Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
Encyclopedia
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI 3-kinases or PI3Ks) are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer. In response to lipopolysaccharide
, PI3K phosphorylates p65, inducing anandamide
synthesis to inhibit NF-κB activation. This is under the control of FAAH
limiting the ability of LPS to increase AEA levels and is also inhibited by wortmannin
and cannabidiol
, one of the only natural compounds to inhibit FAAH.
PI3Ks are a family of related intracellular signal transducer enzymes capable of phosphorylating the 3 position hydroxyl
group of the inositol
ring of phosphatidylinositol
(PtdIns). They are also known as phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases. The pathway, with oncogene
PIK3CA and tumor suppressor PTEN (gene)
, is implicated in insensitivity of cancer tumors to insulin
and IGF1, in calorie restriction
.
and colleagues began with their identification of a previously unknown phosphoinositide kinase associated with the polyoma middle T protein. They observed unique substrate specificity and chromatographic properties of the products of the lipid kinase, leading to the discovery that this phosphoinositide kinase had the unprecedented ability to phosphorylate phosphoinositides on the 3' position of the inositol ring. Subsequently, Cantley and colleagues demonstrated that in vivo the enzyme prefers PtdIns(4,5)P2 as a substrate, producing the novel phosphoinositide PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
.
) in order to regulate glucose uptake through a series of phosphorylation events.
The phosphoinositol-3-kinase family is divided into three different classes: Class I
, Class II
, and Class III
. The classifications are based on primary structure, regulation, and in vitro lipid substrate specificity.
(PI(3)P), Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate
(PI(3,4)P2), and Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
(PI(3,4,5)P3, . The PI3K is activated by G protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors.
Class I PI3K are heterodimeric molecules composed of a regulatory and a catalytic subunit; they are further divided between IA and IB subsets on sequence similarity. Class IA PI3K is composed of a heterodimer between a p110 catalytic subunit and a p85 regulatory subunit. There are five variants of the p85 regulatory subunit, designated p85α, p55α, p50α, p85β, or p55γ. There are also three variants of the p110 catalytic subunit designated p110α, β, or δ catalytic subunit. The first three regulatory subunits are all splice variants of the same gene (Pik3r1), the other two being expressed by other genes (Pik3r2 and Pik3r3, p85β, and p55γ, respectively). The most highly expressed regulatory subunit is p85α; all three catalytic subunits are expressed by separate genes (Pik3ca, Pik3cb, and Pik3cd for p110α, p110β, and p110δ
, respectively). The first two p110 isoforms (α and β) are expressed in all cells, but p110δ is expressed primarily in leukocytes, and it has been suggested that it evolved in parallel with the adaptive immune system. The regulatory p101 and catalytic p110γ subunits comprise the type IB PI3K and are encoded by a single gene each.
The p85 subunits contain SH2
and SH3
domains . The SH2 domains bind preferentially to phosphorylated tyrosine residues in the amino acid sequence context Y-X-X-M.
 Class II
Class II
and III
PI3K are differentiated from the Class I by their structure and function.
Class II comprises three catalytic isoforms (C2α, C2β, and C2γ), but, unlike Classes I and III, no regulatory proteins. Class II catalyse the production of PI(3)P and PI(3,4)P2 from PI; however, little is known about their role in immune cells. C2α and C2β are expressed through the body, however expression of C2γ is limited to hepatocytes.
The distinct feature of Class II PI3Ks is the C-terminal C2 domain. This domain lacks critical Asp residues to coordinate binding of Ca2+, which suggests class II PI3Ks bind lipids in a Ca2+-independent manner.
Class III produces only PI(3)P from PI but are more similar to Class I in structure, as they exist as a heterodimers of a catalytic (Vps34) and a regulatory (Vps15/p150) subunits. Class III seems to be primarily involved in the trafficking of proteins and vesicles. There is, however, evidence to show that they are able to contribute to the effectiveness of several process important to immune cells, not least phagocytosis.
, pleckstrin homology domain
s (PH domains), FYVE domains and other phosphoinositide-binding domains, are recruited to various cellular membranes.
.
