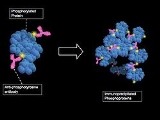
Phosphoproteomics
Encyclopedia
Phosphoproteomics is a branch of proteomics
that identifies, catalogs, and characterizes proteins containing a phosphate group as a post-translational modification
. Phosphorylation
is a key reversible modification that regulates protein function, subcellular localization, complex formation, degradation of proteins and therefore cell signalling networks. With all of these modification results, it is assumed that up to 30% of all proteins may be phosphorylated, some multiple times.
Compared to expression analysis, phosphoproteomics provides two additional layers of information. First, it provides clues on what protein or pathway might be activated because a change in phosphorylation status almost always reflects a change in protein activity. Second, it indicates what proteins might be potential drug targets as exemplified by the kinase inhibitor Gleevec. While phosphoproteomics will greatly expand knowledge about the numbers and types of phosphoproteins, its greatest promise is the rapid analysis of entire phosphorylation based signalling networks.
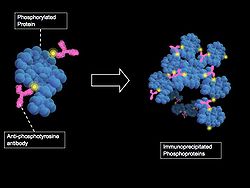 The analysis of the entire complement of phosphorylated proteins in a cell is certainly a feasible option. This is due to the optimization of enrichment protocols for phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides, better fractionation techniques using chromatography, and improvement of methods to selectively visualize phosphorylated residues using mass spectrometry. Although the current procedures for phosphoproteomic analysis are greatly improved, there is still sample loss and inconsistencies with regards to sample preparation, enrichment , and instrumentation. Bioinformatics tools and biological sequence databases are also necessary for high-throughput phosphoproteomic studies.
The analysis of the entire complement of phosphorylated proteins in a cell is certainly a feasible option. This is due to the optimization of enrichment protocols for phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides, better fractionation techniques using chromatography, and improvement of methods to selectively visualize phosphorylated residues using mass spectrometry. Although the current procedures for phosphoproteomic analysis are greatly improved, there is still sample loss and inconsistencies with regards to sample preparation, enrichment , and instrumentation. Bioinformatics tools and biological sequence databases are also necessary for high-throughput phosphoproteomic studies.
Enrichment Strategies
Previous procedures to isolate phosphorylated proteins included radioactive labeling with 32P-labeled ATP
followed by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
or thin layer chromatography. These traditional methods are inefficient because it is impossible to obtain large amounts of proteins required for phosphorylation analysis. Therefore, the current and simplest methods to enrich phosphoproteins are affinity purification using phosphospecific antibodies, immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), strong cation exchange (SCX) chromatography, or titanium dioxide chromatography. Antiphosphotyrosine antibodies have been proven very successful in purification, but fewer reports have been published using antibodies against phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-containing proteins. IMAC enrichment is based on phosphate affinity for immobilized metal chelated to the resin. SCX separates phosphorylated from non-phosphorylated peptides based on the negatively charged phosphate group. Titanium dioxide chromatography is a newer technique that requires significantly less column preparation time. Many phosphoproteomic studies use a combination of these enrichment strategies to obtain the purest sample possible.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Mass spectrometry is currently the best method to adequately compare pairs of protein samples. The two main procedures to perform this task are using isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT) and stable isotopic amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). In the ICAT procedure samples are labeled individually after isolation with mass-coded reagents that modify cysteine residues. In SILAC, cells are cultured separately in the presence of different isotopically labeled amino acids for several cell divisions allowing cellular proteins to incorporate the label. Mass spectrometry is subsequently used to identify phosphoserine, phosphothreonine, and phosphotyrosine-containing peptides.
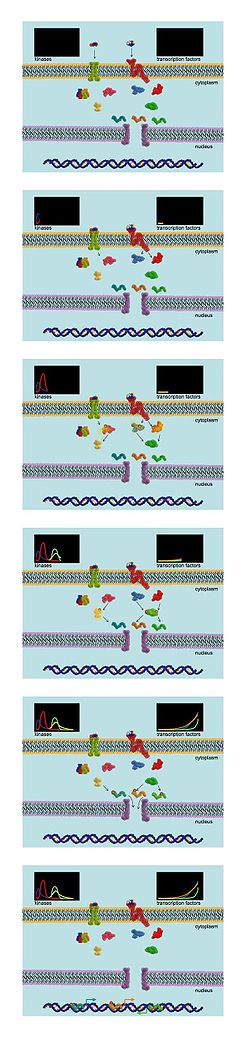 Intracellular signal transduction is primarily mediated by the reversible phosphorylation of various signalling molecules by enzymes dubbed kinases. Kinases transfer phosphate groups from ATP
Intracellular signal transduction is primarily mediated by the reversible phosphorylation of various signalling molecules by enzymes dubbed kinases. Kinases transfer phosphate groups from ATP
to specific serine
, threonine
or tyrosine
residues of target molecules. The resultant phosphorylated protein may have altered activity level, subcellular localization or tertiary structure.
