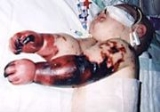
Meningococcemia
Encyclopedia
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis
(also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis
, widespread blood infection (sepsis
) is more damaging and dangerous. Meningitis and Meningococcemia
are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under developed countries worldwide.
The disease's host/pathogen interaction is not fully understood. The pathogen originates harmlessly in a large number of the general population, but thereafter can invade the blood stream and the brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines will depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.
The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 per cent.
While Meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold
(which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva
and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.
. Infected fluid from the meninges then passes into the spinal cord
, causing symptoms including stiff neck, fever
and rash
es. The meninges (and sometimes the brain itself) begin to swell, which affects the central nervous system
.
Even with antibiotics, approximately 1 in 10 victims of meningococcal meningitis will die; However, about as many survivors of the disease lose a limb or their hearing, or suffer permanent brain damage
. The sepsis type of infection is much more deadly, and results in a severe blood poisoning called meningococcal sepsis that affects the entire body. In this case, bacterial toxins rupture blood vessels and can rapidly shut down vital organs. Within hours, patient's health can change from seemingly good to mortally ill.
The N. meningitidis bacterium is surrounded by a slimy outer coat that contains disease-causing endotoxin. While many bacteria produce endotoxin, the levels produced by meningococcal bacteria are 100 to 1,000 times greater (and accordingly more lethal) than normal. As the bacteria multiply and move through the bloodstream, it sheds concentrated amounts of toxin. The endotoxin directly affects the heart, reducing its ability to circulate blood, and also causes pressure on blood vessels throughout the body. As some blood vessels start to hemorrhage, major organs like the lungs and kidneys are damaged.
Patients suffering from meningococcal disease are treated with a large dose of antibiotic
. The systemic antibiotic flowing through the bloodstream rapidly kills the bacteria but, as the bacteria are killed, even more toxin is released. It takes up to several days for the toxin to be neutralized from the body by using continuous liquid treatment and antibiotic therapy.
Meningococcal is often spread through saliva. This can be from kissing or drinking from someone else's cup
(stiff neck), Kernig's sign, severe headache, vomiting, purpura
, photophobia, and sometimes chills, altered mental status, or seizures. Diarrhea or respiratory symptoms are less common. Petechiae is often also present, but does not always occur, so its absence should not be used against the diagnosis of meningococcal disease. Anyone with symptoms of meningococcal meningitis should receive intravenus antibiotics pending results of lumbar puncture
, as delay in treatment worsens the prognosis.
are, at least initially, similar to those of influenza
. Typically, the first symptoms include fever
, nausea
, myalgia, headache, arthralgia
, chills, diarrhea, stiff neck, and malaise. Later symptoms include septic shock
, purpura
, hypotension, cyanosis, petechiae, seizures, anxiety, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
and altered mental status may also occur. Meningococcal sepsis has a higher mortality rate than meningococcal meningitis, but the risk of neurologic sequelae is much lower.
, like many gram-negative
blood infections, can cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
(DIC), a condition where blood starts to clot throughout the body, sometimes causing ischemic tissue damage. DIC also causes bleeding, when the clotting factors are used up, causing the characteristic purpuric rash.
(CSF) and irritating the meninges
- the membranes that line the brain and spinal cord. Sub-Saharan Africa, Americas, Western Europe, UK and Ireland face multifarious challenges, 200 years after the discovery of bacterial meningitis.
Meningococcal pneumonia
can appear during influenza pandemics and in military camps. This is a multilobar, rapidly evolving pneumonia, sometimes associated with septic shock. With prompt treatment with penicillin or chloramphenicol, the prognosis is excellent. Pericarditis
can appear, either as a septic pericarditis with grave prognosis or as a rective pericarditis in the wake of meningitis or septicaemia. Myocarditis
can be a complication of meningococcemia and can be contributive to shock seen in this form of disease. Pharyngitis
and conjunctivitis
can also appear and can constitute the portal of entry for the bacterium. Septic arthritis
due to N. meningitidis can be seen, usually accompanying disseminated infection. Other forms of disease can rarely be seen, like osteomyelitis
, endophthalmitis
and urethritis
.
