
Petechia
Encyclopedia
A petechia is a small (1-2mm) red or purple spot on the body, caused by a minor hemorrhage (broken capillary
blood vessel
s).
"Petechiae" refers to one of the three major classes of purpuric skin conditions. Purpuric eruptions are classified by size into three broad categories. Petechiae is generally used to refer to the smallest of the three classes of purpuric skin eruptions, those that measure less than 3 mm.
(low platelet
counts) when platelet function is inhibited (e.g., as a side effect of medications or during certain infections), or in clotting factor deficiencies. They may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied to an extremity or with excessive coughing or vomiting).
If unsure, petechiae should always be quickly investigated. They can be interpreted as vasculitis
, an inflammation of the blood vessels, which requires immediate treatment to prevent permanent damage. Some malignancies can also cause petechiae to appear. Petechiae should be investigated by a doctor to rule out the more dangerous conditions. Dermatologists can be the most helpful specialists in these conditions because they can more easily identify if the condition is petechiae or some similar looking but less worrisome rash.
The significance of petechiae in children depends on the clinical context in which they arise. Petechiae in children can occur with viral infections. In this instance, they do not necessarily signify a serious illness. However, they are a hallmark signal of some potentially serious illnesses, such as meningococcemia
, leukemia
, and certain causes of thrombocytopenia
, the first of which can cause death within 48 hours of infection. Therefore, their presence should not be ignored.
Non-infectious conditions
Non-diseases
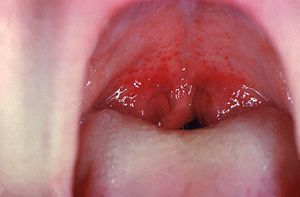 Petechiae on the soft palate
Petechiae on the soft palate
are mainly associated with streptococcal pharyngitis, and as such it is an uncommon but highly specific
finding. 10 to 30 percent of palatal petechiae cases are estimated to be caused by suction such as can be habitual or secondary to fellatio
.
Facial petechiae, especially around the eyes, indicate physical trauma such as by hard bouts of coughing, vomiting or crying.
(eyes) can be a sign of a death by asphyxia
tion. Petechiae are thought to result from an increase of pressure in the vein
s of the head and hypoxic
damage to endothelia
of blood vessels.
Petechiae can be used by police investigators in determining if strangulation has been part of an attack. The documentation of the presence of petechiae on a victim can help police investigators prove the case. Petechiae resulting from strangulation can be relatively tiny and light in color to very bright and pronounced. Petechiae may be seen on the face, in the whites of the eyes or on the inside of the eyelids.
Capillary
Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels and are parts of the microcirculation. They are only 1 cell thick. These microvessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter, connect arterioles and venules, and enable the exchange of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and many other nutrient and waste...
blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s).
"Petechiae" refers to one of the three major classes of purpuric skin conditions. Purpuric eruptions are classified by size into three broad categories. Petechiae is generally used to refer to the smallest of the three classes of purpuric skin eruptions, those that measure less than 3 mm.
Causes
The most common cause of petechiae is through physical trauma such as a hard bout of coughing, vomiting or crying, which can result in facial petechiae, especially around the eyes. Petechiae in this instance are completely harmless and usually disappear within a few days. Petechiae may be a sign of thrombocytopeniaThrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
(low platelet
Platelet
Platelets, or thrombocytes , are small,irregularly shaped clear cell fragments , 2–3 µm in diameter, which are derived from fragmentation of precursor megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is normally just 5 to 9 days...
counts) when platelet function is inhibited (e.g., as a side effect of medications or during certain infections), or in clotting factor deficiencies. They may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied to an extremity or with excessive coughing or vomiting).
If unsure, petechiae should always be quickly investigated. They can be interpreted as vasculitis
Vasculitis
Vasculitis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders that are characterized by inflammatory destruction of blood vessels. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis...
