Outline of Norway
Encyclopedia
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
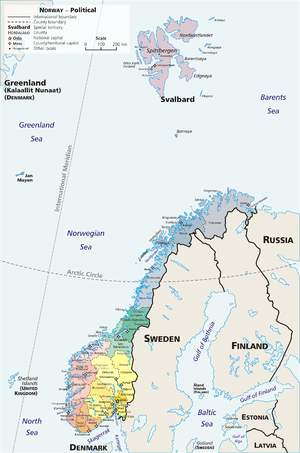
principally located in western Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
of Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. Norway is bordered by Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, while the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and the Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands are an island group situated between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately halfway between Scotland and Iceland. The Faroe Islands are a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark proper and Greenland...
lie to its west across the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
. The country's extensive coastline along the North Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
is home to its famous fjord
Fjord
Geologically, a fjord is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created in a valley carved by glacial activity.-Formation:A fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. Glacial melting is accompanied by rebound of Earth's crust as the ice...
s.
Norway also includes the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
island territories of Svalbard
Svalbard
Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the...
and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
. Norwegian sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
over Svalbard is based upon the Spitsbergen Treaty, but that treaty does not apply to Jan Mayen. Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island is an uninhabited Antarctic volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean, 2,525 km south-southwest of South Africa. It is a dependent territory of Norway and, lying north of 60°S latitude, is not subject to the Antarctic Treaty. The centre of the island is an ice-filled crater of an...
in the South Atlantic Ocean and Peter I Island
Peter I Island
Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway, and along with Queen Maud Land and Bouvet Island comprises one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. Peter I Island is ...
and Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land is a c. 2.7 million-square-kilometre region of Antarctica claimed as a dependent territory by Norway. The territory lies between 20° west and 45° east, between the British Antarctic Territory to the west and the Australian Antarctic Territory to the east. The latitudinal...
in Antarctica are external dependencies
Dependent territory
A dependent territory, dependent area or dependency is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a State, and remains politically outside of the controlling state's integral area....
, but those three entities do not form part of the kingdom.
Since World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Norway has experienced rapid economic growth, and is now amongst the wealthiest countries in the world. Norway is the world's third largest oil exporter after Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
and the petroleum industry
Petroleum industry
The petroleum industry includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transporting , and marketing petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline...
accounts for around a quarter of GDP. It has also rich resources of gas fields, hydropower, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
, forests, and minerals. Norway was the second largest exporter of seafood (in value, after China) in 2006. Other main industries include food processing, shipbuilding, metals, chemicals, mining, fishing and pulp and paper products. Norway has a Scandinavian welfare system and the largest capital reserve per capita of any nation.
Norway was ranked highest of all countries in human development
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
from 2001 to 2006, and came second in 2007 (to fellow Nordic country
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
). It also rated the most peaceful country in the world in a 2007 survey by Global Peace Index
Global Peace Index
The Global Peace Index is an attempt to measure the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. It is the product of Institute for Economics and Peace and developed in consultation with an international panel of peace experts from peace institutes and think tanks with data collected...
. It is a founding member of NATO.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Norway:
General reference
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: - Common English country name: NorwayNorwayNorway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
- Official English country name: The Kingdom of Norway
- Common endonym(s): Norge (bokmålBokmålBokmål is one of two official Norwegian written standard languages, the other being Nynorsk. Bokmål is used by 85–90% of the population in Norway, and is the standard most commonly taught to foreign students of the Norwegian language....
), Noreg (nynorskNynorskNynorsk or New Norwegian is one of two official written standards for the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. The standard language was created by Ivar Aasen during the mid-19th century, to provide a Norwegian alternative to the Danish language which was commonly written in Norway at the...
) or Norga (samiNorthern SamiNorthern or North Sami is the most widely spoken of all Sami languages. The speaking area of Northern Sami covers the northern parts of Norway, Sweden and Finland...
) - Official endonym(s): Kongeriket Norge (bokmålBokmålBokmål is one of two official Norwegian written standard languages, the other being Nynorsk. Bokmål is used by 85–90% of the population in Norway, and is the standard most commonly taught to foreign students of the Norwegian language....
