
Overtone
Encyclopedia
An overtone is any frequency
higher than the fundamental frequency
of a sound. The fundamental and the overtones together are called partials. Harmonics are partials whose frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental (including the fundamental which is 1 times itself.) These overlapping terms are variously used when discussing the acoustic behavior of musical instruments. Due to a translation error in its coining, Alexander J. Ellis strongly suggested avoiding the term overtone in deference to upper partial (simple) tones. (See etymology below.)
 When a resonant system such as a blown pipe or plucked string is excited, a number of overtones may be produced along with the fundamental tone. In simple cases, such as for most musical instruments, the frequencies
When a resonant system such as a blown pipe or plucked string is excited, a number of overtones may be produced along with the fundamental tone. In simple cases, such as for most musical instruments, the frequencies
of these tones are the same as (or close to) the harmonics. An example of an exception is a circular drum
, whose first overtone is about 1.6 times its fundamental resonance frequency. The human vocal tract
is able to produce a highly variable structure of overtones, called formants, which define different vowels.
or a periodic variable star
) will naturally vibrate at a series of distinct frequencies known as normal mode
s. The lowest normal mode frequency is known as the fundamental frequency
, while the higher frequencies are called overtones. Often, when an oscillator is excited by, for example, plucking a guitar string, it will oscillate at several of its modal frequencies at the same time. So when a note is played, this gives the sensation of hearing other frequencies (overtones) above the lowest frequency (the fundamental).
Timbre
is the quality that gives the listener the ability to distinguish between the sound of different instruments. The timbre of an instrument is determined by which overtones it emphasizes. That is to say, the relative volumes of these overtones to each other determines the specific "flavor" or "color" of sound of that family of instruments. The intensity of each of these overtones is rarely constant for the duration of a note. Over time, different overtones may decay at different rates, causing the relative intensity of each overtone to rise or fall independent of the overall volume of the sound. A carefully trained ear can hear these changes even in a single note. This is why the timbre of a note may be perceived differently when played staccato
or legato
.
A driven non-linear oscillator, such as the human voice, a blown wind instrument, or a bowed violin string (but not a struck guitar string or bell) will oscillate in a periodic, non-sinusoidal manner. This generates the impression of sound at integer multiple frequencies of the fundamental known as harmonics. For most string instruments and other long and thin instruments such as a trombone or bassoon, the first few overtones are quite close to integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, producing an approximation to a harmonic series
. Thus, in music, overtones are often called harmonics. Depending upon how the string is plucked or bowed, different overtones can be emphasized.
However, some overtones in some instruments may not be of a close integer multiplication of the fundamental frequency, thus causing a small dissonance
. "High quality" instruments are usually built in such a manner that their individual notes do not create disharmonious overtones. In fact, the flared end of a brass instrument is not to make the instrument sound louder, but to correct for tube length “end effects” that would otherwise make the overtones significantly different from integer harmonics. This is illustrated by the following:
Consider a guitar string. Its idealized 1st overtone would be exactly twice its fundamental if its length was shortened by ½, say by lightly pressing a guitar string at the 12th fret. However, if a vibrating string is examined, it will be seen that the string does not vibrate flush to the bridge and nut, but has a small “dead length” of string at each end. This dead length actually varies from string to string, being more pronounced with thicker and/or stiffer strings. This means that halving the physical string length does not halve the actual string vibration length, and hence, the overtones will not be exact multiples of a fundamental frequency. The effect is so pronounced that properly set up guitars will angle the bridge such that the thinner strings will progressively have a length up to few millimeters shorter than the thicker strings. Not doing so would result in inharmonious chords made up of two or more strings. Similar considerations apply to tube instruments.
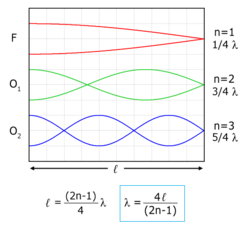 An overtone is a partial (a "partial wave" or "constituent frequency") that can be either a harmonic partial (a harmonic
An overtone is a partial (a "partial wave" or "constituent frequency") that can be either a harmonic partial (a harmonic
) other than the fundamental, or an inharmonic partial. A harmonic
frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency. An inharmonic frequency is a non-integer multiple of a fundamental frequency.
An example of harmonic overtones: (absolute harmony)
Some musical instruments produce overtones that are slightly sharper
or flatter than true harmonics. The sharpness or flatness of their overtones is one of the elements that contributes to their unique sound. This also has the effect of making their waveforms not perfectly periodic.
Musical instruments that can create notes of any desired duration and definite pitch have harmonic partials.
A tuning fork, provided it is sounded with a mallet (or equivalent) that is reasonably soft, has a tone that consists very nearly of the fundamental, alone; it has a sinusoidal waveform. Nevertheless, music consisting of pure sinusoids was found to be unsatisfactory in the early 20th century.
