
Period 8 element
Encyclopedia
A period 8 element is any one of 50 hypothetical chemical element
s belonging to an eighth period
of the periodic table of the elements. They may be referred to using IUPAC systematic element name
s. None of these elements have been created, and it is possible that none have isotopes with stable enough nuclei to receive significant attention anytime soon. It is also probable that, due to drip instabilities, only the lower period-8 elements are physically possible.
If it were possible to produce sufficient quantities of these elements that would allow the study of their chemistry, these elements may well behave very differently from those of previous periods. This is because their electronic configurations may be altered by quantum
and relativistic
effects. This is because the energy levels of the 5g, 6f and 7d orbitals
are so close to each other that they may well exchange electrons with each other. This would result in a large number of elements in the superactinide series that would have extremely similar chemical properties and would be apparently quite unrelated to elements of lower atomic number.
The names given to these unattested elements are all IUPAC systematic names
.
of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number
118. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements concerned. Any additional periods are expected to contain a larger number of elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called g-block, containing 18 elements with partially filled g-orbital
s in each period. An eight-period table containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
in 1969. No elements in this region have been synthesized or discovered in nature. While Seaborg's version of the extended period had the heavier elements following the pattern set by lighter elements, other models do not. Pekka Pyykkö, for example, used computer modeling to calculate the positions of elements up to Z=172, and found that several were displaced from the Madelung rule.
He also suggests that period 8 be split into three parts:
. For example, chemical studies performed in 2007 strongly indicate that ununquadium
possesses non-eka-lead
properties and appears to behave as the first superheavy element that portrays noble-gas
-like properties due to relativistic effects
.
, and it is the first period that includes the g-block
; however, spin-orbit coupling effects reduce the validity of the orbital approximation substantially for elements of high atomic number
.
and unbinilium
, is to have a sensitivity on the order of femtobarns
, which is currently out of reach of even the most advanced facilities.
was attempted in 1985 by bombarding a target of einsteinium
-254 with calcium
-48 ions at the superHILAC accelerator at Berkeley, California. No atoms were identified, leading to a limiting yield of 300 nb.

It is highly unlikely that this reaction will be useful given the extremely difficult task of making
sufficient amounts of Es-254 to make a large enough target to increase the sensitivity of the experiment to the required level, due to the rarity of the element, and extreme rarity of the isotope.
In March–April 2007, the synthesis of unbinilium
was attempted at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions
in Dubna
by bombarding a plutonium
-244 target with iron
-58 ion
s. Initial analysis revealed that no atoms of element 120 were produced providing a limit of 400 fb
for the cross section at the energy studied.

The Russian team are planning to upgrade their facilities before attempting the reaction again.
In April 2007, the team at GSI
attempted to create unbinilium using uranium
-238 and nickel
-64:

No atoms were detected providing a limit of 1.6 pb on the cross section at the energy provided. The GSI repeated the experiment with higher sensitivity in three separate runs from April–May 2007, Jan–March 2008, and Sept–Oct 2008, all with negative results and providing a cross section limit of 90 fb.
elements, which have atomic numbers from 121 onwards, but it is not clear when the filling of the 5g subshell ends. These elements belong to the chemical series of superactinides, characterised by the filling of the 5g and 6f subshells, and they could therefore have different chemical properties that are reminiscent of the actinide
s; however, the proximity of the 5g and 6f subshells and the small gap between them and the 7d and 8p subshells could lead to a large number of elements whose properties are independent of their position in the periodic table.
These elements would only be detectable if they lie near the hypothesised island of stability
. The stability of these elements depends on the location of the island of stability; if the island is centred around a low Z, most superactinides would be too unstable to be detected, but if it is centred around a higher Z, there is a possibility of detecting the lower superactinides.
The first attempt to synthesize unbibium
was performed in 1972 by Flerov et al. at JINR, using the hot fusion reaction:
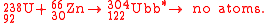
No atoms were detected and a yield limit of 5 mb
(5,000,000 pb
) was measured. Current results (see ununquadium
) have shown that the sensitivity of this experiment was too low by at least 6 orders of magnitude.
In 2000, the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
performed a very similar experiment with much higher sensitivity:

These results indicate that the synthesis of such heavier elements remains a significant challenge and further improvements of beam intensity and experimental efficiency is required. The sensitivity should be increased to 1 fb
.