The p110δ
and p110γ isoforms regulate different aspects of immune responses. PI 3-kinases are also a key component of the insulin signaling pathway. Hence there is great interest in the role of PI 3-kinase signaling in Diabetes mellitus
.
of AKT
binds directly to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
and PtdIns(3,4)P2, which are produced by activated PI 3-kinase. Since PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and PtdIns(3,4)P2 are restricted to the plasma membrane, this results in translocation of AKT to the plasma membrane. Likewise, the phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1
or, rarely referred to as PDPK1) also contains a pleckstrin homology domain that binds directly to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and PtdIns(3,4)P2, causing it to also translocate to the plasma membrane upon activation of PI 3-kinase. The colocalization of activated PDK1 and AKT allows AKT to become phosphorylated by PDK1
on threonine 308, leading to partial activation of AKT. Full activation of AKT occurs upon phosphorylation of serine 473 by the TORC2 complex of the mTOR protein kinase. (The nomenclature can be confusing. Note that PDK1 also refers to the unrelated enzyme Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1. Similarly, TORC2 also refers to the unrelated transcription factor Transducer of Regulated CREB activity 2, which has recently been renamed CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) to reduce the confusion). The "PI3-k/AKT" signaling pathway has been shown to be required for an extremely diverse array of cellular activities - most notably cellular proliferation and survival. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway is stimulated in protection of astrocytes from ceramide-induced apoptosis.
Many other proteins have been identified that are regulated by PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, including Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase
(BTK), General Receptor for Phosphoinositides-1 (GRP1), and the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase
.
that antagonises PI 3-kinase signaling is absent from many tumours. Hence, PI 3-kinase activity contributes significantly to cellular transformation and the development of cancer
.
(LTP). Whether it is required for the expression or the induction of LTP is still debated. In mouse hippocampal CA1 neurons, PI3K is complexed with AMPA Receptor
s and compartmentalized at the postsynaptic density of glutamatergic synapses. PI3K is phosphorylated upon NMDA Receptor
-dependent CaMKII activity, and it then facilitates the insertion of AMPA-R GluR1 subunits into the plasma membrane. This suggests that PI3K is required for the expression of LTP. Furthermore, PI3K inhibitors abolished the expression of LTP in rat hippocampal CA1, but do not affect its induction. Notably, the dependence of late-phase LTP expression on PI3K seems to decrease over time.
However, another study found that PI3K inhibitors suppressed the induction, but not the expression, of LTP in mouse hippocampal CA1. The PI3K pathway
also recruits many other proteins downstream, including mTOR, GSK3β, and PSD-95. The PI3K-mTOR pathway
leads to the phosphorylation of p70S6K, a kinase that facilitates translational activity
, further suggesting that PI3K is required for the protein-synthesis phase of LTP induction instead.
In addition to the class I – class III PI 3-kinases there is a group of more distantly related enzymes that are sometimes referred to as class IV PI 3-kinases. The class IV PI 3-kinases family is composed of ataxia telangiectasia mutated
(ATM), ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related
(ATR), DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) and mammalian Target Of Rapamycin
(mTOR). These members of the PI 3-kinase superfamily are protein serine/threonine kinases.
and LY294002
, although certain members of the class II PI 3-kinase family show decreased sensitivity.
As wortmannin
and LY294002
are broad inhibitors against PI 3-kinases
and a number of unrelated proteins at higher concentrations they are too toxic to be used as therapeutics. A number of pharmaceutical companies have recently been working on PI 3-kinase isoform specific inhibitors including the class I PI 3-kinase, p110δ
isoform specific inhibitors, IC486068 and IC87114, ICOS Corporation..GDC-0941 is a highly selective inhibitor of p110α with little activity against mTOR.
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides , also known as lipoglycans, are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide joined by a covalent bond; they are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, act as endotoxins and elicit strong immune responses in animals.-Functions:LPS is the major...
, PI3K phosphorylates p65, inducing anandamide
Anandamide
Anandamide, also known as N-arachidonoylethanolamide or AEA, is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter. The name is taken from the Sanskrit word ananda, which means "bliss, delight", and amide. It is synthesized from N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways...
synthesis to inhibit NF-κB activation. This is under the control of FAAH
FAAH
Fatty acid amide hydrolase or FAAH is a member of the serine hydrolase family of enzymes. It was first shown to breakdown anandamide in 1993 . In humans, it is encoded by the gene FAAH.-Function:...
limiting the ability of LPS to increase AEA levels and is also inhibited by wortmannin
Wortmannin
Wortmannin, a furanosteroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii,is a specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases . It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly...
and cannabidiol
Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol is a cannabinoid found in Cannabis. It is a major constituent of the plant, representing up to 40% in its extracts.It has displayed sedative effects in animal tests...
