Phosphonium salt
Encyclopedia
A phosphonium salt is a salt containing the phosphonium
(PH4+) ion such as phosphonium iodide (PH4+I−). More commonly, phosphonium refers to a quaternary
organic derivative such as tetraphenylphosphonium chloride
, (C6H5)4P+ Cl- and tetramethylphosphonium iodide,[ P(CH3)4] +I−.
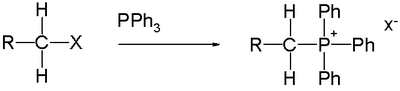
Alkyltriphenylphosphonium salts are widely used for the preparation of Wittig reagents for the Wittig reaction
. Such salts are readily made by the reaction of triphenylphosphine
with an alkyl halide:
The reaction works well if the alkyl group is methyl or an unhindered primary alkyl group (as shown), but it is usually poor with secondary alkyl halides. Tertiary alkyl groups cannot form the ylide. The phosphonium salt is a stable compound which can often be purified by recrystallisation
from ethanol
.
To form the Wittig reagent (ylide
), the phosphonium salt is suspended in a solvent such as diethyl ether
or THF
and a strong base such as phenyllithium
or n-butyllithium
is added.
One study demonstrates the use of benzyl alcohol
s as starting material for the synthesis of phosphonium acetates provided that the arene carries activating group
s:
The phosphonium acetate
group does not have an impact on the subsequent Wittig reaction.
s (R3P) react with halogen
s (X2) to phosphonium halides of the type R3PX2. The compound Ph3PBr2 (high melting solid) formed by reaction of triphenylphosphine
and bromine
is called bromotriphenylphosphonium bromide or dibromotriphenylphosphorane (now defined as a phosphorane
) or simply triphenylphosphine dibromide. The dibromide and dichloride are commercially available as halogenation
reagents for instance in halogenation of alcohol
s and phenol
s .
The compound triphenylphosphine dichloride
, Ph3PCl2, is reported as being an ionic compound
(PPh3Cl)+Cl− in polar solutions and a molecular species with trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry in apolar solution and in the solid state.
Phosphonium
The phosphonium cation describes positively charged polyatomic cations with the chemical formula . Salts of the parent PH4+ are rarely encountered, but this ion is an intermediate in the preparation of the industrially useful tetrakisphosphonium chloride:Organic phosphonium salts are common...
(PH4+) ion such as phosphonium iodide (PH4+I−). More commonly, phosphonium refers to a quaternary
Quaternary compound
In chemistry, a quaternary compound is a cation consisting of a central positively charged nitrogen group atom with four substituents, especially organic groups, discounting hydrogen atoms....
organic derivative such as tetraphenylphosphonium chloride
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula 4PCl, abbreviated Ph4PCl or PPh4Cl. Tetraphenylphosphonium and especially tetraphenylarsonium salts were formerly of interest in gravimetric analysis of perchlorate and related oxyanions. This colourless salt is used to...
, (C6H5)4P+ Cl- and tetramethylphosphonium iodide,
Alkyltriphenylphosphonium salts are widely used for the preparation of Wittig reagents for the Wittig reaction
Wittig reaction
The Wittig reaction is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide....
. Such salts are readily made by the reaction of triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
with an alkyl halide:
- Note that Ph stands for phenyl and X is a halideHalideA halide is a binary compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, or astatide compound. Many salts are halides...
The reaction works well if the alkyl group is methyl or an unhindered primary alkyl group (as shown), but it is usually poor with secondary alkyl halides. Tertiary alkyl groups cannot form the ylide. The phosphonium salt is a stable compound which can often be purified by recrystallisation
Recrystallization (chemistry)
-Chemistry:In chemistry, recrystallization is a procedure for purifying compounds. The most typical situation is that a desired "compound A" is contaminated by a small amount of "impurity B". There are various methods of purification that may be attempted , which includes recrystallization...
from ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
.
To form the Wittig reagent (ylide
Ylide
An ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom directly attached to a hetero atom with a formal positive charge , and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds...
), the phosphonium salt is suspended in a solvent such as diethyl ether
Diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, also known as ethyl ether, simply ether, or ethoxyethane, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula . It is a colorless, highly volatile flammable liquid with a characteristic odor...
or THF
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
and a strong base such as phenyllithium
Phenyllithium
Phenyllithium is an organometallic agent with the empirical formula C6H5Li. It is most commonly used as a metalating agent in organic syntheses and a substitute for Grignard reagents for introducing phenyl groups in organic syntheses...
or n-butyllithium
N-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene...
is added.
One study demonstrates the use of benzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2OH. The benzyl group is often abbreviated "Bn", thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odor. It is a useful solvent due to its polarity, low toxicity, and low vapor...
s as starting material for the synthesis of phosphonium acetates provided that the arene carries activating group
Activating group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is called an activating group if a benzene molecule to which it is attached more readily participates in electrophilic substitution reactions...
s:
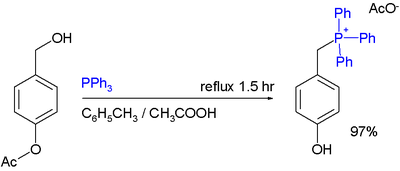
- Note that Ac stands for acetylAcetylIn organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group, the acyl with chemical formula COCH3. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac . The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl...
, the esterEsterEsters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
group is hydrolyzedHydrolysisHydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
to a phenolPhenolPhenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
The phosphonium acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
group does not have an impact on the subsequent Wittig reaction.
Phosphonium halides
PhosphinePhosphine
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine...
s (R3P) react with halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
s (X2) to phosphonium halides of the type R3PX2. The compound Ph3PBr2 (high melting solid) formed by reaction of triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
and bromine
Bromine
Bromine ") is a chemical element with the symbol Br, an atomic number of 35, and an atomic mass of 79.904. It is in the halogen element group. The element was isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jerome Balard, in 1825–1826...
is called bromotriphenylphosphonium bromide or dibromotriphenylphosphorane (now defined as a phosphorane
Phosphorane
A phosphorane is a functional group in organophosphorus chemistry with pentavalent phosphorus. It has the general formula PR5. The parent hydride compound is the unstable molecule PH5...
) or simply triphenylphosphine dibromide. The dibromide and dichloride are commercially available as halogenation
Halogenation
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that incorporates a halogen atom into a molecule in substitution of hydrogen atom. Halogenation takes place in the gas phase. There are four types of halogenation: fluorination, chlorination, bromination, and iodination...
reagents for instance in halogenation of alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s and phenol
Phenol
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
s .
The compound triphenylphosphine dichloride
Triphenylphosphine dichloride
Triphenylphosphine dichloride, Ph3PCl2, is a chlorinating agent widely used in organic chemistry. Applications include the conversion of alcohols and ethers to alkyl chlorides, the cleavage of epoxides to vicinal dichlorides and the chlorination of carboxylic acids to acyl chlorides.- Structure :In...
, Ph3PCl2, is reported as being an ionic compound
Ionic compound
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a lattice structure by ionic bonds. Usually, the positively charged portion consists of metal cations and the negatively charged portion is an anion or polyatomic ion. Ions in ionic compounds are held together...
(PPh3Cl)+Cl− in polar solutions and a molecular species with trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry in apolar solution and in the solid state.