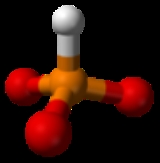
Phosphite
Encyclopedia
A phosphite is a salt of phosphorous acid
. The phosphite ion (PO33−) is a polyatomic ion
with a phosphorus
central atom where phosphorus
has an oxidation state
of +3. Its molecular geometry is approximately tetrahedral
like ammonia
.
Because phosphorous acid
exists as an equilibrium tautomeric mixture of P(OH)3 and HP(O)(OH)2, predominantly the latter, there is some confusion in nomenclature. The IUPAC recommends that the trihydroxy form be called phosphorous acid and its salts phosphites, with the dihydroxy form being called phosphonic acid and its salts phosphonates, but despite this, salts of HP(O)(OH)2 are often called phosphites rather than phosphonates.
The term phosphite is also used to mean phosphite ester
, an organophosphorus
compound with the formula P(OR)3.
, HP(O)(OH)2. Hydrogen bonding between anions leads to polymeric anionic structures. Recently some others, RbHPHO3, CsHPHO3, TlHPHO3 have been prepared by reacting phosphorous acid
with the metal carbonate
. These compounds contain a layer polymeric anion consisting of HPO3 tetrahedra linked by hydrogen bonds. These layers are interleaved by layers of metal cations.
s (or sometimes just phosphites) have the formula (RO)3P. They are prepared by reacting phosphorus trichloride
(or phosphorus tribromide
) with an alcohol
and a tertiary amine
.
PCl3 + 3 ROH + 3 R'3N → P(OR)3 + 3R'3NHCl
(a major plant nutrient
and fertilizer
ingredient), and controversial because phosphites have sometimes been advertised as fertilizers, even though they are converted to phosphate too slowly to serve as a plant's main phosphorus source. Lemoynie and others have described this complicated situation and noted that calling phosphites fertilizers avoided the regulatory complication and negative public perceptions that might have been incurred by registering them as fungicides.
Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with...
. The phosphite ion (PO33−) is a polyatomic ion
Polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a charged species composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded or of a metal complex that can be considered as acting as a single unit in the context of acid and base chemistry or in the formation of salts. The prefix "poly-" means "many," in...
with a phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
central atom where phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
has an oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
of +3. Its molecular geometry is approximately tetrahedral
Tetrahedral molecular geometry
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1 ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in CH4. This molecular geometry is common throughout the first...
like ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
.
Because phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with...
exists as an equilibrium tautomeric mixture of P(OH)3 and HP(O)(OH)2, predominantly the latter, there is some confusion in nomenclature. The IUPAC recommends that the trihydroxy form be called phosphorous acid and its salts phosphites, with the dihydroxy form being called phosphonic acid and its salts phosphonates, but despite this, salts of HP(O)(OH)2 are often called phosphites rather than phosphonates.
The term phosphite is also used to mean phosphite ester
Phosphite ester
A phosphite ester or organophosphite is a type of chemical compound with the general structure P3. Phosphite esters can be considered as esters of phosphorous acid, H3PO3. A simple phosphite ester is trimethylphosphite, P3...
, an organophosphorus
Organophosphorus
Organophosphorus compounds are degradable organic compounds containing carbon–phosphorus bonds , used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment...
compound with the formula P(OR)3.
Acid phosphites
Acid or hydrogen phosphites (which the IUPAC recommends be called acid or hydrogen phosphonates), such as NH4HP(O)2OH, can be prepared from phosphorous acidPhosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with...
, HP(O)(OH)2. Hydrogen bonding between anions leads to polymeric anionic structures. Recently some others, RbHPHO3, CsHPHO3, TlHPHO3 have been prepared by reacting phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with...
with the metal carbonate
Carbonate
In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, . The name may also mean an ester of carbonic acid, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C2....
. These compounds contain a layer polymeric anion consisting of HPO3 tetrahedra linked by hydrogen bonds. These layers are interleaved by layers of metal cations.
