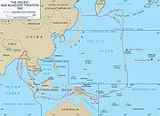
Pacific Theater of Operations
Encyclopedia
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
area of military activity in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
and the countries bordering it, a geographic scope that reflected the operational and administrative command structures of the American forces during that period. (The other areas of the Pacific War
Pacific War
The Pacific War, also sometimes called the Asia-Pacific War refers broadly to the parts of World War II that took place in the Pacific Ocean, its islands, and in East Asia, then called the Far East...
-- the China Burma India Theater, the South-East Asian Theatre
South-East Asian theatre of World War II
The South-East Asian Theatre of World War II was the name given to the campaigns of the Pacific War in Burma , Ceylon, India, Thailand, Indochina, Malaya and Singapore. Conflict in the theatre began when the Empire of Japan invaded Thailand and Malaya from bases located in Indochina on December 8,...
, and Manchurian Theatre
Soviet-Japanese War (1945)
The Soviet-Japanese War of 1945 , began on August 9, 1945, with the Soviet invasion of the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo. The Soviets liberated Manchukuo, Mengjiang , northern Korea, southern Sakhalin, and the Kuril Islands...
-- had their own respective command structures, independent of PTO.)
The Pacific Theater of Operations was one of two areas in which the United States initiated offensive ground combat operations against the Axis powers
Axis Powers
The Axis powers , also known as the Axis alliance, Axis nations, Axis countries, or just the Axis, was an alignment of great powers during the mid-20th century that fought World War II against the Allies. It began in 1936 with treaties of friendship between Germany and Italy and between Germany and...
in late 1942. This included operations by the 32nd and the 41st Infantry Divisions on New Guinea
New Guinea campaign
The New Guinea campaign was one of the major military campaigns of World War II.Before the war, the island of New Guinea was split between:...
, and the 1st Marine Division on Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal campaign
The Guadalcanal Campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by Allied forces, was a military campaign fought between August 7, 1942 and February 9, 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theatre of World War II...
. The other area was the Mediterranean Theater of Operations
Mediterranean Theater of Operations
The Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army was originally called North African Theater of Operations and is an American term for the conflict that took place between the Allies and Axis Powers in North Africa and Italy during World War II...
, beginning with Operation Torch
Operation Torch
Operation Torch was the British-American invasion of French North Africa in World War II during the North African Campaign, started on 8 November 1942....
in November.
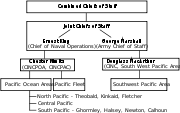
From mid-1942 until the end of the war in 1945, there were two operational commands in the PTO:
- Pacific Ocean AreasPacific Ocean AreasPacific Ocean Areas was a major Allied military command in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands during the Pacific War, and one of two United States commands in the Pacific Theater of Operations. Admiral Chester W. Nimitz of the U.S...
(POA; divided into Central Pacific Area, North Pacific Area and South Pacific Area), commanded by Admiral Chester Nimitz, Commander-in-Chief Pacific Ocean Areas - South West Pacific AreaSouth West Pacific AreaSouth West Pacific Area was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific theatres of World War II, during 1942–45...
(SWPA), commanded by General Douglas MacArthurDouglas MacArthurGeneral of the Army Douglas MacArthur was an American general and field marshal of the Philippine Army. He was a Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s and played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. He received the Medal of Honor for his service in the...
, Supreme Allied Commander South West Pacific Area.
In addition, during 1945, General Carl Spaatz
Carl Spaatz
Carl Andrew "Tooey" Spaatz GBE was an American World War II general and the first Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force. He was of German descent.-Early life:...
commanded the separate U.S. Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific.
Because of the complementary roles of the US Army
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
and the Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
in conducting war in the Pacific theater, there was no single Allied or U.S. commander (comparable to Eisenhower in the ETO
European Theater of Operations
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army was a United States Army formation which directed U.S. Army operations in parts of Europe from 1942 to 1945. It referred to Army Ground Forces, United States Army Air Forces, and Army Service Forces operations north of Italy and the...
) for the PTO. Indeed, the organizational structure was rather complex, requiring the frequent involvement of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the United States Department of Defense who advise the Secretary of Defense, the Homeland Security Council, the National Security Council and the President on military matters...
and the Army and Navy commanders each reporting to both the Secretary of War
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
and the Secretary of the Navy
United States Secretary of the Navy
The Secretary of the Navy of the United States of America is the head of the Department of the Navy, a component organization of the Department of Defense...
. (The consolidation of their respective cabinet departments into the Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
in 1947 addressed subsequent needs for control of joint operations on such large scales.)
The Pacific Ocean theater was one of four major naval theatres of war of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, that pitted forces of the Japan
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
against those of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the British Commonwealth, the Netherlands
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
and France.
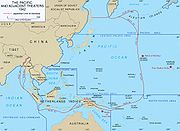
The theater included most of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
and its islands, excluding the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, the Netherlands East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
, the Territory of New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
(including the Bismarck Archipelago
Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea.-History:...
) and the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
(which were part of the Southwest Pacific area.) The Pacific Ocean theater also excluded China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
and mainland Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. It takes its name from 30 March 1942 when it became the major Allied
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
command
Command (military formation)
A command in military terminology is an organisational unit that the individual in Military command has responsibility for. A Commander will normally be specifically appointed into the role in order to provide a legal framework for the authority bestowed...
in the theater, known simply as "Pacific Ocean Areas".
Leaders
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1869 until 1947, when it was dissolved following Japan's constitutional renunciation of the use of force as a means of settling international disputes...
was led by Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto
Isoroku Yamamoto
was a Japanese Naval Marshal General and the commander-in-chief of the Combined Fleet during World War II, a graduate of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy and a student of Harvard University ....