Several experiments have been performed between 2000-2004 at the Flerov laboratory of Nuclear Reactions studying the fission characteristics of the compound nucleus 306Ubb. Two nuclear reactions have been used, namely 248Cm+58Fe and 242Pu+64Ni. The results have revealed how nuclei such as this fission predominantly by expelling closed shell nuclei such as 132Sn (Z=50, N=82). It was also found that the yield for the fusion-fission pathway was similar between 48Ca and 58Fe projectiles, indicating a possible future use of 58Fe projectiles in superheavy element formation.
In a series of experiments, scientists at GANIL have attempted to measure the direct and delayed fission of compound nuclei of elements with Z=114, 120, and 124 in order to probe shell effects in this region and to pinpoint the next spherical proton shell. In 2006, with full results published in 2008, the team provided results from a reaction involving the bombardment of a natural germanium target with uranium ions:
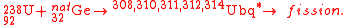
The team reported that they had been able to identify compound nuclei fissioning with half-lives > 10−18 s. Although very short, the ability to measure such decays indicated a strong shell effect at Z=124. A similar phenomenon was found for Z=120
but not for Z=114
.
The first attempt to synthesize unbihexium
was performed in 1971 by Bimbot et al. using the hot fusion reaction:
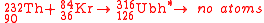
A high energy alpha particle
was observed and taken as possible evidence for the synthesis of unbihexium. Recent research suggests that this is highly unlikely as the sensitivity of experiments performed in 1971 would have been several orders of magnitude too low according to current understanding. To date, no other attempt has been made to synthesize unbihexium.
All other elements in this region of the periodic table and beyond have not received any attempts to synthesise them.
, element 137, is sometimes called feynmanium (symbol Fy) because Richard Feynman
noted that a simplistic interpretation of the relativistic
Dirac equation
runs into problems with electron orbitals at Z > 1/α = 137, suggesting that neutral atoms cannot exist beyond untriseptium, and that a periodic table of elements based on electron orbitals therefore breaks down at this point. However, a more rigorous analysis calculates the limit to be Z ≈ 173.
The Bohr model
exhibits difficulty for atoms with atomic number greater than 137, for the speed of an electron in a 1s electron orbital
, v, is given by

where Z is the atomic number
, and α is the fine structure constant, a measure of the strength of electromagnetic interactions. Under this approximation, any element with an atomic number of greater than 137 would require 1s electrons to be traveling faster than c, the speed of light
. Hence the non-relativistic Bohr model is clearly inaccurate when applied to such an element.
The relativistic
Dirac equation
also has problems for Z > 137, for the ground state energy is
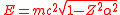
where m is the rest mass of the electron. For Z > 137, the wave function of the Dirac ground state is oscillatory, rather than bound, and there is no gap between the positive and negative energy spectra, as in the Klein paradox
.
More accurate calculations including the effects of the finite size of the nucleus indicate that the binding energy first exceeds 2mc2 for Z > Zcr ≈ 173. For Z > Zcr, if the innermost orbital is not filled, the electric field of the nucleus will pull an electron out of the vacuum, resulting in the spontaneous emission of a positron.
More complete analysis involving relativity shows that the contradiction this particle poses may actually occur in the hypothetical element untriennium (Z = 139; see unsolved problems in chemistry
).
The existence of such atoms is probably theoretically possible (the upper limit for atomic number is likely Z = 173 due to the light-speed limit
, after which assigning electron shells would be nonsensical and heavier elements would only be able to exist as ions), but it is not clear if our technology will ever suffice to synthesise them.
has predicted the electron configuration
s for the period 8 elements. Chemical series information is purely hypothetical and based on periodic trends which may not apply to elements this heavy. Pekka Pyykkö has also predicted the electron configurations for these elements. The predictions are drastically different.
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s belonging to an eighth period
Periodic table period
In the periodic table of the elements, elements are arranged in a series of rows so that those with similar properties appear in vertical columns. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells; with each group across a period, the elements have one more proton and electron...
of the periodic table of the elements. They may be referred to using IUPAC systematic element name
Systematic element name
A systematic element name is the temporary name and symbol assigned to newly synthesized and not yet synthesized chemical elements. In chemistry, a transuranic element receives a permanent name and symbol only after its synthesis has been confirmed. In some cases, this has been a protracted and...
s. None of these elements have been created, and it is possible that none have isotopes with stable enough nuclei to receive significant attention anytime soon. It is also probable that, due to drip instabilities, only the lower period-8 elements are physically possible.
