Photo-oxidation of polymers
Encyclopedia
Photo-oxidation is the degradation of a polymer
surface in the presence of oxygen or ozone. The effect is facilitated by radiant energy
such as UV or artificial light. This process is the most significant factor in weathering of polymers. Photo-oxidation is a chemical change that reduces the polymer's molecular weight. As a consequence of this change the material becomes more brittle, with a reduction in its tensile, impact and elongation strength. Discoloration and loss of surface smoothness accompany photo-oxidation. High temperature and localized stress concentrations are factors that significantly increase the effect of photo-oxidation.

(PC) to decrease the oxidation and photo-yellowing rate caused by solar radiation.
Dyes and pigments are used in polymer materials to provide color changing properties. These additives can reduce the rate of polymer degradation. Cu-phthalocyanine dye can help stabilize against degradation, but in other situations such as photochemical aging can actually accelerate degradation. The excited Cu-phthalocyanine may abstract hydrogen atoms from methyl groups in the PC, which increase the formation of free radicals. This acts as the starting points for the sequential photo-oxidation reactions leading to the degradation of the PC.
Electron transfer sensitization is a mechanism where the excited Cu-phthalocyanine abstracts electrons from PC to form Cu-Ph radical anion and PC radical cations. These species in the presence of oxygen can cause oxidation of the aromatic ring.
The photo-oxidation reactions include chain scission, cross linking and secondary oxidative reactions. The following process steps can be considered:
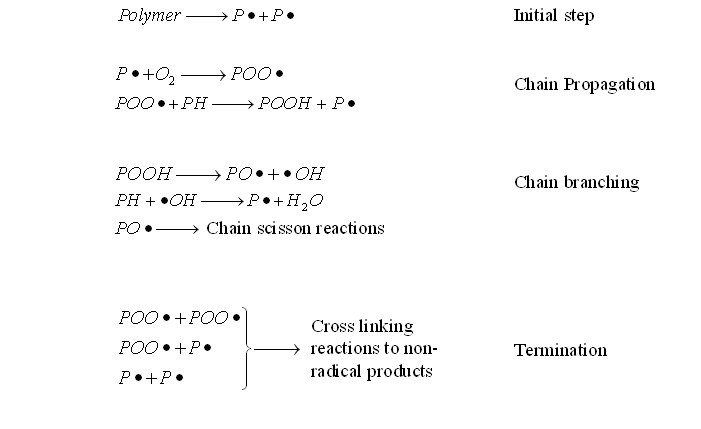
where PH = Polymer
P• = Polymer alkyl radical
PO• = Polymer oxy radical (Polymer alkoxy radical)
POO• = Polymer peroxy radical (Polymer alkylperoxy radical)
POOH = Polymer hydroperoxide
HO• = hydroxy radical
Polymer degradation
Polymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, colour, shape, etc.—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors such as heat, light or chemicals such as acids, alkalis and some salts...
surface in the presence of oxygen or ozone. The effect is facilitated by radiant energy
Radiant energy
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux with respect to time and, like all forms of energy, its SI unit is the joule. The term is used particularly when radiation is emitted by a source into the...
such as UV or artificial light. This process is the most significant factor in weathering of polymers. Photo-oxidation is a chemical change that reduces the polymer's molecular weight. As a consequence of this change the material becomes more brittle, with a reduction in its tensile, impact and elongation strength. Discoloration and loss of surface smoothness accompany photo-oxidation. High temperature and localized stress concentrations are factors that significantly increase the effect of photo-oxidation.

Photo-oxidation protection
Poly(ethylene-naphthalate) (PEN) can be protected by applying a zinc oxide coating, which acts as protective film reducing the diffusion of oxygen. Zinc oxide can also be used on polycarbonatePolycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
(PC) to decrease the oxidation and photo-yellowing rate caused by solar radiation.
Effects of dyes/pigments
Adding pigment light absorbers and photostabilizers, (UV absorbers), are one way to minimise photo-oxidation in polymers. Antioxidants are used to inhibit the formation of hydroperoxides in the photo-oxidation process.Dyes and pigments are used in polymer materials to provide color changing properties. These additives can reduce the rate of polymer degradation. Cu-phthalocyanine dye can help stabilize against degradation, but in other situations such as photochemical aging can actually accelerate degradation. The excited Cu-phthalocyanine may abstract hydrogen atoms from methyl groups in the PC, which increase the formation of free radicals. This acts as the starting points for the sequential photo-oxidation reactions leading to the degradation of the PC.
Electron transfer sensitization is a mechanism where the excited Cu-phthalocyanine abstracts electrons from PC to form Cu-Ph radical anion and PC radical cations. These species in the presence of oxygen can cause oxidation of the aromatic ring.
Chemical mechanism
Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids along or at the end of polymer chains are generated by oxygenated species in photolysis of photo-oxidation. The initiation of photo-oxidation reactions is due to the existence of chromophoric groups in the macromolecules. Photo-oxidation can occur simultaneously with thermal degradation and either one of these effects can accelerate the other.The photo-oxidation reactions include chain scission, cross linking and secondary oxidative reactions. The following process steps can be considered:
- Initial step: Free radical formation can be formed by light photon absorption.
- Chain Propagation step: The free radical reacts with oxygen to produce polymer peroxy radicals (POO•) and generate polymer hydroperoxide (POOH) and new polymer alkyl radical (P•).
- Chain Branching: The formation of polymer oxy radicals (PO•) and hydroxy radicals (HO•) can be formed by photolysis.
- Termination step: Cross linking is a result of the reaction of different free radicals with each other.

where PH = Polymer
P• = Polymer alkyl radical
PO• = Polymer oxy radical (Polymer alkoxy radical)
POO• = Polymer peroxy radical (Polymer alkylperoxy radical)
POOH = Polymer hydroperoxide
HO• = hydroxy radical
Further reading
- Grassie, N & Scott, G 1985, Polymer Degradation Stabilisation, Press Syndicate of University of Cambridge, England
- Schnabel, W 1981, Polymer Degradation: Principles and Practical Applications, Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc, New York
See also
- forensic polymer engineeringForensic polymer engineeringThe study of failure in polymeric products is called forensic polymer engineering. The topic includes the fracture of plastic products, or any other reason why such a product fails in service, or fails to meet its specification...
- Polymer degradationPolymer degradationPolymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, colour, shape, etc.—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors such as heat, light or chemicals such as acids, alkalis and some salts...
- Factors of polymer weatheringFactors of polymer weatheringThe aging of natural and artificial polymeric materials is a natural phenomenon in metals, glass, minerals and other inorganic materials. The main environmental parameters influencing the degradation of polymeric materials is daylight combined with the effects of temperature, moisture and oxygen...

