
Rep-tile
Encyclopedia
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
of tessellation
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
s, a shape that can be dissected
Dissection (geometry)
In geometry, a dissection problem is the problem of partitioning a geometric figure into smaller pieces that may be rearranged into a new figure of equal content. In this context, the partitioning is called simply a dissection...
into smaller copies of the same shape is called a reptile or rep-tile. The shape is labelled as rep-n if the dissection uses n copies. Such a shape necessarily forms the prototile
Prototile
In the mathematical theory of tessellations, a prototile is one of the shapes of a tile in a tessellation.A tessellation of the plane or of any other space is a cover of the space by closed shapes, called tiles, that have disjoint interiors. Some of the tiles may be congruent to one or more others...
for a tiling of the plane, in many cases an aperiodic tiling
Aperiodic tiling
An aperiodic tiling is a tiling obtained from an aperiodic set of tiles. Properly speaking, aperiodicity is a property of particular sets of tiles; any given finite tiling is either periodic or non-periodic...
.
A shape that tiles itself using different sizes is called an irregular rep-tile or irreptile. If the tiling uses n copies, the shape is said to be irrep-n.
If all these sub-tiles are of different sizes then the tiling is additionally described as perfect. A shape that is rep-n or irrep-n is trivially also irrep-(kn − k + n) for any k > 1, by replacing the smallest tile in the rep-n dissection by n even smaller tiles. The order of a shape, whether using rep-tiles or irrep-tiles is the smallest possible number of tiles which will suffice.
Examples
Every squareSquare
-Mathematics and science:* Square , a cryptographic block cipher* Square , a regular quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles* Square number, an integer that is the square of another integer-Construction:...
, rectangle
Rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is any quadrilateral with four right angles. The term "oblong" is occasionally used to refer to a non-square rectangle...
, parallelogram
Parallelogram
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a convex quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure...
, rhombus
Rhombus
In Euclidean geometry, a rhombus or rhomb is a convex quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. The rhombus is often called a diamond, after the diamonds suit in playing cards, or a lozenge, though the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle.Every...
, or triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
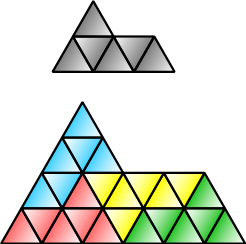
is rep-4. The sphinx hexiamond
Polyiamond
A polyiamond is a polyform whose base form is an equilateral triangle. The word polyiamond is a back-formation from diamond, because this word is often used to describe the shape of a pair of equilateral triangles placed base to base, and the initial "di-" looked like a Greek prefix meaning...
(illustrated) is also rep-4. The Koch snowflake
Koch snowflake
The Koch snowflake is a mathematical curve and one of the earliest fractal curves to have been described...
is irrep-7: six small snowflakes of the same size, together with another snowflake with three times the area of the smaller ones, can combine to form a single larger snowflake.
A right triangle
Right triangle
A right triangle or right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle . The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry.-Terminology:The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse...
with side lengths in the ratio 1:2 is rep-5, and its rep-5 dissection forms the basis of the aperiodic pinwheel tiling
Pinwheel tiling
Pinwheel tilings are non-periodic tilings defined by Charles Radin and based on a construction due to John Conway.They are the first known non-periodic tilings to each have the property that their tiles appear in infinitely many orientations....
.
The international standard ISO 216
ISO 216
ISO 216 specifies international standard paper sizes used in most countries in the world today. It defines the "A" and "B" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available size...
defines sizes of paper sheets using the Lichtenberg ratio
Lichtenberg ratio
In paper sizes, the Lichtenberg ratio is the aspect ratio of 1:√2. The term was proposed by Markus Kuhn in 2002.This aspect ratio has the unique property that cutting any rectangular sheet of paper formed with the Lichtenberg ratio into two equal halves parallel to its shortest sides produces two...
, in which the long side of a rectangular sheet of paper is the square root of two times the short side of the paper. Rectangles in this shape are rep-2. An isosceles right triangle is also rep-2.
External links
- Clarke, A. L. "Reptiles." http://www.recmath.com/PolyPages/PolyPages/Reptiles.htm.
- http://www.meden.demon.co.uk/Fractals/reptiles.html (2001)
- http://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/symmetry/reptile1.htm (1999)