, one of the only natural compounds to inhibit FAAH.
PI3Ks are a family of related intracellular signal transducer enzymes capable of phosphorylating the 3 position hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
group of the inositol
Inositol
Inositol or cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol is a chemical compound with formula 6126 or 6, a sixfold alcohol of cyclohexane. It exists in nine possible stereoisomers, of which the most prominent form, widely occurring in nature, is cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-cyclohexanehexol, or myo-inositol...
ring of phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol is a negatively charged phospholipid and a minor component in the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes....
(PtdIns). They are also known as phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases. The pathway, with oncogene
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
PIK3CA and tumor suppressor PTEN (gene)
PTEN (gene)
Phosphatase and tensin homolog is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the PTEN gene. Mutations of this gene are a step in the development of many cancers....
, is implicated in insensitivity of cancer tumors to insulin
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood, storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscle....
and IGF1, in calorie restriction
Calorie restriction
Caloric restriction , or calorie restriction, is a dietary regimen that restricts calorie intake, where the baseline for the restriction varies, usually being the previous, unrestricted, intake of the subjects...
.
Discovery
The discovery of PI 3-kinases by Lewis CantleyLewis C. Cantley
Lewis C. Cantley is an American cell biologist and biochemist and a professor in the Departments of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the Director of Cancer Research at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, in Boston, Massachusetts...
and colleagues began with their identification of a previously unknown phosphoinositide kinase associated with the polyoma middle T protein. They observed unique substrate specificity and chromatographic properties of the products of the lipid kinase, leading to the discovery that this phosphoinositide kinase had the unprecedented ability to phosphorylate phosphoinositides on the 3' position of the inositol ring. Subsequently, Cantley and colleagues demonstrated that in vivo the enzyme prefers PtdIns(4,5)P2 as a substrate, producing the novel phosphoinositide PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol -triphosphate , abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases phosphorylation on phosphatidylinositol -bisphosphate .-Discovery:...
.
Classes
PI3Ks interact with the IRS (Insulin receptor substrateInsulin receptor substrate
Insulin receptor substrate is an important ligand in the insulin response of human cells.IRS-1, for example, is an IRS protein which contains a phosphotyrosine binding-domain . In addition, the insulin receptor contains a NPXpY domain. The PTB-domain binds the NPXpY domain...
) in order to regulate glucose uptake through a series of phosphorylation events.
The phosphoinositol-3-kinase family is divided into three different classes: Class I
Class I PI 3-kinases
Class I PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that possess a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity, and method of activation...
, Class II
Class II PI 3-kinases
Class II PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation....
, and Class III
Class III PI 3-kinase
Class III PI 3-kinase is a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation....
. The classifications are based on primary structure, regulation, and in vitro lipid substrate specificity.
Class I
Class I PI3Ks are responsible for the production of Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphatePhosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate is a phospholipid found in cell membranes that helps to recruit a range of proteins, many of which are involved in protein trafficking, to the membranes...
(PI(3)P), Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol -bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger...
(PI(3,4)P2), and Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol -triphosphate , abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases phosphorylation on phosphatidylinositol -bisphosphate .-Discovery:...
(PI(3,4,5)P3, . The PI3K is activated by G protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors.
Class I PI3K are heterodimeric molecules composed of a regulatory and a catalytic subunit; they are further divided between IA and IB subsets on sequence similarity. Class IA PI3K is composed of a heterodimer between a p110 catalytic subunit and a p85 regulatory subunit. There are five variants of the p85 regulatory subunit, designated p85α, p55α, p50α, p85β, or p55γ. There are also three variants of the p110 catalytic subunit designated p110α, β, or δ catalytic subunit. The first three regulatory subunits are all splice variants of the same gene (Pik3r1), the other two being expressed by other genes (Pik3r2 and Pik3r3, p85β, and p55γ, respectively). The most highly expressed regulatory subunit is p85α; all three catalytic subunits are expressed by separate genes (Pik3ca, Pik3cb, and Pik3cd for p110α, p110β, and p110δ
P110δ
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene....
, respectively). The first two p110 isoforms (α and β) are expressed in all cells, but p110δ is expressed primarily in leukocytes, and it has been suggested that it evolved in parallel with the adaptive immune system. The regulatory p101 and catalytic p110γ subunits comprise the type IB PI3K and are encoded by a single gene each.
