
Penem
Encyclopedia
Degree of unsaturation
The degree of unsaturation formula is used in organic chemistry to help draw chemical structures. The formula lets the user determine how many rings, double bonds, and triple bonds are present in the compound to be drawn...
β-lactam
Beta-lactam
A β-lactam ring, is a four-membered lactam. It is named as such, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the β-carbon relative to the carbonyl...
.
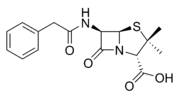
An example is faropenem
Faropenem
Faropenem is an orally-active beta-lactam antibiotic belonging to the penem group.It is resistant to some forms of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase.It is orally available.-Forms:...
.
Penems are similar in structure to carbapenem
Carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of β-lactam antibiotics with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity. They have a structure that renders them highly resistant to most β-lactamases...
s. However, where penems have a sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, carbapenems have another carbon.
There are no naturally occurring penems; all of them are synthetically made.
Nomenclature
β-Lactams are classified according to their core ring structures.- β-Lactams fused to saturatedSaturation (chemistry)In chemistry, saturation has six different meanings, all based on reaching a maximum capacity...
five-membered rings:- β-Lactams containing thiazolidineThiazolidineThiazolidines are a class of heterocyclic organic compounds with a 5-membered saturated ring with a thioether group and an amine group in the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. It is a sulfur analogue of oxazolidine. The drug pioglitazone contains a thiazolidine ring. It is a drug usually indicated...
rings are named penamPenamPenams are a subclass of the broader β-lactam family of antibiotics and related compounds. Penams contain a β-lactam ring fused to a 5-membered ring, where one of the atoms in the ring is a sulfur and the ring is fully saturated. Penicillin is a member of this family of compounds....
s. - β-Lactams containing pyrrolidinePyrrolidinePyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9N. It is a cyclic secondary amine with a five-membered heterocycle containing four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom...
rings are named carbapenamCarbapenamA carbapenam is a β-lactam compound that is a saturated carbapenem. They exist primarily as biosynthetic intermediates on the way to the carbapenem antibiotics....
s. - β-Lactams fused to oxazolidineOxazolidineOxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbons, a nitrogen, a hydrogen, and an oxygen. The oxygen and NH are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon between the oxygen and the nitrogen . All of the carbons in oxazolidines...
rings are named oxapenams or clavamClavamA clavam is a molecule similar to a penam, but with an oxygen substituted for the sulfur. Thus, they are also known as oxapenams.An example is clavulanic acid....
s.
- β-Lactams containing thiazolidine
- β-Lactams fused to unsaturated five-membered rings:
- β-Lactams containing 2,3-dihydrothiazoleThiazoleThiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen; the term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS...
rings are named penemPenemA penem is a type of unsaturated β-lactam.An example is faropenem.Penems are similar in structure to carbapenems. However, where penems have a sulfur, carbapenems have another carbon....
s. - β-Lactams containing 2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolePyrrolePyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3...
rings are named carbapenemCarbapenemCarbapenems are a class of β-lactam antibiotics with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity. They have a structure that renders them highly resistant to most β-lactamases...
s.
- β-Lactams containing 2,3-dihydrothiazole
- β-Lactams fused to unsaturated six-membered rings:
- β-Lactams containing 3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3-thiazineThiazineThiazines are organic compounds containing a ring of four carbon, one nitrogen and one sulfur atom. Chemicals that include thiazine are used for dyes, tranquilizers and insecticides.-See also:*Methylene blue*Phenothiazine*Heterocyclic compound*Morpholine...
rings are named cephemCephemCephems are a sub-group of beta-lactam antibiotics including cephalosporins and cephamycins....
s. - β-Lactams containing 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridinePyridinePyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
rings are named carbacephemCarbacephemA carbacephem is a type of synthetically made antibiotic, based on the structure of cephalosporin, a cephem. Carbacephems are similar to cephems but with a carbon substituted for the sulfur....
s. - β-Lactams containing 3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3-oxazine rings are named oxacephemOxacephemAn oxacephem is a molecule similar to a cephem, but with oxygen substituted for the sulfur. They are synthetically made compounds and have not been discovered in nature.An example is moxalactam.Another example is flomoxef....
s.
- β-Lactams containing 3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3-thiazine
- β-Lactams not fused to any other ring are named monobactams.
Structure
Penem molecules do not occur naturally, and production of penems is an entirely synthetic process.Although structurally distinct, the penems are often confused with the carbapenem
Carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of β-lactam antibiotics with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity. They have a structure that renders them highly resistant to most β-lactamases...
class of drugs.
Five main penem subgroups — thiopenems, oxypenems, aminopenems, alkylpenems, and arylpenems — have been produced and are distinguished by the side chain of the unsaturated five-membered ring. One structurally distinct penem is BRL 42715. This molecule has no substitution at the above position, but has a bulky group atached to the β-lactam ring, and it displays effective inhibition of class C β-lactamase
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases are enzymes produced by some bacteria and are responsible for their resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems . These antibiotics have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam...
s, but no antimicrobial activity.
One possible consequence of these structural differences of penems from other β-lactams may be reduced immunogenicity and immunogenic cross-reactivity