as HIV, TB and Malaria. Cases of meningococcal disease due to Neisseria meningitidis meningococcaemia leading to severe meningoencephalitis
are common among young children and the elderly. Deaths occurring in less than 24-hours are more likely during the disease epidemic seasons in Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa is hit by meningitis disease outbreaks throughout the epidemic season. Climate change contributes significantly the spread of the disease in Benin
, Burkina Faso
, Cameroon
, the Central African Republic
, Chad
, Côte d'Ivoire
, the Democratic Republic of the Congo
, Ethiopia
, Ghana
, Mali
, Niger
, Nigeria
and Togo
. This is an area of Africa where the disease is endemic: meningitis is "silently" present, and there are always a few cases. When the number of cases passes five per population of 100,000 in one week, teams are on alert. Epidemic levels are reached when there have been 100 cases per 100,000 populations over several weeks. Further complicating efforts to halt the spread of meningitis in Africa is the fact that extremely dry, dusty weather conditions which characterize Niger and Burkina Faso from December to June favor the development of epidemics. Overcrowded villages are breeding grounds for bacterial transmission and lead to a high prevalence of respiratory tract infections, which leave the body more susceptible to infection, encouraging the spread of meningitis. IRIN Africa news has been providing the number of deaths for each country since 1995, and a mass vaccination campaign following a community outbreak of Meningococcal disease in Florida
was done by the CDC
.
, Mencevax of GlaxoSmithKline
and NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135
(has not been licensed in the US) of JN-International Medical Corporation
are the commonly used vaccines. Vaccines offer significant protection from three to five years (plain polysaccharide vaccine Menomune, Mencevax and NmVac-4) to more than eight years (conjugate vaccine Menactra).
Travelers to or residents of areas where N. meningitidis is highly endemic or epidemic are at risk of exposure should receive primary immunization against meningococcal disease.
measures, such as handwashing and not sharing drinking cups, can reduce the incidence of infection by limiting exposure. When a case is confirmed, all close contacts with the infected person can be offered antibiotics to reduce the likelihood of the infection spreading to other people. However, rifampin-resistant strains have been reported and the indiscriminate use of antibiotics contributes to this problem. Chemoprophylaxis is commonly used to those close contacts who are at highest risk of carrying the pathogenic strains. Vaccinations are the only answer for reducing the transmission of the Meningococcal disease.
, and then an urgent transfer to hospital for further care. Once in hospital, the antibiotics of choice are usually IV broad spectrum 3rd generation cephalosporins, e.g. cefotaxime
or ceftriaxone
. Benzylpenicillin and chloramphenicol
are also effective. Supportive measures include IV fluids, oxygen, inotropic support, e.g. dopamine or dobutamine and management of raised intracranial pressure
. Steroid therapy may help in some adult patients, but is unlikely to affect long term outcomes.
Complications following meningococcal disease can be divided into early and late groups. Early complications include: raised intracranial pressure, disseminated intravascular coagulation
, seizures, circulatory collapse and organ failure. Later complications are: deafness, blindness, lasting neurological deficits, reduced IQ, and gangrene leading to amputations.
Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life threatening sepsis. N. meningitidis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality during childhood in industrialized countries...
(also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
, widespread blood infection (sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
) is more damaging and dangerous. Meningitis and Meningococcemia
Meningococcemia
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis . It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection is more damaging and dangerous...
are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under developed countries worldwide.
The disease's host/pathogen interaction is not fully understood. The pathogen originates harmlessly in a large number of the general population, but thereafter can invade the blood stream and the brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines will depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.
The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 per cent.
While Meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold
Common cold
The common cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system, caused primarily by rhinoviruses and coronaviruses. Common symptoms include a cough, sore throat, runny nose, and fever...
(which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva
Saliva
Saliva , referred to in various contexts as spit, spittle, drivel, drool, or slobber, is the watery substance produced in the mouths of humans and most other animals. Saliva is a component of oral fluid. In mammals, saliva is produced in and secreted from the three pairs of major salivary glands,...
and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.
Pathogenesis
Meningococcal disease causes life-threatening meningitis and sepsis conditions. In the case of meningitis, bacteria attack the lining between the brain and skull called the meningesMeninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
. Infected fluid from the meninges then passes into the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
, causing symptoms including stiff neck, fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
and rash
Rash
A rash is a change of the skin which affects its color, appearance or texture. A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracked or blistered, swell and may be painful. The causes, and...
es. The meninges (and sometimes the brain itself) begin to swell, which affects the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
.