Phosphoproteomic analyses are ideal for the study of the dynamics of signalling networks. In one study design, cells are exposed to SILAC labelling and then stimulated by a specific growth factor. The cells are collected at various timepoints, and the lysates are combined for analysis by tandem MS. This allows experimenters to track the phosphorylation state of many phosphoproteins in the cell over time. The ability to measure the global phosphorylation state of many proteins at various time points makes this approach much more powerful than traditional biochemical methods for analyzing signalling network behavior.
One study was able to simultaneously measure the fold-change in phosphorylation state of 127 proteins between unstimulated and EphrinB1-stimulated cells. Of these 127 proteins, 40 showed increased phosphorylation with stimulation by EphrinB1. The researchers were able to use this information in combination with previously published data to construct a signal transduction network for the proteins downstream of the EphB2 receptor.
Another recent phosphoproteomic study included large-scale identification and quantification of phosphorylation events triggered by the anti-diuretic hormone vasopressin in kidney collecting duct. A total of 714 phosphorylation sites on 223 unique phosphoproteins were identified, including three novel phosphorylation sites in the vasopressin-sensitive water channel aquaporin-2 (AQP2).
research has focused on changes to the phosphoproteome during tumor
development. Phosphoproteins could be cancer markers useful to cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. In fact, research has shown that there are distinct phosphotyrosine proteomes of breast and liver tumors. There is also evidence of hyperphosphorylation at tyrosine residues in breast tumors but not in normal tissues. Findings like these suggest that it is possible to mine the tumor phosphoproteome for potential biomarkers.
Increasing amounts of data are available suggesting that distinctive phosphoproteins exist in various tumors and that phosphorylation profiling could be used to fingerprint cancers from different origins. In addition, systematic cataloguing of tumor-specific phosphoproteins in individual patients could reveal multiple causative players during cancer formation. By correlating this experimental data to clinical data such as drug response and disease outcome, potential cancer markers could be identified for diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of drug response, and potential drug targets.
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
that identifies, catalogs, and characterizes proteins containing a phosphate group as a post-translational modification
Posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification is the chemical modification of a protein after its translation. It is one of the later steps in protein biosynthesis, and thus gene expression, for many proteins....
. Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
is a key reversible modification that regulates protein function, subcellular localization, complex formation, degradation of proteins and therefore cell signalling networks. With all of these modification results, it is assumed that up to 30% of all proteins may be phosphorylated, some multiple times.
Compared to expression analysis, phosphoproteomics provides two additional layers of information. First, it provides clues on what protein or pathway might be activated because a change in phosphorylation status almost always reflects a change in protein activity. Second, it indicates what proteins might be potential drug targets as exemplified by the kinase inhibitor Gleevec. While phosphoproteomics will greatly expand knowledge about the numbers and types of phosphoproteins, its greatest promise is the rapid analysis of entire phosphorylation based signalling networks.
Overview of phosphoproteomic analysis
A sample large-scale phosphoproteomic analysis includes- Cultured cells undergo SILACSilacSILAC is a technique based on mass spectrometry that detects differences in protein abundance among samples using non-radioactive isotopic labeling. It is a popular method for quantitative proteomics.-Procedure:Two populations of cells are cultivated in cell culture...
encoding. - Cells are stimulated with factor of interest (eg. growth factor, hormone).
- Stimulation can occur for various lengths of time for temporal analysis.
- Cells are lysed and enzymatically digested.
- Peptides are separated using ion exchange chromatographyIon exchange chromatographyIon-exchange chromatography is a process that allows the separation of ions and polar molecules based on their charge. It can be used for almost any kind of charged molecule including large proteins, small nucleotides and amino acids. The solution to be injected is usually called a sample, and the...
. - Phosphopeptides are enriched using phosphospecific antibodies, immobilized metal affinity chromatographyAffinity chromatographyAffinity chromatography is a method of separating biochemical mixtures and based on a highly specific interaction such as that between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, or receptor and ligand.-Uses:Affinity chromatography can be used to:...
or titanium dioxide (TiO2) chromatographyChromatographyChromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
. - Phosphopeptides are analyzed using mass spectrometryMass spectrometryMass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
. - Peptides are sequenced and analyzed.
Tools and methods

Enrichment Strategies
Previous procedures to isolate phosphorylated proteins included radioactive labeling with 32P-labeled ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
followed by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge...
or thin layer chromatography. These traditional methods are inefficient because it is impossible to obtain large amounts of proteins required for phosphorylation analysis. Therefore, the current and simplest methods to enrich phosphoproteins are affinity purification using phosphospecific antibodies, immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), strong cation exchange (SCX) chromatography, or titanium dioxide chromatography. Antiphosphotyrosine antibodies have been proven very successful in purification, but fewer reports have been published using antibodies against phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-containing proteins. IMAC enrichment is based on phosphate affinity for immobilized metal chelated to the resin. SCX separates phosphorylated from non-phosphorylated peptides based on the negatively charged phosphate group. Titanium dioxide chromatography is a newer technique that requires significantly less column preparation time. Many phosphoproteomic studies use a combination of these enrichment strategies to obtain the purest sample possible.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Mass spectrometry is currently the best method to adequately compare pairs of protein samples. The two main procedures to perform this task are using isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT) and stable isotopic amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). In the ICAT procedure samples are labeled individually after isolation with mass-coded reagents that modify cysteine residues. In SILAC, cells are cultured separately in the presence of different isotopically labeled amino acids for several cell divisions allowing cellular proteins to incorporate the label. Mass spectrometry is subsequently used to identify phosphoserine, phosphothreonine, and phosphotyrosine-containing peptides.
