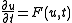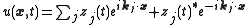Pattern formation
Encyclopedia
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically
) orderly outcomes of self-organisation
and the common principles behind similar pattern
s.
In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fates
in space and time. Pattern formation is controlled by genes. The role of genes in pattern formation is best understood in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly).
Animal markings, segmentation of animals, phyllotaxis
, neuronal activation patterns like tonotopy
, predator-prey equations' trajectories.
In developmental biology, pattern formation describes the mechanism by which initially equivalent cells in
a developing tissue assume complex forms and functions by coordinated cell fate
control. Pattern
formation is genetically controlled, and often involves each cell in a field sensing and responding to its position along a morphogen
gradient, followed by short distance cell-to-cell communication through cell signaling
pathways to refine the initial pattern. In this context, a field of cells is the group of cells whose fates are affected by responding to the same set positional information cues. This conceptual model was first described as French flag model
in the 1960s.
. The development of Drosophila is particularly well studied, and it is representative of a major class of animals, the insects or insect
a. Other multicellular organisms sometimes use similar mechanisms for axis formation, although the relative importance of signal transfer between the earliest cells of many developing organisms is greater than in the example described here.
systems and Turing Patterns
, cloud formation
s in stripes or rolls. Ripples in icicles. Washboard patterns on dirtroads. Dendrites
in solidification
, liquid crystal
s, the structure of foam
s .
have been used to generate organic-looking textures for more realistic shading
of 3d objects
.
A popular photoshop plugin, KPT 6
, included a filter called 'KPT reaction'. Reaction produced reaction-diffusion
style patterns based on the supplied seed image.
A similar effect to 'kpt reaction' can be achieved, with a little patience, by repeatedly sharpening and then blurring an image in many graphics applications. If other filters are used, such as emboss
or edge detection
, different types of effects can be achieved.
In addition, computers are often used to simulate
the biological, physical or chemical processes -described above- that lead to pattern formation, and they are then able to display the results in a realistic way (applications of virtual reality for Science). Calculations - using models like Reaction-diffusion or MClone
- are based on the actual mathematical equations designed by the scientists to model the studied phenomena.
model of the system (the Swift-Hohenberg equation is one such model) of the form
where F is generically a nonlinear differential operator
, and postulating solutions of the form
where the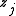 are complex amplitudes associated to different modes in the solution and the
are complex amplitudes associated to different modes in the solution and the 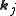 are the wave-vectors associated to a lattice
are the wave-vectors associated to a lattice
, e.g. a square or hexagonal lattice in two dimensions. There is in general no rigorous justification for this restriction to a lattice.
Symmetry considerations can now be taken into account, and evolution equations obtained for the complex amplitudes governing the solution. This reduction puts the problem into the form of a system of first-order ODE
s, which can be analysed using standard methods (see dynamical system
s). The same formalism can also be used to analyse bifurcation
s in pattern-forming systems, for example to analyse the formation of convection
rolls in a Rayleigh-Bénard experiment as the temperature is increased.
Such analysis predicts many of the quantitative features of such experiments - for example, the ODE reduction predicts hysteresis
in convection experiments as patterns of rolls and hexagons compete for stability. The same hysteresis has been observed experimentally.
Similarity
-Specific definitions:Different fields provide differing definitions of similarity:-In computer science:* string metric, aka string similarity* semantic similarity in computational linguistics-In other fields:...
) orderly outcomes of self-organisation
Self-organization
Self-organization is the process where a structure or pattern appears in a system without a central authority or external element imposing it through planning...
and the common principles behind similar pattern
Pattern
A pattern, from the French patron, is a type of theme of recurring events or objects, sometimes referred to as elements of a set of objects.These elements repeat in a predictable manner...
s.
In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fates
Cell fate determination
Within the field of developmental biology one goal is to understand how a particular cell develops into the final cell type , essentially how a cell’s fate is determined. Within an embryo, 4 processes play out at the cellular and tissue level to essentially create the final organism...
in space and time. Pattern formation is controlled by genes. The role of genes in pattern formation is best understood in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly).
Biology
- See also: Regional specificationRegional specificationIn the field of developmental biology, regional specification is the process by which different areas are identified in the development of the early embryo. The process by which the cells become specified differs between organisms.-Cell fate determination:...
, Morphogenetic fieldMorphogenetic fieldIn developmental biology, a morphogenetic field is a group of cells able to respond to discrete, localized biochemical signals leading to the development of specific morphological structures or organs. The spatial and temporal extent of the embryonic fields are dynamic, and within the field is a...
Animal markings, segmentation of animals, phyllotaxis
Phyllotaxis
In botany, phyllotaxis or phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves on a plant stem .- Pattern structure :...
, neuronal activation patterns like tonotopy
Tonotopy
In physiology, tonotopy is the spatial arrangement of where sounds of different frequency are processed in the brain. Tones close to each other in terms of frequency are represented in topologically neighbouring regions in the brain...
, predator-prey equations' trajectories.