Even with antibiotics, approximately 1 in 10 victims of meningococcal meningitis will die; However, about as many survivors of the disease lose a limb or their hearing, or suffer permanent brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
. The sepsis type of infection is much more deadly, and results in a severe blood poisoning called meningococcal sepsis that affects the entire body. In this case, bacterial toxins rupture blood vessels and can rapidly shut down vital organs. Within hours, patient's health can change from seemingly good to mortally ill.
The N. meningitidis bacterium is surrounded by a slimy outer coat that contains disease-causing endotoxin. While many bacteria produce endotoxin, the levels produced by meningococcal bacteria are 100 to 1,000 times greater (and accordingly more lethal) than normal. As the bacteria multiply and move through the bloodstream, it sheds concentrated amounts of toxin. The endotoxin directly affects the heart, reducing its ability to circulate blood, and also causes pressure on blood vessels throughout the body. As some blood vessels start to hemorrhage, major organs like the lungs and kidneys are damaged.
Patients suffering from meningococcal disease are treated with a large dose of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
. The systemic antibiotic flowing through the bloodstream rapidly kills the bacteria but, as the bacteria are killed, even more toxin is released. It takes up to several days for the toxin to be neutralized from the body by using continuous liquid treatment and antibiotic therapy.
Meningococcal is often spread through saliva. This can be from kissing or drinking from someone else's cup
Meningitis
The patient with meningococcal meningitis typically presents with high fever, meningismMeningism
Meningism is the triad of nuchal rigidity , photophobia and headache. It is a sign of irritation of the meninges, such as seen in meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhages and various other diseases...
(stiff neck), Kernig's sign, severe headache, vomiting, purpura
Purpura
Purpura is the appearance of red or purple discolorations on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. They are caused by bleeding underneath the skin...
, photophobia, and sometimes chills, altered mental status, or seizures. Diarrhea or respiratory symptoms are less common. Petechiae is often also present, but does not always occur, so its absence should not be used against the diagnosis of meningococcal disease. Anyone with symptoms of meningococcal meningitis should receive intravenus antibiotics pending results of lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
A lumbar puncture is a diagnostic and at times therapeutic procedure that is performed in order to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for biochemical, microbiological, and cytological analysis, or very rarely as a treatment to relieve increased intracranial pressure.-Indications:The...
, as delay in treatment worsens the prognosis.
Meningococcemia
Symptoms of meningococcemiaMeningococcemia
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis . It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection is more damaging and dangerous...
are, at least initially, similar to those of influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
. Typically, the first symptoms include fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, myalgia, headache, arthralgia
Arthralgia
Arthralgia literally means joint pain; it is a symptom of injury, infection, illnesses or an allergic reaction to medication....
, chills, diarrhea, stiff neck, and malaise. Later symptoms include septic shock
Septic shock
Septic shock is a medical emergency caused by decreased tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery as a result of severe infection and sepsis, though the microbe may be systemic or localized to a particular site. It can cause multiple organ dysfunction syndrome and death...
, purpura
Purpura
Purpura is the appearance of red or purple discolorations on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. They are caused by bleeding underneath the skin...
, hypotension, cyanosis, petechiae, seizures, anxiety, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome ', previously known as multiple organ failure or multisystem organ failure , is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis...
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome , also known as respiratory distress syndrome or adult respiratory distress syndrome is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung....
and altered mental status may also occur. Meningococcal sepsis has a higher mortality rate than meningococcal meningitis, but the risk of neurologic sequelae is much lower.
Meningococcemia
MeningococcemiaMeningococcemia
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis . It carries a high mortality rate if untreated. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection is more damaging and dangerous...
, like many gram-negative
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
blood infections, can cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation , also known as disseminated intravascular coagulopathy or consumptive coagulopathy, is a pathological activation of coagulation mechanisms that happens in response to a variety of diseases. DIC leads to the formation of small blood clots inside the blood...
(DIC), a condition where blood starts to clot throughout the body, sometimes causing ischemic tissue damage. DIC also causes bleeding, when the clotting factors are used up, causing the characteristic purpuric rash.
Meningitis
Meningococcal meningitis is a consequence of bacteria entering the cerebrospinal fluidCerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) and irritating the meninges
Meninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
- the membranes that line the brain and spinal cord. Sub-Saharan Africa, Americas, Western Europe, UK and Ireland face multifarious challenges, 200 years after the discovery of bacterial meningitis.