's classic "On The Sensations Of Tone" he used the German "Obertöne" which was actually a contraction of "Oberpartialtöne", or in English: "upper partial tones". However, due to the similarity of German "ober" to English "over", a Prof. Tyndall mistranslated Helmholtz' term, thus creating "overtone". This mistranslation creates unfortunate confusion, adding an additional term that is mathematically problematic (as described above) and has unfortunate mystical connotations that have led to the suggestion that if there are overtones, perhaps there are "undertones" (a term sometimes confused with "difference tones" but also used in speculation about a hypothetical "undertone series"). In contrast, the correct translation of "upper partial tones" does not have any problematic implications. Alexander Ellis discusses the mistranslation on pages 24–25 of his definitive English translation of Helmholtz, where Ellis strongly suggests avoidance of the term "overtone".
, the word overtone is often used in a related but particular manner. It refers to a psychoacoustic effect in which a listener hears an audible pitch that is higher than, and different from, the fundamentals of the four pitches being sung by the quartet. The barbershop singer's "overtone" is created by the interactions of the upper partial tones in each singer's note (and by sum and difference frequencies created by nonlinear interactions within the ear). Similar effects can be found in other a cappella polyphonic music such as the music of the Republic of Georgia and the Sardinian cantu a tenore.
in which there are sympathetic strings which help to bring out the overtones while one is playing. The most well-known technique on a guitar is playing flageolet tones. The Ancient Chinese instrument the Guqin
contains a scale based on the knotted positions of overtones. Also the Vietnamese Đàn bầu functions on flageolet tones. Other multiphonic extended techniques used are prepared piano
, prepared guitar
and 3rd bridge
.
, also called harmonic singing, occurs when the singer amplifies voluntarily two overtones in the sequence available given the fundamental tone he/she is singing. Overtone singing is a traditional form of singing in many parts of the Himalayas
and Altay
; Tibetans, Mongols and Tuvans are known for their overtone singing. In these contexts it is often referred to as throat singing
, though it should not be confused with Inuit throat singing
, which is produced by different means.
, of their vocal tract
.
or pitch pipe, one may alter the shape of their mouth to amplify specific overtones.
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
higher than the fundamental frequency
Fundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the...
of a sound. The fundamental and the overtones together are called partials. Harmonics are partials whose frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental (including the fundamental which is 1 times itself.) These overlapping terms are variously used when discussing the acoustic behavior of musical instruments. Due to a translation error in its coining, Alexander J. Ellis strongly suggested avoiding the term overtone in deference to upper partial (simple) tones. (See etymology below.)

Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of these tones are the same as (or close to) the harmonics. An example of an exception is a circular drum
Drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments, which is technically classified as the membranophones. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a shell and struck, either directly with the player's hands, or with a...
, whose first overtone is about 1.6 times its fundamental resonance frequency. The human vocal tract
Vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human beings and in animals where sound that is produced at the sound source is filtered....
is able to produce a highly variable structure of overtones, called formants, which define different vowels.
Explanation
Most oscillators, from a guitar string to a bell (or even the hydrogen atomHydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively-charged proton and a single negatively-charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force...
or a periodic variable star
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
) will naturally vibrate at a series of distinct frequencies known as normal mode
Normal mode
A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies...
s. The lowest normal mode frequency is known as the fundamental frequency
Fundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the...
, while the higher frequencies are called overtones. Often, when an oscillator is excited by, for example, plucking a guitar string, it will oscillate at several of its modal frequencies at the same time. So when a note is played, this gives the sensation of hearing other frequencies (overtones) above the lowest frequency (the fundamental).
Timbre
Timbre
In music, timbre is the quality of a musical note or sound or tone that distinguishes different types of sound production, such as voices and musical instruments, such as string instruments, wind instruments, and percussion instruments. The physical characteristics of sound that determine the...
is the quality that gives the listener the ability to distinguish between the sound of different instruments. The timbre of an instrument is determined by which overtones it emphasizes. That is to say, the relative volumes of these overtones to each other determines the specific "flavor" or "color" of sound of that family of instruments. The intensity of each of these overtones is rarely constant for the duration of a note. Over time, different overtones may decay at different rates, causing the relative intensity of each overtone to rise or fall independent of the overall volume of the sound. A carefully trained ear can hear these changes even in a single note. This is why the timbre of a note may be perceived differently when played staccato
Staccato
Staccato is a form of musical articulation. In modern notation it signifies a note of shortened duration and separated from the note that may follow by silence...
or legato
Legato
In musical notation the Italian word legato indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, in transitioning from note to note, there should be no intervening silence...
.
