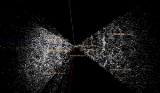
Redshift quantization
Encyclopedia
Redshift quantization is the hypothesis
that the redshift
s of cosmologically distant objects (in particular galaxies
) tend to cluster around multiples of some particular value. Since there is a correlation of distance
and redshift as expressed in Hubble's Law
, redshift quantization would either indicate a quantization of the distances of galaxies from the Earth or a problem with the redshift-distance correlation, either of which would have serious implications for cosmology
. Many scientists who oppose the Big Bang
theory, including Halton Arp
, have referred to observations claimed to be in favor of redshift quantization as reason to reject the standard account of the origin and evolution of the universe
(they do not, of course, reject evolution itself).
In 1973, astronomer William G. Tifft
was the first to report evidence of such clustering (before that see György Paál
). Recent redshift survey
s of quasars (QSOs) have produced no evidence of quantization in excess of what is expected due to galaxy cluster
ing,
and consequently most cosmologists dispute the existence of redshift quantization beyond a minimal trace due to the distribution of galaxies across voids and filaments.
"Redshift quantization" has also been called redshift periodicity, redshift discretization, preferred redshifts, and redshift-magnitude bands.
was the first to investigate possible redshift quantization, or "redshift-magnitude banding correlation", as he first called it. In 1973, he wrote:
Tifft, now Professor Emeritus at the University of Arizona
, suggested that this observation conflicted with standard cosmological scenarios. He states in summary:
All of these studies were performed before the tremendous advances in redshift cataloging that would be made at the end of the 1990s. Since that time, the number of galaxies for which astronomers have measured redshifts has increased by several orders of magnitude.
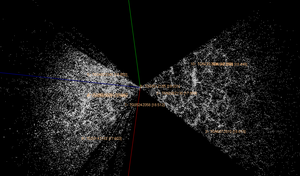 After Tifft made his proposal, discussion of it was generally confined to detractors of standard cosmology. Nevertheless, it was nearly 20 years before other researchers tried to corroborate his findings. After a brief flurry of interest, the consensus in the astronomical community became that any quantization was either coincidental or due to so-called geometrical effects. Current observations and models of large-scale structure models trace filamentary
After Tifft made his proposal, discussion of it was generally confined to detractors of standard cosmology. Nevertheless, it was nearly 20 years before other researchers tried to corroborate his findings. After a brief flurry of interest, the consensus in the astronomical community became that any quantization was either coincidental or due to so-called geometrical effects. Current observations and models of large-scale structure models trace filamentary
superclusters and voids
that cause most galaxies in a rough statistical sense to have correlated positions, but such groupings would not allow for a strength of periodicity required if it were a hallmark characteristic of the redshifts of galaxies. As such with exceedingly few exceptions, modern cosmology researchers have suggested that redshift quantizations are manifestations of well-understood phenomena, or not present at all.
In 1987, E. Sepulveda suggested that a geometric paradigm based on the polytrope theory could account for all redshift periodicities, and that:
In 2002, Hawkins et al. found no evidence for a redshift quantization in the 2dF survey and found using Napier's own guidelines for testing redshift periodicity that none, in fact, could be detected in the sample:
In 2005, Tang and Zhang:
A 2006 historical review of study of the redshift periodicity of galaxies by Bajan, et al., concludes that "in our opinion the existence of redshift periodicity among galaxies is not well established."
In 2006, Martin Bell and D. McDiarmid, reported: "Six Peaks Visible in the Redshift Distribution of 46,400 SDSS
Quasars Agree with the Preferred Redshifts Predicted by the Decreasing Intrinsic Redshift Model". The pair acknowledged that selection effects were already reported to cause the most prominent of the peaks. Nevertheless, these peaks were included in their analysis anyway with Bell and McDiarmid questioning whether selection effects could account for the periodicity, but not including any analysis of this beyond cursory cross-survey comparisons in the discussion section of their paper. There is a brief response to this paper in a comment in section 5 of Schneider et al. (2007) where they note that all "periodic" structure disappears after the previously known selection effects are accounted for.