If it were possible to produce sufficient quantities of these elements that would allow the study of their chemistry, these elements may well behave very differently from those of previous periods. This is because their electronic configurations may be altered by quantum
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
and relativistic
Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
effects. This is because the energy levels of the 5g, 6f and 7d orbitals
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
are so close to each other that they may well exchange electrons with each other. This would result in a large number of elements in the superactinide series that would have extremely similar chemical properties and would be apparently quite unrelated to elements of lower atomic number.
The names given to these unattested elements are all IUPAC systematic names
Systematic element name
A systematic element name is the temporary name and symbol assigned to newly synthesized and not yet synthesized chemical elements. In chemistry, a transuranic element receives a permanent name and symbol only after its synthesis has been confirmed. In some cases, this has been a protracted and...
.
History
There are currently seven periods in the periodic tablePeriodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
118. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements concerned. Any additional periods are expected to contain a larger number of elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called g-block, containing 18 elements with partially filled g-orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
s in each period. An eight-period table containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg was an American scientist who won the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "discoveries in the chemistry of the transuranium elements", contributed to the discovery and isolation of ten elements, and developed the actinide concept, which led to the current arrangement of the...
in 1969. No elements in this region have been synthesized or discovered in nature. While Seaborg's version of the extended period had the heavier elements following the pattern set by lighter elements, other models do not. Pekka Pyykkö, for example, used computer modeling to calculate the positions of elements up to Z=172, and found that several were displaced from the Madelung rule.
Aufbau principle model
This model would hold if electron configurations always followed the Madelung rule exactly.| 119 Uue Ununennium Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali... |
120 Ubn Unbinilium Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120.... |
121 Ubu Unbiunium Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table... |
122 Ubb Unbibium Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122.... |
123 Ubt |
124 Ubq Unbiquadium Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124.... |
125 Ubp |
126 Ubh Unbihexium Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:... |
127 Ubs |
128 Ubo |
129 Ube |
130 Utn |
131 Utu |
132 Utb |
133 Utt |
134 Utq |
135 Utp |
136 Uth |
137 Uts Untriseptium Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible... |
138 Uto |
139 Ute |
140 Uqn |
141 Uqu |
142 Uqb |
143 Uqt |
144 Uqq |
145 Uqp |
146 Uqh |
147 Uqs |
148 Uqo |
149 Uqe |
150 Upn |
151 Upu |
152 Upb |
153 Upt |
154 Upq |
155 Upp |
156 Uph |
157 Ups |
158 Upo |
159 Upe |
160 Uhn |
161 Uhu |
162 Uhb |
163 Uht |
164 Uhq |
165 Uhp |
166 Uhh |
167 Uhs |
168 Uho |
Pyykkö model
Pyykkö predicts that the orbital shells will fill up in this order:- 8s,
- 5g,
- the first two spaces of 8p,
- 6f,
- 7d,
- 9s,
- the first two spaces of 9p,
- the rest of 8p.
He also suggests that period 8 be split into three parts:
- 8a, containing 8s,
- 8b, containing the first two elements of 8p,
- 8c, containing 7d and the rest of 8p.
| 8 | 119 Uue Ununennium Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali... |
120 Ubn Unbinilium Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120.... |
121 Ubu Unbiunium Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table... |
122 Ubb Unbibium Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122.... |
123 Ubt |
124 Ubq Unbiquadium Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124.... |
125 Ubp |
126 Ubh Unbihexium Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:... |
127 Ubs |
128 Ubo |
129 Ube |
130 Utn |
131 Utu |
132 Utb |
133 Utt |
134 Utq |
135 Utp |
136 Uth |
137 Uts Untriseptium Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible... |
138 Uto |
141 Uqu |
142 Uqb |
143 Uqt |
144 Uqq |
145 Uqp |
146 Uqh |
147 Uqs |
148 Uqo |
149 Uqe |
150 Upn |
151 Upu |
152 Upb |
153 Upt |
154 Upq |
155 Upp |
156 Uph |
157 Ups |
158 Upo |
159 Upe |
160 Uhn |
161 Uhu |
162 Uhb |
163 Uht |
164 Uhq |
139 Ute |
140 Uqn |
169 Uhe |
170 Usn |
171 Usu |
172 Usb |
| 9 | 165 Uhp |
166 Uhh |
167 Uhs |
168 Uho |
Periodic trends
Periodic trends may not continue to hold at such high atomic number, and in fact may already break down in the late seventh periodPeriod 7 element
A period 7 element is one of the chemical elements in the seventh row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical...