, until he was killed in an attack by U.S. fighter planes in April 1943. Yamamoto was succeeded by Admiral Mineichi Koga
Mineichi Koga
- Notes :...
(1943–44) and Admiral Soemu Toyoda (1944–45).
Admiral, later Fleet Admiral Chester W. Nimitz commanded the vast majority of Allied naval forces in the Pacific Ocean during the period 1941–45. The Allied Pacific Ocean Areas (POA) command was formed in March 1942. The POA was further divided into the North, Central, and South Pacific Areas, with subordinate commanders. Nimitz retained direct control of the Central Pacific Area (CENPAC). General Douglas MacArthur commanded the Southwest Pacific Theater, administratively separate from Nimitz's command and strategically equal.
Major campaigns and battles


- Central Pacific Theater
- Attack on Pearl HarborAttack on Pearl HarborThe attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
7 December 1941 - Battle of Wake IslandBattle of Wake IslandThe Battle of Wake Island began simultaneously with the Attack on Pearl Harbor and ended on 23 December 1941, with the surrender of the American forces to the Empire of Japan...
7–23 December 1941 - Doolittle RaidDoolittle RaidThe Doolittle Raid, on 18 April 1942, was the first air raid by the United States to strike the Japanese Home Islands during World War II. By demonstrating that Japan itself was vulnerable to American air attack, it provided a vital morale boost and opportunity for U.S. retaliation after the...
18 April 1942 - Battle of the Coral SeaBattle of the Coral SeaThe Battle of the Coral Sea, fought from 4–8 May 1942, was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval and air forces from the United States and Australia. The battle was the first fleet action in which aircraft carriers engaged...
4–8 May 1942 - Battle of MidwayBattle of MidwayThe Battle of Midway is widely regarded as the most important naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II. Between 4 and 7 June 1942, approximately one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea and six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States Navy decisively defeated...
4–6 June 1942 - Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaignGilbert and Marshall Islands campaignIn the Pacific Theater of World War II, the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign, from November 1943 through February 1944, were key strategic operations of the United States Pacific Fleet and Marine Corps in the Central Pacific. The campaign was preceded by a raid on Makin Island by U.S...
1943–44- Makin Island raidMakin Island raidThe Makin Island Raid was an attack by the United States Marine Corps on Japanese military forces on Makin Island in the Pacific Ocean...
17–18 August 1942 - Battle of TarawaBattle of TarawaThe Battle of Tarawa, code named Operation Galvanic, was a battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II, largely fought from November 20 to November 23, 1943. It was the first American offensive in the critical central Pacific region....
20 November 1943 - Battle of KwajaleinBattle of KwajaleinThe Battle of Kwajalein was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought from 31 January-3 February 1944, on Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Employing the hard-learned lessons of the battle of Tarawa, the United States launched a successful twin assault on the main islands of...
1 February 1944 - Battle of EniwetokBattle of Eniwetok-External links:* *...
17 February 1944
- Makin Island raid
- Mariana and Palau Islands campaignMariana and Palau Islands campaignThe Mariana and Palau Islands campaign, also known as Operation Forager, was an offensive launched by United States forces against Imperial Japanese forces in the Mariana Islands and Palau in the Pacific Ocean between June and November, 1944 during the Pacific War...
1944- Battle of SaipanBattle of SaipanThe Battle of Saipan was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on the island of Saipan in the Mariana Islands from 15 June-9 July 1944. The Allied invasion fleet embarking the expeditionary forces left Pearl Harbor on 5 June 1944, the day before Operation Overlord in Europe was...
15 June 1944 - Battle of the Philippine SeaBattle of the Philippine SeaThe Battle of the Philippine Sea was a decisive naval battle of World War II which effectively eliminated the Imperial Japanese Navy's ability to conduct large-scale carrier actions. It took place during the United States' amphibious invasion of the Mariana Islands during the Pacific War...
19–21 June 1944 - Battle of Guam (1944) 21 July
- Battle of TinianBattle of TinianThe Battle of Tinian was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on the island of Tinian in the Mariana Islands from 24 July 1944 to 1 August 1944.-Background:...
24 July 1944 - Battle of PeleliuBattle of PeleliuThe Battle of Peleliu, codenamed Operation Stalemate II, was fought between the United States and the Empire of Japan in the Pacific Theater of World War II, from September–November 1944 on the island of Peleliu, present-day Palau. U.S...
15 September 1944 - Battle of AngaurBattle of AngaurThe Battle of Angaur was a battle of the Pacific campaign in World War II, fought on the island of Angaur in the Palau Islands from 17 —30 September 1944.-Background:...
17 September 1944
- Battle of Saipan
- Volcano and Ryukyu Islands campaignVolcano and Ryukyu Islands campaign-Further reading:...
1945- Battle of Iwo JimaBattle of Iwo JimaThe Battle of Iwo Jima , or Operation Detachment, was a major battle in which the United States fought for and captured the island of Iwo Jima from the Empire of Japan. The U.S...
19 February 1945 - Battle of OkinawaBattle of OkinawaThe Battle of Okinawa, codenamed Operation Iceberg, was fought on the Ryukyu Islands of Okinawa and was the largest amphibious assault in the Pacific War of World War II. The 82-day-long battle lasted from early April until mid-June 1945...
1 April 1945
- Battle of Iwo Jima
- Attack on Pearl Harbor
- North Pacific Theater
- Aleutian Islands Campaign 1942–43
- Battle of the Komandorski IslandsBattle of the Komandorski IslandsThe Battle of the Komandorski Islands was one of the most unusual engagements of World War II. It was a naval battle which took place on 27 March 1943 in the North Pacific area of the Pacific Ocean, near the Soviet Komandorski Islands.-Background:...
26 March 1943