) or Kongeriket Noreg (nynorskNynorskNynorsk or New Norwegian is one of two official written standards for the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. The standard language was created by Ivar Aasen during the mid-19th century, to provide a Norwegian alternative to the Danish language which was commonly written in Norway at the...
) - Adjectival(s): Norwegian
- Demonym(s): Norwegian(s)NorwegiansNorwegians constitute both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegian people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in United States, Canada and Brazil.-History:Towards the end of the 3rd...
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Norway - ISO country codes: NO, NOR, 578
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:NOISO 3166-2:NOISO 3166-2:NO is the entry for Norway in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Norway, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .no.no.no is the Internet country code top-level domain for Norway. Registrations are processed via accredited registrars and internationalized domain names may also be registered ....
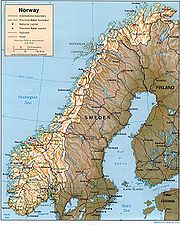
Geography of Norway
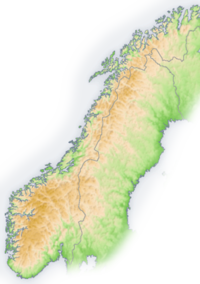
- Norway is: a NordicNordic countriesThe Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
countryCountryA country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously... - Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Northern EuropeNorthern EuropeNorthern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
- ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
- Scandinavia
- Northern Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Central European TimeCentral European TimeCentral European Time , used in most parts of the European Union, is a standard time that is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time . The time offset from UTC can be written as +01:00...
(UTC+01), Central European Summer TimeCentral European Summer TimeCentral European Summer Time is one of the names of the Daylight saving time offset using the UTC offset of UTC+02:00, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in most European countries. During the winter, Central European Time is used...
(UTC+02) - Extreme points of NorwayExtreme points of NorwayThe extreme points of Norway include the coordinates that are further north, south, east or west than any other location in Norway; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northern-most point is Rossøya on Svalbard, the southern-most is Pysen in Mandal, the eastern-most is...
- High: GaldhøpiggenGaldhøpiggenGaldhøpiggen is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia and Northern Europe, at 2,469 m above sea level...
2469 m (8,100 ft) - Low: Norwegian SeaNorwegian SeaThe Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea in the North Atlantic Ocean, northwest of Norway. It is located between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea and adjoins the North Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a...
0 m
- High: Galdhøpiggen
- Land boundaries: 2,542 km
- Northern Hemisphere
Environment of Norway

- Climate of Norway
- Environmental issues in Norway
- Festningen Geotope Protected AreaFestningen Geotope Protected AreaFestningen Geotope Protected Area is located at the outermost edge of Grønfjorden's mouth to Isfjorden on Nordenskiöld Land, Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. The profile is a cliff which runs along the coast from Kapp Starostin to Festningsodden. It covers an areas of , of which is on land and ...
- Ecoregions in Norway
- Renewable energy in NorwayRenewable energy in NorwayNorway is a heavy producer of renewable energy, first of all due to good resources in hydropower. Over 99% of the electricity production in mainland Norway is covered by hydropower plants...
- Geology of NorwayGeology of NorwayThe geology of Norway encompasses the history of earth that can be interpreted by rock types found in Norway, and the associated sedimentological history of soils and rock types....
- Protected areas of NorwayProtected areas of NorwayProtected areas of Norway include:* National parks of Norway:Category:Nature_reserves_in_NorwayAbout 14.3 percent of the mainland of Norway is protected. Of this, ca. 8.3 percent is national parks, 1.3 percent is nature reserves and 4.7 percent otherwise protected.IUCN aims to protect at least 15...
- Biosphere reserves in Norway
- National parks of Norway
- Wildlife of Norway
- Flora of Norway
- Fauna of Norway
- Birds of Norway
- Mammals of Norway
Natural geographic features of Norway
- Fjords of Norway
- Glaciers of Norway
- Islands of Norway
- Lakes of Norway
- Mountains of Norway
- Rivers of Norway
- World Heritage Sites in Norway
Administrative divisions of Norway
- Provinces of Norway
- Districts of NorwayDistricts of NorwayThe country Norway is historically divided into a number of districts. Many districts have deep historical roots, and only partially coincide with today's administrative units of counties and municipalities. The districts are defined by geographical features, often valleys, mountain ranges, fjords,...