. For example, chemical studies performed in 2007 strongly indicate that ununquadium
Ununquadium
Ununquadium is the temporary name of a radioactive chemical element with the temporary symbol Uuq and atomic number 114. There is no proposed name yet, although flerovium has been discussed in the media.About 80 decays of atoms of...
possesses non-eka-lead
Mendeleev's predicted elements
Professor Dmitri Mendeleev published the first Periodic Table of the Atomic Elements in 1869 based on properties which appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest....
properties and appears to behave as the first superheavy element that portrays noble-gas
Noble gas
The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity...
-like properties due to relativistic effects
Relativistic quantum chemistry
Relativistic quantum chemistry invokes quantum chemical and relativistic mechanical arguments to explain elemental properties and structure, especially for heavy elements of the periodic table....
.
Elements
Period 8 is divided into five blocksBlock (periodic table)
A block of the periodic table of elements is a set of adjacent groups. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. The respective highest-energy electrons in each element in a block belong to the same atomic orbital type...
, and it is the first period that includes the g-block
G-block
There are currently seven periods in the periodic table of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number 118. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the...
; however, spin-orbit coupling effects reduce the validity of the orbital approximation substantially for elements of high atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
.
s-block
The elements in the s-block of period 8 have atomic numbers 119 and 120. The necessary condition for synthesising the s-block elements of period 8, ununenniumUnunennium
Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali...
and unbinilium
Unbinilium
Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120....
, is to have a sensitivity on the order of femtobarns
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
, which is currently out of reach of even the most advanced facilities.
Attempts at synthesis
The synthesis of ununenniumUnunennium
Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali...
was attempted in 1985 by bombarding a target of einsteinium
Einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein...
-254 with calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
-48 ions at the superHILAC accelerator at Berkeley, California. No atoms were identified, leading to a limiting yield of 300 nb.

It is highly unlikely that this reaction will be useful given the extremely difficult task of making
sufficient amounts of Es-254 to make a large enough target to increase the sensitivity of the experiment to the required level, due to the rarity of the element, and extreme rarity of the isotope.
In March–April 2007, the synthesis of unbinilium
Unbinilium
Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120....
was attempted at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
The Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, JINR , in Dubna, Moscow Oblast , Russia, is an international research centre for nuclear sciences, with 5500 staff members, 1200 researchers including 1000 Ph.D.s from eighteen member states The Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, JINR , in Dubna, Moscow...
in Dubna
Dubna
Dubna is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It has a status of naukograd , being home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research centre and one of the largest scientific foundations in the country. It is also home to MKB Raduga, a defence aerospace company...
by bombarding a plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
-244 target with iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-58 ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s. Initial analysis revealed that no atoms of element 120 were produced providing a limit of 400 fb
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
for the cross section at the energy studied.

The Russian team are planning to upgrade their facilities before attempting the reaction again.
In April 2007, the team at GSI
Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
The GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research GmbH in the Wixhausen suburb of Darmstadt, Germany is a federally and state co-funded heavy ion research center. The current director of GSI is Horst Stöcker who succeeded Walter F...
attempted to create unbinilium using uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
-238 and nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
-64:

No atoms were detected providing a limit of 1.6 pb on the cross section at the energy provided. The GSI repeated the experiment with higher sensitivity in three separate runs from April–May 2007, Jan–March 2008, and Sept–Oct 2008, all with negative results and providing a cross section limit of 90 fb.
g-block
Period 8 is the first period to have g-blockG-block
There are currently seven periods in the periodic table of chemical elements, culminating with atomic number 118. If further elements with higher atomic numbers than this are discovered, they will be placed in additional periods, laid out to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the...
elements, which have atomic numbers from 121 onwards, but it is not clear when the filling of the 5g subshell ends. These elements belong to the chemical series of superactinides, characterised by the filling of the 5g and 6f subshells, and they could therefore have different chemical properties that are reminiscent of the actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s; however, the proximity of the 5g and 6f subshells and the small gap between them and the 7d and 8p subshells could lead to a large number of elements whose properties are independent of their position in the periodic table.