In developmental biology, pattern formation describes the mechanism by which initially equivalent cells in
a developing tissue assume complex forms and functions by coordinated cell fate
Cell fate determination
Within the field of developmental biology one goal is to understand how a particular cell develops into the final cell type , essentially how a cell’s fate is determined. Within an embryo, 4 processes play out at the cellular and tissue level to essentially create the final organism...
control. Pattern
formation is genetically controlled, and often involves each cell in a field sensing and responding to its position along a morphogen
Morphogen
A morphogen is a substance governing the pattern of tissue development, and the positions of the various specialized cell types within a tissue...
gradient, followed by short distance cell-to-cell communication through cell signaling
Cell signaling
Cell signaling is part of a complex system of communication that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity as well as normal tissue...
pathways to refine the initial pattern. In this context, a field of cells is the group of cells whose fates are affected by responding to the same set positional information cues. This conceptual model was first described as French flag model
French flag model
The French Flag Model is a conceptual definition of a morphogen, described by Lewis Wolpert in the 1960s. A morphogen is rigorously defined as a signaling molecule that acts directly on cells to produce specific cellular responses dependent on morphogen concentration...
in the 1960s.
Anterior-posterior axis patterning in Drosophila
One of the best understood examples of pattern formation is the patterning along the future head to tail (antero-posterior) axis of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogasterDrosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting from Charles W...
. The development of Drosophila is particularly well studied, and it is representative of a major class of animals, the insects or insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
a. Other multicellular organisms sometimes use similar mechanisms for axis formation, although the relative importance of signal transfer between the earliest cells of many developing organisms is greater than in the example described here.
- See Drosophila embryogenesisDrosophila embryogenesisDrosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate...
Growth of Bacterial Colonies
Bacterial colonies show a large variety of beautiful patterns formed during colony growth. Experiments show that the resulting shapes depend on the growth conditions. In particular, stresses (hardness of the culture medium, lack of nutrients, etc.) seem to enhance the complexity of the resulting patterns.- See Bacterial patternsBacterial patternsThe formation of patterns in the growth of bacterial colonies has extensively been studied experimentally. Resulting morphologies appear to depend on the growth conditions...
Vegetation patterns
In arid area, vegetation show a large variety of spatial regular patterns. Patterns are modulated by aridity and slope and arise as the consequence of resource redistribution and concentration.- See Tiger bushTiger bushTiger bush is a patterned vegetation community consisting of alternating bands of trees or shrubs, separated by bare ground or low herb cover, that run roughly parallel to contour lines of equal elevation...
Chemistry
see reaction-diffusionReaction–diffusion system
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which explain how the concentration of one or more substances distributed in space changes under the influence of two processes: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the...
systems and Turing Patterns
- Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
- Liesegang ringsLiesegang ringsLiesegang rings are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction, under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection.-History:...
Physics
Bénard cells, LaserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
, cloud formation
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
s in stripes or rolls. Ripples in icicles. Washboard patterns on dirtroads. Dendrites
Dendrite (crystal)
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a typical multi-branching tree-like form. Dendritic crystal growth is very common and illustrated by snowflake formation and frost patterns on a window. Dendritic crystallization forms a natural fractal pattern...
in solidification
Freezing
Freezing or solidification is a phase change in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. The reverse process is melting....
, liquid crystal
Liquid crystal
Liquid crystals are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. For instance, an LC may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of LC phases, which can be...
s, the structure of foam
Foam
-Definition:A foam is a substance that is formed by trapping gas in a liquid or solid in a divided form, i.e. by forming gas regions inside liquid regions, leading to different kinds of dispersed media...
s .
Computer graphics
Some types of automataFinite state machine
A finite-state machine or finite-state automaton , or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model used to design computer programs and digital logic circuits. It is conceived as an abstract machine that can be in one of a finite number of states...
have been used to generate organic-looking textures for more realistic shading
Shader
In the field of computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that is used primarily to calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility...
of 3d objects
3D modeling
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical representation of any three-dimensional surface of object via specialized software. The product is called a 3D model...
.
A popular photoshop plugin, KPT 6
Kai's Power Tools
Kai's Power Tools are a set of API plugins created by Kai Krause that were designed for use with Adobe Systems Photoshop and Corel Photo-Paint. Kai's Power Tools were sold to Corel when MetaCreations was closed....
, included a filter called 'KPT reaction'. Reaction produced reaction-diffusion
Reaction–diffusion system
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which explain how the concentration of one or more substances distributed in space changes under the influence of two processes: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the...
style patterns based on the supplied seed image.
A similar effect to 'kpt reaction' can be achieved, with a little patience, by repeatedly sharpening and then blurring an image in many graphics applications. If other filters are used, such as emboss
Image embossing
Image embossing is a computer graphics technique in which each pixel of an image is replaced either by a highlight or a shadow, depending on light/dark boundaries on the original image. Low contrast areas are replaced by a gray background. The filtered image will represent the rate of color change...
or edge detection
Edge detection
Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aim at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities...
, different types of effects can be achieved.
