
Quaternary compound
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
, a quaternary compound is a cation consisting of a central positively charged nitrogen group
atom with four substituents, especially organic
(alkyl and aryl
) groups, discounting hydrogen
atoms.
The best known quaternary compounds are quaternary ammonium cation
s, having a nitrogen
atom at the centre. For example, in the following reaction, the nitrogen
atom is said to be quaternized as it has gone from 3 to 4 substituents:
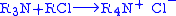
Other examples include substituted phosphonium salt
s (R4P
+), substituted arsonium salts (R4As
+) like arsenobetaine
, as well as some arsenic
containing superconductors. Substituted stibonium (R4Sb
+) and bismuthonium salts (R4Bi
+) have also been described.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a quaternary compound is a cation consisting of a central positively charged nitrogen group
Nitrogen group
The nitrogen group is a periodic table group consisting of nitrogen , phosphorus , arsenic , antimony , bismuth and ununpentium ....
atom with four substituents, especially organic
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
(alkyl and aryl
Aryl
In the context of organic molecules, aryl refers to any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, be it phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, indolyl, etc....
) groups, discounting hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms.
The best known quaternary compounds are quaternary ammonium cation
Quaternary ammonium cation
Quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure NR4+, R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged,...
s, having a nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom at the centre. For example, in the following reaction, the nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom is said to be quaternized as it has gone from 3 to 4 substituents:
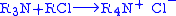
Other examples include substituted phosphonium salt
Phosphonium salt
A phosphonium salt is a salt containing the phosphonium ion such as phosphonium iodide . More commonly, phosphonium refers to a quaternary organic derivative such as tetraphenylphosphonium chloride, 4P+ Cl- and tetramethylphosphonium iodide, [P4]+I−.Alkyltriphenylphosphonium salts are widely...
s (R4P
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
+), substituted arsonium salts (R4As
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid...
+) like arsenobetaine
Arsenobetaine
Arsenobetaine is an organoarsenic compound that is the main source of arsenic found in fish. It is the arsenic analog of trimethylglycine, commonly known as betaine...
, as well as some arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid...
containing superconductors. Substituted stibonium (R4Sb
Antimony
Antimony is a toxic chemical element with the symbol Sb and an atomic number of 51. A lustrous grey metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite...
+) and bismuthonium salts (R4Bi
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead...
+) have also been described.