Other types
As with any gram negative bacterium, N. meningitidis can infect a variety of sites.Meningococcal pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
can appear during influenza pandemics and in military camps. This is a multilobar, rapidly evolving pneumonia, sometimes associated with septic shock. With prompt treatment with penicillin or chloramphenicol, the prognosis is excellent. Pericarditis
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium . A characteristic chest pain is often present.The causes of pericarditis are varied, including viral infections of the pericardium, idiopathic causes, uremic pericarditis, bacterial infections of the precardium Pericarditis is an inflammation of...
can appear, either as a septic pericarditis with grave prognosis or as a rective pericarditis in the wake of meningitis or septicaemia. Myocarditis
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of heart muscle . It resembles a heart attack but coronary arteries are not blocked.Myocarditis is most often due to infection by common viruses, such as parvovirus B19, less commonly non-viral pathogens such as Borrelia burgdorferi or Trypanosoma cruzi, or as a...
can be a complication of meningococcemia and can be contributive to shock seen in this form of disease. Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
and conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis refers to inflammation of the conjunctiva...
can also appear and can constitute the portal of entry for the bacterium. Septic arthritis
Arthritis
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
due to N. meningitidis can be seen, usually accompanying disseminated infection. Other forms of disease can rarely be seen, like osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis simply means an infection of the bone or bone marrow...
, endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis is an inflammation of the internal coats of the eye. It is a dreaded complication of all intraocular surgeries, particularly cataract surgery, with possible loss of vision and the eye itself. Infectious etiology is the most common and various bacteria and fungi have been isolated as...
and urethritis
Urethritis
Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptom is painful or difficult urination.-Causes:The disease is classified as either gonococcal urethritis, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, or non-gonococcal urethritis , most commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis...
.
Meningococcal disease in Africa
The importance of meningitis disease is as significant in AfricaAfrica
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
as HIV, TB and Malaria. Cases of meningococcal disease due to Neisseria meningitidis meningococcaemia leading to severe meningoencephalitis
Meningoencephalitis
Meningoencephalitis is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the meninges, and encephalitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the brain.-Causes:...
are common among young children and the elderly. Deaths occurring in less than 24-hours are more likely during the disease epidemic seasons in Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa is hit by meningitis disease outbreaks throughout the epidemic season. Climate change contributes significantly the spread of the disease in Benin
Benin
Benin , officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It borders Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east and Burkina Faso and Niger to the north. Its small southern coastline on the Bight of Benin is where a majority of the population is located...
, Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso – also known by its short-form name Burkina – is a landlocked country in west Africa. It is surrounded by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Côte d'Ivoire to the southwest.Its size is with an estimated...
, Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
, the Central African Republic
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic , is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It borders Chad in the north, Sudan in the north east, South Sudan in the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo in the south, and Cameroon in the west. The CAR covers a land area of about ,...
, Chad
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
, Côte d'Ivoire
Côte d'Ivoire
The Republic of Côte d'Ivoire or Ivory Coast is a country in West Africa. It has an area of , and borders the countries Liberia, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso and Ghana; its southern boundary is along the Gulf of Guinea. The country's population was 15,366,672 in 1998 and was estimated to be...
, the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a state located in Central Africa. It is the second largest country in Africa by area and the eleventh largest in the world...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
, Ghana
Ghana
Ghana , officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south...
, Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
, Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
, Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
and Togo
Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic , is a country in West Africa bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, on which the capital Lomé is located. Togo covers an area of approximately with a population of approximately...
. This is an area of Africa where the disease is endemic: meningitis is "silently" present, and there are always a few cases. When the number of cases passes five per population of 100,000 in one week, teams are on alert. Epidemic levels are reached when there have been 100 cases per 100,000 populations over several weeks. Further complicating efforts to halt the spread of meningitis in Africa is the fact that extremely dry, dusty weather conditions which characterize Niger and Burkina Faso from December to June favor the development of epidemics. Overcrowded villages are breeding grounds for bacterial transmission and lead to a high prevalence of respiratory tract infections, which leave the body more susceptible to infection, encouraging the spread of meningitis. IRIN Africa news has been providing the number of deaths for each country since 1995, and a mass vaccination campaign following a community outbreak of Meningococcal disease in Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
was done by the CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
.