, and even geocentrists
have referred to observations claimed to be in favor of redshift quantization as reason to reject the standard account of the origin and evolution of the universe
.
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
that the redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
s of cosmologically distant objects (in particular galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
) tend to cluster around multiples of some particular value. Since there is a correlation of distance
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" to Earth...
and redshift as expressed in Hubble's Law
Hubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
, redshift quantization would either indicate a quantization of the distances of galaxies from the Earth or a problem with the redshift-distance correlation, either of which would have serious implications for cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
. Many scientists who oppose the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
theory, including Halton Arp
Halton Arp
Halton Christian Arp is an American astronomer. He is known for his 1966 Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, which catalogues many examples of interacting and merging galaxies...
, have referred to observations claimed to be in favor of redshift quantization as reason to reject the standard account of the origin and evolution of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
(they do not, of course, reject evolution itself).
In 1973, astronomer William G. Tifft
William G. Tifft
William G. Tifft is Emeritus Professor/Astronomer at the University of Arizona. His main interests are in galaxies, superclusters and what Tifft calls redshift problems . He was influential in the development of the first redshift surveys and was an early proponent of manned space astronomy,...
was the first to report evidence of such clustering (before that see György Paál
György Paál
Paál György was a Hungarian astronomer and cosmologist.- Work :In the late 50-s Paál studied the quasar and galaxy cluster distributions. In 1970 from redshift quantization he came up with the idea that the Universe might has nontrivial topological structure.In 1992, G. Paal, et al. and A...
). Recent redshift survey
Redshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
s of quasars (QSOs) have produced no evidence of quantization in excess of what is expected due to galaxy cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
ing,
and consequently most cosmologists dispute the existence of redshift quantization beyond a minimal trace due to the distribution of galaxies across voids and filaments.
"Redshift quantization" has also been called redshift periodicity, redshift discretization, preferred redshifts, and redshift-magnitude bands.
Original investigation by William G. Tifft
William G. TifftWilliam G. Tifft
William G. Tifft is Emeritus Professor/Astronomer at the University of Arizona. His main interests are in galaxies, superclusters and what Tifft calls redshift problems . He was influential in the development of the first redshift surveys and was an early proponent of manned space astronomy,...
was the first to investigate possible redshift quantization, or "redshift-magnitude banding correlation", as he first called it. In 1973, he wrote:
- "Using more than 200 redshifts in Coma, Perseus, and A2199, the presence of a distinct band-related periodicity in redshifts is indicated. Finally, a new sample of accurate redshifts of bright Coma galaxiesComa cluster of galaxiesThe Coma Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies. Along with the Leo Cluster , it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster. It is located in and takes its name from the constellation Coma Berenices.The cluster's mean distance...
on a single band is presented, which shows a strong redshift periodicity of 220 km s−1. An upper limit of 20 km s−1 is placed on the internal Doppler redshift component of motion in the Coma cluster".
Tifft, now Professor Emeritus at the University of Arizona
University of Arizona
The University of Arizona is a land-grant and space-grant public institution of higher education and research located in Tucson, Arizona, United States. The University of Arizona was the first university in the state of Arizona, founded in 1885...
, suggested that this observation conflicted with standard cosmological scenarios. He states in summary:
- "Throughout the development of the program it has seemed increasingly clear that the redshift has properties inconsistent with a simple velocity and/or cosmic scale change interpretation. Various implications have been pointed out from time to time, but basically the work is observationally driven."
Subsequent work by other researchers
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, four studies on redshift quantization were performed:- In 1989, Martin R. Croasdale reported finding a quantization of redshifts using a different sample of galaxies in increments of 72 km/s (Δz = ).
- In 1990, Bruce Guthrie and William Napier reported finding a "possible periodicity" of the same magnitude for a slightly larger data set limited to bright spiral galaxiesSpiral galaxyA spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as...
and excluding other types - In 1992, Guthrie and Napier proposed the observation of a different periodicity in increments of Δz = in a sample of 89 galaxies
- In 1992, G. Paal, et al. and A. Holba, et al. reanalyzed the redshift data from a fairly large sample of galaxies and concluded that there was an unexplained periodicity of redshifts.