, an inflammation of the blood vessels, which requires immediate treatment to prevent permanent damage. Some malignancies can also cause petechiae to appear. Petechiae should be investigated by a doctor to rule out the more dangerous conditions. Dermatologists can be the most helpful specialists in these conditions because they can more easily identify if the condition is petechiae or some similar looking but less worrisome rash.
The significance of petechiae in children depends on the clinical context in which they arise. Petechiae in children can occur with viral infections. In this instance, they do not necessarily signify a serious illness. However, they are a hallmark signal of some potentially serious illnesses, such as meningococcemia
Meningococcemia
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis . It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection is more damaging and dangerous...
, leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, and certain causes of thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
, the first of which can cause death within 48 hours of infection. Therefore, their presence should not be ignored.
List of associated conditions
Infections- Bolivian hemorrhagic feverBolivian hemorrhagic feverBolivian hemorrhagic fever , also known as black typhus or Ordog Fever, is a hemorrhagic fever and zoonotic infectious disease originating in Bolivia after infection by Machupo virus....
- Boutonneuse feverBoutonneuse feverBoutonneuse fever is a fever as a result of a Rickettsia infection caused by the bacterium Rickettsia conorii and transmitted by the dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus...
- Cerebral malaria
- Congenital cytomegalovirus
- Congenital syphilisCongenital syphilisCongenital syphilis is syphilis present in utero and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with secondary syphilis. Untreated syphilis results in a high risk of a bad outcome of pregnancy, including mulberry molars in the fetus. Syphilis can cause miscarriages, premature births,...
- Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic feverCrimean-Congo hemorrhagic feverCrimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever is a widespread tick-borne viral disease, a zoonosis of domestic animals and wild animals, that may affect humans. The pathogenic virus, especially common in East and West Africa, is a member of the Bunyaviridae family of RNA viruses. Clinical disease is rare in...
- Dengue feverDengue feverDengue fever , also known as breakbone fever, is an infectious tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash that is similar to measles...
- Duke's diseaseDuke's diseaseDukes' disease or fourth disease is an exanthem.It is named for Clement Dukes.Some of these eruptions are characteristic of the causative virus, but in most cases one must be satisfied with the diagnosis of viral rash....
- EbolaEbolaEbola virus disease is the name for the human disease which may be caused by any of the four known ebolaviruses. These four viruses are: Bundibugyo virus , Ebola virus , Sudan virus , and Taï Forest virus...
- EndocarditisEndocarditisEndocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves . Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or even on intracardiac devices...
- H1N1H1N1'Influenza A virus is a subtype of influenza A virus and was the most common cause of human influenza in 2009. Some strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and cause a small fraction of all influenza-like illness and a small fraction of all seasonal influenza. H1N1 strains caused a few percent of...
- Hanta virus
- Infectious mononucleosisInfectious mononucleosisInfectious mononucleosis is an infectious, widespread viral...
- Marburg virusMarburg virusMarburg virus disease is the name for the human disease caused by any of the two marburgviruses Marburg virus and Ravn virus...
- Neisseria meningitidisNeisseria meningitidisNeisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life threatening sepsis. N. meningitidis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality during childhood in industrialized countries...
- Rocky mountain spotted feverRocky Mountain spotted feverRocky Mountain spotted fever is the most lethal and most frequently reported rickettsial illness in the United States. It has been diagnosed throughout the Americas. Some synonyms for Rocky Mountain spotted fever in other countries include “tick typhus,” “Tobia fever” , “São Paulo fever” or “febre...
- Scarlet feverScarlet feverScarlet fever is a disease caused by exotoxin released by Streptococcus pyogenes. Once a major cause of death, it is now effectively treated with antibiotics...
- TyphusTyphusEpidemic typhus is a form of typhus so named because the disease often causes epidemics following wars and natural disasters...
