Radiographic equipment
Encyclopedia
This is a page devoted to the basic equipment used for radiographic work, both medical and industrial.
power supply that is applied on a usually sealed X-ray tube. This produces the emission of electrons from the cathode of the tube and the emission of X-rays when these hit a target located at the anode side.
In industrial radiography
, energy goes from 20 to several hundreds of kV according to the application. In medical radiography
voltage from 20 kV in mammography up to 150 kV for chest radiography are used for diagnostic. Energy can go up to 250 kV for radiotherapy applications.
. One of the leading makers of radiographic equipment is the Source Production & Equipment Co., Inc. http://www.spec150.com
It might be possible to use Cs-137 as a photon source for radiography but this isotope has the disadvantage that it is always diluted with inactive caesium isotopes. This means that it is difficult to get a physically small source, a large radioactive volume of the source will make it impossible to get the finest detail from a radiographic examination.
Both cobalt-60 and caesium-137 have only a few gamma energies, which makes them close to monochromatic. The photon energy of cobalt-60 is higher than that if caesium-137, which allows cobalt sources to be used to examine thicker sections of metals than those that could be examined with Cs-137. Iridium-192 has a lower photon energy than cobalt-60 and its gamma spectrum is complex (many lines of very different energies), but this can be an advantage as this can give better contrast for the final photographs.
It has been known for many years that an inactive iridium
or cobalt
metal object can be machined to size. In the case of cobalt it is common to alloy
it with nickel to improve the mechanical properties. In the case of iridium a thin wire or rod could be used. These precursor materials can then be placed within stainless steel
containers, which are leak tested before being converted into radioactive sources. These objects can be processed by neutron activation
to form gamma emitting radioisotopes. The stainless steel has only a small ability to be activated and the small activity due to 55Fe and 63Ni are unlikely to pose a problem in the final application because these isotopes are beta
emitters, which have very weak gamma emission. The 59Fe that might form has a short
half-life, so by allowing a cobalt source to stand for a year much of this isotope decays away.
The source is often a small object that must be transported to the work site in a shielded container. It is normal to position the film, clear the area where the work is to be done, and add shielding (collimators) to reduce the size of the controlled area
before exposing the radioactive source. A series of different designs have been developed for radiographic "cameras". Rather than the "camera" being a device that accepts photons to record a picture, the "camera" in industrial radiography is the radioactive photon source.
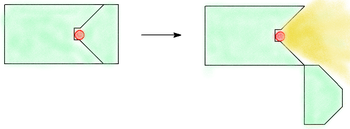 Another design for a torch is one where the source is placed in a metal wheel, this can turn inside the camera to move between the exposed and storage sites.
Another design for a torch is one where the source is placed in a metal wheel, this can turn inside the camera to move between the exposed and storage sites.
 .
.
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1199_web.pdf. This method is similar to brachytherapy
when performed with the remote afterloading method. An example of a cable-based design would have the source stored in a block of lead
or depleted uranium
with an S-shaped passage through the block. In its safe position the source is held in the centre of the block by a metal wire extending in both directions. To use the source, a drive cable is attached to one end of the wire, and a guide tube is attached to the opposite side of the block. A hand-operated winch pushes the source out of the shield and along the guide tube to where it is needed.
detector, which is an array of silicon
diode
s. Such equipment has been used for the X-ray version of high speed flash photography. For example diesel fuel that has been doped with cerium
has been used to investigate the operation of fuel injectors in a diesel engine
.http://www.chess.cornell.edu/Test/pubs/2002/research/microsecond.pdfhttp://www.dxcicdd.com/05/PDF/Jin_Wang_1.pdf.