The p85 subunits contain SH2
SH2 domain
The SH2 domain is a structurally conserved protein domain contained within the Src oncoprotein and in many other intracellular signal-transducing proteins...
and SH3
SH3 domain
The SRC Homology 3 Domain is a small protein domain of about 60 amino acids residues first identified as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk and the non-catalytic parts of enzymes such as phospholipase and several cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases such as Abl and Src...
domains . The SH2 domains bind preferentially to phosphorylated tyrosine residues in the amino acid sequence context Y-X-X-M.
Classes II and III

Class II PI 3-kinases
Class II PI 3-kinases are a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation....
and III
Class III PI 3-kinase
Class III PI 3-kinase is a subgroup of the enzyme family, phosphoinositide 3-kinase that share a common protein domain structure, substrate specificity and method of activation....
PI3K are differentiated from the Class I by their structure and function.
Class II comprises three catalytic isoforms (C2α, C2β, and C2γ), but, unlike Classes I and III, no regulatory proteins. Class II catalyse the production of PI(3)P and PI(3,4)P2 from PI; however, little is known about their role in immune cells. C2α and C2β are expressed through the body, however expression of C2γ is limited to hepatocytes.
The distinct feature of Class II PI3Ks is the C-terminal C2 domain. This domain lacks critical Asp residues to coordinate binding of Ca2+, which suggests class II PI3Ks bind lipids in a Ca2+-independent manner.
Class III produces only PI(3)P from PI but are more similar to Class I in structure, as they exist as a heterodimers of a catalytic (Vps34) and a regulatory (Vps15/p150) subunits. Class III seems to be primarily involved in the trafficking of proteins and vesicles. There is, however, evidence to show that they are able to contribute to the effectiveness of several process important to immune cells, not least phagocytosis.
Human genes
| group | gene | protein | aliases | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| class 2 | PIK3C2A PIK3C2A Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing alpha polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2A gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, class 2, alpha polypeptide | PI3K-C2α | 2.7.1.154 Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase In enzymology, a phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate, whereas its two products are ADP and 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4-bisphosphate.This... |
| PIK3C2B PIK3C2B Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing beta polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2B gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, class 2, beta polypeptide | PI3K-C2β | ||
| PIK3C2G PIK3C2G Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing gamma polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2G gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, class 2, gamma polypeptide | PI3K-C2γ | ||
| class 3 | PIK3C3 PIK3C3 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C3 gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, class 3 | Vps34 | 2.7.1.137 |
| class 1 catalytic | PIK3CA | PI3K, catalytic, alpha polypeptide | p110-α | 2.7.1.153 Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase In enzymology, a phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate, whereas its two products are ADP and 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol... |
| PIK3CB PIK3CB Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CB gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, catalytic, beta polypeptide | p110-β | ||
| PIK3CG PIK3CG Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CG gene.-Interactions:PIK3CG has been shown to interact with PIK3CD, KRAS, PIK3R5 and BCR gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, catalytic, gamma polypeptide | p110-γ | ||
| PIK3CD P110δ Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.... |
PI3K, catalytic, delta polypeptide | p110-δ | ||
| class 1 regulatory | PIK3R1 PIK3R1 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.-Interactions:PIK3R1 has been shown to interact with EPH receptor A2, KHDRBS1, Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2, Janus kinase 2, GAB2, CD117, BCAR1, CD28, SHB, EZR, PIK3CD, GAB1, HRAS,... |
PI3K, regulatory subunit 1 (alpha) | p85-α | N/A |
| PIK3R2 PIK3R2 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R2 gene.-Interactions:PIK3R2 has been shown to interact with FYN, HER2/neu, Epidermal growth factor, Cbl gene, PIK3CD, CRKL and Macrophage colony-stimulating factor.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, regulatory subunit 2 (beta) | p85-β | ||
| PIK3R3 PIK3R3 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R3 gene.-Interactions:PIK3R3 has been shown to interact with Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, IRS1 and Retinoblastoma protein.... |
PI3K, regulatory subunit 3 (gamma) | p55-γ | ||
| PIK3R4 PIK3R4 Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 4, also known as PI3-kinase regulatory subunit 4 or PI3-kinase p150 subunit or phosphoinositide 3-kinase adaptor protein, or VPS15 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R4 gene.... |
PI3K, regulatory subunit 4 | p150 | ||
| PIK3R5 PIK3R5 Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R5 gene.-Further reading:... |
PI3K, regulatory subunit 5 | p101 | ||
| PIK3R6 | PI3K, regulatory subunit 6 | p87 |
Mechanism
The various 3-phosphorylated phosphoinositides that are produced by PI 3-kinases (PtdIns3P, PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns(3,5)P2, and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) function in a mechanism by which an assorted group of signalling proteins, containing PX domainPX domain
The PX domain is a phosphoinositide-binding structural domain involved in targeting of proteins to cell membranes.This domain was first found in P40phox and p47phox domains of NADPH oxidase...