Pyrophosphites
Pyrophosphites (diphosphites) can be produced by gently heating acid phosphites under reduced pressure. They contain the ion, H2P2O52−which can be formulated [HP(O)2O−P(O)2H]2−.Naming of phosphite ions
The traditional name for HPO32− is phosphite, and for HPO2(OH)− is hydrogenphosphite or acid phosphite. However IUPAC recommendations are that HPO32− is to be named hydrogenphosphite or phosphonate, HPO2(OH)− is to be named dihydrogenphosphite or hydrogenphosphonate and phosphite is reserved for the hypothetical PO33− ion.Synthesis of phosphite esters
Organophosphorus compounds called phosphite esterPhosphite ester
A phosphite ester or organophosphite is a type of chemical compound with the general structure P3. Phosphite esters can be considered as esters of phosphorous acid, H3PO3. A simple phosphite ester is trimethylphosphite, P3...
s (or sometimes just phosphites) have the formula (RO)3P. They are prepared by reacting phosphorus trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride is a chemical compound of phosphorus and chlorine, having chemical formula PCl3. Its shape is trigonal pyramidal. It is the most important of the three phosphorus chlorides. It is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of organophosphorus compounds...
(or phosphorus tribromide
Phosphorus tribromide
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula PBr3. It fumes in air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is widely used in the laboratory for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides.-Preparation:...
) with an alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and a tertiary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
.
PCl3 + 3 ROH + 3 R'3N → P(OR)3 + 3R'3NHCl
Use in plants
Inorganic phosphites have been applied to crops to combat fungus-like pathogens of the order Oomycetes. The situation is confusing because of the similarity in name between phosphite and phosphatePhosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
(a major plant nutrient
Plant nutrition
'Plant Nutrition is the study of the chemical elements that are necessary for growth. In 1972, E. Epstein defined 2 criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth:# in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle or...
and fertilizer
Fertilizer
Fertilizer is any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin that is added to a soil to supply one or more plant nutrients essential to the growth of plants. A recent assessment found that about 40 to 60% of crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use...
ingredient), and controversial because phosphites have sometimes been advertised as fertilizers, even though they are converted to phosphate too slowly to serve as a plant's main phosphorus source. Lemoynie and others have described this complicated situation and noted that calling phosphites fertilizers avoided the regulatory complication and negative public perceptions that might have been incurred by registering them as fungicides.
See also
- OrganophosphorusOrganophosphorusOrganophosphorus compounds are degradable organic compounds containing carbon–phosphorus bonds , used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment...
- PhosphinePhosphinePhosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine...
- PR3 - Phosphine oxidePhosphine oxidePhosphine oxides are either inorganic phosphorus compounds such as phosphoryl trichloride or organophosphorus compounds with the formula OPR3, where R = alkyl or aryl...
- OPR3 - PhosphinitePhosphinitePhosphinites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PR2. They are esters of phosphinous acid.-See also:*Phosphine - PR3*Phosphine oxide - OPR3*Phosphonite - P2R*Phosphite - P3*Phosphinate - OPR2*Phosphonate - OP2R...
- P(OR)R2 - PhosphonitePhosphonitePhosphonites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P2R. They are derivivatives of phosphonous acid.- See also :*Phosphine - PR3*Phosphine oxide - OPR3*Phosphinite - PR2*Phosphinate - OPR2...
- P(OR)2R - PhosphinatePhosphinatePhosphinates are organophosphorus compounds with the formula OPR2.-See also:*Phosphine - PR3*Phosphine oxide - OPR3*Phosphinite - PR2*Phosphonite - P2R*Phosphite - P3*Phosphonate - OP2R*Phosphate - OP3...
- OP(OR)R2 - PhosphonatePhosphonatePhosphonates or phosphonic acids are organic compounds containing C-PO2 or C-PO2 groups . Bisphosphonates were first synthesized in 1897 by Von Baeyer and Hofmann. An example of such a bisphosphonate is HEDP . Since the work of Schwarzenbach in 1949, phosphonic acids are known as effective...
- OP(OR)2R - PhosphatePhosphateA phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
- OP(OR)3

