
Polynomial (hyperelastic model)
Encyclopedia
The polynomial hyperelastic material
model is a phenomenological model of rubber elasticity
. In this model, the strain energy density function
is of the form of a polynomial in the two invariants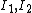 of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor.
of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor.
The strain energy density function for the polynomial model is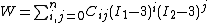
where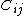 are material constants and
are material constants and 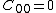 .
.
For compressible materials, a dependence of volume is added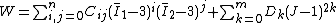
where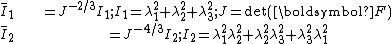
In the limit where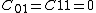 , the polynomial model reduces to the Neo-Hookean solid
, the polynomial model reduces to the Neo-Hookean solid
model. For a compressible Mooney-Rivlin material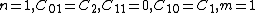 and we have
and we have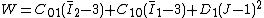
Hyperelastic material
A hyperelastic or Green elastic material is a type of constitutive model for ideally elastic material for which the stress-strain relationship derives from a strain energy density function. The hyperelastic material is a special case of a Cauchy elastic material.For many materials, linear elastic...
model is a phenomenological model of rubber elasticity
Rubber Elasticity
Rubber elasticity, a well-known example of hyperelasticity, describes the mechanical behavior of many polymers, especially those with crosslinking. Invoking the theory of rubber elasticity, one considers a polymer chain in a crosslinked network as an entropic spring. When the chain is stretched,...
. In this model, the strain energy density function
Strain energy density function
A strain energy density function or stored energy density function is a scalar valued function that relates the strain energy density of a material to the deformation gradient....
is of the form of a polynomial in the two invariants
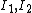 of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor.
of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor.The strain energy density function for the polynomial model is
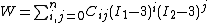
where
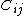 are material constants and
are material constants and 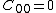 .
.For compressible materials, a dependence of volume is added
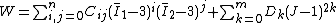
where
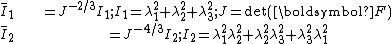
In the limit where
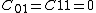 , the polynomial model reduces to the Neo-Hookean solid
, the polynomial model reduces to the Neo-Hookean solidNeo-Hookean solid
A Neo-Hookean solid is a hyperelastic material model, similar to Hooke's law, that can be used for predicting the nonlinear stress-strain behavior of materials undergoing large deformations. The model was proposed by Ronald Rivlin in 1948. In contrast to linear elastic materials, a the...
model. For a compressible Mooney-Rivlin material
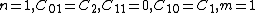 and we have
and we have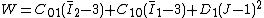
See also
- Hyperelastic materialHyperelastic materialA hyperelastic or Green elastic material is a type of constitutive model for ideally elastic material for which the stress-strain relationship derives from a strain energy density function. The hyperelastic material is a special case of a Cauchy elastic material.For many materials, linear elastic...
- Strain energy density functionStrain energy density functionA strain energy density function or stored energy density function is a scalar valued function that relates the strain energy density of a material to the deformation gradient....
- Mooney-Rivlin solid
- Finite strain theory
- Stress measuresStress measuresThe most commonly used measure of stress is the Cauchy stress. However, several other measures of stress can be defined. Some such stress measures that are widely used in continuum mechanics, particularly in the computational context, are:...