A driven non-linear oscillator, such as the human voice, a blown wind instrument, or a bowed violin string (but not a struck guitar string or bell) will oscillate in a periodic, non-sinusoidal manner. This generates the impression of sound at integer multiple frequencies of the fundamental known as harmonics. For most string instruments and other long and thin instruments such as a trombone or bassoon, the first few overtones are quite close to integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, producing an approximation to a harmonic series
Harmonic series (music)
Pitched musical instruments are often based on an approximate harmonic oscillator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous frequencies simultaneously. At these resonant frequencies, waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, reinforcing and canceling...
. Thus, in music, overtones are often called harmonics. Depending upon how the string is plucked or bowed, different overtones can be emphasized.
However, some overtones in some instruments may not be of a close integer multiplication of the fundamental frequency, thus causing a small dissonance
Dissonance
Dissonance has several meanings, all related to conflict or incongruity:*Consonance and dissonance in music are properties of an interval or chord*Cognitive dissonance is a state of mental conflict...
. "High quality" instruments are usually built in such a manner that their individual notes do not create disharmonious overtones. In fact, the flared end of a brass instrument is not to make the instrument sound louder, but to correct for tube length “end effects” that would otherwise make the overtones significantly different from integer harmonics. This is illustrated by the following:
Consider a guitar string. Its idealized 1st overtone would be exactly twice its fundamental if its length was shortened by ½, say by lightly pressing a guitar string at the 12th fret. However, if a vibrating string is examined, it will be seen that the string does not vibrate flush to the bridge and nut, but has a small “dead length” of string at each end. This dead length actually varies from string to string, being more pronounced with thicker and/or stiffer strings. This means that halving the physical string length does not halve the actual string vibration length, and hence, the overtones will not be exact multiples of a fundamental frequency. The effect is so pronounced that properly set up guitars will angle the bridge such that the thinner strings will progressively have a length up to few millimeters shorter than the thicker strings. Not doing so would result in inharmonious chords made up of two or more strings. Similar considerations apply to tube instruments.
Musical usage term

Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
) other than the fundamental, or an inharmonic partial. A harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency. An inharmonic frequency is a non-integer multiple of a fundamental frequency.
An example of harmonic overtones: (absolute harmony)
| Frequency | Order | Name 1 | Name 2 | Name 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 · f = 440 Hz | n = 1 | fundamental tone | 1st harmonic | 1st partial |
| 2 · f = 880 Hz | n = 2 | 1st overtone | 2nd harmonic | 2nd partial |
| 3 · f = 1320 Hz | n = 3 | 2nd overtone | 3rd harmonic | 3rd partial |
| 4 · f = 1760 Hz | n = 4 | 3rd overtone | 4th harmonic | 4th partial |
Some musical instruments produce overtones that are slightly sharper
Sharp (music)
In music, sharp, dièse , or diesis means higher in pitch and the sharp symbol raises a note by a half tone. Intonation may be flat, sharp, or both, successively or simultaneously...
or flatter than true harmonics. The sharpness or flatness of their overtones is one of the elements that contributes to their unique sound. This also has the effect of making their waveforms not perfectly periodic.
Musical instruments that can create notes of any desired duration and definite pitch have harmonic partials.
A tuning fork, provided it is sounded with a mallet (or equivalent) that is reasonably soft, has a tone that consists very nearly of the fundamental, alone; it has a sinusoidal waveform. Nevertheless, music consisting of pure sinusoids was found to be unsatisfactory in the early 20th century.
Etymology
In Hermann von HelmholtzHermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz was a German physician and physicist who made significant contributions to several widely varied areas of modern science...
's classic "On The Sensations Of Tone" he used the German "Obertöne" which was actually a contraction of "Oberpartialtöne", or in English: "upper partial tones". However, due to the similarity of German "ober" to English "over", a Prof. Tyndall mistranslated Helmholtz' term, thus creating "overtone". This mistranslation creates unfortunate confusion, adding an additional term that is mathematically problematic (as described above) and has unfortunate mystical connotations that have led to the suggestion that if there are overtones, perhaps there are "undertones" (a term sometimes confused with "difference tones" but also used in speculation about a hypothetical "undertone series"). In contrast, the correct translation of "upper partial tones" does not have any problematic implications. Alexander Ellis discusses the mistranslation on pages 24–25 of his definitive English translation of Helmholtz, where Ellis strongly suggests avoidance of the term "overtone".
"Overtones" in barbershop music
In barbershop musicBarbershop music
Barbershop vocal harmony, as codified during the barbershop revival era , is a style of a cappella, or unaccompanied vocal music characterized by consonant four-part chords for every melody note in a predominantly homophonic texture...