Non-infectious conditions
- Hypocalcemia
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpuraIdiopathic thrombocytopenic purpuraIdiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is the condition of having an abnormally low platelet count of no known cause . As most incidents of ITP appear to be related to the production of antibodies against platelets, immune thrombocytopenic purpura or immune thrombocytopenia are terms also used to...
- LeukemiaLeukemiaLeukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
- Celiac Disease
- Aplastic anaemia
- ScurvyScurvyScurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic...
- LupusLupusLupus most commonly refers to the disease systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus may also refer to:-Medicine:* Lupus erythematosus, a chronic autoimmune disease with several different forms...
- Childhood protein-energy malnutrition such as KwashiorkorKwashiorkorKwashiorkor is an acute form of childhood protein-energy malnutrition characterized by edema, irritability, anorexia, ulcerating dermatoses, and an enlarged liver with fatty infiltrates. The presence of edema caused by poor nutrition defines kwashiorkor...
or MarasmusMarasmusMarasmus is a form of severe protein-energy malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency.A child with marasmus looks emaciated. Body weight may be reduced to less than 80% of the average weight that corresponds to the height . Marasmus occurrence increases prior to age 1, whereas kwashiorkor... - Erythroblastosis fetalis
- Henoch-Schönlein purpuraHenoch-Schönlein purpuraHenoch–Schönlein purpura is a disease of the skin and other organs that most commonly affects children. In the skin, the disease causes palpable purpura ; often with joint and abdominal pain...
- Kawasaki diseaseKawasaki diseaseKawasaki disease , also known as Kawasaki syndrome, lymph node syndrome and mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is an autoimmune disease in which the medium-sized blood vessels throughout the body become inflamed. It is largely seen in children under five years of age...
- Schamberg's disease
Non-diseases
- Gua ShaGua ShaGua sha , literally "to scrape away fever" in Chinese , is an ancient medical treatment....
, a Chinese treatment that scrapes the skin - High-G trainingHigh-G trainingHigh-G training is done by aviators and astronauts who are subject to high levels of acceleration . It is designed to prevent a g-induced Loss Of Consciousness , a situation when g-forces move the blood away from the brain to the extent that consciousness is lost.Incidents of acceleration-induced...
- Hickey (injury)Hickey (injury)A hickey, kiss mark or love bite , is a bruise or mark caused by the kissing or sucking of the skin...
Causes of particular types

Soft palate
The soft palate is the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone....
are mainly associated with streptococcal pharyngitis, and as such it is an uncommon but highly specific
Sensitivity and specificity
Sensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
finding. 10 to 30 percent of palatal petechiae cases are estimated to be caused by suction such as can be habitual or secondary to fellatio
Fellatio
Fellatio is an act of oral stimulation of a male's penis by a sexual partner. It involves the stimulation of the penis by the use of the mouth, tongue, or throat. The person who performs fellatio can be referred to as the giving partner, and the other person is the receiving partner...
.
Facial petechiae, especially around the eyes, indicate physical trauma such as by hard bouts of coughing, vomiting or crying.
Forensics
Petechiae on the face and conjunctivaConjunctiva
The conjunctiva covers the sclera and lines the inside of the eyelids. It is composed of rare stratified columnar epithelium.-Function:...
(eyes) can be a sign of a death by asphyxia
Asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of severely deficient supply of oxygen to the body that arises from being unable to breathe normally. An example of asphyxia is choking. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which primarily affects the tissues and organs...
tion. Petechiae are thought to result from an increase of pressure in the vein
Vein
In the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
s of the head and hypoxic
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
damage to endothelia
Endothelium
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. These cells are called endothelial cells. Endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart...
of blood vessels.
Petechiae can be used by police investigators in determining if strangulation has been part of an attack. The documentation of the presence of petechiae on a victim can help police investigators prove the case. Petechiae resulting from strangulation can be relatively tiny and light in color to very bright and pronounced. Petechiae may be seen on the face, in the whites of the eyes or on the inside of the eyelids.