These elements would only be detectable if they lie near the hypothesised island of stability
Island of stability
The island of stability in nuclear physics describes a set of as-yet undiscovered isotopes of transuranium elements which are theorized to be much more stable than others...
. The stability of these elements depends on the location of the island of stability; if the island is centred around a low Z, most superactinides would be too unstable to be detected, but if it is centred around a higher Z, there is a possibility of detecting the lower superactinides.
Attempts at synthesis
The only elements in this region of the periodic table to have had attempts to synthesise them are elements 122, 124 and 126.The first attempt to synthesize unbibium
Unbibium
Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122....
was performed in 1972 by Flerov et al. at JINR, using the hot fusion reaction:
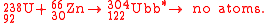
No atoms were detected and a yield limit of 5 mb
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
(5,000,000 pb
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
) was measured. Current results (see ununquadium
Ununquadium
Ununquadium is the temporary name of a radioactive chemical element with the temporary symbol Uuq and atomic number 114. There is no proposed name yet, although flerovium has been discussed in the media.About 80 decays of atoms of...
) have shown that the sensitivity of this experiment was too low by at least 6 orders of magnitude.
In 2000, the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung
The GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research GmbH in the Wixhausen suburb of Darmstadt, Germany is a federally and state co-funded heavy ion research center. The current director of GSI is Horst Stöcker who succeeded Walter F...
performed a very similar experiment with much higher sensitivity:

These results indicate that the synthesis of such heavier elements remains a significant challenge and further improvements of beam intensity and experimental efficiency is required. The sensitivity should be increased to 1 fb
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
.
Several experiments have been performed between 2000-2004 at the Flerov laboratory of Nuclear Reactions studying the fission characteristics of the compound nucleus 306Ubb. Two nuclear reactions have been used, namely 248Cm+58Fe and 242Pu+64Ni. The results have revealed how nuclei such as this fission predominantly by expelling closed shell nuclei such as 132Sn (Z=50, N=82). It was also found that the yield for the fusion-fission pathway was similar between 48Ca and 58Fe projectiles, indicating a possible future use of 58Fe projectiles in superheavy element formation.
In a series of experiments, scientists at GANIL have attempted to measure the direct and delayed fission of compound nuclei of elements with Z=114, 120, and 124 in order to probe shell effects in this region and to pinpoint the next spherical proton shell. In 2006, with full results published in 2008, the team provided results from a reaction involving the bombardment of a natural germanium target with uranium ions:
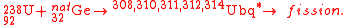
The team reported that they had been able to identify compound nuclei fissioning with half-lives > 10−18 s. Although very short, the ability to measure such decays indicated a strong shell effect at Z=124. A similar phenomenon was found for Z=120
Unbinilium
Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120....
but not for Z=114
Ununquadium
Ununquadium is the temporary name of a radioactive chemical element with the temporary symbol Uuq and atomic number 114. There is no proposed name yet, although flerovium has been discussed in the media.About 80 decays of atoms of...
.
The first attempt to synthesize unbihexium
Unbihexium
Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:...
was performed in 1971 by Bimbot et al. using the hot fusion reaction:
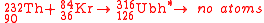
A high energy alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
was observed and taken as possible evidence for the synthesis of unbihexium. Recent research suggests that this is highly unlikely as the sensitivity of experiments performed in 1971 would have been several orders of magnitude too low according to current understanding. To date, no other attempt has been made to synthesize unbihexium.
All other elements in this region of the periodic table and beyond have not received any attempts to synthesise them.
Feynmanium
UntriseptiumUntriseptium
Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible...
, element 137, is sometimes called feynmanium (symbol Fy) because Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman was an American physicist known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics and the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as in particle physics...
noted that a simplistic interpretation of the relativistic
Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
Dirac equation
Dirac equation
The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. It provided a description of elementary spin-½ particles, such as electrons, consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and...
runs into problems with electron orbitals at Z > 1/α = 137, suggesting that neutral atoms cannot exist beyond untriseptium, and that a periodic table of elements based on electron orbitals therefore breaks down at this point. However, a more rigorous analysis calculates the limit to be Z ≈ 173.
