Outline of Finland
Encyclopedia
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
located in Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. Finland has borders with Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
to the west, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
to the east, and Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
to the north, while Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn...
. The capital city is Helsinki
Helsinki
Helsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
.
Around 5.3 million people reside in Finland, with the majority concentrated in the southern part of country. It is the eighth largest country in Europe in terms of area and the most sparsely populated country in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
. The native language for most of the population is Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
, a member of the Uralic language family
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
most closely related to Estonian
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
and one of the four EU languages
Languages of the European Union
The languages of the European Union are languages used by people within the member states of the European Union. They include the twenty-three official languages of the European Union along with a range of others...
not of Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
origin. The second official language, Swedish
Swedish language
Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish...
, is spoken by a 5.5 percent minority. Finland is a democratic, parliamentary
Parliamentary system
A parliamentary system is a system of government in which the ministers of the executive branch get their democratic legitimacy from the legislature and are accountable to that body, such that the executive and legislative branches are intertwined....
republic
Republicanism
Republicanism is the ideology of governing a nation as a republic, where the head of state is appointed by means other than heredity, often elections. The exact meaning of republicanism varies depending on the cultural and historical context...
with a central government and local governments in 415 municipalities. Greater Helsinki
Greater Helsinki
Greater Helsinki and the smaller Helsinki Metropolitan Area or Capital Region refer to two regions of different size surrounding Helsinki, the capital of Finland...
(including Helsinki
Helsinki
Helsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
, Espoo
Espoo
Espoo is the second largest city and municipality in Finland. The population of the city of Espoo is . It is part of the Helsinki Metropolitan Area along with the cities of Helsinki, Vantaa, and Kauniainen. Espoo shares its eastern border with Helsinki and Vantaa, while enclosing Kauniainen....
, Vantaa
Vantaa
Vantaa is a city and municipality in Finland. Helsinki, Vantaa, Espoo and Kauniainen make up the Helsinki Metropolitan Area.Vantaa, with its population of , is the fourth most populated city of Finland. The biggest airport in Finland, the Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, is located there...
and Kauniainen) totals a million residents and a third of the GDP. Other major cities include Tampere
Tampere
Tampere is a city in southern Finland. It is the most populous inland city in any of the Nordic countries. The city has a population of , growing to approximately 300,000 people in the conurbation and over 340,000 in the metropolitan area. Tampere is the third most-populous municipality in...
, Turku
Turku
Turku is a city situated on the southwest coast of Finland at the mouth of the Aura River. It is located in the region of Finland Proper. It is believed that Turku came into existence during the end of the 13th century which makes it the oldest city in Finland...
, and Oulu
Oulu
Oulu is a city and municipality of inhabitants in the region of Northern Ostrobothnia, in Finland. It is the most populous city in Northern Finland and the sixth most populous city in the country. It is one of the northernmost larger cities in the world....
.
Finland was historically part of Sweden and from 1809 an autonomous Grand Duchy
Grand Duchy of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland was the predecessor state of modern Finland. It existed 1809–1917 as part of the Russian Empire and was ruled by the Russian czar as Grand Prince.- History :...
within the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. Finland's declaration of independence
Finland's declaration of independence
The Finnish declaration of independence was adopted by the Parliament of Finland on 6 December 1917. It declared Finland an independent and sovereign nation state rather than an autonomous Russian Grand duchy.-Revolution in Russia:...
in 1917 from Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
was followed by a civil war, wars against the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany
Military history of Finland during World War II
From 1939 to 1945, Finland fought three wars: the Winter War alone against the Soviet Union, the Continuation War with Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union, and the Lapland War against Nazi Germany...
, and a period of official neutrality during the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. Finland joined the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
in 1955 and the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
in 1995 and participates in the Eurozone
Eurozone
The eurozone , officially called the euro area, is an economic and monetary union of seventeen European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their common currency and sole legal tender...
. Finland has been ranked the second most stable country in the world, in a survey based on social, economic, political, and military indicators.
