
Restricted Open-shell Hartree-Fock
Encyclopedia
Restricted open-shell Hartree–Fock (ROHF) is a variant of Hartree–Fock theory for open shell
molecules. It uses doubly occupied molecular orbitals as far as possible and then singly occupied orbitals for the unpaired electrons. This is the simple picture for open shell molecules but it is difficult to implement.
The foundations of the ROHF method were first formulated by Roothaan in a celebrated paper and then extended by various authors, see e.g.
for in-depth discussions.
As with restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, it leads to Roothaan equations
written in the form of a generalized eigenvalue problem
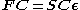
Where F is the so-called Fock matrix
(which is a function of C), C is a matrix of coefficients, S is the overlap matrix
of the basis functions, and is the (diagonal, by convention) matrix of orbital energies. Unlike restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, the form of the Fock matrix is not unique. Different so-called canonicalisations can be used leading to different orbitals and different orbital energies, but the same total wavefunction, total energy, and other observables.
is the (diagonal, by convention) matrix of orbital energies. Unlike restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, the form of the Fock matrix is not unique. Different so-called canonicalisations can be used leading to different orbitals and different orbital energies, but the same total wavefunction, total energy, and other observables.
In contrast to unrestricted Hartree–Fock (UHF), the ROHF wave function is a satisfactory eigenfunction of the total spin operator -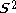 (i.e. no Spin contamination
(i.e. no Spin contamination
).
Developing post-Hartree–Fock methods based on a ROHF wave function is inherently more difficult than using a UHF wave function, due to the lack of a unique set of molecular
orbitals.
However, different choices of reference orbitals have shown to provide similar results, and thus many different post-Hartree–Fock methods have been implemented in a variety of electronic structure packages.
Many (but not all) of these post-Hartree–Fock methods are completely invariant
with respect to orbital choice (assuming that no orbitals are "frozen" and
thus not correlated).
The ZAPT2 version of Møller–Plesset perturbation theory specifies the choice of orbitals.
Open shell
In the context of atomic orbitals, an open shell is a valence shell which is not completely filled with electrons or that has not given all of its valence electrons through chemical bonds with other atoms or molecules during a chemical reaction. Atoms generally reach a noble gas configuration in a...
molecules. It uses doubly occupied molecular orbitals as far as possible and then singly occupied orbitals for the unpaired electrons. This is the simple picture for open shell molecules but it is difficult to implement.
The foundations of the ROHF method were first formulated by Roothaan in a celebrated paper and then extended by various authors, see e.g.
for in-depth discussions.
As with restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, it leads to Roothaan equations
Roothaan equations
The Roothaan equations are a representation of the Hartree-Fock equation in a non orthonormal basis set which can be of Gaussian-type or Slater-type. It applies to closed-shell molecules or atoms where all molecular orbitals or atomic orbitals, respectively, are doubly occupied. This is generally...
written in the form of a generalized eigenvalue problem
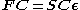
Where F is the so-called Fock matrix
Fock matrix
In the Hartree-Fock method of quantum mechanics, the Fock matrix is a matrix approximating the single-electron energy operator of a given quantum system in a given set of basis vectors....
(which is a function of C), C is a matrix of coefficients, S is the overlap matrix
Overlap matrix
The overlap matrix is a square matrix, used in quantum chemistry to describe the inter-relationship of a set of basis vectors of a quantum system. In particular, if the vectors are orthogonal to one another, the overlap matrix will be diagonal. In addition, if the basis vectors form an...
of the basis functions, and
 is the (diagonal, by convention) matrix of orbital energies. Unlike restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, the form of the Fock matrix is not unique. Different so-called canonicalisations can be used leading to different orbitals and different orbital energies, but the same total wavefunction, total energy, and other observables.
is the (diagonal, by convention) matrix of orbital energies. Unlike restricted Hartree–Fock theory for closed shell molecules, the form of the Fock matrix is not unique. Different so-called canonicalisations can be used leading to different orbitals and different orbital energies, but the same total wavefunction, total energy, and other observables.In contrast to unrestricted Hartree–Fock (UHF), the ROHF wave function is a satisfactory eigenfunction of the total spin operator -
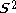 (i.e. no Spin contamination
(i.e. no Spin contaminationSpin contamination
In computational chemistry, spin contamination is the artificial mixing of different electronic spin-states. This can occur when an approximate orbital-based wave function is represented in an unrestricted form – that is, when the spatial parts of α and β spin-orbitals are permitted to differ....
).
Developing post-Hartree–Fock methods based on a ROHF wave function is inherently more difficult than using a UHF wave function, due to the lack of a unique set of molecular
orbitals.
However, different choices of reference orbitals have shown to provide similar results, and thus many different post-Hartree–Fock methods have been implemented in a variety of electronic structure packages.
Many (but not all) of these post-Hartree–Fock methods are completely invariant
Invariant
Invariant and invariance may have several meanings, among which are:- Computer science :* Invariant , an Expression whose value doesn't change during program execution* A type in overriding that is neither covariant nor contravariant...
with respect to orbital choice (assuming that no orbitals are "frozen" and
thus not correlated).
The ZAPT2 version of Møller–Plesset perturbation theory specifies the choice of orbitals.