Phosphoproteomics in the study of signal transduction

Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
to specific serine
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
, threonine
Threonine
Threonine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH3. Its codons are ACU, ACA, ACC, and ACG. This essential amino acid is classified as polar...
or tyrosine
Tyrosine
Tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. Its codons are UAC and UAU. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group...
residues of target molecules. The resultant phosphorylated protein may have altered activity level, subcellular localization or tertiary structure.
Phosphoproteomic analyses are ideal for the study of the dynamics of signalling networks. In one study design, cells are exposed to SILAC labelling and then stimulated by a specific growth factor. The cells are collected at various timepoints, and the lysates are combined for analysis by tandem MS. This allows experimenters to track the phosphorylation state of many phosphoproteins in the cell over time. The ability to measure the global phosphorylation state of many proteins at various time points makes this approach much more powerful than traditional biochemical methods for analyzing signalling network behavior.
One study was able to simultaneously measure the fold-change in phosphorylation state of 127 proteins between unstimulated and EphrinB1-stimulated cells. Of these 127 proteins, 40 showed increased phosphorylation with stimulation by EphrinB1. The researchers were able to use this information in combination with previously published data to construct a signal transduction network for the proteins downstream of the EphB2 receptor.
Another recent phosphoproteomic study included large-scale identification and quantification of phosphorylation events triggered by the anti-diuretic hormone vasopressin in kidney collecting duct. A total of 714 phosphorylation sites on 223 unique phosphoproteins were identified, including three novel phosphorylation sites in the vasopressin-sensitive water channel aquaporin-2 (AQP2).
Phosphoproteomics in the study of cancer
Since the inception of phosphoproteomics, cancerCancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
research has focused on changes to the phosphoproteome during tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
development. Phosphoproteins could be cancer markers useful to cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. In fact, research has shown that there are distinct phosphotyrosine proteomes of breast and liver tumors. There is also evidence of hyperphosphorylation at tyrosine residues in breast tumors but not in normal tissues. Findings like these suggest that it is possible to mine the tumor phosphoproteome for potential biomarkers.
Increasing amounts of data are available suggesting that distinctive phosphoproteins exist in various tumors and that phosphorylation profiling could be used to fingerprint cancers from different origins. In addition, systematic cataloguing of tumor-specific phosphoproteins in individual patients could reveal multiple causative players during cancer formation. By correlating this experimental data to clinical data such as drug response and disease outcome, potential cancer markers could be identified for diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of drug response, and potential drug targets.
Limitations
While phosphoproteomics has greatly expanded knowledge about the numbers and types of phosphoproteins, along with their role in signaling networks, there are still a few limitations to these techniques. To begin with, isolation methods such as anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies do not distinguish between isolating tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and proteins associated with tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. Therefore, even though phosphorylation dependent protein-protein interactions are very important, it is important to remember that a protein detected by this method is not necessarily a direct substrate of any tyrosine kinase. Only by digesting the samples before immunoprecipitation can isolation of only phosphoproteins and temporal profiles of individual phosphorylaiton sites be produced. Another limitation is that some relevant proteins will likely be missed since no extraction condition is all encompassing. It is possible that proteins with low stoichiometry of phosphorylation, in very low abundance, or phosphorylated as a target for rapid degradation will be lost.See also
- SILACSilacSILAC is a technique based on mass spectrometry that detects differences in protein abundance among samples using non-radioactive isotopic labeling. It is a popular method for quantitative proteomics.-Procedure:Two populations of cells are cultivated in cell culture...
- chromatographyChromatographyChromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
- affinity chromatographyAffinity chromatographyAffinity chromatography is a method of separating biochemical mixtures and based on a highly specific interaction such as that between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, or receptor and ligand.-Uses:Affinity chromatography can be used to:...
- ion exchange chromatographyIon exchange chromatographyIon-exchange chromatography is a process that allows the separation of ions and polar molecules based on their charge. It can be used for almost any kind of charged molecule including large proteins, small nucleotides and amino acids. The solution to be injected is usually called a sample, and the...
- mass spectrometryMass spectrometryMass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
External links
- Phosida Phosphorylation Site Database
- Analysis of Signal Transduction YouTube Video
- CDPD Collecting Duct Phosphoprotein Database