Finland has seen excellent results in many international comparisons of national performance such as the share of high-technology manufacturing, the rate of gross domestic product growth, and the protection of civil liberties.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Finland:
General reference
- Pronunciation: ˈfɪnlənd
- Common English country name: FinlandFinlandFinland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Finland
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): Finnish
- Demonym(s): Finns
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Finland - International rankings of Finland
- ISO country codes: FI, FIN, 246
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:FIISO 3166-2:FIISO 3166-2:FI is the entry for Finland in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Finland, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .fi.fi.fi is the Internet country code top-level domain for Finland. It is operated by FICORA, the Finnish Communications Regulatory Authority....
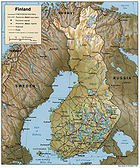
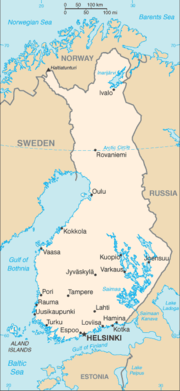
Geography of Finland
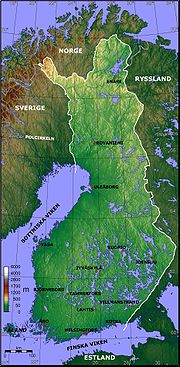
- Finland is: a NordicNordic countriesThe Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
countryCountryA country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously... - Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Northern EuropeNorthern EuropeNorthern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
- ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
- Scandinavia
- Northern Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern European TimeEastern European TimeEastern European Time is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in some European countries that also use Eastern European Summer Time as a summer daylight saving time.- Usage :...
(UTC+02), Eastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer Time is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone, 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries...
(UTC+03) - Extreme points of FinlandExtreme points of FinlandThis is a list of the extreme points of Finland, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.*Northernmost Point — Nuorgam, Utsjoki, Lapland at - also the northernmost point of the European Union...
- High: HaltiHaltiHalti is the highest fell in Finland, at above sea level, and thus the highest point in the country. The Halti fell is located in the municipality of Enontekiö in the province of Lapland at the border between Finland and Norway. The summit of Halti at is actually in Norway and it is known as...
1324 m (4,344 ft) - Low: Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
0 m
- High: Halti
- Land boundaries: 2,654 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Russia 1,313 km
Russia 1,313 km Norway 727 km
Norway 727 km Sweden 614 km
Sweden 614 km
- Coastline: 1,250 km
- Population of Finland: 5,356,900 (March 6, 2010) - 112th most populous country
- Area of Finland: 338,145 km2
- Atlas of Finland
Environment of Finland

- Climate of Finland
- Environmental issues in FinlandEnvironmental issues in FinlandEnvironmental issues in Finland discuss the environmental issue in Finland.- Climate change :Finland was among the top five greenhouse gas emitters in 2001: The consumption emissions per capita of greenhouse gases in 2001 of the top 5 countries were US 29 tonnes, Australia 21 tonnes, Canada 20...
- Ecoregions in Finland
- Renewable energy in FinlandRenewable energy in FinlandRenewable energy in Finland of electricity was : Water 60%, forest industry black liquor 22%, other wood residues 16%, wind power 0.2% and other RE 1 %. The European objectives are: 22% renewable source electricity and 12% renewable of primary energy in 2010 . This includes e.g...
- Geology of Finland
- Protected areas of FinlandProtected areas of FinlandThe protected areas of Finland include national parks, nature reserves and other areas, with a purpose of conserving areas of all of Finland's ecosystems and biotopes.Protected areas include:...
- Biosphere reserves in Finland
- National parks of Finland
- Wildlife of Finland
- Flora of Finland
- Fauna of FinlandFauna of FinlandThis is a list of the fauna of Finland. Finland borders Sweden to the west, Russia to the east, and Norway to the north, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland, allowing an ecological mix. Finland contains many species of mammals, birds, and fish, but only a few reptiles and...
- Birds of Finland
- Mammals of Finland
Natural geographic features of Finland
- Islands of Finland
- Lakes of Finland
- Rivers of Finland
- World Heritage Sites in Finland
Ecoregions of Finland
- Main article: Ecoregions in Finland
Administrative divisions of Finland
- Main article: Administrative divisions of FinlandAdministrative divisions of Finland||As of 1 January 2010, Finland is divided into:* 6 Regional State Administrative Agencies plus Åland – replacing the old division of six provinces* 20 regions * the regions are divided into 72 sub-regions...