Some examples of radiography using a 5 MeV electron LINAC driving a bremsstrahlung
source (1 mm Tungsten
on a 9 mm copper
sheet) can be seen here.http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/p05/PAPERS/RPAP036.PDF
As an alternative high energy pulsed proton
beams can be used for the high speed examination of objects.http://www.lanl.gov/quarterly/q_w03/pro_rad.shtml
s. This type of radiography is called Neutron Radiography (NR, Nray, N-Ray) or Neutron Imaging. Neutron Radiography can see very different things than X-rays, because neutrons can pass with ease through lead and steel but are stopped by plastics, water and oils. Neutron sources include radioactive (241Am/Be and Cf) sources, electrically driven D-T reactions in vacuum tubes and conventional critical nuclear reactors. It might be possible to use a neutron
amplifier to increase the neutron flux.http://www.tfd.chalmers.se/~valeri/Mars/Mo-o-f10.pdf
Photon sources
There are many types of sources for high energy X-ray and gamma photons.http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/P066_scr.pdfX-ray sources
X-ray generators are made of a high voltageHigh voltage
The term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
power supply that is applied on a usually sealed X-ray tube. This produces the emission of electrons from the cathode of the tube and the emission of X-rays when these hit a target located at the anode side.
In industrial radiography
Industrial radiography
Industrial Radiography is the use of ionizing radiation to view objects in a way that cannot be seen otherwise. It is not to be confused with the use of ionizing radiation to change or modify objects; radiography's purpose is strictly viewing. Industrial radiography has grown out of engineering,...
, energy goes from 20 to several hundreds of kV according to the application. In medical radiography
Medical radiography
Radiography is the use of ionizing electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays to view objects. Although not technically radiographic techniques, imaging modalities such as PET and MRI are sometimes grouped in radiography because the radiology department of hospitals handle all forms of imaging...
voltage from 20 kV in mammography up to 150 kV for chest radiography are used for diagnostic. Energy can go up to 250 kV for radiotherapy applications.
Radioisotope sources
These have the advantage that they do not need a supply of electrical power to function, but they have the disadvantage that they can not be turned off. Also it is difficult, using radioactivity, to create a small and compact source that offers the photon flux possible with a normal sealed X-ray tubeX-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that produces X-rays. They are used in X-ray machines. X-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, an ionizing radiation with wavelengths shorter than ultraviolet light...
. One of the leading makers of radiographic equipment is the Source Production & Equipment Co., Inc. http://www.spec150.com
It might be possible to use Cs-137 as a photon source for radiography but this isotope has the disadvantage that it is always diluted with inactive caesium isotopes. This means that it is difficult to get a physically small source, a large radioactive volume of the source will make it impossible to get the finest detail from a radiographic examination.
Both cobalt-60 and caesium-137 have only a few gamma energies, which makes them close to monochromatic. The photon energy of cobalt-60 is higher than that if caesium-137, which allows cobalt sources to be used to examine thicker sections of metals than those that could be examined with Cs-137. Iridium-192 has a lower photon energy than cobalt-60 and its gamma spectrum is complex (many lines of very different energies), but this can be an advantage as this can give better contrast for the final photographs.
It has been known for many years that an inactive iridium
Iridium
Iridium is the chemical element with atomic number 77, and is represented by the symbol Ir. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum family, iridium is the second-densest element and is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C...
or cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
metal object can be machined to size. In the case of cobalt it is common to alloy
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
it with nickel to improve the mechanical properties. In the case of iridium a thin wire or rod could be used. These precursor materials can then be placed within stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
containers, which are leak tested before being converted into radioactive sources. These objects can be processed by neutron activation
Neutron activation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus often decays immediately by emitting particles such as neutrons, protons, or alpha...
to form gamma emitting radioisotopes. The stainless steel has only a small ability to be activated and the small activity due to 55Fe and 63Ni are unlikely to pose a problem in the final application because these isotopes are beta
Beta particle
Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain types of radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles emitted are a form of ionizing radiation also known as beta rays. The production of beta particles is termed beta decay...
emitters, which have very weak gamma emission. The 59Fe that might form has a short
half-life, so by allowing a cobalt source to stand for a year much of this isotope decays away.