- Municipalities of NorwayMunicipalities of NorwayNorway is divided into 19 administrative regions, called counties , and 430 municipalities...
- Municipalities of Norway
- Districts of Norway
Municipalities of Norway
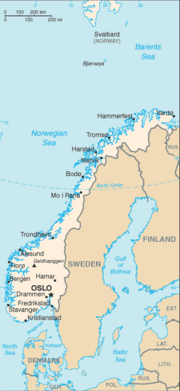
- Capital of Norway: Oslo
- Cities of Norway
Government and politics of Norway
- Main article: Government of Norway and Politics of NorwayPolitics of NorwayPolitics in Norway take place in the framework of a parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy. Executive power is exercised by the King's council, the cabinet, led by the Prime Minister of Norway. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Storting, elected...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: - Capital of Norway: Oslo
- Elections in NorwayElections in NorwayNorway elects its legislature on a national level. The parliament, the Storting , has 169 members elected for a four year term by the proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies.Norway has a multi-party system, with numerous parties in which no one party often has a chance of gaining...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Norway
- Political scandals of Norway
- Taxation in NorwayTaxation in NorwayTaxation in Norway is levied by the central government, the county municipality and the municipality . The tax level in Norway is among the highest in the world. In 2009 the total tax revenue was 41.0 % of the gross domestic product . Many direct and indirect taxes exist. The most important...
Executive branch of the government of Norway
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: Harald V of NorwayHarald V of NorwayHarald V is the king of Norway. He succeeded to the throne of Norway upon the death of his father Olav V on 17 January 1991...
, - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of NorwayPrime Minister of NorwayThe Prime Minister of Norway is the political leader of Norway and the Head of His Majesty's Government. The Prime Minister and Cabinet are collectively accountable for their policies and actions to the Sovereign, to Stortinget , to their political party, and ultimately the...
, - Cabinet of NorwayCabinet of NorwayThe Cabinet of Norway is a formal body composed of the most senior government ministers chosen by the Prime Minister, and functions as the collective decision-making organ constituting the executive branch of the Kingdom. It is referred to as the Council of State , and simultaneously play the role...
Legislative branch of the government of Norway
- Parliament of Norway (unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Norway
- Supreme Court of NorwaySupreme Court of NorwayThe Supreme Court of Norway was established in 1815 on the basis of the Constitution of Norway's §88, prescribing an independent judiciary. It is located in Oslo and is Norway's highest court...
Foreign relations of Norway
- Diplomatic missions in Norway
- Diplomatic missions of NorwayDiplomatic missions of NorwayThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Norway, excluding honorary consulates.-Europe:** Vienna ** Baku ** Brussels ** Sarajevo ** Sofia ** Zagreb ** Prague...
International organization membership
The Kingdom of Norway is a member of:- African Development Bank Group (AfDB) (nonregional member)
- Arctic CouncilArctic CouncilThe Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum which addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic.- History of the Arctic Council :...
- Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) (nonregional member) - Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Council of the Baltic Sea StatesCouncil of the Baltic Sea StatesThe Council of the Baltic Sea States is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension, including trafficking in human...
(CBSS) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Free Trade AssociationEuropean Free Trade AssociationThe European Free Trade Association or EFTA is a free trade organisation between four European countries that operates parallel to, and is linked to, the European Union . EFTA was established on 3 May 1960 as a trade bloc-alternative for European states who were either unable to, or chose not to,...
(EFTA) - European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
- European Space AgencyEuropean Space AgencyThe European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
(ESA) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Inter-American Development BankInter-American Development BankThe Inter-American Development Bank is the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean...
(IADB) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Chamber of CommerceInternational Chamber of CommerceThe International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its hundreds of thousands of member companies in over 130 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise....