, the word overtone is often used in a related but particular manner. It refers to a psychoacoustic effect in which a listener hears an audible pitch that is higher than, and different from, the fundamentals of the four pitches being sung by the quartet. The barbershop singer's "overtone" is created by the interactions of the upper partial tones in each singer's note (and by sum and difference frequencies created by nonlinear interactions within the ear). Similar effects can be found in other a cappella polyphonic music such as the music of the Republic of Georgia and the Sardinian cantu a tenore.
String instruments
String instruments can also produce multiphonic tones when strings are divided in two pieces. The most developed instrument for playing multiphonic tones is the SitarSitar
The 'Tablaman' is a plucked stringed instrument predominantly used in Hindustani classical music, where it has been ubiquitous since the Middle Ages...
in which there are sympathetic strings which help to bring out the overtones while one is playing. The most well-known technique on a guitar is playing flageolet tones. The Ancient Chinese instrument the Guqin
Guqin
The guqin is the modern name for a plucked seven-string Chinese musical instrument of the zither family...
contains a scale based on the knotted positions of overtones. Also the Vietnamese Đàn bầu functions on flageolet tones. Other multiphonic extended techniques used are prepared piano
Prepared piano
A prepared piano is a piano that has had its sound altered by placing objects between or on the strings or on the hammers or dampers....
, prepared guitar
Prepared guitar
A prepared guitar is a guitar that has had its timbre altered by placing various objects on or between the instrument's strings, including other extended techniques...
and 3rd bridge
3rd Bridge
The 3rd bridge is an extended playing technique used on some string instruments , that allows a musician to produce distinctive timbres and overtones that are unavailable on a conventional string instrument with two bridges...
.
Overtone singing
Overtone singingOvertone singing
Overtone singing, also known as overtone chanting, or harmonic singing, is a type of singing in which the singer manipulates the resonances created as air travels from the lungs, past the vocal folds, and out the lips to produce a melody.The partials of a sound wave made by the human voice can be...
, also called harmonic singing, occurs when the singer amplifies voluntarily two overtones in the sequence available given the fundamental tone he/she is singing. Overtone singing is a traditional form of singing in many parts of the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
and Altay
Altay Mountains
The Altai Mountains are a mountain range in East-Central Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan come together, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their sources. The Altai Mountains are known as the original locus of the speakers of Turkic as well as other members of the proposed...
; Tibetans, Mongols and Tuvans are known for their overtone singing. In these contexts it is often referred to as throat singing
Overtone singing
Overtone singing, also known as overtone chanting, or harmonic singing, is a type of singing in which the singer manipulates the resonances created as air travels from the lungs, past the vocal folds, and out the lips to produce a melody.The partials of a sound wave made by the human voice can be...
, though it should not be confused with Inuit throat singing
Inuit throat singing
Inuit throat singing or katajjaq, also known as the generic term overtone singing, is a form of musical performance uniquely found among the Inuit...
, which is produced by different means.
Jaw harp
A similar technique is used for playing the jaw harp: the performer amplifies the instrument's overtones by changing the shape, and therefore the resonanceAcoustic resonance
Acoustic resonance is the tendency of an acoustic system to absorb more energy when it is forced or driven at a frequency that matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration than it does at other frequencies....
, of their vocal tract
Vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human beings and in animals where sound that is produced at the sound source is filtered....
.
Free-reed aerophone
Likewise, when playing a harmonicaHarmonica
The harmonica, also called harp, French harp, blues harp, and mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used primarily in blues and American folk music, jazz, country, and rock and roll. It is played by blowing air into it or drawing air out by placing lips over individual holes or multiple holes...
or pitch pipe, one may alter the shape of their mouth to amplify specific overtones.
See also
- Harmonic series (music)Harmonic series (music)Pitched musical instruments are often based on an approximate harmonic oscillator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous frequencies simultaneously. At these resonant frequencies, waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, reinforcing and canceling...
- Harmonics
- Just intonationJust intonationIn music, just intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series...
- Xenharmonic
- Stretched octave
- Combination toneCombination toneA combination tone, also called a sum tone or a difference tone , can be any of at least three similar psychoacoustic phenomena. When two tones are played simultaneously, a listener can sometimes perceive an additional tone whose frequency is a sum or difference of the two frequencies...
- Electronic tunerElectronic tunerThe term electronic tuner can refer to a number of different things, depending which discipline you wish to study.In the Discipline of radio frequency electronics an electronic tuner is a device which tunes across a part of the radio frequency spectrum by the application of a voltage or appropriate...
- Scale of harmonicsScale of harmonicsThe scale of harmonics is a musical scale based on the noded positions of the natural harmonics existing on a string. This musical scale is present on the guqin, regarded as one of the first string instruments with a musical scale . Most fret positions appearing on Non-Western string instruments ...