- Provinces of FinlandProvinces of FinlandThe state of Finland consisted of six provinces between the years 1997 and 2009. The provincial authority was part of the central government's executive branch, not directly elected. The system was created in 1634, and its makeup was changed drastically in 1997, when the number of the provinces...
- Regions of FinlandRegions of FinlandFinland consists of 19 regions called in Finnish and in Swedish. The regions are governed by regional councils, which serve as forums of cooperation for the municipalities of a region. The main tasks of the regions are regional planning and development of enterprise and education. In addition,...
- Sub-regions of FinlandSub-regions of FinlandIn 2009 Finland is divided into 70 sub-regions . The sub-regions are formed by groups of municipalities within the 19 regions of Finland...
- Sub-regions of Finland
- Regions of Finland
Municipalities of Finland
- Capital of Finland: Helsinki
- Cities of Finland
Government and politics of Finland
- Main article: Government of FinlandGovernment of FinlandFinland is a republic with a representative democracy governed accordingly to the principles of parliamentarism. Legislative power is vested in the Parliament of Finland . Executive power is exercised by the Cabinet, officially termed Council of State , which is led by the Prime Minister, the Head...
and Politics of FinlandPolitics of FinlandPolitics of Finland takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic and of a multi-party system. The President of Finland is the head of state, leads the foreign policy, and is the Commander-in-chief of the Defense Forces. The Prime Minister of Finland is the head...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: semi-presidentialSemi-presidential systemThe semi-presidential system is a system of government in which a president and a prime minister are both active participants in the day-to-day administration of the state...
representative democraticRepresentative democracyRepresentative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
republicRepublicA republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of... - Capital of Finland: Helsinki
- Elections in FinlandElections in FinlandElections in Finland gives information on election and election results in Finland.On national level Finland elects a head of state — the President of the Republic — and a legislature. The president is elected for a six-year term by direct popular vote...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Finland
- Political scandals of Finland
- Taxation in FinlandTaxation in FinlandTaxation in Finland is carried out by the State of Finland, mainly through Finnish Tax Administration, an agency of Ministry of Finance. Finnish Customs , Finnish Transport Agency and Finnish Transport Safety Agency also collect taxes...
Executive branch of the government of Finland
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of FinlandPresident of FinlandThe President of the Republic of Finland is the nation's head of state. Under the Finnish constitution, executive power is vested in the President and the government, with the President possessing extensive powers. The President is elected directly by the people of Finland for a term of six years....
, - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of FinlandPrime Minister of FinlandThe Prime Minister is the Head of Government of Finland. The Prime Minister is appointed by the President, who is the Head of State. The current Prime Minister is Jyrki Katainen of the National Coalition Party.-Overview:...
, - Cabinet of Finland
Legislative branch of the government of Finland
- Parliament of FinlandParliament of FinlandThe Eduskunta , is the parliament of Finland. The unicameral parliament has 200 members and meets in the Parliament House in Helsinki. The latest election to the parliament took place on April 17, 2011.- Constitution :...
(unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Finland
- General Courts of Finland
- District Courts of Finland
- Courts of Appeals of Finland
- Supreme Court of FinlandSupreme Court of FinlandThe Supreme Court of Finland , located in Helsinki, consists of a President and at minimum 15, currently 18 other Justices, usually working in five-judge panels...
- Administrative Courts of Finland
- Regional Administrative Courts of Finland
- Supreme Administrative Court of FinlandSupreme Administrative Court of FinlandThe Supreme Administrative Court of Finland is the highest court in the Finnish administrative court system, parallel to the Supreme Court of Finland. Its jurisdiction covers the legality of the decisions of government officials, and its decisions are final...
- Special Courts of Finland
- Market Court of Finland
- Labour Court of Finland
- Insurance Court of Finland
- High Court of Impeachment of Finland
Foreign relations of Finland
- Diplomatic missions in Finland
- Diplomatic missions of Finland
International organization membership
The Republic of Finland is a member of:- African Development Bank Group (AfDB) (nonregional member)
- Arctic CouncilArctic CouncilThe Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum which addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic.- History of the Arctic Council :...
- Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) (nonregional member) - Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Council of the Baltic Sea StatesCouncil of the Baltic Sea StatesThe Council of the Baltic Sea States is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension, including trafficking in human...
(CBSS) - Economic and Monetary UnionEconomic and monetary unionAn economic and monetary union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of an economic union with a monetary union. It is to be distinguished from a mere monetary union , which does not involve a common market. This is the fifth stage of economic integration...
(EMU) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Investment BankEuropean Investment BankThe European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
(EIB) - European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
- European Space AgencyEuropean Space AgencyThe European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
(ESA) - European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Group of 9Group of 9The Group of Nine was a group of nine European states that meet occasionally to discuss matters of mutual interest.-Members: The Group of Nine was a group of nine European states that meet occasionally to discuss matters of mutual interest.-Members: The Group of Nine was a group of nine...
(G9) - Inter-American Development BankInter-American Development BankThe Inter-American Development Bank is the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean...
(IADB) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Chamber of CommerceInternational Chamber of CommerceThe International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its hundreds of thousands of member companies in over 130 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise....
(ICC) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Energy AgencyInternational Energy AgencyThe International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
(IEA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM)
- International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM) (guest)
- Nordic CouncilNordic CouncilThe Nordic Council is a geo-political, inter-parliamentary forum for co-operation between the Nordic countries. It was established following World War II and its first concrete result was the introduction in 1952 of a common labour market and free movement across borders without passports for the...
(NC) - Nordic Investment BankNordic Investment BankThe Nordic Investment Bank is an international financial institution founded in the mid-1970s by the five Nordic countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. In 2005, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland...
(NIB) - Nuclear Energy AgencyNuclear Energy AgencyThe Nuclear Energy Agency is an intergovernmental multinational agency that is organized under the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development...
(NEA) - Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Paris ClubParis ClubThe Paris Club is an informal group of financial officials from 19 of some of the world's biggest economies, which provides financial services such as war funding, debt restructuring, debt relief, and debt cancellation to indebted countries and their creditors...
- Partnership for PeacePartnership for PeacePartnership for Peace is a North Atlantic Treaty Organisation program aimed at creating trust between NATO and other states in Europe and the former Soviet Union; 22 States are members...
(PFP) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Schengen Convention
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesUnited Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesThe Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees , also known as The UN Refugee Agency is a United Nations agency mandated to protect and support refugees at the request of a government or the UN itself and assists in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to...
(UNHCR) - United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - United Nations Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan (UNMOGIP)
- United Nations Mission in LiberiaUnited Nations Mission in LiberiaThe United Nations Mission in Liberia is a peace-keeping force established in September 2003 to monitor a ceasefire agreement in Liberia following the resignation of President Charles Taylor and the conclusion of the Second Liberian Civil War....
(UNMIL) - United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS)
- United Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationUnited Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationThe United Nations Truce Supervision Organization is an organization founded on 29 May 1948 for peacekeeping in the Middle East. Its primary task was providing the military command structure to the peace keeping forces in the Middle East to enable the peace keepers to observe and maintain the...
(UNTSO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) (observer) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) - Zangger CommitteeZangger CommitteeThe Zangger Committee, also known as the Nuclear Exporters Committee, sprang from Article III.2 of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons which entered into force on March 5, 1970...
(ZC)
Law and order in Finland
- Main article: Law of Finland
- Capital punishment in FinlandCapital punishment in FinlandCapital punishment in Finland has been abolished de jure.As of 1823 in the Grand Duchy of Finland, death sentences were commuted to transportation to Siberia or life sentences. The last person to be executed in peacetime was Tahvo Putkonen, on July 8, 1825...
- Constitution of FinlandConstitution of FinlandThe Constitution of Finland is the supreme source of national law of Finland. It defines the basis, structures and organisation of government, the relationship between the different constitutional organs, and lays out the fundamental rights of Finnish citizens...
- Crime in FinlandCrime in Finland-Statistics:Offences recorded by the police6)1980199020002004 per 1,000 people5)All offences480,964848,978763,391787,964150.46Offences against the Penal Code1)221,106435,1544)530,270540,867103.28...
