
Phrase structure rules
Encyclopedia
Phrase-structure rules are a way to describe a given language's syntax
. They are used to break down a natural language
sentence into its constituent parts (also known as syntactic categories) namely phrasal categories and lexical categories (aka parts of speech). Phrasal categories include the noun phrase
, verb phrase
, and prepositional phrase; lexical categories include noun
, verb
, adjective
, adverb
, and many others. Phrase structure rules were commonly used in transformational grammar
(TGG), although they were not an invention of TGG; rather, early TGG's added to phrase structure rules (the most obvious example being transformations; see the page transformational grammar
for an overview of the development of TGG.) A grammar which uses phrase structure rules is called a phrase structure grammar
- except in computer science
, where it is known as just a grammar
, usually context-free
. Phrase structure grammars stand in contrast to dependency grammars
.
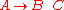 , meaning that the constituent
, meaning that the constituent
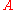 is separated into the two subconstituents
is separated into the two subconstituents 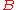 and
and  .
.
Some examples correct inter alia for natural
English language
are:
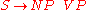
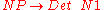
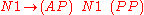
The first rule reads: An S consists of an NP followed by a VP. This means A sentence consists of a noun phrase followed by a verb phrase. The next one: A noun phrase consists of a determiner followed by a noun.
Further explanations of the constituents: S
, Det
, NP
, VP
, AP
, PP
Associated with phrase structure rules is a famous example of a grammatically correct sentence. The sentence was constructed by Noam Chomsky
as an illustration that syntactically but not semantically correct sentences are possible.
Colorless green ideas sleep furiously
can be diagrammed as a phrase tree, as below:
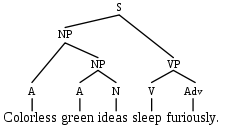 where S represents a grammatical sentence. The theory of antisymmetry
where S represents a grammatical sentence. The theory of antisymmetry
proposed in the early '90s by Richard Kayne is an attempt to derive phrase structure from a single axiom. A phrase tree can be represented by a ultrametric, see Mark D. Roberts http://arXiv.org/abs/cs.CL/9810012.
instead. Here phrase structures are not derived from rules that combine words, but from the specification or instantiation of syntactic schemata or configurations, often expressing some kind of semantic content independently of the specific words that appear in them. This approach is essentially equivalent to a system of phrase structure rules combined with a noncompositional semantic
theory, since grammatical formalisms based on rewriting rules are generally equivalent in power to those based on substitution into schemata.
So, in this type of approach, instead of being derived from the application of a number of phrase structure rules, the sentence "colorless green ideas sleep furiously" would be generated by filling the words into the slots of a schema having the following structure:
(NP(ADJ N) VP(V) AP(ADV))
And which would express the following conceptual content
X DOES Y IN THE MANNER OF Z
Though they are noncompositional, such models are monotonic. This approach is highly developed within Construction grammar
, and has had some influence in Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar
and Lexical functional grammar
.
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
. They are used to break down a natural language
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
sentence into its constituent parts (also known as syntactic categories) namely phrasal categories and lexical categories (aka parts of speech). Phrasal categories include the noun phrase
Noun phrase
In grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
, verb phrase
Verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase or VP is a syntactic unit composed of at least one verb and the dependents of that verb. One can distinguish between two types of VPs, finite VPs and non-finite VPs . While phrase structure grammars acknowledge both, dependency grammars reject the existence of a...
, and prepositional phrase; lexical categories include noun
Noun
In linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
, verb
Verb
A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
, adjective
Adjective
In grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
, adverb
Adverb
An adverb is a part of speech that modifies verbs or any part of speech other than a noun . Adverbs can modify verbs, adjectives , clauses, sentences, and other adverbs....
, and many others. Phrase structure rules were commonly used in transformational grammar
Transformational grammar
In linguistics, a transformational grammar or transformational-generative grammar is a generative grammar, especially of a natural language, that has been developed in the Chomskyan tradition of phrase structure grammars...
(TGG), although they were not an invention of TGG; rather, early TGG's added to phrase structure rules (the most obvious example being transformations; see the page transformational grammar
Transformational grammar
In linguistics, a transformational grammar or transformational-generative grammar is a generative grammar, especially of a natural language, that has been developed in the Chomskyan tradition of phrase structure grammars...
for an overview of the development of TGG.) A grammar which uses phrase structure rules is called a phrase structure grammar
Phrase structure grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammars as defined by phrase structure rules, i.e. rewrite rules of the type studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue...
- except in computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, where it is known as just a grammar
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
, usually context-free
Context-free grammar
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar is a formal grammar in which every production rule is of the formwhere V is a single nonterminal symbol, and w is a string of terminals and/or nonterminals ....
. Phrase structure grammars stand in contrast to dependency grammars
Dependency grammar
Dependency grammar is a class of modern syntactic theories that are all based on the dependency relation and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency grammars are distinct from phrase structure grammars , since they lack phrasal nodes. Structure is determined by...
.
Definition
Phrase structure rules are usually of the form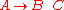 , meaning that the constituent
, meaning that the constituentConstituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that functions as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down...
 is separated into the two subconstituents
is separated into the two subconstituents  and
and  .
.Some examples correct inter alia for natural
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
English language
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
are:
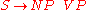
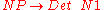
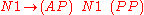
The first rule reads: An S consists of an NP followed by a VP. This means A sentence consists of a noun phrase followed by a verb phrase. The next one: A noun phrase consists of a determiner followed by a noun.
Further explanations of the constituents: S
Sentence (linguistics)
In the field of linguistics, a sentence is an expression in natural language, and often defined to indicate a grammatical unit consisting of one or more words that generally bear minimal syntactic relation to the words that precede or follow it...
