
Rational quadratic covariance function
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the rational quadratic covariance function
is used in spatial statistics, geostatistics
, machine learning
, image analysis, and other fields where multivariate statistical analysis is conducted on metric space
s. It is commonly used to define the statistical covariance
between measurements made at two points that are d units distant from each other. Since the covariance only depends on distances between points, it is stationary
. If the distance is Euclidean distance
, the rational quadratic covariance function is also isotropic.
The rational quadratic covariance between two points separated by d distance units is given by
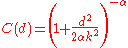
where α and k are non-negative parameter
s of the covariance.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the rational quadratic covariance function
Covariance function
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together and the covariance function describes the variance of a random variable process or field...
is used in spatial statistics, geostatistics
Geostatistics
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including petroleum geology, hydrogeology, hydrology, meteorology,...
, machine learning
Machine learning
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, is a scientific discipline concerned with the design and development of algorithms that allow computers to evolve behaviors based on empirical data, such as from sensor data or databases...
, image analysis, and other fields where multivariate statistical analysis is conducted on metric space
Metric space
In mathematics, a metric space is a set where a notion of distance between elements of the set is defined.The metric space which most closely corresponds to our intuitive understanding of space is the 3-dimensional Euclidean space...
s. It is commonly used to define the statistical covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between measurements made at two points that are d units distant from each other. Since the covariance only depends on distances between points, it is stationary
Stationary process
In the mathematical sciences, a stationary process is a stochastic process whose joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time or space...
. If the distance is Euclidean distance
Euclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space...
, the rational quadratic covariance function is also isotropic.
The rational quadratic covariance between two points separated by d distance units is given by
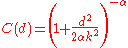
where α and k are non-negative parameter
Parameter
Parameter from Ancient Greek παρά also “para” meaning “beside, subsidiary” and μέτρον also “metron” meaning “measure”, can be interpreted in mathematics, logic, linguistics, environmental science and other disciplines....
s of the covariance.

