
Permanganate
Encyclopedia
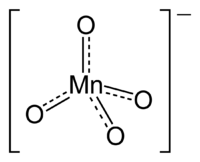
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
containing the manganate(VII) ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
, (MnO4−). Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidizing agent
Oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent can be defined as a substance that removes electrons from another reactant in a redox chemical reaction...
. The ion has tetrahedral geometry
Tetrahedral molecular geometry
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1 ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in CH4. This molecular geometry is common throughout the first...
. Permanganate solutions are purple in color and are stable in neutral
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
or slightly alkaline media.
In an acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
ic solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the colourless +2 oxidation state of the manganese(II)
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
(Mn2+) ion.
- 8 + MnO4− + 5 e− → Mn2+ + 4 H2O
In a strongly bas
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
ic solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the green +6 oxidation state of the manganate
Manganate
In inorganic nomenclature, a manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity with manganese as the central atom. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate anion, MnO, also known as manganate because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state...
MnO42−.
- MnO4− + e− → MnO42−
In a neutral medium however, it gets reduced to the brown +4 oxidation state of manganese dioxide MnO2.
- 2 H2O + MnO4− + 3 e− → MnO2 + 4 OH−
Production
Permanganates can be produced by oxidation of manganeseManganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
compounds such as manganese chloride or manganese sulfate by strong oxidizing agents, for instance, sodium hypochlorite or lead dioxide:
- 2 MnCl2 + 5 NaClO + 6 NaOH → 2 NaMnO4 + 9 NaCl+ 3 H2O
- 2 MnSO4 + 5 PbO2+ 3 H2SO4 → 2 HMnO4 + 5 PbSO4 + 2 H2O
It may also be produced by the dismutation of manganate
Manganate
In inorganic nomenclature, a manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity with manganese as the central atom. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate anion, MnO, also known as manganate because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state...
s, with manganese dioxide as a side-product:
- 3 Na2MnO4 + 2 H2O → 2 NaMnO4 + MnO2 + 4 NaOH
Properties
Permanganates(VII) are saltSalt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
s of permanganic acid. Permanganate(VII) is a strong oxidizer, and similar to perchlorate
Perchlorate
Perchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid . They occur both naturally and through manufacturing. They have been used as a medicine for more than 50 years to treat thyroid gland disorders. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a...
. It is therefore in common use in qualitative analysis that involves redox reactions (permanganometry). Besides this, it is stable.
It is a useful reagent, though with organic compounds, not very selective.
Manganates(VII) are not very stable thermally. For instance, potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula KMnO4. It is a salt consisting of K+ and MnO4− ions. Formerly known as permanganate of potash or Condy's crystals, it is a strong oxidizing agent. It dissolves in water to give intensely purple solutions, the...
decomposes at 230 °C to potassium manganate
Potassium manganate
Potassium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2MnO4. This green-colored salt is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate , a common chemical...
and manganese dioxide, releasing oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
gas:
- 2 KMnO4 → K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
A permanganate can oxidize an amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
to a nitro compound
Nitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
, an alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
to a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
, an aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
to a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
, a terminal alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
to a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
, oxalic acid
Oxalic acid
Oxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations...
to carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, and an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
to a diol
Diol
A diol or glycol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom...
. This list not exhaustive.
In alkene oxidations one intermediate is a cyclic Mn(V) species:
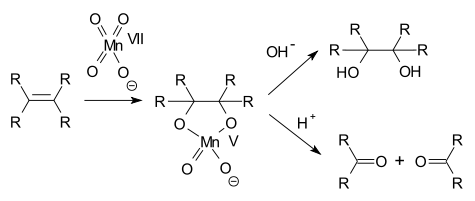
Compounds
- Ammonium permanganateAmmonium permanganateAmmonium permanganate is the chemical compound NH4MnO4, or NH3·HMnO4. It is soluble in water. It is a strong oxidizer, owing to its permanganate anion, and it is a moderately strong explosive, owing to the combination of oxidizer permanganate anion and reducing ammonium cation...
, NH4MnO4 - Calcium permanganateCalcium permanganateCalcium permanganate is an oxidizing agent. It consists of the metal calcium and two permanganate ions. It is noncombustible, but it will accelerate the burning of combustible material. If the combustible material is finely divided, the mixture may be explosive. Contact with liquid combustible...
, Ca(MnO4)2 - Potassium permanganatePotassium permanganatePotassium permanganate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula KMnO4. It is a salt consisting of K+ and MnO4− ions. Formerly known as permanganate of potash or Condy's crystals, it is a strong oxidizing agent. It dissolves in water to give intensely purple solutions, the...
, KMnO4 - Sodium permanganateSodium permanganateSodium permanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaMnO4. It is closely related to the more commonly encountered potassium permanganate, but it is generally less desirable, because it is more expensive, absorbs water from the atmosphere, and has a low melting point...
, NaMnO4
See also
- PerchloratePerchloratePerchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid . They occur both naturally and through manufacturing. They have been used as a medicine for more than 50 years to treat thyroid gland disorders. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a...
, a similar ion with a chlorine(VII) center - ChromateChromateChromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO42−. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr2O72−. They are oxyanions of chromium in the oxidation state +6. They are moderately strong oxidizing agents.- Chemical properties :...
, which is isoelectronic with permanganate