- Human rights in FinlandHuman rights in FinlandHuman rights in Finland are protected by the constitution and extensive domestic safeguards, in addition to the country's active membership in most international human rights treaties....
- LGBT rights in Finland
- Freedom of religion in Finland
- Law enforcement in FinlandLaw enforcement in FinlandLaw enforcement in Finland falls under the jurisdiction of the Finnish Police, a national police agency.The Finnish Police is divided into 24 local departments and three national agencies...
Military of Finland
- Main article: Military of Finland
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Finland
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Finland
- Navy of Finland
- Air Force of Finland
- Special forces of Finland
- Military history of Finland
- Military ranks of Finland
History of Finland
- Main article: History of FinlandHistory of FinlandThe land area that now makes up Finland was settled immediately after the Ice Age, beginning from around 8500 BCE. Most of the region was part of the Kingdom of Sweden from the 13th century to 1809, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire, becoming the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland. The...
, Timeline of the history of Finland, and Current events of Finland
- Economic history of Finland
- Military history of Finland
Culture of Finland
- Main article: Culture of FinlandCulture of FinlandThe culture of Finland combines indigenous heritage, as represented for example by the country's Uralic national language Finnish, and the sauna, with common Nordic and European culture. Because of its history and geographic location Finland has been influenced by the adjacent areas' various...
- Architecture of FinlandArchitecture of FinlandThe architecture of Finland has a notable history spanning over 800 years and the architecture has contributed to several styles internationally, such as Nordic modernism, through the works of Alvar Aalto.....
- Cuisine of FinlandCuisine of FinlandFinnish cuisine is notable for generally combining traditional country fare and haute cuisine with contemporary continental style cooking. Fish and meat play a prominent role in traditional Finnish dishes from the western part of the country, while the dishes from the eastern part have...
- Ethnic minorities in Finland
- Festivals in Finland
- Humor in Finland
- Languages of FinlandLanguages of FinlandThe two “national” languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. The official minority languages are three Sami languages, Romani, Finnish Sign Language and the Karelian language.-Finnish:...
- Media in Finland
- National symbols of Finland
- Coat of arms of FinlandCoat of arms of FinlandThe coat of arms of Finland is a crowned lion on a red field, the right forepaw replaced with an armoured hand brandishing a sword, trampling on a saber with the hindpaws...
- Flag of FinlandFlag of FinlandThe flag of Finland , also called Siniristilippu , dates from the beginning of the 20th century. On a white background, it features a blue Nordic cross, which represents Christianity. The state flag has a coat of arms in the centre, but is otherwise identical to the civil flag. The swallow-tailed...
- National anthem of Finland
- Coat of arms of Finland
- People of Finland
- Prostitution in Finland
- Public holidays in FinlandPublic holidays in FinlandAll official holidays in Finland are established by acts of Parliament. The official holidays can be divided into Christian and non-Christian holidays. The main Christian holidays are Christmas, New Year's Day, Epiphany, Easter, Ascension day, Pentecost, Midsummer Day, and All Saints' Day...
- Records of Finland
- Religion in FinlandReligion in FinlandMost people in Finland are at least nominally members of a Christian church, but since the 1980s, there has been a rapid increase in the number of people without religious affiliation. Prior to Christianisation, Finnish paganism was the primary religion....
- Buddhism in FinlandBuddhism in FinlandBuddhism in Finland represents a very small percentage of that nation's religious practices. Out of the 5,238,460 people living in Finland, only 0.1% of the population is identified as being Buddhist....
- Christianity in Finland
- Hinduism in FinlandHinduism in FinlandHinduism is a very minor religious faith in Finland. The main established religion in Finland is Christianity, especially Lutheran Christianity....
- Islam in FinlandIslam in FinlandIslam is a minority religion in Finland. The first Muslims were Tatars who immigrated mainly between 1870 and 1920. After that there were decades with generally a small number of immigration in Finland. Since the late 20th century the number of Muslims in Finland has increased rapidly due to...