In addition, computers are often used to simulate
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
the biological, physical or chemical processes -described above- that lead to pattern formation, and they are then able to display the results in a realistic way (applications of virtual reality for Science). Calculations - using models like Reaction-diffusion or MClone
MClone
MClone, or Clonal Mosaic, is a pattern formation algorithm proposed in 1998 used specially for simulating giraffes and members of the Phelidae family of the mammalians. It was primarily proposed as a 2D model and lately was extended to 3D...
- are based on the actual mathematical equations designed by the scientists to model the studied phenomena.
Analysis
The analysis of pattern-forming systems often consists of finding a PDEPartial differential equation
In mathematics, partial differential equations are a type of differential equation, i.e., a relation involving an unknown function of several independent variables and their partial derivatives with respect to those variables...
model of the system (the Swift-Hohenberg equation is one such model) of the form
where F is generically a nonlinear differential operator
Differential operator
In mathematics, a differential operator is an operator defined as a function of the differentiation operator. It is helpful, as a matter of notation first, to consider differentiation as an abstract operation, accepting a function and returning another .This article considers only linear operators,...
, and postulating solutions of the form
where the
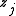 are complex amplitudes associated to different modes in the solution and the
are complex amplitudes associated to different modes in the solution and the 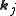 are the wave-vectors associated to a lattice
are the wave-vectors associated to a latticeLattice (group)
In mathematics, especially in geometry and group theory, a lattice in Rn is a discrete subgroup of Rn which spans the real vector space Rn. Every lattice in Rn can be generated from a basis for the vector space by forming all linear combinations with integer coefficients...
, e.g. a square or hexagonal lattice in two dimensions. There is in general no rigorous justification for this restriction to a lattice.
Symmetry considerations can now be taken into account, and evolution equations obtained for the complex amplitudes governing the solution. This reduction puts the problem into the form of a system of first-order ODE
ODE
ODE may refer to:* Ohio Department of Education, the state education agency of Ohio* Omicron Delta Epsilon, an international honor society in the field of economics* Open Dynamics Engine, a real-time physics engine...
s, which can be analysed using standard methods (see dynamical system
Dynamical system
A dynamical system is a concept in mathematics where a fixed rule describes the time dependence of a point in a geometrical space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, and the number of fish each springtime in a...
s). The same formalism can also be used to analyse bifurcation
Bifurcation
Bifurcation means the splitting of a main body into two parts.Bifurcation or Bifurcated may refer to:*Bifurcation , the division of issues in a trial for example the division of a page into two parts....
s in pattern-forming systems, for example to analyse the formation of convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
rolls in a Rayleigh-Bénard experiment as the temperature is increased.
Such analysis predicts many of the quantitative features of such experiments - for example, the ODE reduction predicts hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
in convection experiments as patterns of rolls and hexagons compete for stability. The same hysteresis has been observed experimentally.
See also
- MathematicaMathematicaMathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...
- FractalFractalA fractal has been defined as "a rough or fragmented geometric shape that can be split into parts, each of which is a reduced-size copy of the whole," a property called self-similarity...
- MorphogenesisMorphogenesisMorphogenesis , is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape...
- Reaction-diffusionReaction–diffusion systemReaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which explain how the concentration of one or more substances distributed in space changes under the influence of two processes: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the...
- Regional specificationRegional specificationIn the field of developmental biology, regional specification is the process by which different areas are identified in the development of the early embryo. The process by which the cells become specified differs between organisms.-Cell fate determination:...
- embryogenesisEmbryogenesisEmbryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
- embryoEmbryoAn embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
- model organismModel organismA model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the organism model will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are in vivo models and are widely used to...
- Drosophila embryogenesisDrosophila embryogenesisDrosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate...
- Tagmosis
- Projective GeometryProjective geometryIn mathematics, projective geometry is the study of geometric properties that are invariant under projective transformations. This means that, compared to elementary geometry, projective geometry has a different setting, projective space, and a selective set of basic geometric concepts...
- Gradient Pattern AnalysisGradient pattern analysisGradient pattern analysis is a geometric computing method for characterizing symmetry breaking of an ensemble of asymmetric vectors regularly distributed in a square lattice. Usually, the lattice of vectors represent the first-order gradient of a scalar field, here an M x M square amplitude matrix...
- Lee SegelLee SegelLee Segel was an applied mathematician primarily at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and the Weizmann Institute of Science. He is particularly known for his work in the spontaneous appearance of order in convection, slime molds and chemotaxis....
- MCloneMCloneMClone, or Clonal Mosaic, is a pattern formation algorithm proposed in 1998 used specially for simulating giraffes and members of the Phelidae family of the mammalians. It was primarily proposed as a 2D model and lately was extended to 3D...
- Three-phase traffic theory
External links
- SpiralZoom.com, an educational website about the science of pattern formation, spirals in nature, and spirals in the mythic imagination.
- TexRDTexRDTexRD is a small but singular software which generates animated random texturesbased on reaction-diffusion.-Principles:Complex chemical reactions between several fluids...
, a free software to experiment pattern formation with different kinds of reaction-diffusion models (simulations in 2 dimensions; basic interface with text parameters) - '15-line Matlab code', A simple 15-line Matlab program to simulate 2D pattern formation for reaction-diffusion model.