, pleckstrin homology domain
Pleckstrin homology domain
Pleckstrin homology domain is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton....
s (PH domains), FYVE domains and other phosphoinositide-binding domains, are recruited to various cellular membranes.
Function
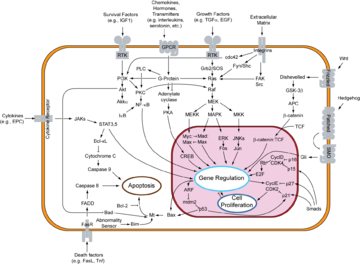
PI 3-kinases have been linked to an extraordinarily diverse group of cellular functions, including cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking. Many of these functions relate to the ability of class I PI 3-kinases to activate protein kinase B (PKB, aka Akt) as in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathwayPI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signalling pathway important in apoptosis and hence cancer e.g. breast cancerand non-small-cell lung cancer.]PI3K activation activates AKT which activates mTOR....
.
The p110δ
P110δ
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene....
and p110γ isoforms regulate different aspects of immune responses. PI 3-kinases are also a key component of the insulin signaling pathway. Hence there is great interest in the role of PI 3-kinase signaling in Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
.
Mechanism
The pleckstrin homology domainPleckstrin homology domain
Pleckstrin homology domain is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton....
of AKT
AKT
Akt, also known as Protein Kinase B , is a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a key role in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, cell proliferation, apoptosis, transcription and cell migration.-Family members:...
binds directly to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol -triphosphate , abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases phosphorylation on phosphatidylinositol -bisphosphate .-Discovery:...
and PtdIns(3,4)P2, which are produced by activated PI 3-kinase. Since PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and PtdIns(3,4)P2 are restricted to the plasma membrane, this results in translocation of AKT to the plasma membrane. Likewise, the phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1
Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1
In the field of biochemistry, 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1, also known as PDPK1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PDPK1 gene.PDPK1 is also known as "PDK1"...
or, rarely referred to as PDPK1) also contains a pleckstrin homology domain that binds directly to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and PtdIns(3,4)P2, causing it to also translocate to the plasma membrane upon activation of PI 3-kinase. The colocalization of activated PDK1 and AKT allows AKT to become phosphorylated by PDK1
PDK1
[Pyruvate dehydrogenase [lipoamide]] kinase isozyme 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDK1 gene. It codes for an isozyme of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase ....
on threonine 308, leading to partial activation of AKT. Full activation of AKT occurs upon phosphorylation of serine 473 by the TORC2 complex of the mTOR protein kinase. (The nomenclature can be confusing. Note that PDK1 also refers to the unrelated enzyme Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1. Similarly, TORC2 also refers to the unrelated transcription factor Transducer of Regulated CREB activity 2, which has recently been renamed CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) to reduce the confusion). The "PI3-k/AKT" signaling pathway has been shown to be required for an extremely diverse array of cellular activities - most notably cellular proliferation and survival. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway is stimulated in protection of astrocytes from ceramide-induced apoptosis.
Many other proteins have been identified that are regulated by PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, including Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase
Bruton's tyrosine kinase
Bruton's tyrosine kinase is a type of kinase enzyme implicated in the primary immunodeficiency disease X-linked agammaglobulinemia . Its exact mechanism of action remains unknown, but it plays a crucial role in B cell maturation as well as mast cell activation through the high-affinity IgE receptor...
(BTK), General Receptor for Phosphoinositides-1 (GRP1), and the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase
OGT (gene)
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine--peptide N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 110 kDa subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OGT gene.-Interactions:OGT has been shown to interact with Host cell factor C1 and SIN3A.-Further reading:...
.