Bohr model breakdown
The Bohr model
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with electrostatic forces providing attraction,...
exhibits difficulty for atoms with atomic number greater than 137, for the speed of an electron in a 1s electron orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
, v, is given by

where Z is the atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
, and α is the fine structure constant, a measure of the strength of electromagnetic interactions. Under this approximation, any element with an atomic number of greater than 137 would require 1s electrons to be traveling faster than c, the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
. Hence the non-relativistic Bohr model is clearly inaccurate when applied to such an element.
The Dirac equation
The relativistic
Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
Dirac equation
Dirac equation
The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. It provided a description of elementary spin-½ particles, such as electrons, consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and...
also has problems for Z > 137, for the ground state energy is
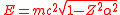
where m is the rest mass of the electron. For Z > 137, the wave function of the Dirac ground state is oscillatory, rather than bound, and there is no gap between the positive and negative energy spectra, as in the Klein paradox
Klein paradox
In 1929, physicist Oskar Klein obtained a surprising result by applying the Dirac equation to the familiar problem of electron scattering from a potential barrier. In nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, electron tunneling into a barrier is observed, with exponential damping...
.
More accurate calculations including the effects of the finite size of the nucleus indicate that the binding energy first exceeds 2mc2 for Z > Zcr ≈ 173. For Z > Zcr, if the innermost orbital is not filled, the electric field of the nucleus will pull an electron out of the vacuum, resulting in the spontaneous emission of a positron.
More complete analysis involving relativity shows that the contradiction this particle poses may actually occur in the hypothetical element untriennium (Z = 139; see unsolved problems in chemistry
Unsolved problems in chemistry
Unsolved problems in chemistry tend to be questions of the kind "Can we make X chemical compound?", "Can we analyse it?", "Can we purify it?" and are commonly solved rather quickly, but may just as well require considerable efforts to be solved. However, there are also some questions with deeper...
).
f-block
The relativstic and quantum effects for the electron clouds of these elements are expected to be even more sensitive than those for the g-block elements, because these elements have higher atomic number. If these elements could actually be observed, they would likely be observed to have similar chemical properties, but the effect of the closeness of the 5g and 6f subshells is unclear and difficult to predict because of the relativistic and quantum effects.The existence of such atoms is probably theoretically possible (the upper limit for atomic number is likely Z = 173 due to the light-speed limit
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, after which assigning electron shells would be nonsensical and heavier elements would only be able to exist as ions), but it is not clear if our technology will ever suffice to synthesise them.
d-block and p-block
Although element 153 would likely be taken to be a superactinide based on previous periods, the electron configurations for later elements would likely be nothing more than mathematical extrapolation because of the extreme quantum and relativistic effects the electron clouds will experience. In the unlikely case that their chemical properties may eventually be studied, it is likely that all existing classifications will be inadequate to describe them.Electron configurations
Leonard I. SchiffLeonard I. Schiff
Leonard Isaac Schiff was born in Fall River, Massachusetts on March 29, 1915 and died on Jan 21, 1971.He was a physicist best known for his book Quantum Mechanics.-Education:...
has predicted the electron configuration
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure...
s for the period 8 elements. Chemical series information is purely hypothetical and based on periodic trends which may not apply to elements this heavy. Pekka Pyykkö has also predicted the electron configurations for these elements. The predictions are drastically different.
