5, 10, 20 & 50 senti, as well as 1 kroon. The 1 kroon was struck in cupronickel, the others in aluminum-bronze. However, in 1997, nickel-plated steel 20 senti were introduced, followed by aluminum-bronze 1 kroon in 1998. 5 senti coins were not...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: EEK
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Estonia
- Energy in EstoniaEnergy in EstoniaEnergy in Estonia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Estonia. Energy policy of Estonia describes the politics of Estonia related to energy. Electricity sector in Estonia is the main article of electricity in Estonia....
- Energy policy of Estonia
- Oil industry in Estonia
- Health care in Estonia
- Estonia Stock Exchange
- Mining in Estonia
- Tourism in Estonia
- Transport in EstoniaTransport in EstoniaTransport in Estonia relies mainly on road and rail network. For transport in the Soviet Union, see Transport in the Soviet Union.- Roads :*total: 57,565 km *paved: 12,926 km...
- Airports in Estonia
- Rail transport in EstoniaRail transport in EstoniaThe rail transport system in Estonia consists of circa of railway lines, of which are currently in public use. The infrastructure of the railway network is mostly owned by the state and is regulated and surveyed by the Estonian Railway Inspectorate ....
- Roads in Estonia
- Water supply and sanitation in Estonia
See also
- Index of Estonia-related articles
- List of Estonia-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the European UnionMember State of the European UnionA member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...