- Judaism in Finland
- Sikhism in Finland
- Buddhism in Finland
- World Heritage Sites in Finland
Art in Finland
- Art in Finland
- Cinema of Finland
- Literature of Finland
- Music of FinlandMusic of FinlandThe music of Finland can be roughly divided in the following three categories.Folk music is typically influenced by Karelian traditional tunes and lyrics of the Kalevala metre. Karelian heritage has traditionally been perceived as the purest expression of Finnic myths and beliefs, thought to be...
- Television in Finland
- Theatre in Finland
Sports in Finland
- Main article: Sports in Finland
- Football in FinlandFootball in FinlandFootball in Finland, unlike in most European countries, is not the most popular spectator sport, as it falls behind ice hockey, which enjoys a huge amount of popularity in the country. Football tops ice hockey in the number of registered players and as a popular hobby...
- Finland at the OlympicsFinland at the OlympicsFinland first participated at the Olympic Games in 1908, and has sent athletes to compete in every Summer Olympic Games and every Winter Olympic Games since then. Finland was also the host nation for the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki....
Economy and infrastructure of Finland
- Main article: Economy of FinlandEconomy of FinlandFinland has a highly industrialised, mixed economy with a per capita output equal to that of other western economies such as France, Germany, Sweden or the United Kingdom. The largest sector of the economy is services at 65.7 percent, followed by manufacturing and refining at 31.4 percent. Primary...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 34th (thirty-fourth)
- Agriculture in Finland
- Banking in Finland
- National Bank of Finland
- Communications in FinlandCommunications in FinlandFinland has excellent communications, and is considered one of the most advanced information societies in the world.-Telephones:Telephones – main lines in use:2.368 million Telephones – mobile cellular:...
- Internet in FinlandInternet in Finland- History :FUNET was created 1984 to link Finnish universities. The .fi top-level domain was registered 1986. FICIX was created in 1993 to interconnect Finnish IP networks and commercial sales of Internet connection began....
- Internet in Finland
- Companies of Finland
- Currency of FinlandCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: EuroEuroThe euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
(see also: Euro topics)- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: EUREuroThe euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Finland
- Energy in FinlandEnergy in FinlandFinland lacks domestic sources of fossil energy and must import substantial amounts of petroleum, natural gas, and other energy resources, including uranium for nuclear power.-Overview:...
- Energy policy of FinlandEnergy policy of FinlandEnergy policy of Finland describes the politics of Finland related to energy. Energy in Finland describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Finland. Electricity sector in Finland is the main article of electricity in Finland....
- Oil industry in Finland
- Energy policy of Finland
- Health care in Finland
- Mining in Finland
- Finland Stock Exchange
- Tourism in FinlandTourism in FinlandFinland attracted over 5 million tourists in 2005, with most coming from Sweden. The value added by tourism is about 2.4% of the Finnish GDP, and provides around 60,000 jobs. The Finnish tourism brand is stated by the Finland Promotion Board...
- Transport in FinlandTransport in FinlandThe transport system of Finland is well-developed.The extensive road system is utilized by most internal cargo and passenger traffic. , the country's network of main roads has a total length of around and all public roads . The motorway network totals with additional reserved only for motor...
- Airports in Finland
- Rail transport in FinlandRail transport in FinlandThe Finnish railway network consists of a total of 5,919 km of railways built with Russian gauge track. Passenger trains are operated by the private state-owned VR Group. They serve all the major cities and many rural areas, though railway connections are available to fewer places than bus...
- Roads in Finland
- Water supply and sanitation in Finland
See also
- Index of Finland-related articles
- List of Finland-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the European UnionMember State of the European UnionA member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
- The Finnish Government – Official governmental site
- The President of Finland – Official site of the President of the Republic of Finland
- Parliament of Finland – Official Parliamentary site
- ThisisFINLAND – Main portal to Finland (administered by the Ministry for Foreign Affairs of FinlandMinistry for Foreign Affairs (Finland)The Ministry for Foreign Affairs is a ministry in the Finnish Government and is responsible for preparing and implementing the government's foreign policy.-Organisation:...
) - Visit Finland – The official travel and tourism guide by the Finnish Tourist Board
- Helsinki.fi – Capital of FinlandHelsinkiHelsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
's city portal - Today's weather by the Finnish Meteorological Institute

