
Polyatomic ion
Encyclopedia
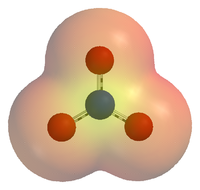
Chemical species
Chemical species are atoms, molecules, molecular fragments, ions, etc., being subjected to a chemical process or to a measurement. Generally, a chemical species can be defined as an ensemble of chemically identical molecular entities that can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a...
(ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
) composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
or of a metal complex
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
that can be considered as acting as a single unit in the context of acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
and base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
or in the formation of salts. The prefix "poly-" means "many," in Greek, but even ions of two atoms are commonly referred to as polyatomic. In older literature, a polyatomic ion is also referred to as a radical
Radical (chemistry)
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons on an open shell configuration. Free radicals may have positive, negative, or zero charge...
, and less commonly, as a radical group. In contemporary usage, the term radical refers to free radicals which are (not necessarily charged) species with an unpaired electron.
For example, a hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
ion is made of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom: its chemical formula is −. It has a charge of −1
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
. An ammonium
Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic cation with the chemical formula NH. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia...
ion is made up of one nitrogen atom and four hydrogen atoms: its chemical formula is +. It has charge of +1.
A polyatomic ion can often be considered as the conjugate acid
Conjugate acid
Within the Brønsted–Lowry acid-base theory , a conjugate acid is the acid member, HX, of a pair of two compounds that transform into each other by gain or loss of a proton. A conjugate acid can also be seen as the chemical substance that releases, or donates, a proton in the forward chemical...
or conjugate base of a neutral molecule. For example the sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
anion, 2−, is derived from H2SO4
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
which can be regarded as SO3
Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. In the gaseous form, this species is a significant pollutant, being the primary agent in acid rain. It is prepared on massive scales as a precursor to sulfuric acid.-Structure and bonding:Gaseous SO3 is a trigonal planar molecule of...
+ H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
.
Nomenclature
There are two "rules" that can be used for learning the nomenclature of polyatomic ions. First, when the prefix bi- is added to a name, a hydrogen is added to the ion's formula and its charge is increased by 1, the latter being a consequence of the hydrogen ion carrying a +1 charge. An alternate to the bi- prefix is to use the word hydrogen in its place: the anion derived from H+ + CO32−Carbonate
In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, . The name may also mean an ester of carbonic acid, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C2....
, HCO3−
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid...
can be called either bicarbonate or hydrogen carbonate.
Note that many of the common polyatomic anions are conjugate bases of acids derived from the oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
s of non-metallic
Nonmetal
Nonmetal, or non-metal, is a term used in chemistry when classifying the chemical elements. On the basis of their general physical and chemical properties, every element in the periodic table can be termed either a metal or a nonmetal...
elements. For example the sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
anion, 2−, is derived from H2SO4
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
which can be regarded as SO3
Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. In the gaseous form, this species is a significant pollutant, being the primary agent in acid rain. It is prepared on massive scales as a precursor to sulfuric acid.-Structure and bonding:Gaseous SO3 is a trigonal planar molecule of...
+ H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
.
The second rule looks at the number of oxygens in an ion. Consider the chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
oxoanion
Oxyanion
An oxyanion or oxoanion is a chemical compound with the generic formula AxOyz− . Oxoanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxoanions are determined by the octet rule...
family:
| oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
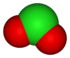
| anion name | chloride Chloride The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water... |
hypochlorite Hypochlorite The hypochlorite ion, also known as chlorate anion is ClO−. A hypochlorite compound is a chemical compound containing this group, with chlorine in oxidation state +1.Hypochlorites are the salts of hypochlorous acid... |
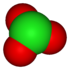
chlorite Chlorite The chlorite ion is ClO2−. A chlorite is a compound that contains this group,with chlorine in oxidation state +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous acid.-Oxidation states:... |
chlorate Chlorate The chlorate anion has the formula ClO. In this case, the chlorine atom is in the +5 oxidation state. "Chlorate" can also refer to chemical compounds containing this anion; chlorates are the salts of chloric acid. "Chlorate", when followed by a roman numeral in parentheses, e.g... |
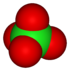
perchlorate Perchlorate Perchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid . They occur both naturally and through manufacturing. They have been used as a medicine for more than 50 years to treat thyroid gland disorders. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a... |
| formula | − | − | − | − | − |
| structure |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
First, think of the -ate ion as being the "base" name, in which case the addition of a per- prefix adds an oxygen. Changing the -ate suffix to -ite will reduce the oxygens by one, and keeping the suffix -ite and adding the prefix hypo- reduces the number of oxygens by two. In all situations, the charge is not affected. The naming pattern follows within many different oxyanion series based on a standard root for that particular series. The -ite has one less oxygen than the -ate, but different -ate anions might have different numbers of oxygen atoms.
These rules will not work with all polyatomic ions, but they do work with the most common ones (sulfate, phosphate, nitrate, chlorate).
Examples of common polyatomic ions
The following tables give examples of commonly-encountered polyatomic ions. Only a few representatives are given, as the number of polyatomic ions encountered in practice is very large.| Anions | |
|---|---|
| Acetate Acetate An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In... (ethanoate) |
or |
| Benzoate | or |
| Bicarbonate Bicarbonate In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid... (hydrogen carbonate) |
|
| Carbonate Carbonate In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, . The name may also mean an ester of carbonic acid, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C2.... |
|
| Cyanide Cyanide A cyanide is a chemical compound that contains the cyano group, -C≡N, which consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. Cyanides most commonly refer to salts of the anion CN−. Most cyanides are highly toxic.... |
|
| Hydroxide Hydroxide Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a... |
|
| Nitrate Nitrate The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a... |
|
| Phosphate Phosphate A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in... |
|
| Sulfate Sulfate In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:... |
| Cations | |
|---|---|
| Ammonium Ammonium The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic cation with the chemical formula NH. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia... |
|
| Hydronium Hydronium In chemistry, a hydronium ion is the cation , a type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. This cation is often used to represent the nature of the proton in aqueous solution, where the proton is highly solvated... |
|
| Mercury(I) Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... |
|
| Tropylium Tropylium ion In organic chemistry, the tropylium ion is an aromatic species with a formula of [C7H7]+. Its name derives from the molecule tropine . Salts of the tropylium cation can be stable, e.g. tropylium tetrafluoroborate... |
See also
- Monatomic ionMonatomic ionA monatomic ion is an ion consisting of one or more atoms of a single element . For example calcium carbonate consists of the monatomic ion Ca2+ and the polyatomic ion CO32-....
- Salt (chemistry)
- Mass spectrometryMass spectrometryMass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
- Hydrogen peroxideHydrogen peroxideHydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
- MoleculeMoleculeA molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
- Hydrogen molecular ion
External links
- List of polyatomic ions
- A Beginner's Guide To Polyatomic Ions.
- Tables of Common Polyatomic Ions, including PDBProtein Data BankThe Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
files