, Det
Determiner phrase
In linguistics, a determiner phrase is a syntactic category, a phrase headed by a determiner. The noun phrase is strictly speaking a determiner phrase, and NP designates a constituent of the noun phrase, taken to be the complement of the determiner. This is opposed to the traditional view that...
, NP
Noun phrase
In grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
, VP
Verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase or VP is a syntactic unit composed of at least one verb and the dependents of that verb. One can distinguish between two types of VPs, finite VPs and non-finite VPs . While phrase structure grammars acknowledge both, dependency grammars reject the existence of a...
, AP
Adjectival phrase
The term adjectival phrase, adjective phrase, or sometimes phrasal adjective may refer to any one of three types of grammatical phrase....
, PP
Associated with phrase structure rules is a famous example of a grammatically correct sentence. The sentence was constructed by Noam Chomsky
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, and activist. He is an Institute Professor and Professor in the Department of Linguistics & Philosophy at MIT, where he has worked for over 50 years. Chomsky has been described as the "father of modern linguistics" and...
as an illustration that syntactically but not semantically correct sentences are possible.
Colorless green ideas sleep furiously
Colorless green ideas sleep furiously
"Colorless green ideas sleep furiously" is a sentence composed by Noam Chomsky in his 1957 Syntactic Structures as an example of a sentence that is grammatically correct but semantically nonsensical. The term was originally used in his 1955 thesis "Logical Structures of Linguistic Theory"...
can be diagrammed as a phrase tree, as below:

Antisymmetry
In linguistics, antisymmetry is a theory of syntactic linearization presented in Richard Kayne's 1994 monograph The Antisymmetry of Syntax. The crux of this theory is that hierarchical structure in natural language maps universally onto a particular surface linearization, namely...
proposed in the early '90s by Richard Kayne is an attempt to derive phrase structure from a single axiom. A phrase tree can be represented by a ultrametric, see Mark D. Roberts http://arXiv.org/abs/cs.CL/9810012.
Alternative approaches
A number of theories of grammar dispense with the notion of phrase structure rules and operate with the notion of schemaSchema (psychology)
A schema , in psychology and cognitive science, describes any of several concepts including:* An organized pattern of thought or behavior.* A structured cluster of pre-conceived ideas....
instead. Here phrase structures are not derived from rules that combine words, but from the specification or instantiation of syntactic schemata or configurations, often expressing some kind of semantic content independently of the specific words that appear in them. This approach is essentially equivalent to a system of phrase structure rules combined with a noncompositional semantic
Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning. It focuses on the relation between signifiers, such as words, phrases, signs and symbols, and what they stand for, their denotata....
theory, since grammatical formalisms based on rewriting rules are generally equivalent in power to those based on substitution into schemata.
So, in this type of approach, instead of being derived from the application of a number of phrase structure rules, the sentence "colorless green ideas sleep furiously" would be generated by filling the words into the slots of a schema having the following structure:
(NP(ADJ N) VP(V) AP(ADV))
And which would express the following conceptual content
X DOES Y IN THE MANNER OF Z
Though they are noncompositional, such models are monotonic. This approach is highly developed within Construction grammar
Construction grammar
The term construction grammar covers a family of theories, or models, of grammar that are based on the idea that the primary unit of grammar is the grammatical construction rather than the atomic syntactic unit and the rule that combines atomic units, and that the grammar of a language is made up...
, and has had some influence in Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar is a highly lexicalized, non-derivational generative grammar theory developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science and uses Ferdinand de...
and Lexical functional grammar
Lexical functional grammar
Lexical functional grammar is a grammar framework in theoretical linguistics, a variety of generative grammar. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to...
.
See also
- AntisymmetryAntisymmetryIn linguistics, antisymmetry is a theory of syntactic linearization presented in Richard Kayne's 1994 monograph The Antisymmetry of Syntax. The crux of this theory is that hierarchical structure in natural language maps universally onto a particular surface linearization, namely...
- Bare Phrase Structure
- ClauseClauseIn grammar, a clause is the smallest grammatical unit that can express a complete proposition. In some languages it may be a pair or group of words that consists of a subject and a predicate, although in other languages in certain clauses the subject may not appear explicitly as a noun phrase,...
- Context free grammar
- Extended Backus–Naur FormExtended Backus–Naur formIn computer science, Extended Backus–Naur Form is a family of metasyntax notations used for expressing context-free grammars: that is, a formal way to describe computer programming languages and other formal languages. They are extensions of the basic Backus–Naur Form metasyntax notation.The...
, the direct equivalent in formal language theory - ID/LP grammarID/LP grammarAn ID/LP grammar is a formal grammar that distinguishes immediate dominance constraints from linear precedence constraints. Whereas traditional phrase structure rules incorporate dominance and precedence into a single rule, ID/LP maintains separate rule sets which need not be processed...
- Natural language understandingNatural language understandingNatural language understanding is a subtopic of natural language processing in artificial intelligence that deals with machine reading comprehension....
- PhrasePhraseIn everyday speech, a phrase may refer to any group of words. In linguistics, a phrase is a group of words which form a constituent and so function as a single unit in the syntax of a sentence. A phrase is lower on the grammatical hierarchy than a clause....
- Phrase structure grammarPhrase structure grammarThe term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammars as defined by phrase structure rules, i.e. rewrite rules of the type studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue...
- Sentence (linguistics)Sentence (linguistics)In the field of linguistics, a sentence is an expression in natural language, and often defined to indicate a grammatical unit consisting of one or more words that generally bear minimal syntactic relation to the words that precede or follow it...