Prevention
The most important form of prevention is a vaccine against N. meningitidis. Different countries have different strains of the bacteria and therefore use different vaccines. Five serogroups, A, B, C, Y and W135 are responsible for virtually all cases of the disease in humans. Vaccines are currently available against four of the five strains, and a vaccine against the B strain is in development. Menveo of Novartis vaccines Menactra, Menomune of Sanofi-AventisSanofi-Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Paris, France, the world's fourth-largest by prescription sales. Sanofi engages in the research and development, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical products for sale principally in the prescription market, but the...
, Mencevax of GlaxoSmithKline
GlaxoSmithKline
GlaxoSmithKline plc is a global pharmaceutical, biologics, vaccines and consumer healthcare company headquartered in London, United Kingdom...
and NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135
NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135
NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135 is the commercial name of the Meningococcal meningitis polysaccharide serogroups A,C,Y and W-135 vaccine of JN-International Medical Corporation...
(has not been licensed in the US) of JN-International Medical Corporation
JN-International Medical Corporation
JN-International Medical Corporation is a U.S. based biopharmaceutical corporation which since 1998 has been focused on developing vaccines and diagnostics for infectious disease for developing countries. This private corporation was founded in 1998 by Dr. Jeeri R. Reddy with the help of Dr. Kelly F...
are the commonly used vaccines. Vaccines offer significant protection from three to five years (plain polysaccharide vaccine Menomune, Mencevax and NmVac-4) to more than eight years (conjugate vaccine Menactra).
Children
Children 2–10 years of age who are at high risk for meningococcal disease such as certain chronic medical conditions and travel to or reside in countries with hyperendemic or epidemic meningococcal disease should receive primary immunization. Although safety and efficacy of the vaccine have not been established in children younger than 2 years of age and under outbreak control, the unconjugated vaccine can be considered....Children and adolescents 11 years of age or older
It is recommended that primary immunization against meningococcal disease with Meningitis A,C,Y and W-135 vaccines for all young adolescents at 11–12 years of age and all unvaccinated older adolescents at 15 years of age. Although conjugate vaccines are the preferred meningococcal vaccine in adolescents 11 years of age or older, polysaccharide vaccines are an acceptable alternative if the conjugated vaccine is unavailable.Adults
College Students who plan to live in dormitories receive primary immunization with Meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines, although the risk for meningococcal disease for co-eds 18–24 years of age is similar to that of the general population of similar age. College students consider vaccination against meningococcal disease to reduce their risk for the disease and state that college healthcare providers should take a proactive role in providing information about meningococcal disease to students and their parents. Routine primary immunization against meningococcal disease is recommended for most adults living in endemic areas or planning to travel to such areas. Although conjugate vaccines are the preferred meningococcal vaccine in adults 55 years of age or younger, polysaccharide vaccines are an acceptable alternative for adults in this age group if the conjugated vaccine is unavailable. Since safety and efficacy of conjugate vaccines in adults older than 55 years of age have not been established to date, polysaccharide vaccines should be used for primary immunization in this group.Medical staff and laboratory personnel
Health care people should receive routine immunization against meningococcal disease for laboratory personnel who are routinely exposed to isolates of N. meningitidis. Laboratory personnel and medical staff are at risk of exposure to N. meningitides or to patients with meningococcal disease. Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) recommendations regarding immunization of health-care workers that routine vaccination of health-care personnel is recommended, Any individual 11–55 years of age who wishes to reduce their risk of meningococcal disease may receive Meningitis A,C,Y and W-135 vaccines and those older than 55 years of age. Under certain circumstances if unvaccinated health-care personnel cannot get vaccinated and who have intensive contact with oropharyngeal secretions of infected patients and who do not use proper precautions should receive anti-infective prophylaxis against meningococcal infection (i.e., 2-day regimen of oral rifampin or a single dose of IM ceftriaxone or a single dose of oral ciprofloxacin).Military recruits
Because the risk of meningococcal disease is increased among military recruits, all military recruits routinely receive primary immunization against the disease.Travelers and tourists
Immunization against meningococcal disease is not a requirement for entry into any country, unlike Yellow fever. Only Saudi Arabia require that travelers to their country for the annual Hajj and Umrah pilgrimage have a certificate of vaccination against meningococcal disease issued not more than 3 years and not less than 10 days before arrival in Saudi Arabia.Travelers to or residents of areas where N. meningitidis is highly endemic or epidemic are at risk of exposure should receive primary immunization against meningococcal disease.