- In 1994, A. Holba, et al. also reanalyzed the redshift data of quasars and concluded that there was unexplained periodicity of redshifts in this sample, too.
All of these studies were performed before the tremendous advances in redshift cataloging that would be made at the end of the 1990s. Since that time, the number of galaxies for which astronomers have measured redshifts has increased by several orders of magnitude.
Evaluation and criticism

Galaxy filament
In physical cosmology, galaxy filaments, also called supercluster complexes or great walls, are, so far, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe. They are massive, thread-like structures with a typical length of 50 to 80 megaparsecs h-1 that form the boundaries between large voids in...
superclusters and voids
Void (astronomy)
In astronomy, voids are the empty spaces between filaments, the largest-scale structures in the Universe, that contain very few, or no, galaxies. They were first discovered in 1978 during a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson at the Kitt Peak National Observatory...
that cause most galaxies in a rough statistical sense to have correlated positions, but such groupings would not allow for a strength of periodicity required if it were a hallmark characteristic of the redshifts of galaxies. As such with exceedingly few exceptions, modern cosmology researchers have suggested that redshift quantizations are manifestations of well-understood phenomena, or not present at all.
In 1987, E. Sepulveda suggested that a geometric paradigm based on the polytrope theory could account for all redshift periodicities, and that:
- "The smallest periodicities (Δz = 72, 144 km/s) are due to parallel line segments of galactic clustering. The largest (Δz = 0.15) are due to circumferential circuits around the universe. Intermediate periodicities are due to other geometric irregularities. These periodicities or apparent quantizations are relics or faithful fossils of a real quantization that occurred in the primordial atom."
In 2002, Hawkins et al. found no evidence for a redshift quantization in the 2dF survey and found using Napier's own guidelines for testing redshift periodicity that none, in fact, could be detected in the sample:
- Given that there are almost eight times as many data points in this sample as in the previous analysis by Burbidge & Napier (2001), we must conclude that the previous detection of a periodic signal arose from the combination of noise and the effects of the window function.
In 2005, Tang and Zhang:
- ".. used the publicly available data from the Sloan Digital Sky SurveySloan Digital Sky SurveyThe Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project was named after the Alfred P...
and 2dF QSO redshift survey to test the hypothesis that QSOs are ejected from active galaxies with periodic noncosmological redshifts. For two different intrinsic redshift models, [..] and find there is no evidence for a periodicity at the predicted frequency in log(1+z), or at any other frequency. "
A 2006 historical review of study of the redshift periodicity of galaxies by Bajan, et al., concludes that "in our opinion the existence of redshift periodicity among galaxies is not well established."
In 2006, Martin Bell and D. McDiarmid, reported: "Six Peaks Visible in the Redshift Distribution of 46,400 SDSS
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project was named after the Alfred P...
Quasars Agree with the Preferred Redshifts Predicted by the Decreasing Intrinsic Redshift Model". The pair acknowledged that selection effects were already reported to cause the most prominent of the peaks. Nevertheless, these peaks were included in their analysis anyway with Bell and McDiarmid questioning whether selection effects could account for the periodicity, but not including any analysis of this beyond cursory cross-survey comparisons in the discussion section of their paper. There is a brief response to this paper in a comment in section 5 of Schneider et al. (2007) where they note that all "periodic" structure disappears after the previously known selection effects are accounted for.
Redshift quantization and creationist cosmology
A number of creationistsCreationist cosmologies
Creationist cosmologies encompass a variety of theories of Young Earth creationists that are designed to support the religious belief that the universe is only a few thousand years old, in line with a literal reading of Genesis...
, and even geocentrists
Modern geocentrism
Modern geocentrism is the belief held by some extant groups that Earth is the center of the universe as described by classical geocentric models. This belief is often based on Biblical verses...
have referred to observations claimed to be in favor of redshift quantization as reason to reject the standard account of the origin and evolution of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
.