(ICC) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Energy AgencyInternational Energy AgencyThe International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
(IEA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO)
- International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM) (guest)
- Nordic CouncilNordic CouncilThe Nordic Council is a geo-political, inter-parliamentary forum for co-operation between the Nordic countries. It was established following World War II and its first concrete result was the introduction in 1952 of a common labour market and free movement across borders without passports for the...
(NC) - Nordic Investment BankNordic Investment BankThe Nordic Investment Bank is an international financial institution founded in the mid-1970s by the five Nordic countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. In 2005, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland...
(NIB) - North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Nuclear Energy AgencyNuclear Energy AgencyThe Nuclear Energy Agency is an intergovernmental multinational agency that is organized under the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development...
(NEA) - Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Paris ClubParis ClubThe Paris Club is an informal group of financial officials from 19 of some of the world's biggest economies, which provides financial services such as war funding, debt restructuring, debt relief, and debt cancellation to indebted countries and their creditors...
- Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Schengen Convention
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesUnited Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesThe Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees , also known as The UN Refugee Agency is a United Nations agency mandated to protect and support refugees at the request of a government or the UN itself and assists in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to...
(UNHCR) - United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - United Nations Institute for Training and ResearchUnited Nations Institute for Training and ResearchThe United Nations Institute for Training and Research was established in 1965 following a "for the training of personnel, particularly from developing Member States, for administrative and operational assignments with the United Nations and the specialized agencies, both at Headquarters and in...
(UNITAR) - United Nations Interim Force in LebanonUnited Nations Interim Force in LebanonThe United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, or UNIFIL, was created by the United Nations, with the adoption of Security Council Resolution 425 and 426 on 19 March 1978, to confirm Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon which Israel had invaded five days prior, restore international peace and security,...
(UNIFIL) - United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS)
- United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near EastUnited Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near EastUnited Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East is a relief and human development agency, providing education, health care, social services and emergency aid to 5 million Palestine refugees living in Jordan, Lebanon and Syria, as well as in the West Bank and the Gaza...
(UNRWA) - United Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationUnited Nations Truce Supervision OrganizationThe United Nations Truce Supervision Organization is an organization founded on 29 May 1948 for peacekeeping in the Middle East. Its primary task was providing the military command structure to the peace keeping forces in the Middle East to enable the peace keepers to observe and maintain the...
(UNTSO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) (associate) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) - Zangger CommitteeZangger CommitteeThe Zangger Committee, also known as the Nuclear Exporters Committee, sprang from Article III.2 of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons which entered into force on March 5, 1970...
(ZC)
Law and order in Norway
- Capital punishment in NorwayCapital punishment in NorwayCapital punishment in Norway was abolished in peacetime with the criminal law that was passed in 1902 with enforcement beginning in 1905. Capital punishment was also abolished in times of war in 1979....
- Constitution of NorwayConstitution of NorwayThe Constitution of Norway was first adopted on May 16, 1814 by the Norwegian Constituent Assembly at Eidsvoll , then signed and dated May 17...
- Crime in Norway
- Human rights in Norway
- LGBT rights in Norway
- Freedom of religion in Norway
- Law enforcement in NorwayLaw enforcement in NorwayLaw enforcement in Norway is the direct responsibility of the Norwegian Police Service. However, other agencies subordinate to the Minister of Justice and the Police, such as the National Security Authority and Police Security Agency also play a role. The Norwegian Police Service is controlled by...
Military of Norway
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Norway
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Norway
- Navy of Norway
- Air Force of Norway
- Special forces of Norway
- Military history of NorwayMilitary history of NorwayThe Military history of Norway commences before the Viking age with the internal wars fought between regional kings to obtain the supreme kingship og the whole of Norway. The most famous period of Norwegian history and thus military history is the Viking age, but the early Middle Ages was the era...
- Military ranks of Norway
Culture of Norway
- Architecture of NorwayArchitecture of NorwayThe architecture of Norway has evolved in response to changing economic conditions, technological advances, demographic fluctuations and cultural shifts...
- Cuisine of NorwayCuisine of NorwayNorwegian cuisine in its traditional form is based largely on the raw materials readily available in Norway and its mountains, wilderness and coast...