The source is often a small object that must be transported to the work site in a shielded container. It is normal to position the film, clear the area where the work is to be done, and add shielding (collimators) to reduce the size of the controlled area
Controlled area
In telecommunication, the term controlled area is an area in which uncontrolled movement will not result in compromise of classified information, that is designed to provide administrative control and safety, or that serves as a buffer for controlling access to limited-access areas...
before exposing the radioactive source. A series of different designs have been developed for radiographic "cameras". Rather than the "camera" being a device that accepts photons to record a picture, the "camera" in industrial radiography is the radioactive photon source.
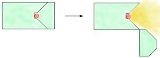
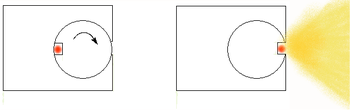
Torch design of radiographic cameras
One design is best thought of as being like a torch. The radioactive source is placed inside a shielded box, a hinge allowed part of the shielding to be peeled back exposing the source so allowing the photons to leave the radiography camera.

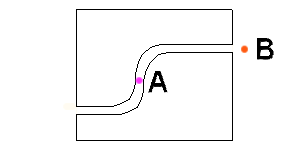
Cable-based design of radiographic cameras
One group of designs uses a radioactive source that comes out on a cable from a shielded container http://ean.cepn.asso.fr/pdf/program5/session%202/3_giese.PDF. One such unit was involved in an accident in BoliviaBolivia
Bolivia officially known as Plurinational State of Bolivia , is a landlocked country in central South America. It is the poorest country in South America...
http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1199_web.pdf. This method is similar to brachytherapy
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy , also known as internal radiotherapy, sealed source radiotherapy, curietherapy or endocurietherapy, is a form of radiotherapy where a radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment...
when performed with the remote afterloading method. An example of a cable-based design would have the source stored in a block of lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
or depleted uranium
Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope U-235 than natural uranium . Uses of DU take advantage of its very high density of 19.1 g/cm3...
with an S-shaped passage through the block. In its safe position the source is held in the centre of the block by a metal wire extending in both directions. To use the source, a drive cable is attached to one end of the wire, and a guide tube is attached to the opposite side of the block. A hand-operated winch pushes the source out of the shield and along the guide tube to where it is needed.

Microsecond X-ray pulses
It is possible using a particle accelerator to generate a short pulse of high energy electrons, these electrons are used to create X-rays by braking radiation.http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/p01/PAPERS/WOAA008.PDF. The X-rays are detected using a semiconductorSemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
detector, which is an array of silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s. Such equipment has been used for the X-ray version of high speed flash photography. For example diesel fuel that has been doped with cerium
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight...
has been used to investigate the operation of fuel injectors in a diesel engine
Diesel engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber...
.http://www.chess.cornell.edu/Test/pubs/2002/research/microsecond.pdfhttp://www.dxcicdd.com/05/PDF/Jin_Wang_1.pdf.
Some examples of radiography using a 5 MeV electron LINAC driving a bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon because energy is conserved. The term is...
source (1 mm Tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
on a 9 mm copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
sheet) can be seen here.http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/p05/PAPERS/RPAP036.PDF
As an alternative high energy pulsed proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
beams can be used for the high speed examination of objects.http://www.lanl.gov/quarterly/q_w03/pro_rad.shtml
Neutron sources
In some cases, industrial radiography is done with neutronNeutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s. This type of radiography is called Neutron Radiography (NR, Nray, N-Ray) or Neutron Imaging. Neutron Radiography can see very different things than X-rays, because neutrons can pass with ease through lead and steel but are stopped by plastics, water and oils. Neutron sources include radioactive (241Am/Be and Cf) sources, electrically driven D-T reactions in vacuum tubes and conventional critical nuclear reactors. It might be possible to use a neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
amplifier to increase the neutron flux.http://www.tfd.chalmers.se/~valeri/Mars/Mo-o-f10.pdf