| Chemical element Chemical element A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements... |
Chemical series | Electron configuration Electron configuration In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure... (according to Schiff) |
||
| 119 | Uue | Ununennium Ununennium Ununennium also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uue and has the atomic number 119. To date, attempted syntheses of this element have been unsuccessful. Since it is below the alkali... |
Alkali metal Alkali metal The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium... |
[Uuo] 8s1 |
| 120 | Ubn | Unbinilium Unbinilium Unbinilium , also called eka-radium or element 120, is the temporary, systematic element name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubn and has the atomic number 120.... |
Alkaline earth metal Alkaline earth metal The alkaline earth metals are a group in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkaline earth metals are called the group 2 elements. Previously, they were called the Group IIA elements . The alkaline earth metals contain beryllium , magnesium , calcium , strontium , barium and... |
[Uuo] 8s2 |
| 121 | Ubu | Unbiunium Unbiunium Unbiunium , also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is the temporary name of a hypothetical chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubu and has the atomic number 121. It would be the first element in the g-block of the periodic table... |
Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 |
| 122 | Ubb | Unbibium Unbibium Unbibium , also referred to as eka-thorium or element 122, is the temporary name of a currently unknown chemical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubb and the atomic number 122.... |
Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d2 |
| 123 | Ubt | Unbitrium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g2 |
| 124 | Ubq | Unbiquadium Unbiquadium Unbiquadium , also known as eka-uranium or element 124, is the temporary name of a hypothetical element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Ubq and atomic number 124.... |
Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g3 |
| 125 | Ubp | Unbipentium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g4 |
| 126 | Ubh | Unbihexium Unbihexium Unbihexium , also known as eka-plutonium or element 126, is a hypothetical chemical element with atomic number 126 and symbol Ubh. It is of interest because of its location at the peak of the hypothesized island of stability.-History:... |
Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g5 |
| 127 | Ubs | Unbiseptium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g6 |
| 128 | Ubo | Unbioctium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g7 |
| 129 | Ube | Unbiennium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 5g9 |
| 130 | Utn | Untrinilium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g9 |
| 131 | Utu | Untriunium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g10 |
| 132 | Utb | Untribium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g11 |
| 133 | Utt | Untritrium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g12 |
| 134 | Utq | Untriquadium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g13 |
| 135 | Utp | Untripentium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g14 |
| 136 | Uth | Untrihexium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g15 |
| 137 | Uts | Untriseptium Untriseptium Untriseptium , also known as eka-dubnium or element 137, is a hypothetical chemical element which has not been observed to occur naturally, nor has it yet been synthesised. Due to drip instabilities, it is not known if this element is physically possible... |
Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g16 |
| 138 | Uto | Untrioctium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 5g18 |
| 139 | Ute | Untriennium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 5g18 |
| 140 | Uqn | Unquadnilium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f1 5g18 |
| 141 | Uqu | Unquadunium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f2 5g18 |
| 142 | Uqb | Unquadbium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f3 5g18 |
| 143 | Uqt | Unquadtrium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f4 5g18 |
| 144 | Uqq | Unquadquadium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f6 5g18 |
| 145 | Uqp | Unquadpentium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f7 5g18 |
| 146 | Uqh | Unquadhexium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f7 5g18 |
| 147 | Uqs | Unquadseptium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f8 5g18 |
| 148 | Uqo | Unquadoctium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f10 5g18 |
| 149 | Uqe | Unquadennium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f11 5g18 |
| 150 | Upn | Unpentnilium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f12 5g18 |
| 151 | Upu | Unpentunium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f13 5g18 |
| 152 | Upb | Unpentbium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 6f14 5g18 |
| 153 | Upt | Unpenttrium | Superactinide | [Uuo] 8s2 7d1 6f14 5g18 |
| 154 | Upq | Unpentquadium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d2 6f14 5g18 |
| 155 | Upp | Unpentpentium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d3 6f14 5g18 |
| 156 | Uph | Unpenthexium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d4 6f14 5g18 |
| 157 | Ups | Unpentseptium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d5 6f14 5g18 |
| 158 | Upo | Unpentoctium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d6 6f14 5g18 |
| 159 | Upe | Unpentennium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d7 6f14 5g18 |
| 160 | Uhn | Unhexnilium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d8 6f14 5g18 |
| 161 | Uhu | Unhexunium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s1 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 162 | Uhb | Unhexbium | Transition metal Transition metal The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some... |
[Uuo] 8s2 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 163 | Uht | Unhextrium | Post-transition metal Post-transition metal In chemistry, the term post-transition metal is used to describe the category of metallic elements to the right of the transition elements on the periodic table... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p1 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 164 | Uhq | Unhexquadium | Post-transition metal Post-transition metal In chemistry, the term post-transition metal is used to describe the category of metallic elements to the right of the transition elements on the periodic table... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p2 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 165 | Uhp | Unhexpentium | Post-transition metal Post-transition metal In chemistry, the term post-transition metal is used to describe the category of metallic elements to the right of the transition elements on the periodic table... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p3 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 166 | Uhh | Unhexhexium | Post-transition metal Post-transition metal In chemistry, the term post-transition metal is used to describe the category of metallic elements to the right of the transition elements on the periodic table... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p4 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 167 | Uhs | Unhexseptium | Halogen Halogen The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p5 7d10 6f14 5g18 |
| 168 | Uho | Unhexoctium | Noble gas Noble gas The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity... |
[Uuo] 8s2 8p6 7d10 6f14 5g18 |