- Languages of NorwayLanguages of NorwayThere are a large number of languages spoken in Norway. Of these, the Norwegian language is the most widely spoken and the main official language of the country.-Norwegian:...
- Media in Norway
- National symbols of Norway
- Coat of arms of NorwayCoat of arms of NorwayThe coat of arms of Norway is a crowned, golden lion rampant holding an axe with an argent blade, on a crowned, triangular and red escutcheon. Its elements originate from personal insignias for the royal house in the High Middle Ages, thus being among the oldest in Europe...
- Flag of NorwayFlag of NorwayThe flag of Norway is red with an indigo blue Scandinavian cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog, the flag of Denmark.- History :...
- National anthem of Norway
- Coat of arms of Norway
- People of Norway
- Prostitution in NorwayProstitution in NorwayProstitution in Norway is only illegal in that paying for sex is a crime...
- Public holidays in NorwayPublic holidays in NorwayHolidays in Norway...
- Religion in NorwayReligion in NorwayNominal religion in Norway is mostly Protestant with 78.9% belonging to the state Evangelical Lutheran Church of Norway. Early Norwegians, like all of the people of Scandinavia, believed in Norse paganism; the Sámi having a shamanistic religion...
- Buddhism in NorwayBuddhism in NorwayBuddhism in Norway has existed since the beginning of the 1970s, after immigration from countries with Buddhist populations, mainly Vietnam. Buddhistforbundet in Norway was established as a religious society in 1979 by two Buddhist groups who wanted to create a common organization to preserve...
- Christianity in NorwayChristianity in NorwayChristianity is the largest religion in Norway. Norway has historically been called a Christian country, but according to the most recent Eurobarometer Poll 2005, only 32% of the Norwegian population say they believe there is a God. A majority of the population are members of the Church of Norway...
- Church of NorwayChurch of NorwayThe Church of Norway is the state church of Norway, established after the Lutheran reformation in Denmark-Norway in 1536-1537 broke the ties to the Holy See. The church confesses the Lutheran Christian faith...
- Roman Catholicism in NorwayRoman Catholicism in NorwayRoman Catholicism in Norway is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope, the Curia in Rome and the Scandinavian Bishops Conference.There are about 83,000 - 230,000 Catholics in the country, 70% of whom were born abroad...
- Pentecostalism in NorwayPentecostalism in NorwayPentecostal congregations in Norway is the largest Protestant free church in Norway with a total membership at 39,590 people in 2009....
- Evangelical Lutheran Free Church of NorwayEvangelical Lutheran Free Church of NorwayThe Evangelical Lutheran Free Church, or the Free Church as it is commonly known, is a nationwide Lutheran church in Norway consisting of 81 congregations and 21,817 baptized members. It was founded in 1877 in Moss. It should not be confused with the Church of Norway, though both churches are...
- Baptism in NorwayBaptism in NorwayThe Norwegian Baptist Union is a baptist community in Norway.Most countries have a number of Baptist societies or associations of Baptist churches. In Norway, we find only a Baptist community, but there are independent Baptist congregation outside the Baptist community, which is not organized as a...
- Orthodoxy in NorwayOrthodoxy in NorwayOrthodoxy in Norway is a small minority religion in Norway with 8,492 official members in 2010, up from 2,315 in 2000.- History of the Orthodox Church in Norway :...
- Adventism in NorwayAdventism in NorwayAdventist congregations in Norway is a protestant free church in Norway with a total mempership of 5,086 people in 2009 in about 70 local churches....
- Church of Norway
- Hinduism in NorwayHinduism in NorwayIn Norway 0.1% of the total population are Hindus, of South Asian descent and around 75% of those are Tamil Hindus from Sri Lanka.-Ethnic Background of Hindus in Norway:...
- Islam in NorwayIslam in NorwayIslam is the largest minority religion in Norway, which consist between 2.0% and 3.4% of the population. In 2007, government statistics registered 79,068 members of Islamic congregations in Norway, about 10% more than in 2006. 56% lived in the counties of Oslo and Akershus...