HIV-infected individuals
HIV-infected individuals are likely to be at increased risk for meningococcal disease; HIV-infected individuals who wish to reduce their risk of meningococcal disease may receive primary immunization against meningococcal disease. Although efficacy of Meningitis A,C,Y and W-135 vaccines have not been evaluated in HIV-infected individuals to date, HIV-infected individuals 11–55 years of age may receive primary immunization with the conjugated vaccine. Vaccination against meningitis do not decrease CD4+ T-cell counts or increase viral load in HIV-infected individuals and there has been no evidence that the vaccines adversely affect survival.Household and other close contacts of individuals with invasive meningococcal disease
Protective levels of anticapsular antibodies are not achieved until 7–14 days following administration of a meningococcal vaccine, vaccination cannot prevent early onset disease in these contacts and usually is not recommended following sporadic cases of invasive meningococcal disease. Unlike developed countries, in sub-Saharan Africa and other under developed countries, entire families live in a single room of a house. Meningococcal infection is usually introduced into a household by an asymptomatic person. Carriage then spreads through the household, reaching infants usually after one or more other household members have been infected. Disease is most likely to occur in infants and young children who lack immunity to the strain of organism circulating and who subsequently acquire carriage of an invasive strain. By preventing susceptible contacts from acquiring infection by directly inhibiting colonization. Close contacts are defined as those persons who could have had intimate contact with the patient’s oral secretions such as through kissing or sharing of food or drink. The importance of the carrier state in meningococcal disease is well known. In developed countries the disease transmission usually occurs in day care, schools and large gatherings where usually disease transmission could occur. Because the meningococcal organism is transmitted by respiratory droplets and is susceptible to drying, it has been postulated that close contact is necessary for transmission. Therefore, the disease transmission to other susceptible person cannot be prevented. Meningitis occurs sporadically throughout the year, and since the organism has no known reservoir outside of man, asymptomatic carriers are usually the source of transmission. Additionally, basic hygieneHygiene
Hygiene refers to the set of practices perceived by a community to be associated with the preservation of health and healthy living. While in modern medical sciences there is a set of standards of hygiene recommended for different situations, what is considered hygienic or not can vary between...
measures, such as handwashing and not sharing drinking cups, can reduce the incidence of infection by limiting exposure. When a case is confirmed, all close contacts with the infected person can be offered antibiotics to reduce the likelihood of the infection spreading to other people. However, rifampin-resistant strains have been reported and the indiscriminate use of antibiotics contributes to this problem. Chemoprophylaxis is commonly used to those close contacts who are at highest risk of carrying the pathogenic strains. Vaccinations are the only answer for reducing the transmission of the Meningococcal disease.
Treatment and prognosis
When meningococcal disease is suspected, treatment must be started immediately and should not be delayed while waiting for investigations. Treatment in primary care usually involves prompt intramuscular administration of benzylpenicillinBenzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin G, is the gold standard type of penicillin. 'G' in the name 'Penicillin G' refers to 'Gold Standard'. Penicillin G is typically given by a parenteral route of administration because it is unstable in the hydrochloric acid of the stomach...
, and then an urgent transfer to hospital for further care. Once in hospital, the antibiotics of choice are usually IV broad spectrum 3rd generation cephalosporins, e.g. cefotaxime
Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Like other third-generation cephalosporins, it has broad spectrum activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria...
or ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Like other third-generation cephalosporins, it has broad spectrum activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. In most cases, it is considered to be equivalent to cefotaxime in terms of safety and efficacy...
. Benzylpenicillin and chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial that became available in 1949. It is considered a prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic, alongside the tetracyclines, and as it is both cheap and easy to manufacture it is frequently found as a drug of choice in the third world.Chloramphenicol is...
are also effective. Supportive measures include IV fluids, oxygen, inotropic support, e.g. dopamine or dobutamine and management of raised intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
. Steroid therapy may help in some adult patients, but is unlikely to affect long term outcomes.
Complications following meningococcal disease can be divided into early and late groups. Early complications include: raised intracranial pressure, disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation , also known as disseminated intravascular coagulopathy or consumptive coagulopathy, is a pathological activation of coagulation mechanisms that happens in response to a variety of diseases. DIC leads to the formation of small blood clots inside the blood...
, seizures, circulatory collapse and organ failure. Later complications are: deafness, blindness, lasting neurological deficits, reduced IQ, and gangrene leading to amputations.