Cancers
The class IA PI 3-kinase p110α is mutated in many cancers. Many of these mutations cause the kinase to be more active. The PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 phosphatase PTENPTEN
PTEN may mean:* Patterson-UTI Energy, Inc., which trades on the NASDAQ stock market under the symbol 'PTEN'* Prime Time Entertainment Network* PTEN , a human tumour suppressor gene on chromosome 10...
that antagonises PI 3-kinase signaling is absent from many tumours. Hence, PI 3-kinase activity contributes significantly to cellular transformation and the development of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
.
Learning and memory
PI3K has also been implicated in Long-term potentiationLong-term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation is a long-lasting enhancement in signal transmission between two neurons that results from stimulating them synchronously. It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength...
(LTP). Whether it is required for the expression or the induction of LTP is still debated. In mouse hippocampal CA1 neurons, PI3K is complexed with AMPA Receptor
AMPA receptor
The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor is a non-NMDA-type ionotropic transmembrane receptor for glutamate that mediates fast synaptic transmission in the central nervous system . Its name is derived from its ability to be activated by the artificial glutamate analog AMPA...
s and compartmentalized at the postsynaptic density of glutamatergic synapses. PI3K is phosphorylated upon NMDA Receptor
NMDA receptor
The NMDA receptor , a glutamate receptor, is the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function....
-dependent CaMKII activity, and it then facilitates the insertion of AMPA-R GluR1 subunits into the plasma membrane. This suggests that PI3K is required for the expression of LTP. Furthermore, PI3K inhibitors abolished the expression of LTP in rat hippocampal CA1, but do not affect its induction. Notably, the dependence of late-phase LTP expression on PI3K seems to decrease over time.
However, another study found that PI3K inhibitors suppressed the induction, but not the expression, of LTP in mouse hippocampal CA1. The PI3K pathway
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signalling pathway important in apoptosis and hence cancer e.g. breast cancerand non-small-cell lung cancer.]PI3K activation activates AKT which activates mTOR....
also recruits many other proteins downstream, including mTOR, GSK3β, and PSD-95. The PI3K-mTOR pathway
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signalling pathway important in apoptosis and hence cancer e.g. breast cancerand non-small-cell lung cancer.]PI3K activation activates AKT which activates mTOR....
leads to the phosphorylation of p70S6K, a kinase that facilitates translational activity
, further suggesting that PI3K is required for the protein-synthesis phase of LTP induction instead.
PI 3-kinases as protein kinases
Many of the PI 3-kinases appear to have a serine/threonine kinase activity in vitro; however, it is unclear whether this has any role in vivo.In addition to the class I – class III PI 3-kinases there is a group of more distantly related enzymes that are sometimes referred to as class IV PI 3-kinases. The class IV PI 3-kinases family is composed of ataxia telangiectasia mutated
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis...
(ATM), ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related
Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ATR also known as ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein or FRAP-related protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATR gene...
(ATR), DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) and mammalian Target Of Rapamycin
Mammalian target of rapamycin
The mammalian target of rapamycin also known as mechanistic target of rapamycin or FK506 binding protein 12-rapamycin associated protein 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FRAP1 gene...
(mTOR). These members of the PI 3-kinase superfamily are protein serine/threonine kinases.
Inhibition
All PI 3-kinases are inhibited by the drugs wortmanninWortmannin
Wortmannin, a furanosteroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii,is a specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases . It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly...
and LY294002
LY294002
LY294002 is a morpholine derivative of quercetin. It is a potent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases . Two of these are the proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase and the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform...
, although certain members of the class II PI 3-kinase family show decreased sensitivity.
PI 3-kinases inhibitors as therapeutics
As wortmannin
Wortmannin
Wortmannin, a furanosteroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii,is a specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases . It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly...
and LY294002
LY294002
LY294002 is a morpholine derivative of quercetin. It is a potent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases . Two of these are the proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase and the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform...
are broad inhibitors against PI 3-kinases
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor
A Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor is a potential medical drug that functions by inhibiting a Phosphoinositide 3-kinase enzyme which is part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which plays a key role in cancer. Inhibiting this pathway often suppresses tumor growth.There are a number of different...
and a number of unrelated proteins at higher concentrations they are too toxic to be used as therapeutics. A number of pharmaceutical companies have recently been working on PI 3-kinase isoform specific inhibitors including the class I PI 3-kinase, p110δ
P110δ
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene....
isoform specific inhibitors, IC486068 and IC87114, ICOS Corporation..GDC-0941 is a highly selective inhibitor of p110α with little activity against mTOR.