- Judaism in Norway
- Buddhism in Norway
- World Heritage Sites in Norway
Art in Norway
- Cinema of NorwayCinema of NorwayNorway has had a notable cinema industry for some time. In the early 21st century a few Norwegian film directors have had the opportunity to go to Hollywood to direct various independent films.-1940s:*Tante Pose *Bastard *Tørres Snørtevold...
- Literature of Norway
- Music of NorwayMusic of NorwayMusic based on traditional Norwegian form usually includes minor or modal scales , making a sober and haunting sound. Pure major key dance music forms also exist. Prior to the 18th century, there is scant written record of what kind of music was played in Norway, but there is a large aural tradition...
- Television in NorwayTelevision in NorwayTelevision in Norway was introduced in 1954. Nowadays, 40% of the population have cable TV, and 30% have satellite TV. Another 30% have terrestrial television only.- Analogue terrestrial television :...
Sports in Norway
- Football in NorwayFootball in NorwayFootball is the most popular sport in Norway in terms of active membership . The Football Association of Norway was founded in 1902 and the first international match was played in 1908. There are 1,822 registered football clubs and about 25,000 teams...
- Norway at the Olympics
- Rugby league in NorwayRugby league in NorwayRugby league is a developing team sport in Norway. The sport is administered there by Rugby League Norge, which was set up in late 2008.-History:Continuing the pattern set by such European nations as Czech Republic, Germany and Lebanon, Norway are new to the game. In February 2008, Norway were...
Economy and infrastructure of Norway
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 23rd (twenty-third)
- Agriculture in Norway
- Banking in Norway
- National Bank of Norway
- Communications in NorwayCommunications in NorwayNorway has a relatively advanced telecommunications structure. There are about as many cellular phone subscription as there are inhabitants in the country , while the number of fixed line telephone subscriptions is declining towards 2 million...
- Internet in NorwayInternet in NorwayADSL became available to private consumers around late 2000.Depending on the provider, offered speeds range from 512/128 kbit/s to as high as 8/1 Mbit/s for ADSL, while ADSL2+ is slowly becoming available with speeds reaching up to 24/1.5 Mbit/s....
- Internet in Norway
- Companies of Norway
- Currency of NorwayCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: KroneNorwegian kroneThe krone is the currency of Norway and its dependent territories. The plural form is kroner . It is subdivided into 100 øre. The ISO 4217 code is NOK, although the common local abbreviation is kr. The name translates into English as "crown"...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: NOK
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Norway
- Energy in NorwayEnergy in NorwaySince the discovery of North Sea oil in Norwegian waters during the late 1960s, exports of oil and gas have become very important elements of the economy of Norway...
- Energy policy of Norway
- Oil industry in Norway
- Mining in Norway
- Norway Stock Exchange
- Tourism in NorwayTourism in NorwayThe main tourist attractions of Norway are the fjord-indented coastline and its mountains, the unspoiled nature of the inner parts of the country, and the cities and smaller towns.-Attractions:...
- Transport in NorwayTransport in NorwayTransport in Norway is highly influenced by Norway's low population density, narrow shape and long coastline. Norway has old water transport traditions, but road, rail and air transport have increased in importance during the 20th century...
- Whaling in NorwayWhaling in NorwayWhaling in Norway involves the hunting of the Minke whale for the purpose of using the whale meat for human consumption, generally in Northern Norway. This hunting has occurred since the early 20th Century, and some still continue the practice in the modern day.- History :Norwegian whaling has a...
Infrastructure of Norway
- Health care in Norway
- Transportation in Norway
- Airports in Norway
- Rail transport in NorwayRail transport in NorwayThe Norwegian railway system comprises 4,087 km of track of which 2,622 km is electrified and 242 km double track. There are 696 tunnels and 2760 bridges....
- Roads in Norway
- Water supply and sanitation in Norway
See also
- Index of Norway-related articles
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
- Norway.no, Norway's official portal.
- Norway.info
- Minifacts about Norway from Statistics Norway
- VisitNorway.com, official travel guide to Norway.
- Gymlink.no, a directory of gyms in Norway for visitors and tourists.
- Olive.no, a guide to restaurants in Norway.
- Pictures from Norway




