
Phosphatidate phosphatase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a phosphatidate phosphatase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
:
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are 3-sn-phosphatidate and H2O
, whereas its two products
are 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
and phosphate
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
s, specifically those acting on phosphoric monoester
bonds. This enzyme participates in 4 metabolic pathways
: glycerolipid, glycerophospholipid
, ether lipid
, and sphingolipid metabolism.
. Their main role is in lipid signaling and in phospholipid head-group remodeling.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
:
- a 3-sn-phosphatidate + H2O
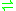 a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + phosphate
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + phosphate
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are 3-sn-phosphatidate and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or a diacylglycerol , is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages....
and phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s, specifically those acting on phosphoric monoester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
bonds. This enzyme participates in 4 metabolic pathways
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
: glycerolipid, glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes.-Structures:...
, ether lipid
Ether lipid
Ether lipids are lipids in which one or more of the carbon atoms on glycerol is bonded to an alkyl chain via an ether linkage, as opposed to the usual ester linkage.-Types:...
, and sphingolipid metabolism.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is 3-sn-phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include:- phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP),
- acid phosphatidyl phosphatase,
- phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase,
- phosphatidate phosphohydrolase, and
- lipid phosphate phosphohydrolase (LPP).
Types
There are several different genes that codify for phosphatidate phosphatases. They been classified in two groups (type I and type II) based on their cellular localization and substrate specificity.Type I
Type I phosphatidate phosphatases are soluble enzymes that can associate to membranes. There are found mainly in the cytosol and the nucleus. Codified by a group of genes named Lipin they are substrate specific only to phosphatidate. There are speculated to be involved in the de novo synthesis of glycerolipids.Type II
Type II phosphatidate phospatases are transmembrane enzymes found mainly in the plasma membrane. They can also dephosphorylate other substrates beside phosphatidate therefore are also known as lipid-phosphate phosphataseLipid-phosphate phosphatase
In enzymology, a lipid-phosphate phosphatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction-10-hydroxy-9-octadecanoate + H2O \rightleftharpoons -9,10-dihydroxyoctadecanoate + phosphate...
. Their main role is in lipid signaling and in phospholipid head-group remodeling.
Genes
Human genes that encode phosphatidate phosphatases include:- PPAP2APPAP2ALipid phosphate phosphohydrolase 1 also known as phosphatidic acid phosphatase 2a is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPAP2A gene.- Function :...
(LPP1) – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A - PPAP2BPPAP2BLipid phosphate phosphohydrolase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPAP2B gene.-Further reading:...
(LPP3) – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2B - PPAP2C (LPP2) – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2C
- PPAPDC1APPAPDC1APhosphatidate phosphatase PPAPDC1A also known as phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPAPDC1A gene. PPAPDC1A has phosphatidate phosphatase activity....
(PPC1A) – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1A - PPAPDC1B (PPC1B) – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1B
- PPAPDC2 – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 2
- PPAPDC3 – phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 3
- LPPR2 – lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 2
- LPPR3 – lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3
- LPPR4 – lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 4
- LPIN1LPIN1Lipin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPIN1 gene.- Clinical significance :This gene represents a candidate gene for human lipodystrophy, characterized by loss of body fat, fatty liver, hypertriglyceridemia, and insulin resistance...
– lipin 1 - LPIN2 – lipin 2
- LPIN3 – lipin 3

